Abstract
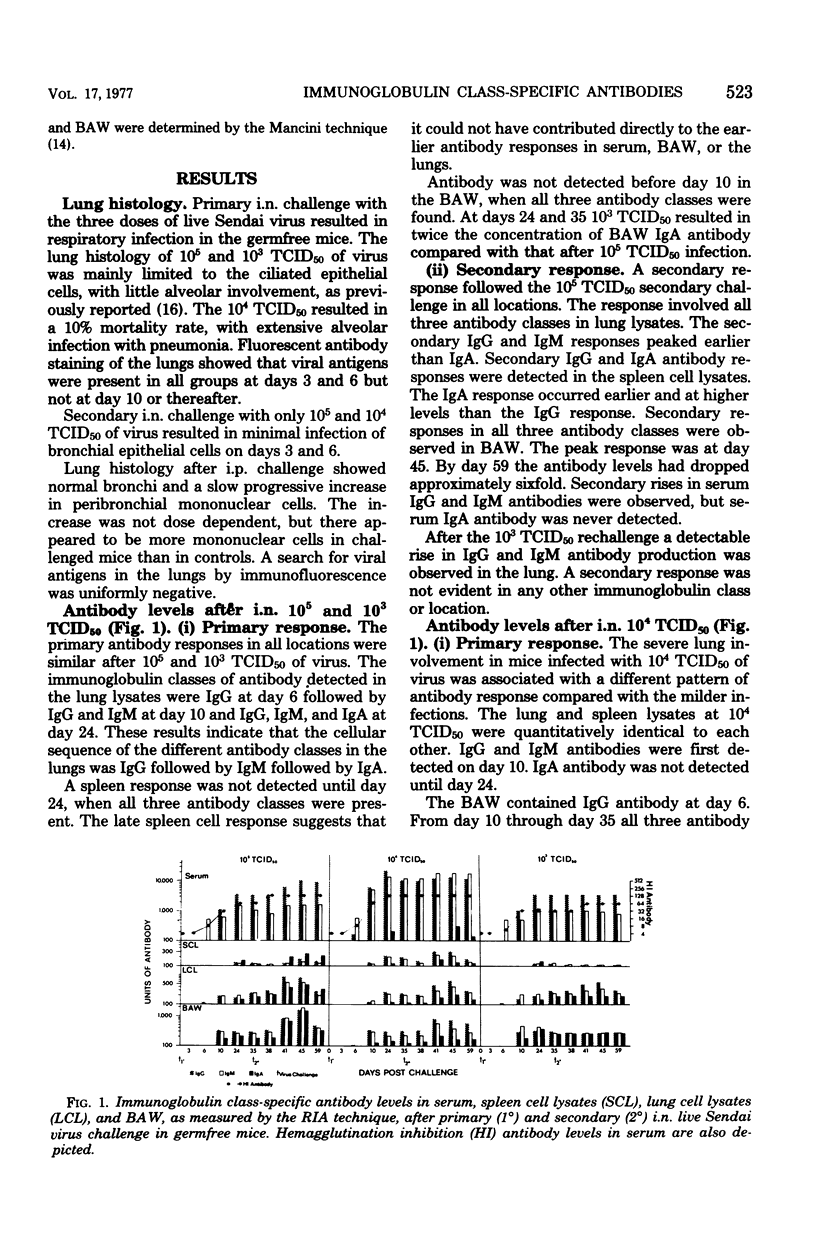
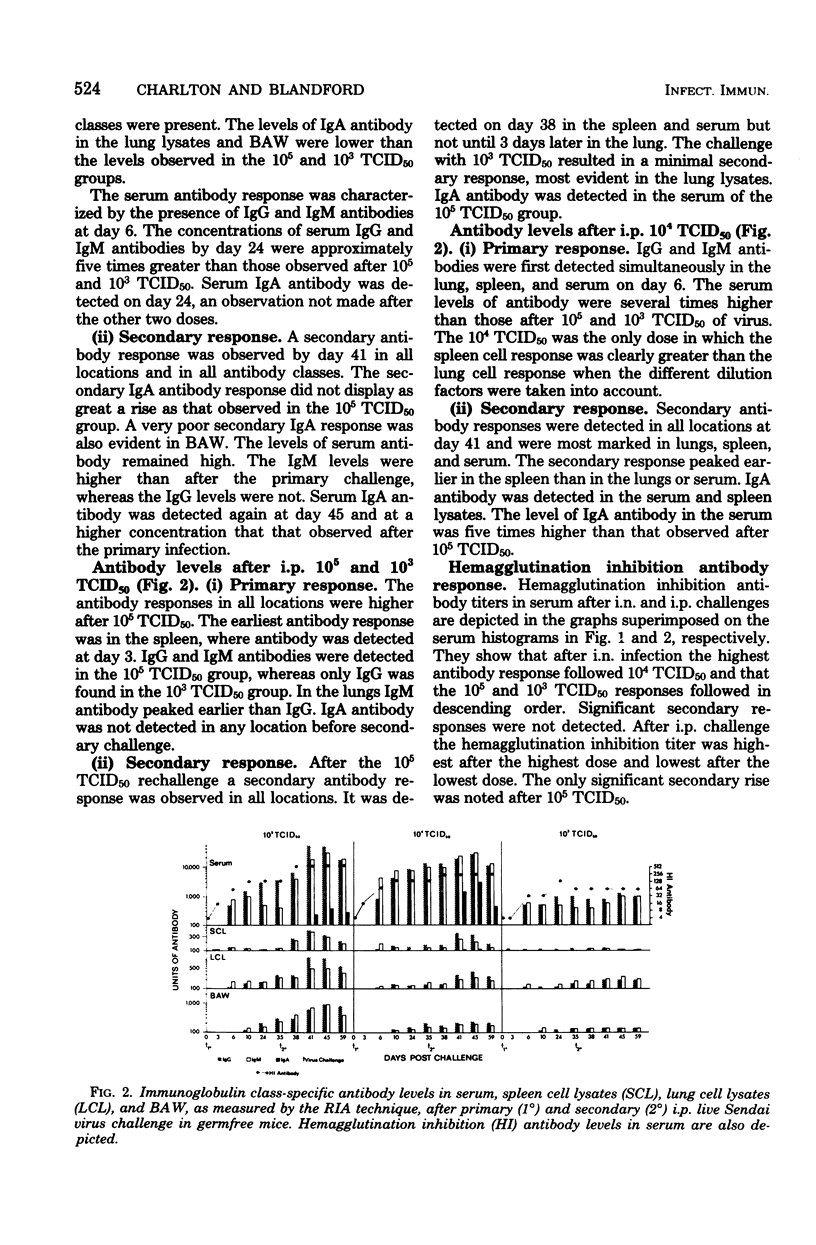
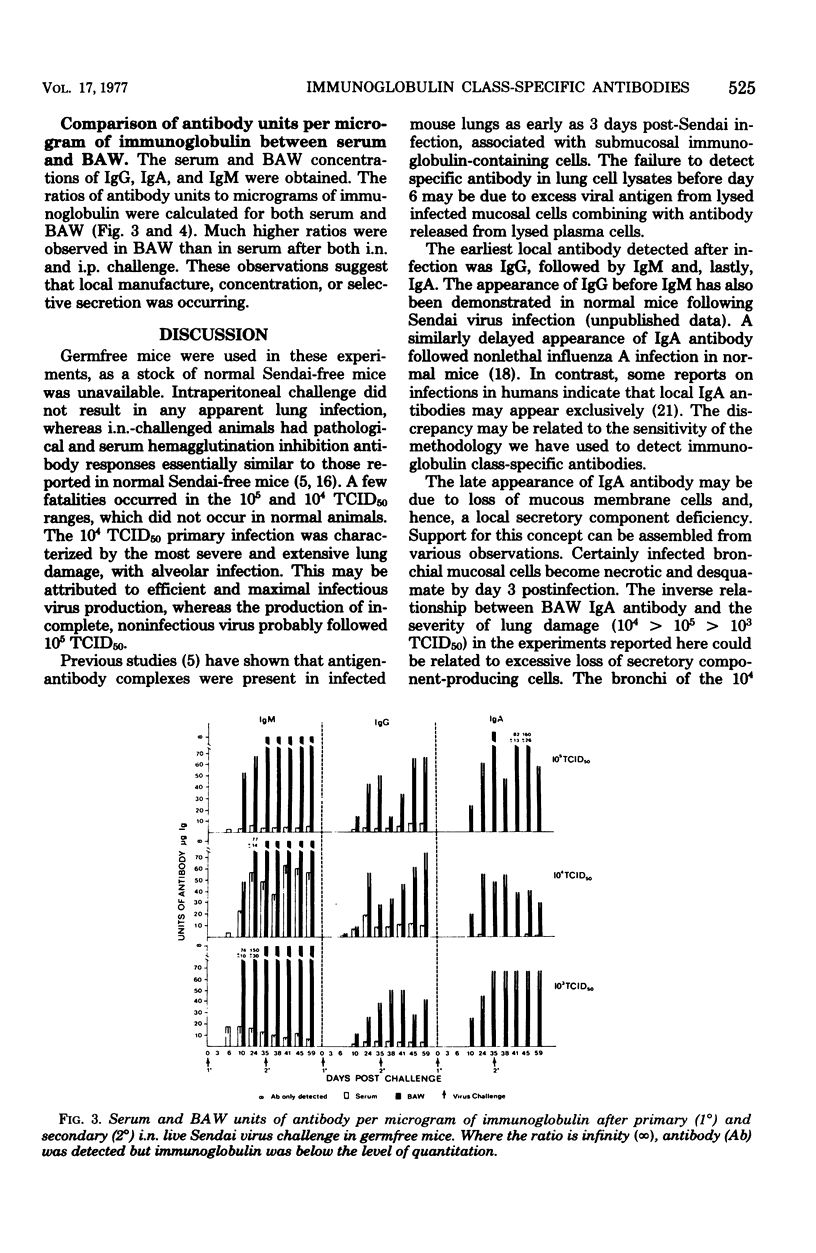
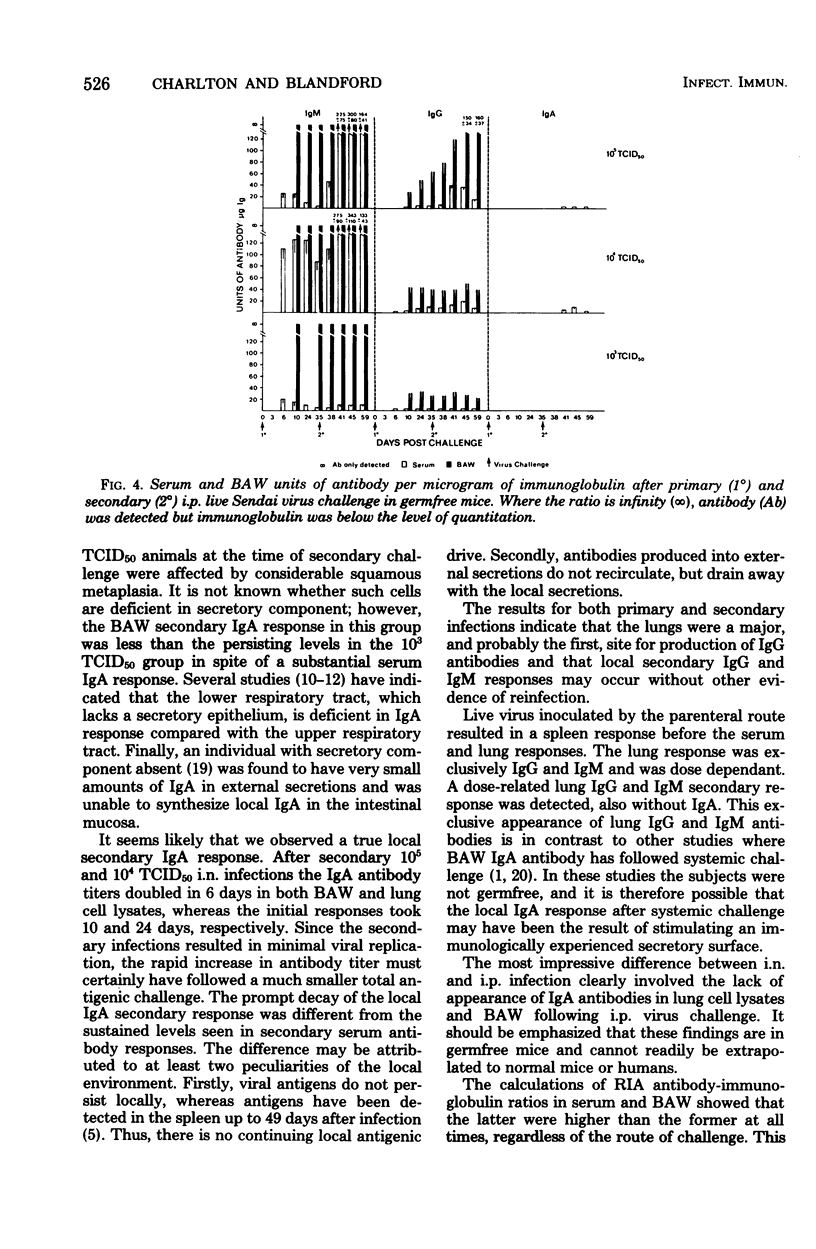
Immunoglobulin class-specific antibodies were measured by a solid-phase radioimmunoassay in serum, bronchoalveolar washings (BAW), lung cell lysates, and spleen cell lysates in germfree mice after intranasal (i.n.) and intraperitoneal (i.p.) primary and secondary 105, 104, and 103 mean tissue culture infective doses (TCID50) of live parainfluenza 1 (Sendai) virus. The earliest antibody detected in lungs after i.n. virus challenge was immunoglobulin G (IgG), followed by IgM and, lastly, IgA. The local IgA response after both primary and secondary i.n. virus challenge was lowest after the severest infection. It is suggested that the delayed appearance of IgA antibody and the lower response after severe lung damage may be related to a temporary local secretory component-producing cell deficiency. The lungs were a major source of serum IgG antibody after both primary and secondary i.n. virus challenge. Only IgG and IgM antibodies were detectable in lung cell lysates after the i.n. 103 TCID50 secondary response. A secondary response was detected in IgG, IgA, and IgM after secondary i.n. challenge with the other two doses. The lung response to all of primary and secondary i.p. doses of virus was exclusively IgG and IgM. Calculation of radioimmunoassay antibody per microgram of IgG, IgA, and IgM in serum and BAW after both i.n. and i.p. virus challenges showed that, when BAW antibody was present, the