Abstract
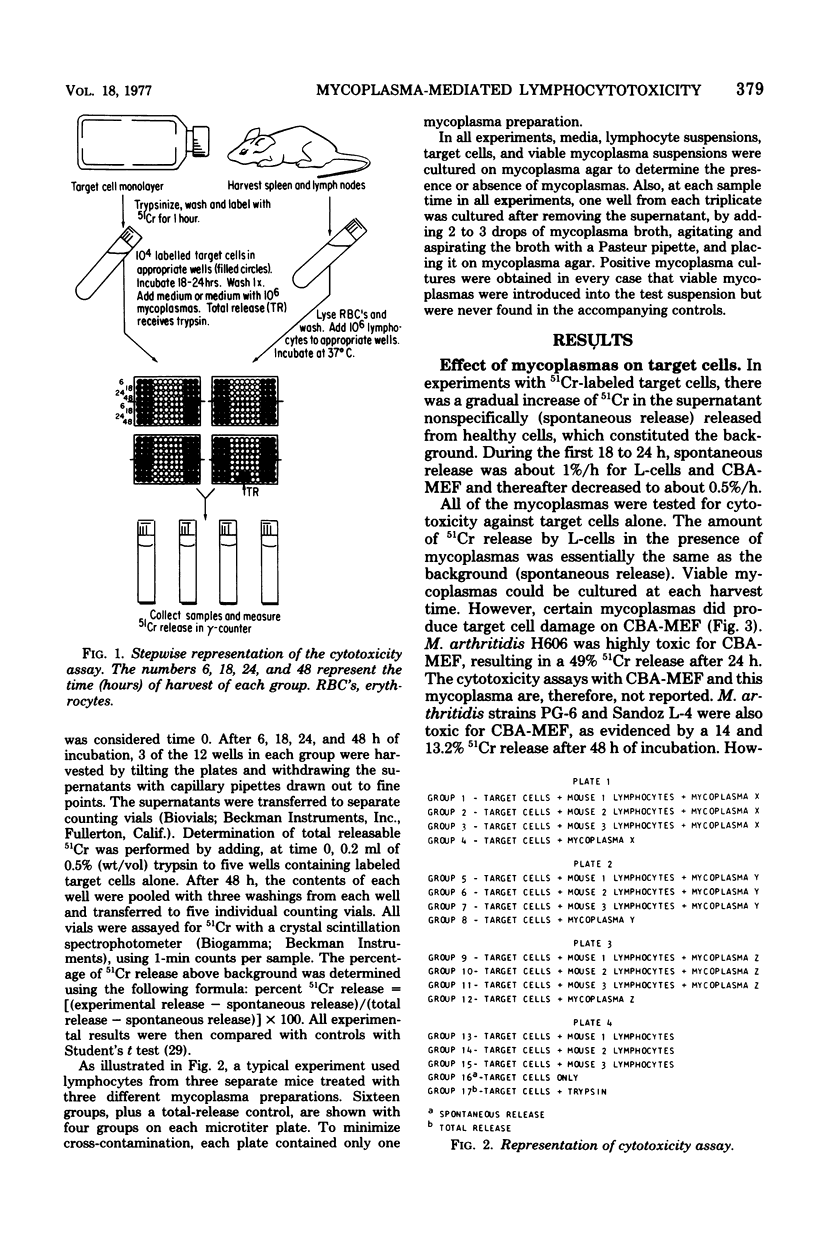
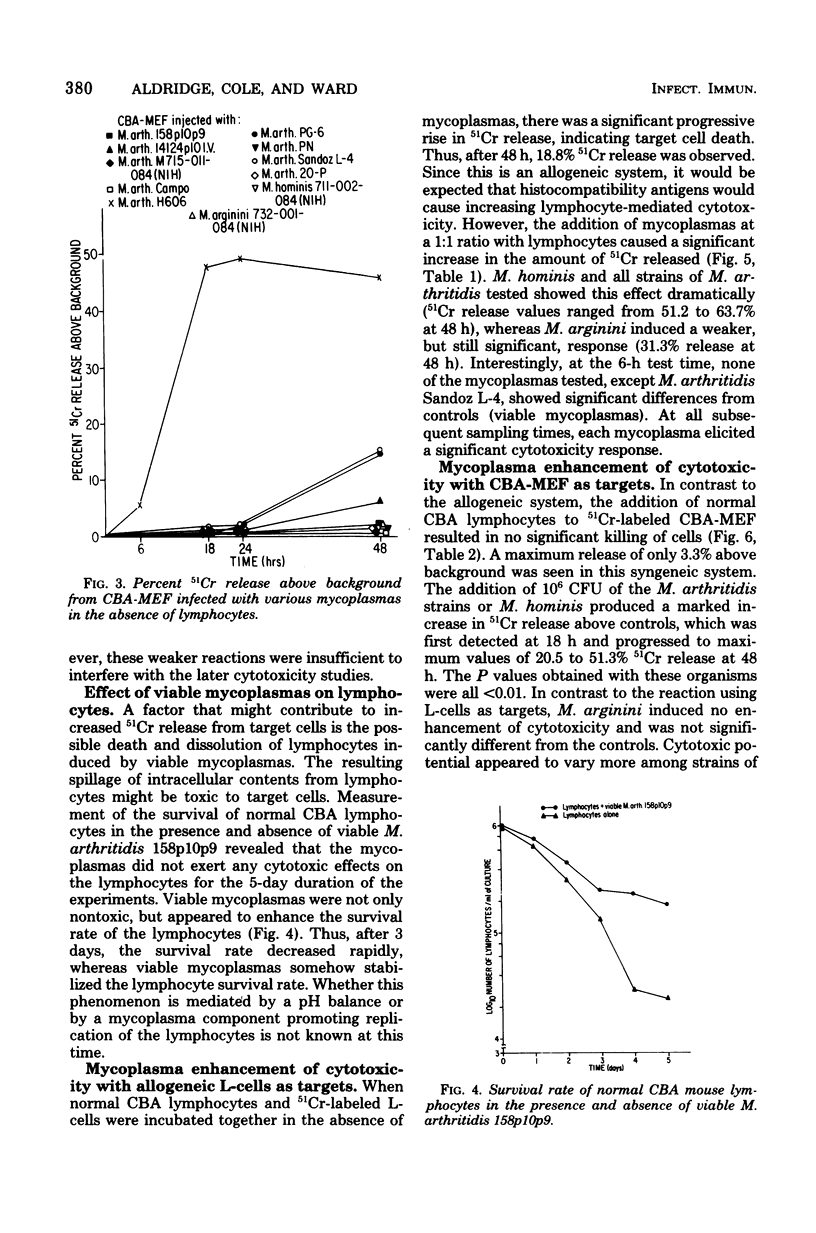
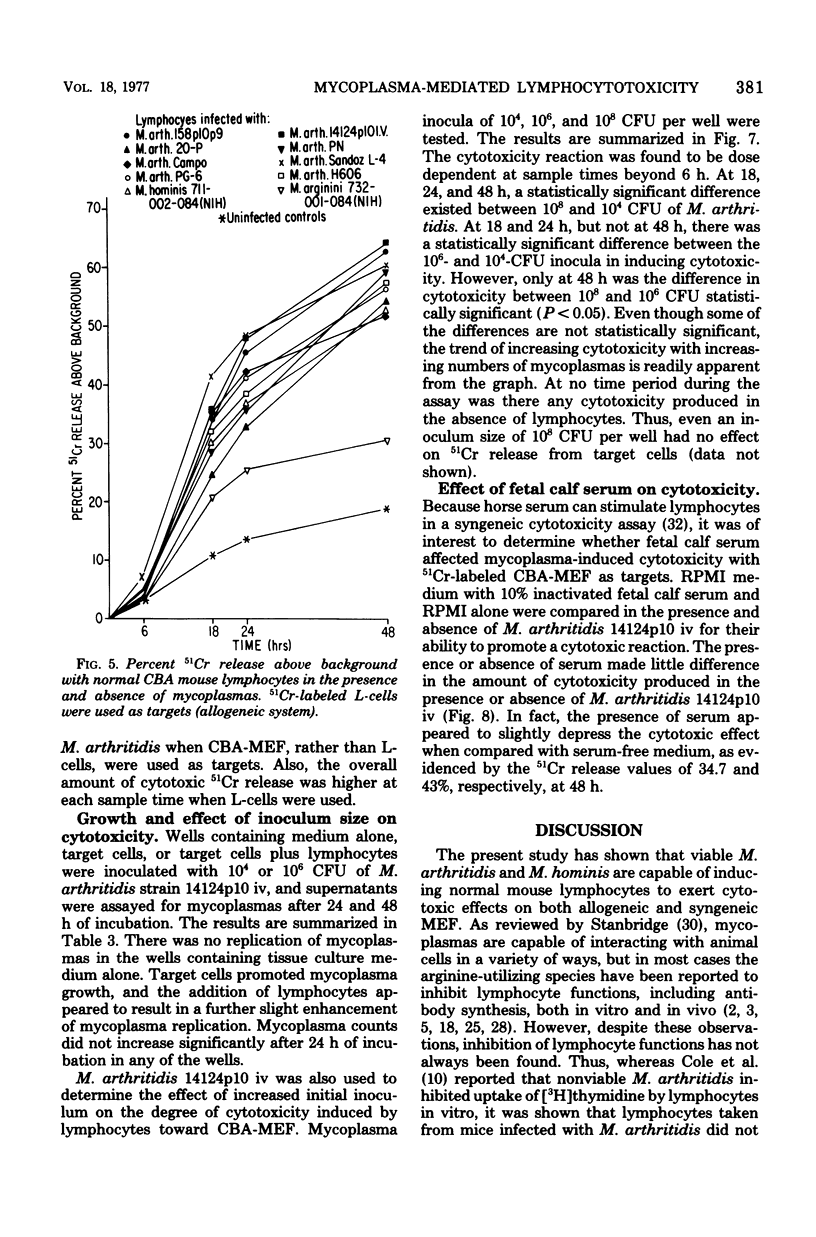
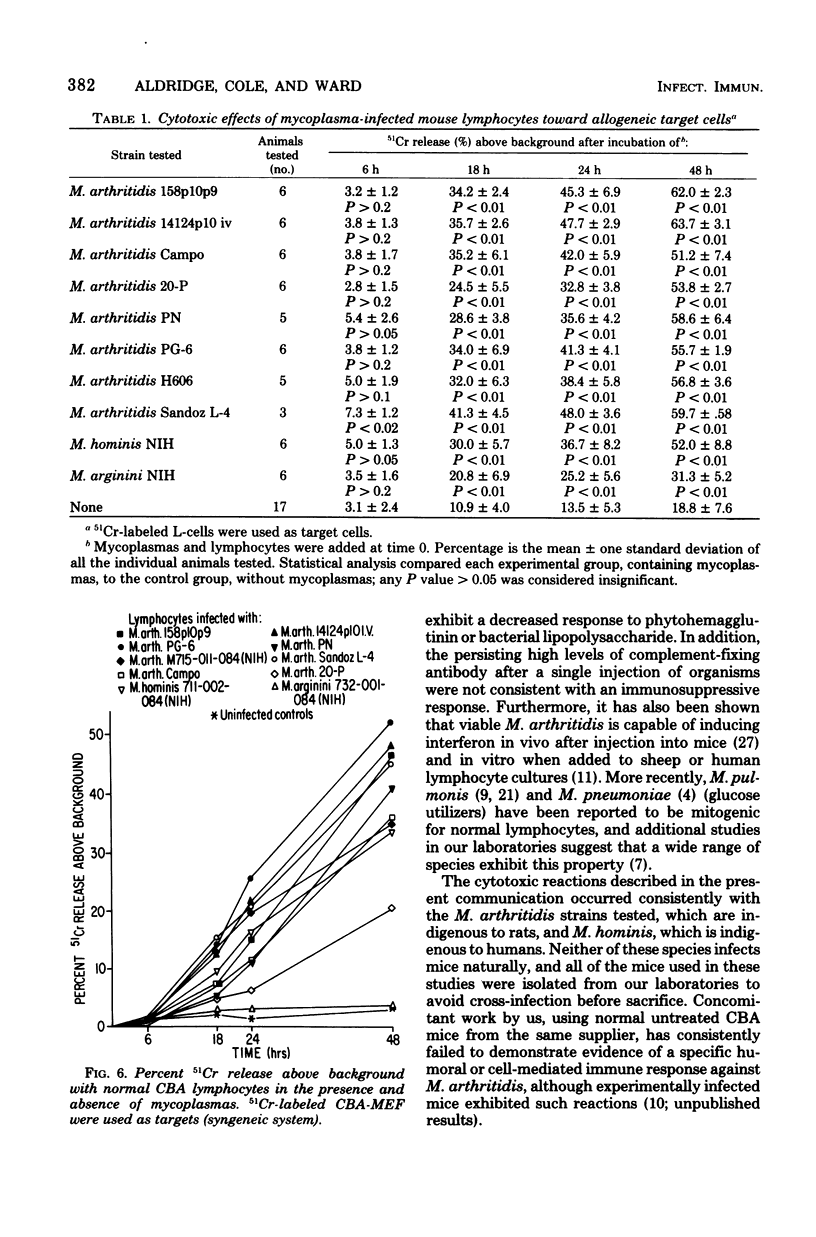
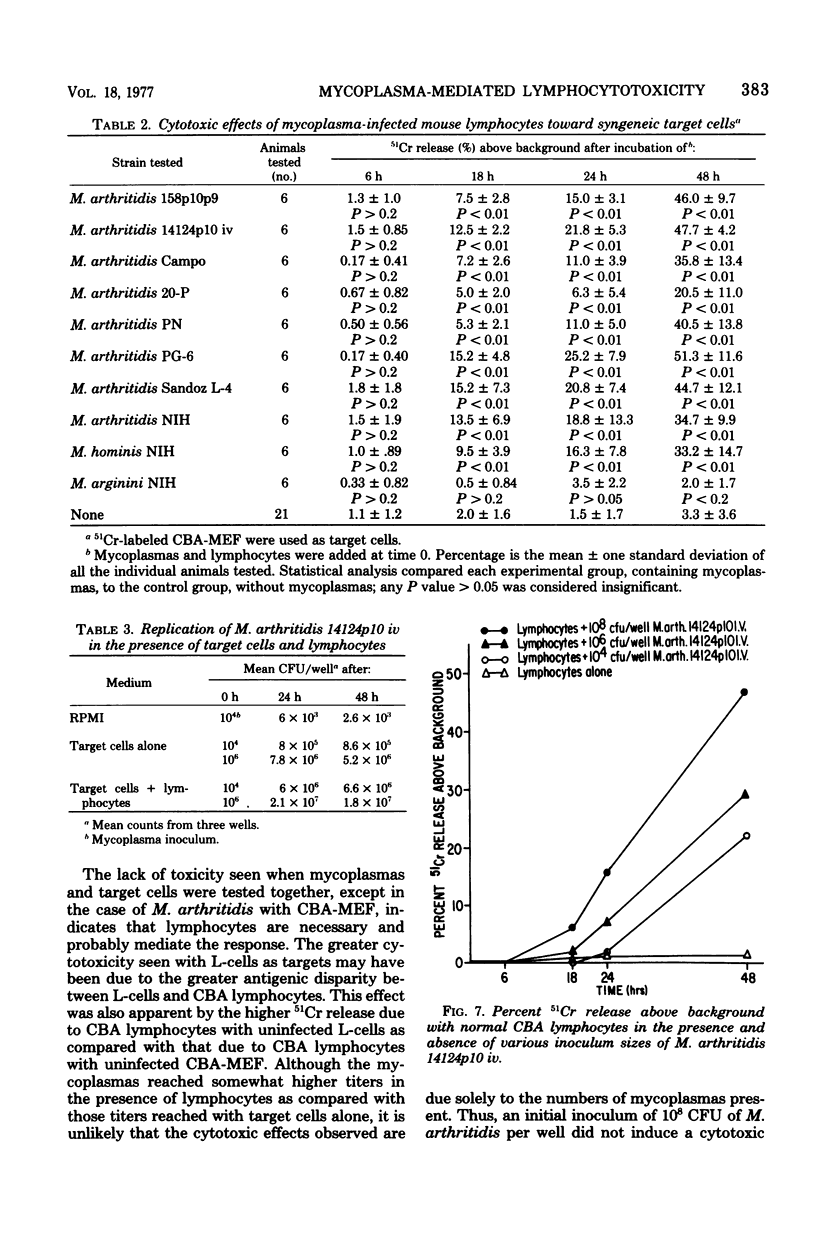
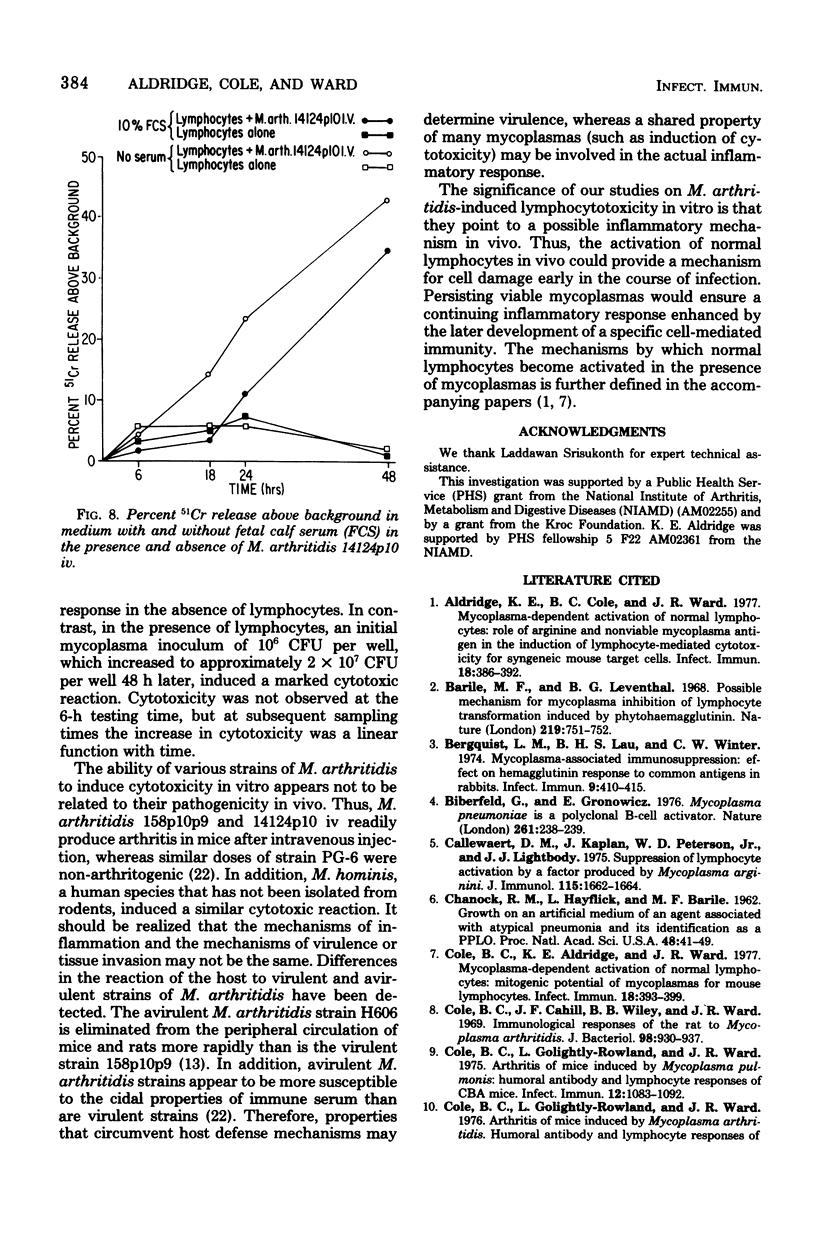
Mycoplasma arthritidis, M. hominis, and M. arginini were tested for their ability to induce a cytotoxic response from normal CBA mouse lymphocytes against 51Cr-labeled allogeneic target cells. In most cases, the mycoplasmas alone were not toxic for the target cells. Furthermore, the mycoplasmas did not result in decreased lymphocyte viability but, in fact, contributed to enhanced lymphocyte survival. In the absence of normal CBA lymphocytes, mycoplasmas alone did not induce a significant amount of cell damage in either the allogeneic or the syngeneic target cells. Strains of M. arthritidis and M. hominis, when added to the lymphocyte-target cell mixtures, induced statistically significant increases in 51Cr release from both target cell types at each assay period after 6 h. The release of 51Cr was taken as a measure of cell death. M. arginini induced only low levels of cytotoxicity or none at all. Both arthritogenic and non-arthritogenic strains of M. arthritidis induced the cytotoxic response. The degree of cytotoxicity produced was directly related to the size of the initial inoculum. The presence or absence of serum in the culture medium did not contribute significantly to the cytotoxicity response.