Abstract
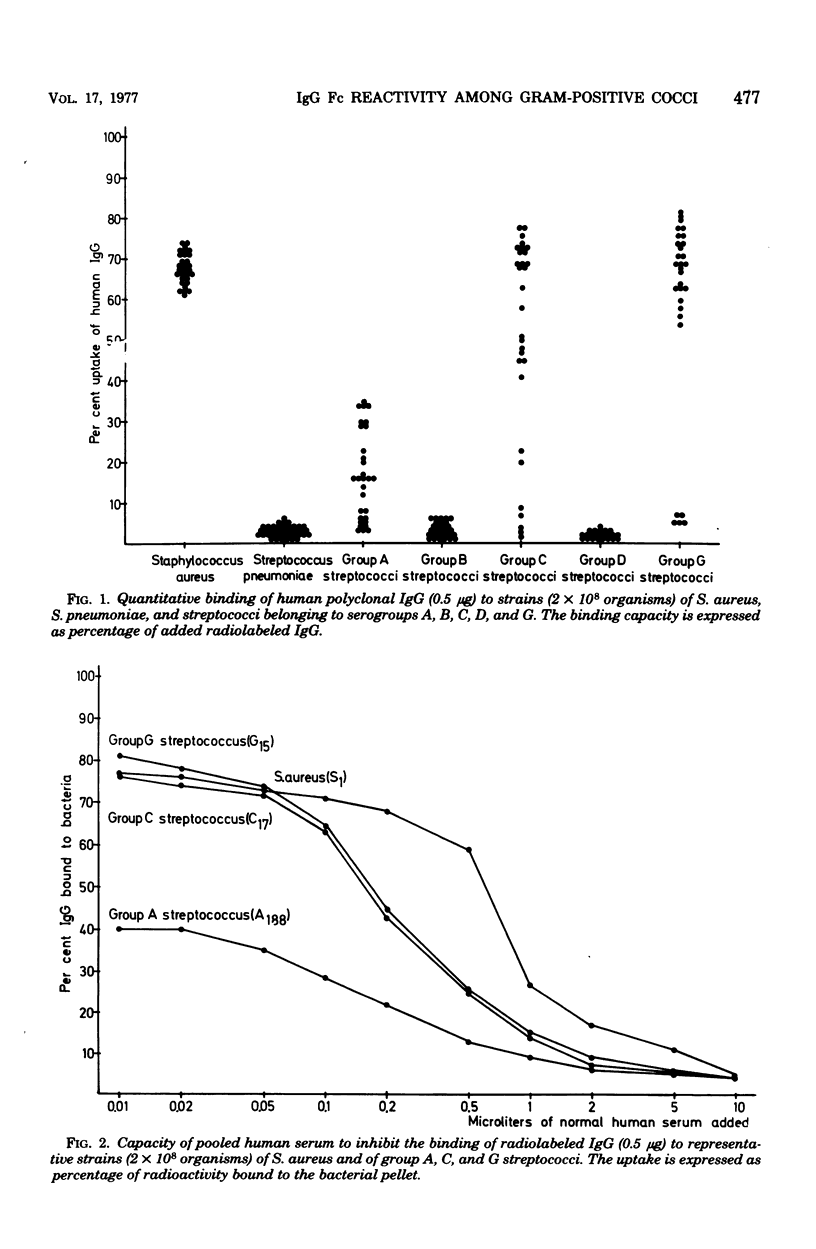
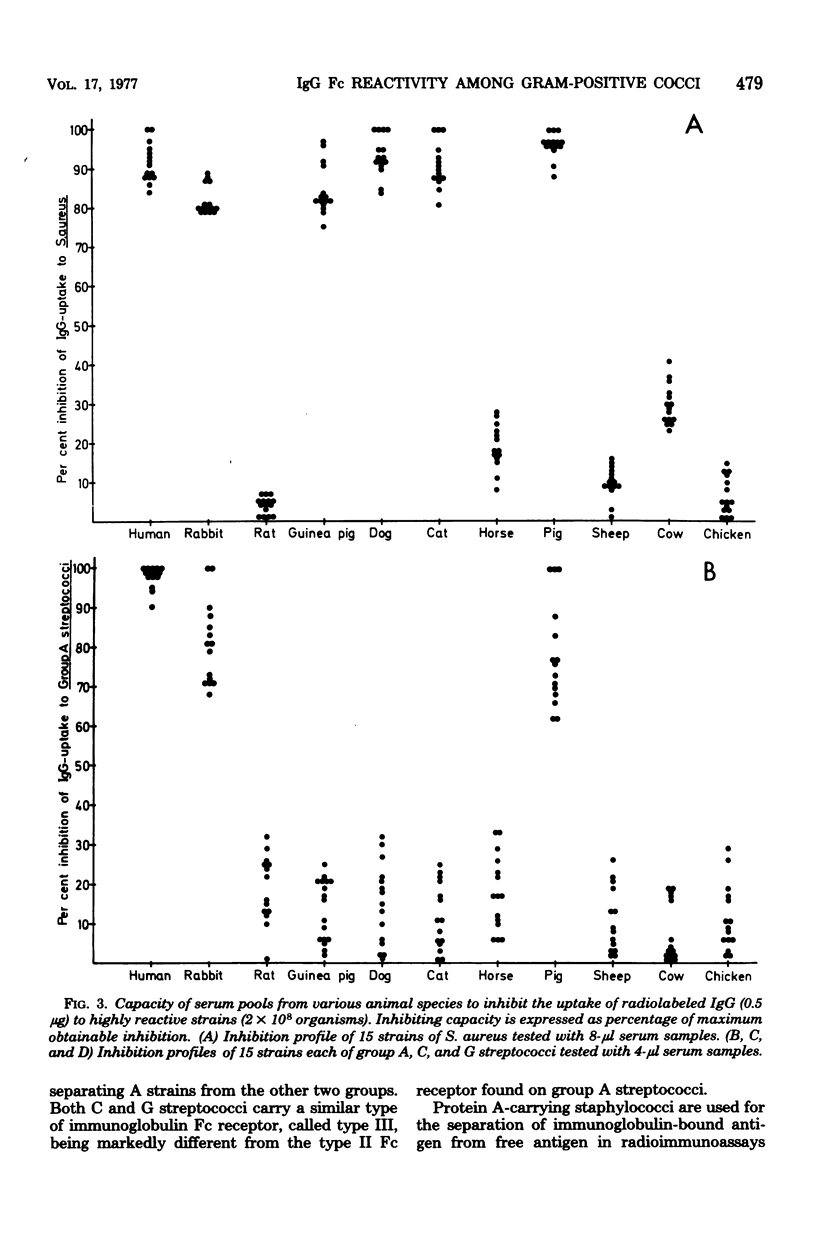
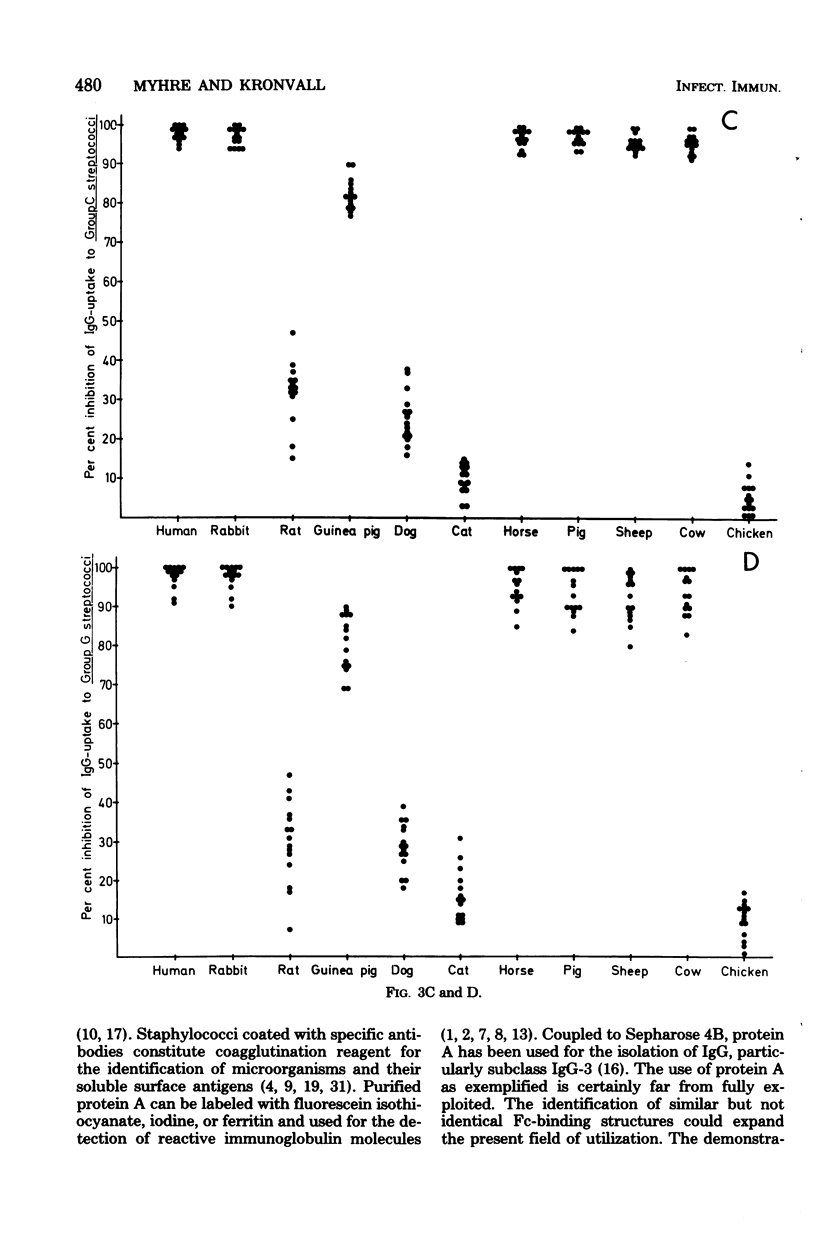
Two hundred and thirty strains of various gram-positive cocci were tested for quantitative, nonimmune binding of radiolabeled human polyclonal immunoglobulin G (IgG). The majority of coagulase-positive staphylococci and streptococci belonging to serogroups C and G showed a high uptake of IgG. The binding of immunoglobulin to group A streptococci was considerably less, with a number of strains completely negative. None of the pneumococcal or the group B or D streptococcal strains displayed any binding capacity. Heterogeneity of the IgG reactivity of various reactive strains was studied in an inhibition assay using 10 different animal serum pools. Three different inhibition patterns were seen, each of them revealing a striking degree of homogeneity within single bacterial species. Staphylococcus aureus and group A streptococci, respectively, constituted two homogeneous groups which differed markedly from each other and from C and G streptococci. No differences were observed between group C and G streptococci. Based on the profound differences between these homogeneous groups, three major types of Fc receptors could be defined. Type I and II Fc receptors were found on S. aureus and on group A streptococci, respectively. Fc receptor type III represented the immunoglobulin-binding structure of both group C and G streptococci.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biberfield P., Ghetie V., Sjöquist J. Demonstration and assaying of IgG antibodies in tissues and on cells by labeled staphylococcal protein A. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Jan;6(3):249–259. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bächi T., Dorval G., Wigzell H., Binz H. Staphylococcal protein A in immunoferritin techniques. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(3):241–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen P., Holm S. E. Purification of immunolobulin G Fc-reactive factor from Streptococcus azgazardah. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1976 Jun;84(3):196–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen P., Kahlmeter G., Jonsson S., Kronvall G. New method for the serological grouping of Streptococci with specific antibodies adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):881–885. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.881-885.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen P., Kronvall G. Capacity of group A, B, C, D, and G streptococci to agglutinate sensitized sheep red cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Feb;82(1):19–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen P., Oxelius V. A. Quantitation of the uptake of human IgG by some streptococci groups A, B, C, and G. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Aug;82(4):475–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorval G., Welsh K. I., Wigzell H. A radioimmunoassay of cellular surface antigens on living cells using iodinated soluble protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Jun;7(2-3):237–250. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorval G., Welsh K. I., Wigzell H. Labeled staphylococcal protein A as an immunological probe in the analysis of cell surface markers. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(4):405–411. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards E. A., Hilderbrand R. L. Method for identifying Salmonella and Shigella directly from the primary isolation plate by coagglutination of protein A-containing staphylococci sensitized with specific antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Mar;3(3):339–343. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.3.339-343.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figenschau K. J., Ulstrup J. C. Staphylococcal radioimmunoassay for hepatitis B antigen and antibody. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Jun;82(3):422–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02346.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Nordström K. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus: the biological significance of its reaction with IgG. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):252–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsum U., Hjelm E., Jonsell G. Antibody-coated bacteria in the urine of children with urinary tract infections. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1976 Sep;65(5):639–642. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1976.tb04944.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N. M proteins of group A streptococci. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):57–86. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.57-86.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe M., Fölling I. Recognition of two distinct groups of human IgM and IgA based on different binding to staphylococci. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(4):471–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm H. Isolation of IgG3 from normal human sera and from a patient with multiple myeloma by using protein A-sepharose 4B. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(7):633–640. