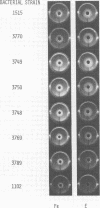
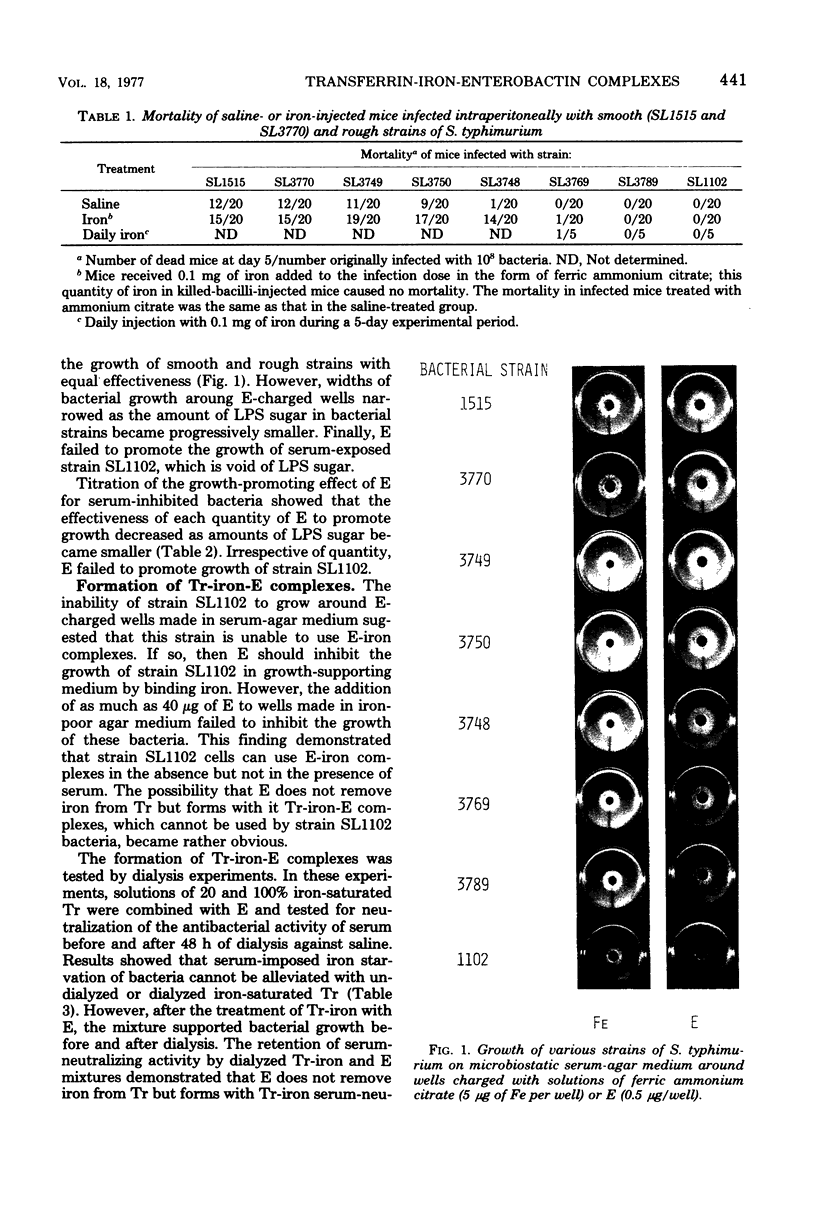
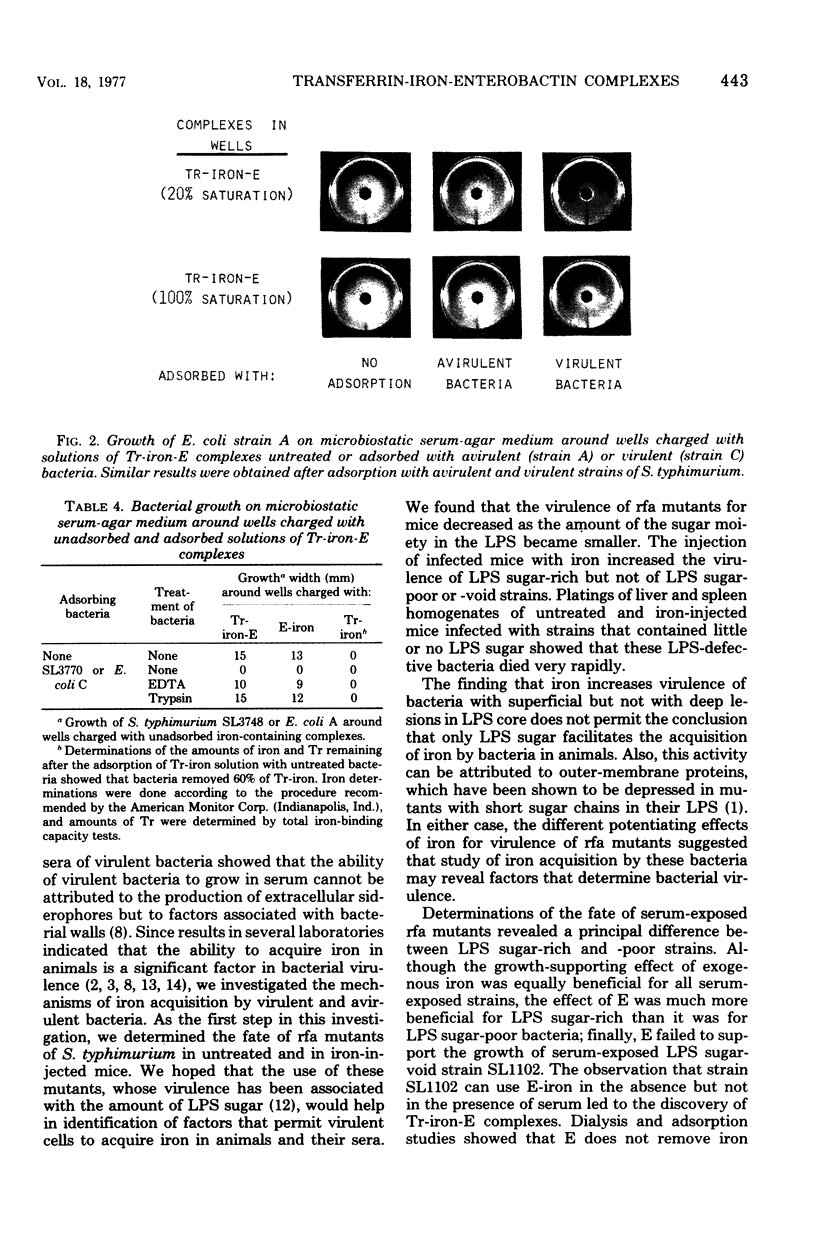
Abstract
Two smooth and six rough strains of Salmonella typhimurium with progressively smaller amounts of sugar and protein in their outer membrane were tested for degree of virulence in normal and iron-injected mice and for ability to acquire iron in mammalian sera. The rate of mortality showed that bacterial virulence for mice was lowered with progressive decrease of outer-membrane sugar and protein. Iron injections increased the rate of mortality in mice infected either with smooth strains or with superficially rough strains but were without effect in mice infected with deep rough strains. In in vitro experiments, iron promoted with equal effectiveness the growth of all serum-exposed bacterial strains, whereas enterobactin (E) was much more effective in promoting the growth of smooth and superficial rough than in promoting that of deep rough strains. Various experiments showed that deep rough strains cannot grow in E-supplemented serum because they are not able to use the transferrin-iron-E complexes that E forms with transferrin-iron. This failure to use transferrin-iron-E complexes by deep rough strains was found to be due to the inability of these strains to absorb iron containing complexes to their outer membrane. Adsorption studies with chemically treated bacteria showed that the receptor of transferrin-iron-E or E-iron complexes is a protein of the outer membrane of bacterial cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F., Spudich E. N., Nikaido H. Protein composition of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: effect of lipopolysaccharide mutations. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):406–416. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.406-416.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. M., Bullen J. J. The effect of passage and iron on the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Jan;25(1):65–68. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden C. A., Kochan I., Spriggs D. R. Role of mycobactin in the growth and virulence of tubercle bacilli. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):34–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.34-40.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guterman S. K. Colicin B: mode of action and inhibition by enterochelin. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1217–1224. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1217-1224.