Abstract
The use of multi-parametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging (T2-weighted, MR Spectroscopy (MRS), Diffusion-weighted (DWI)) has recently shown great promise for diagnosing and staging prostate cancer (CaP) in vivo. Such imaging has also been utilized for evaluating the early effects of radiotherapy (RT) (e.g. intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), proton beam therapy, brachytherapy) in the prostate with the overarching goal being to successfully predict short- and long-term patient outcome. Qualitative examination of post-RT changes in the prostate using MRI is subject to high inter- and intra-observer variability. Consequently, there is a clear need for quantitative image segmentation, registration, and classification tools for assessing RT changes via multi-parametric MRI to identify (a) residual disease, and (b) new foci of cancer (local recurrence) within the prostate. In this paper, we present a computerized image segmentation, registration, and classification toolkit called CADOnc©, and leverage it for evaluating (a) spatial extent of disease pre-RT, and (b) post-RT related changes within the prostate. We demonstrate the applicability of CADOnc© in studying IMRTrelated changes using a cohort of 7 multi-parametric (T2w, MRS, DWI) prostate MRI patient datasets. First, the different MRI protocols from pre- and post-IMRT MRI scans are affinely registered (accounting for gland shrinkage), followed by automated segmentation of the prostate capsule using an active shape model. A number of feature extraction schemes are then applied to extract multiple textural, metabolic, and functional MRI attributes on a per-voxel basis. An AUC of 0.7132 was achieved for automated detection of CaP on pre-IMRT MRI (via integration of T2w, DWI, MRS features); evaluated on a per-voxel basis against radiologist-derived annotations. CADOnc© also successfully identified a total of 40 out of 46 areas where disease-related changes (both absence and recurrence) occurred post-IMRT, based on changes in the expression of quantitative MR imaging biomarkers. CADOnc© thus provides an integrated platform of quantitative analysis tools to evaluate treatment response in vivo, based on multi-parametric MRI data.
1. Introduction
An estimated 217,730 new cases of prostate cancer (CaP) are expected to be diagnosed in 2010 in the United States alone. Of these approximately 17% will undergo some form of radiation therapy (RT) (e.g. intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), proton beam therapy, brachytherapy) as treatment for clinically localized disease1. Early identification of non-responders via the use of imaging will allow for modification of the therapy [1], as well as provide clues about long-term patient outcome. Currently, differentiation between local or systemic recurrence of CaP (which have radically different prognoses and treatment regimens) is only appreciable on trans-rectal ultrasound, that too at a relatively advanced stage [1].
Multi-parametric (T2-weighted, MR Spectroscopy (MRS), Diffusion-weighted (DWI)) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has shown great potential in early detection and staging of CaP [2]. Pre-RT CaP extent on multi-parametric MRI data is characterized by (a) low T2w signal intensity, generally located in the peripheral zone [3], (b) MR spectra with elevated levels of choline and reduced levels of citrate, (c) significantly low apparent diffusion co-efficient (ADC) values (from DWI), as compared to benign tissue.
Post-RT, successful treatment of CaP on MRI is characterized by uniform T2w signal intensity without focal abnormalities, while locally recurrent CaP is characterized by hypo-intense regions of smooth texture [4]. MRS shows an absence of citrate, as well as low metabolic activity in cases of successful treatment. Elevated levels of choline in post-RT MRS is associated with locally recurrent CaP [4]. Post-RT DWI shows an overall increase in ADC values within the entire prostate when CaP is successfully treated. Unchanged or decreased ADC values correspond to locally recurrent CaP [5].
While such multi-parametric MRI-based biomarkers for evaluating RT-related changes within CaP regions have been identified, the qualitative examination of post-RT MRI is associated with poor detection rates due to (a) diffuse T2w signal intensity and indistinct zonal anatomy on T2w MRI [6], (b) adverse effects of post-biopsy hemorrhage and hormonal therapy on metabolic peaks [7], and (c) significant gland shrinkage and distortion post-RT [1]. Automated quantitative assessment of RT changes via multi-parametric MRI may thus allow accurate identification of (a) residual disease, and (b) new foci of cancer (local recurrence) within the prostate. This can, in turn, allow development of multi-parametric MRI based classifiers to help better predict short- and long-term patient outcome.