ratio in BAW was always higher than that in serum. This finding in the i.n. mice, together with the presence of IgA antibody-containing cells in the lungs, strongly indicates local manufacture and secretion of IgA antibodies in these animals and suggests that the same conclusion could apply to local IgG and IgM antibodies after both i.n. and i.p. challenges.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellanti J. A., Sanga R. L., Klutinis B., Brandt B., Artenstein M. S. Antibody responses in serum and nasal secretions of children immunized with inactivated and attenuated measles-virus vaccines. N Engl J Med. 1969 Mar 20;280(12):628–633. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196903202801202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandford G. Arthus reaction and pneumonia. Br Med J. 1970 Mar 21;1(5698):758–759. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5698.758-d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandford G., Heath R. B. Studies on the immune response and pathogenesis of Sendai virus infection of mice. I. The fate of viral antigens. Immunology. 1972 Apr;22(4):637–649. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandford G., Heath R. B. Studies on the immune response and pathogenesis of Sendai virus infection of mice. II. The immunoglobulin class of plasma cells in the bronchial sub-mucosa. Immunology. 1974 Mar;26(3):667–671. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandford G. Studies on the immune response and pathogenesis of Sendai virus infection of mice. III. The effects of cyclophosphamide. Immunology. 1975 May;28(5):871–883. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H., Greenberg H. B., James W. D., Horswood R. L., Couch R. B., Chanock R. M. Antibody to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in nasal secretions and sputa of experimentally infected human volunteers. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):612–620. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.612-620.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlton D., Blandford G. A solid phase micro-radioimmunoassay to detect minute amounts of Ig class specific anti-viral antibody in a mouse model system. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Oct;8(4):319–330. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONNELLEY M. Studies in experimental immunology of influenza. VII. An improved complement-fixation technique. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1951 Mar;29(2):137–146. doi: 10.1038/icb.1951.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernald G. W., Clyde W. A., Jr, Bienenstock J. Immunoglobulin-containing cells in lungs of hamsters infected with Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Immunol. 1972 May;108(5):1400–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford R. J., Jr, Kuhn C. Immunologic competence of alveolar cells. I. The plaque-forming response to particulate and soluble antigens. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 May;107(5):763–770. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.107.5.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltreider H. B., Kyselka L., Salmon S. E. Immunology of the lower respiratory tract. II. The plaque-forming response of canine lymphoid tissues to sheep erythrocytes after intrapulmonary or intravenous immunization. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):263–270. doi: 10.1172/JCI107761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson T. W., Cureton R. J., Heath R. B. The pathogenesis of Sendai virus infection in the mouse lung. J Med Microbiol. 1968 Aug;1(1):89–95. doi: 10.1099/00222615-1-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott G. H., Sydiskis R. J. Responses of mice immunized with influenza virus by serosol and parenteral routes. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):696–703. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.696-703.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strober W., Krakauer R., Klaeveman H. L., Reynolds H. Y., Nelson D. L. Secretory component deficiency. A disorder of the IgA immune system. N Engl J Med. 1976 Feb 12;294(7):351–356. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197602122940701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman R. H., Ganguly R. Immunity to infections on secretory surfaces. J Infect Dis. 1974 Oct;130(4):419–440. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman R. H., Jurgensen P. F., Olsen G. N., Ganguly R., Johnson J. E., 3rd Immune response of the human respiratory tract. I. Immunoglobulin levels and influenza virus vaccine antibody response. J Immunol. 1973 Jul;111(1):38–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