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochan I., Cahall D. L., Golden C. A. Employment of tuberculostasis in serum-agar medium for the study of production and activity of Mycobactin. Infect Immun. 1971 Aug;4(2):130–137. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.2.130-137.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochan I., Kvach J. T., Wiles T. I. Virulence-associated acquisition of iron in mammalian serum by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1977 Apr;135(4):623–632. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.4.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo T. T., Stocker B. A. Mapping of rfa Genes in Salmonella typhimurium by ES18 and P22 Transduction and by Conjugation. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):48–57. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.48-57.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L., Shovlin V. K., Mergenhagen S. E. Physical, chemical, and immunological properties of lipopolysaccharide released from Escherichia coli by ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 25;243(24):6384–6391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckey M., Neilands J. B. Iron transport in Salmonella typhimurium LT-2: prevention, by ferrichrome, of adsorption of bacteriophages ES18 and ES18.h1 to a common cell envelope receptor. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):1036–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.1036-1037.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyman M. B., Steward J. P., Roantree R. J. Characterization of the virulence and antigenic structure of Salmonella typhimurium strains with lipopolysaccharide core defects. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1539–1542. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1539-1542.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Finkelstein R. A. Pathogenesis and immunology of experimental gonococcal infection: role of iron in virulence. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1313–1318. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1313-1318.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Iron-Binding Catechols and Virulence in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):445–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.445-456.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayne R., Frick K., Neilands J. B. Siderophore protection against colicins M, B, V, and Ia in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.7-12.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]