Recently, a number of schemes for automated computerized image analysis of in vivo multi-parametric prostate MRI have been presented [8, 9], with the primary focus being the accurate detection of presence and extent of CaP on pre-treatment MR data alone. To our knowledge, there is no current work on developing quantitative image analysis schemes to (a) examine multi-parametric MRI biomarkers pre- and post-RT, or (b) determine the effectiveness of therapy by examining quantitative changes in the expression of these imaging biomarkers pre- and post-RT.
In this paper, we present CADOnc©, a novel comprehensive segmentation, registration, and classification framework for quantifying changes in disease extent post-radiation therapy. CADOnc© is particularly suited to address the unique challenges in quantifying RT-related prostate changes by (a) accounting for changes in the overall size and shape of the prostate pre- and post-RT (gland shrinkage due to radiation treatment [1]) via a novel spatially constrained registration scheme, (b) accurate delineation of the prostate region-of-interest (ROI) on pre- and post-RT MRI data using a robust statistical shape model [10] that is able to compensate for the loss of image resolution post-RT, and (c) quantitatively integrating structural, metabolic, and functional image features from T2w MRI, MRS, and DWI data for detection, comparison, and assessment of RT-related changes within the prostate ROI. In this work we leverage CADOnc© to evaluate (a) pre-IMRT disease, and (b) post-IMRT related changes using multi-parametric prostate MRI (T2w, MRS, DWI) on a cohort of 7 patient datasets. Figure 1 presents an overview of CADOnc©, showing the interplay between the different modules.
Fig. 1.
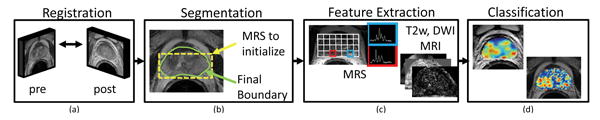
Organization of modules comprising CADOnc©, (a) registration of pre- and post-RT data to overcome changes in the overall size and shape of the prostate, (b) segmentation to accurately delineate the prostate region-of-interest, (c) feature extraction to quantify structural, metabolic, and functional image attributes, (d) classification to analyze changes in the expression of multi-parametric MR imaging biomarkers.
2. Registration Of Pre- And Post-Treatment MR Imagery
Registration of the pre-treatment T2w prostate image scene to the post-treatment T2w prostate MRI scene is uniquely complicated by (1) changes in the overall shape and size of the prostate gland (which is known to shrink, post-RT [1]), (2) differing acquisition parameters, and (3) image intensity artifacts due to RT effects.
Bounding boxes containing the prostate on and are selected, obviating the need for elastic registration to model non-linear deformations in peripheral pelvic anatomy.
A spatially constrained mutual information (MI) similarity measure is used to drive the affine transformation of onto . Only those voxels of and that fall within the bounding box (selected in step 1) are considered in the calculation of MI (chosen for its robustness to non-linear intensity relationships [11]).
A 3D affine transformation with 12 degrees of freedom, encoding rotation, translation, shear, and scale, is implemented (as presented in [11]) to accurately align the prostate between and .
T2w MRI and MRS are known to be in implicit alignment, but MRS information is obtained at a coarser resolution. MRS data is hence resampled to the finer T2w MRI voxel resolution.
Alignment of T2w and ADC maps is done based on available voxel sizes and locations (automatically extracted from DICOM headers). In the case of post-RT MRS and ADC maps, the transformation from step 3 is applied to map all the data into the pre-treatment coordinate frame C (associated with ).
3. Automated Segmentation Of Prostate Capsule on T2W MRI Data
This module utilizes a novel, fully automated Active Shape Model (ASM) scheme for delineation of the prostate capsule on in vivo T2w MR imagery [10]. This technique, developed by our group and presented in [10], leverages multi-protocol data as follows,
First, a texture-based support vector machine (SVM) is constructed to be able to classify voxels within the prostate ROI.
A single midgland slice is selected from each test study. Corresponding MRS data is identified as either prostatic or extra-prostatic via a replicated k-means spectral clustering scheme [10] . This yields a bounding box of spectra from within the prostate.