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge K. E., Cole B. C., Ward J. R. Mycoplasma-dependent activation of normal lymphocytes: role of arginine and nonviable mycoplasma antigen in the induction of lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity for syngeneic mouse target cells. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):386–392. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.386-392.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barile M. F., Leventhal B. G. Possible mechanism for Mycoplasma inhibition of lymphocyte transformation induced by phytohaemagglutinin. Nature. 1968 Aug 17;219(5155):750–752. doi: 10.1038/219751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergquist L. M., Lau B. H., Winter C. E. Mycoplasma-associated immunosuppression: effect on hemagglutinin response to common antigens in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):410–415. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.410-415.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld G., Gronowicz E. Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a polyclonal B-cell activator. Nature. 1976 May 20;261(5557):238–239. doi: 10.1038/261238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R. M., HAYFLICK L., BARILE M. F. Growth on artificial medium of an agent associated with atypical pneumonia and its identification as a PPLO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:41–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callewaert D. M., Kaplan J., Peterson W. D., Jr, Lightbody J. J. Suppression of lymphocyte activation by a factor produced by Mycoplasma arginini. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1662–1664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coke B. C., Ward J. R., Golightly-Rowland C., Trapp G. A. Chronic proliferative arthritis of mice induced by Mycoplasma arthritidis. II. Serological responses of the lost and effect of vaccines. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):431–440. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.431-440.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Aldridge K. E., Ward J. R. Mycoplasma-dependent activation of normal lymphocytes: mitogenic potential of mycoplasmas for mouse lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):393–399. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.393-399.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Cahill J. F., Wiley B. B., Ward J. R. Immunological responses of the rat to Mycoplasma arthritidis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):930–937. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.930-937.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Golightly-Rowland L., Ward J. R. Arthritis of mice induced by Mycoplasma arthritidis. Humoral antibody and lymphocyte responses of CBA mice. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Feb;35(1):14–22. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Golightly-Rowland L., Ward J. R. Arthritis of mice induced by Mycoplasma pulmonis: humoral antibody and lymphocyte responses of CBA mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1083–1092. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1083-1092.