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson S., Kronvall G. The use of protein A-containing Staphylococcus aureus as a solid phase anti-IgG reagent in radioimmunoassays as exemplified in the quantitation of alpha-fetoprotein in normal human adult serum. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Jan;4(1):29–33. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A rapid slide-agglutination method for typing pneumococci by means of specific antibody adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. J Med Microbiol. 1973 May;6(2):187–190. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A surface component in group A, C, and G streptococci with non-immune reactivity for immunoglobulin G. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1401–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Holmberg O., Ripa T. Protein A in Staphylococcus aureus strains of human and bovine origin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(5):735–742. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Quie P. G., Williams R. C., Jr Quantitation of staphylococcal protein A: Determination of equilibrium constant and number of protein A residues on bacteria. J Immunol. 1970 Feb;104(2):273–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Williams R. C., Jr Differences in anti-protein A activity among IgG subgroups. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):828–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind I. Correlation between the occurrence of protein A and some other properties in Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(5):702–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxted W. R., Potter E. V. The presence of type 12 M-protein antigen in group G streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Oct;49(1):119–125. doi: 10.1099/00221287-49-1-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens C. G., Reed W. P., Kronvall G., Williams R. C., Jr Reactions between certain strains of pneumococci and Fc of IgG. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):1955–1960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suksanong M., Dajani A. S. Detection of Haemophilus influenzae type b antigens in body fluids, using specific antibody-coated staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):81–85. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.81-85.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winblad S., Ericson C. Sensitized sheep red cells as a reactant for Staphylococcus aureus protein A. Methodology and epidemiology with special reference to weakly reacting methicillin-resistant strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Feb;81(1):150–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