The SVM classifier from Step 1 is used to identify prostatic voxels within the bounding box identified in Step 2, resulting in a boundary initialization.
The ASM transforms a known mean shape of the prostate (detailed in [10]) to the boundary initialization from Step 3, resulting in the gland capsule segmentation for this slice.
This segmentation is extended to the base and apex to yield a delineation of the prostate ROI (as described in [10]) on as well as on the ADC map.
4. Feature Extraction and Identifying RT-Related Changes On Multi-Parametric MRI
Prior to quantitatively integrating the multi-parametric MRI data, we first quantify the information captured by each protocol in terms of structural, metabolic, and functional information (Table 1).
Table 1.
Summary of qualitative changes in multi-parametric MRI imaging parameters pre- and post-RT, and the corresponding quantitative features used by CADOnc© to characterize each protocol.
| Pre-RT appearance | Post-RT appearance | CADOnc© features | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T2w | low T2w signal intensity in peripheral zone |
Hypo-intense regions, smooth texture No change in residual CaP regions |
1st order statistics, Kirsch/Sobel (gradients) 2nd order co-occurrence (Haralick) |
| MRS | elevated levels of Ach reduced levels of Acit |
Nearly absent Acit, polyamines in benign, CaP Residual CaP has elevated Ach, Acr |
[Ach, Acr, Acit, Ach+cr/Acit, Ach/Acr] |
| DWI | significantly low ADC compared to benign |
Increased ADC in entire prostate compared to pre-RT Residual CaP lower ADC compared to benign areas |
Raw ADC values, gradients 1st and 2nd order statistics |
A. Structural (T2W)
A texture feature vector (Fpre(c)) is calculated from each pre-RT T2w MRI image at voxel level, based on extracting features which have previously demonstrated discriminability for CaP detection [9]. Post-RT, signal intensity alone is considered.
B. Metabolic (MRS)
For pre-RT MRS, area under the choline (Ach), creatine (Acr), and citrate peaks (Acit), as well as associated ratios, are calculated, yielding the metabolic peak area vector Gpre(c). Kurhanewicz et al [2] have suggested that these features are highly indicative of the presence of CaP. Only Ach and Acr are considered post-RT, due to the known absence of citrate [4].
C. Functional (ADC)
Both texture and ADC values are considered when analyzing pre-RT DWI MRI, yielding the feature vector Epre(c). Post-RT, ADC values alone (no texture) are considered.
In order to determine CaP regions on pre-RT MRI, an automated classifier (in this work, Random Forests [12] (RF)) is trained based off the fused representation vector Xpre(c) = [Epre(c), Fpre(c), Gpre(c)]. Treatment related changes are observed via parametric heatmaps reflecting differences in (1) T2w MRI intensity, (2) Ach/Acr ratios, and (3) ADC values, pre- and post-IMRT.
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Data description
7 in vivo endorectal multi-parametric MRI patient datasets were acquired from the University of California, San Francisco. All patients underwent external beam radiotherapy after initial MRI acquisition (1.5 Tesla, GE Signa), with supplementary neo-adjuvant hormonal therapy. Post RT, patients were reimaged via MRI (3 Tesla, GE Signa). Radiologist annotations of CaP and benign regions were obtained on a per-MRS voxel basis, and used as surrogate ground truth labels for CaP extent. A total of 25 slices with CaP (pre-RT) were identified for analysis via CADOnc©. All of these MRI sections had associated CaP annotations pre- and post-RT. One study out of the 7 included T2w, MRS, and ADC maps (from DWI), while the remaining 6 comprised MRS and T2w MRI alone.
5.2. Experiment 1: Identifying CaP on pre-RT MRI
A RF classifier was constructed for Xpre(c) based on the available surrogate ground truth labels for CaP extent; the objective being to discriminate between CaP and benign regions. A leave-one-out cross validation strategy was adopted to evaluate the effectiveness of the RF, such that at each iteration, slices corresponding to a single study were held out for testing, while the remaining were used in training. This was repeated until all the slices from all the studies had been evaluated. Receiver-Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was then performed based on overlap with ground truth labels on a per-voxel basis. The integrated multi-parametric MRI classifier yielded an average area under the ROC curve of 0.71±0.11, with a corresponding accuracy of 0.65±0.15; averaged over all 7 studies (Table 3). Figures 2(a)-(d) show representative results of CADOnc© for CaP detection. ADC information was not considered in this experiment as it was not available for all the studies.