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Overall J. C., Jr, Lombardi P. S., Glasgow L. A. Induction of interferon in ovine and human lymphocyte cultures by mycoplasmas. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):88–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.88-94.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Ward J. R. Fate of intravenously injected Mycoplasma arthritidis in rodents and effect of vaccines. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):416–425. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.416-425.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Ward J. R. Interaction of Mycoplasma arthritidis and other mycoplasmas with murine peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):691–699. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.691-699.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Ward J. R., Jones R. S., Cahill J. F. Chronic proliferative arthritis of mice induced by Mycoplasma arthritidis. I. Induction of disease and histopathological characteristics. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):344–355. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.344-355.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Ward J. R., Martin C. H. Hemolysin and peroxide activity of Mycoplasma species. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2022–2030. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2022-2030.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copperman R., Morton H. E. Reversible inhibition of mitosis in lymphocyte cultures by non-viable Mycoplasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Dec;123(3):790–795. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny F. W., Taylor-Robinson D., Allison A. C. The role of thymus-dependent immunity in Mycoplasma pulmonis infections of mice. J Med Microbiol. 1972 Aug;5(3):327–336. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-3-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg H., Nicolet J. Extensive transformation of lymphocytes by a mycoplasma organism. Nat New Biol. 1973 Dec 5;246(153):143–146. doi: 10.1038/newbio246143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golightly-Rowland L., Cole B. C., Ward J. R., Wiley B. B. Effect of Animal Passage on Arthritogenic and Biological Properties of Mycoplasma arthritidis. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):538–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.538-545.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. Tissue cultures and mycoplasmas. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Jun;23(Suppl):285+–285+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson E., Reinius S., Rimaila-Pärnänen E., Tuuri S. Studies on the pathogenicity for rat of a mycoplasma isolated from rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Feb;83(1):61–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00071.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaklamanis E., Pavlatos M. The immunosuppressive effect of mycoplasma infection. I. Effect on the humoral and cellular response. Immunology. 1972 Apr;22(4):695–702. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Cole B. C., Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Induction of interferon in mice by mycoplasmas. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1296–1301. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1296-1301.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simberkoff M. S., Thorbecke G. J., Thomas L. Studies of PPLO infection. V. Inhibition of lymphocyte mitosis and antibody formation by mycoplasmal extracts. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1163–1181. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. Mycoplasmas and cell cultures. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Jun;35(2):206–227. doi: 10.1128/br.35.2.206-227.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G., Taylor-Robinson D., Fernald G. W. Reduction in the severity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced pneumonia in hamsters by immunosuppressive treatment with antithymocyte sera. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Aug;7(3):343–348. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-3-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsui I., Everett N. B. Specific versus nonspecific target cell destruction by T lymphocytes sensitized in vitro. I. Kinetics. Cell Immunol. 1974 Mar 15;10(3):344–358. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD J. R., JONES R. S. The pathogenesis of mycoplasma (PPLO) arthritis in rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1962 Apr;5:163–175. doi: 10.1002/art.1780050205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