Table 3.
Quantitative results on a per-study basis for CADOnc©, summarizing AUC and accuracy values for Experiment 1, as well as number of treatment change hotspots identified in Experiment 2.
| Study no | (Pre-RT) CAD AUC |
(Pre-RT) CAD Accuracy |
TP hotspots | FN hotspots |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.81 | 0.74 | 7 | 0 |
| 2 | 0.48 | 0.32 | 4 | 1 |
| 3 | 0.76 | 0.69 | 4 | 2 |
| 4 | 0.71 | 0.68 | 4 | 1 |
| 5 | 0.77 | 0.70 | 4 | 0 |
| 6 | 0.73 | 0.72 | 9 | 1 |
| 7 | 0.74 | 0.70 | 8 | 1 |
| Avg | 0.71 | 0.65 | 40 | 6 |
Fig. 2.
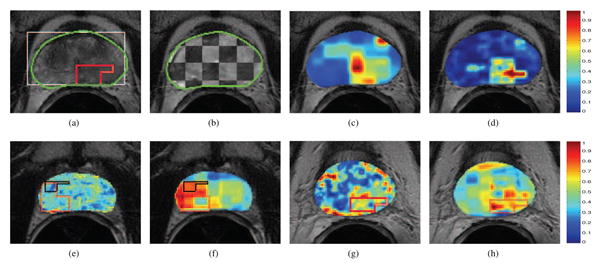
(a) Pre-RT T2w MRI image, with bounding box initialization to the segmentation algorithm in white (from MRS) and final prostate boundary delineation result shown in green. The red outline corresponds to the radiologist annotated CaP extent for this image. (b) Checkerboard overlay of aligned and within the prostate ROI (outlined in green) showing accurate registration of pre- and post-RT T2w MRI data. CAD results via (c) (Ach + Acr)/Aci ratios, (d) integrated multi-parametric MRI information (red corresponds to a higher probability of CaP presence). Note high accuracy and specificity of (d) when compared to red outline in (a). Difference (L1 norm) heatmaps shown for 2 different studies, using (e) T2w intensity, (f), (h) Ach/Acr ratio, and (g) ADC values; taken between pre- and post-RT data. Red corresponds to areas of most change, blue corresponds to areas of least change, while the pre- and post-RT CaP extents (if any) are outlined in red and black respectively. In (e) residual CaP post-RT shows no change in T2w MR intensity (deep blue region within the black outline). Note that in (f), (g), (h) area of significant change in the heatmap corresponds to the successfully treated CaP region post-RT (red outline).
5.3. Experiment 2: Identifying RT-related changes on MRI
46 regions of definitive treatment change (called “hotspots”) were identified across the 25 images considered, based on the pre- and post-RT CaP label information. These included regions of (1) successful treatment, (2) partially successful treatment, and (3) local recurrence (detailed in Table 2). Multi-parametric difference maps for each slice were calculated as scaled absolute differences (L1 norm) between pre- and post-RT images corresponding to each of T2w intensity, Ach/Acr ratios (from MRS), and ADC maps, respectively. Per-study qualitative examination results of multi-parametric MRI difference maps are summarized in Table 3. Of a total of 46 hotspots, T2w signal intensity difference maps identified 29, while 34 were identified via MRS. A consensus between the hotspot maps for each protocol (MRS, T2w) via the logical OR operator allowed for successful identification of 40 of the 46 hotspots. For the single study where such information was available, ADC difference maps successfully identified 4 out of 7 hotspots present (Study 1). Corresponding detection rates for this study based on T2w and MRS information were 3 and 7 hotspots, respectively. Figures 2(e) - (h) show representative difference maps (from 2 different studies) demonstrating significant change in regions of residual CaP extent (Figs 2(e)-(f)), as well as successful treatment (Figs 2(g)-(h)).
Table 2.
Different RT outcomes with corresponding effects on CaP presence and extent.
| Treatment response | Residual CaP | New CaP occurrence |
|---|---|---|
| Successful treatment | N | N |
| Partially successful treatment | Y | N |
| Local recurrence | Y | Y |
| N | Y |
6. Concluding Remarks
In this paper, we presented CADOnc©, the first scheme to quantitatively evaluate the effects of radiation therapy on the prostate. CADOnc© was successfully applied to identifying treatment-related changes in the prostate post-IMRT, using multi-parametric (T2w, MRS, DWI) MRI. Specifically, CADOnc© was applied to (a) align pre- and post-treatment multi-parametric MRI data to facilitate per-voxel identification of changes in the expression of imaging biomarkers, (b) identified CaP on pre-treatment MRI by fusing the structural, functional and metabolic information available from MRI (AUC of 0.7132), (c) quantified differences in multi-parametric MRI biomarkers post-RT with successful identification of 40 out of 46 treatment change hotspots. CADOnc© is intended to lay the platform for quantitative evaluation and comparison of multiple different RT strategies (proton beam therapy, brachytherapy) in the future, with ultimately being able to predict patients who will suffer biochemical failure or local recurrence.
Acknowledgments
This work was made possible via grants from the Wallace H. Coulter Foundation, National Cancer Institute (Grant Nos. R01CA136535, R01CA140772, and R03CA143991), The Cancer Institute of New Jersey, and the Department of Defense Prostate Cancer Research Program (W81XWH-09, W81XWH-08-1-0072). This is an invited paper in the special session on “Imaging the Prostate: Histology and In Vivo”.
Footnotes
American Cancer Society, CaPSURE
References
- 1.Pucar D, et al. The role of imaging in the detection of prostate cancer local recurrence after radiation therapy and surgery. Curr Opin Urol. 2008;18(1):87–97. doi: 10.1097/MOU.0b013e3282f13ac3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kurhanewicz J, et al. Combined magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopic imaging approach to molecular imaging of prostate cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2002;16(4):451–63. doi: 10.1002/jmri.10172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schiebler ML, et al. Current role of MR imaging in the staging of adenocarcinoma of the prostate. Radiology. 1993;189(2):339–352. doi: 10.1148/radiology.189.2.8210358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Coakley FV, et al. Endorectal MR imaging and MR spectroscopic imaging for locally recurrent prostate cancer after external beam radiation therapy: preliminary experience. Radiology. 2004;233(no. 2):441–8. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2332032086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Song I, et al. Assessment of Response to Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer: Value of Diffusion-Weighted MRI at 3 T. Am J Roentgenol. 2010;194(no. 6):W477–482. doi: 10.2214/AJR.09.3557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Westphalen AC, et al. T2-Weighted endorectal magnetic resonance imaging of prostate cancer after external beam radiation therapy. Int Braz J Urol. 2009;35(2):171–80. doi: 10.1590/s1677-55382009000200007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zapotoczna A, et al. Current role and future perspectives of magnetic resonance spectroscopy in radiation oncology for prostate cancer. Neoplasia. 2007;9(6):455–63. doi: 10.1593/neo.07277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Liu X, et al. Prostate Cancer Segmentation With Simultaneous Estimation of Markov Random Field Parameters and Class. IEEE Tran Med Imag. 2009;28(6):906–915. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2009.2012888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tiwari P, Madabhushi A, et al. Spectral embedding based probabilistic boosting tree (ScEPTre): classifying high dimensional heterogeneous biomedical data. MICCAI. 2009;12:844–51. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-04271-3_102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Toth R, Madabhushi A, et al. A magnetic resonance spectroscopy driven initialization scheme for active shape model based prostate segmentation. Med Img Anal. 2010 doi: 10.1016/j.media.2010.09.002. In Press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chappelow J, Madabhushi A, et al. Elastic Registration of Multimodal Prostate MRI and Histology via Multi-Attribute Combined Mutual Information. Med Phys. 2010 doi: 10.1118/1.3560879. Accepted. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Breiman Leo. Arcing Classifiers. Ann Stat. 1998;26(3):801–824. [Google Scholar]


