Abstract
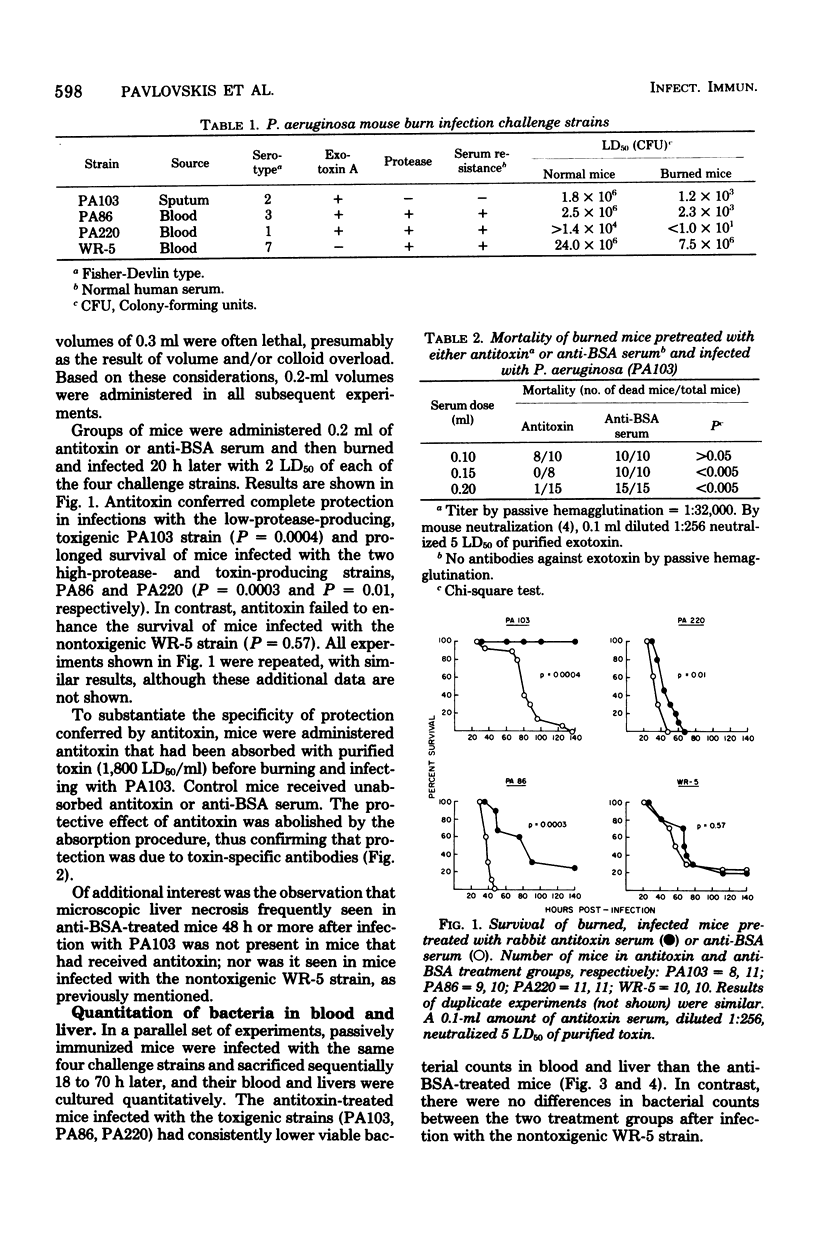
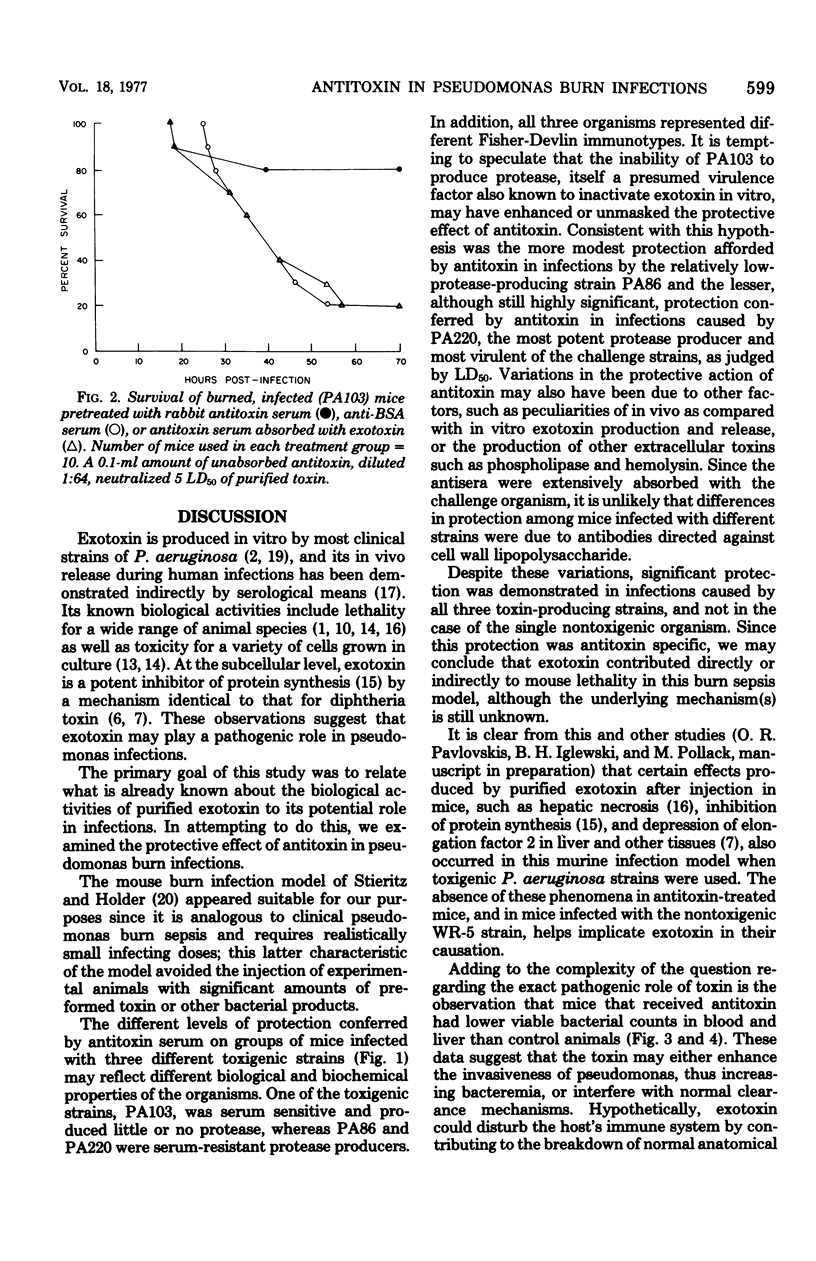
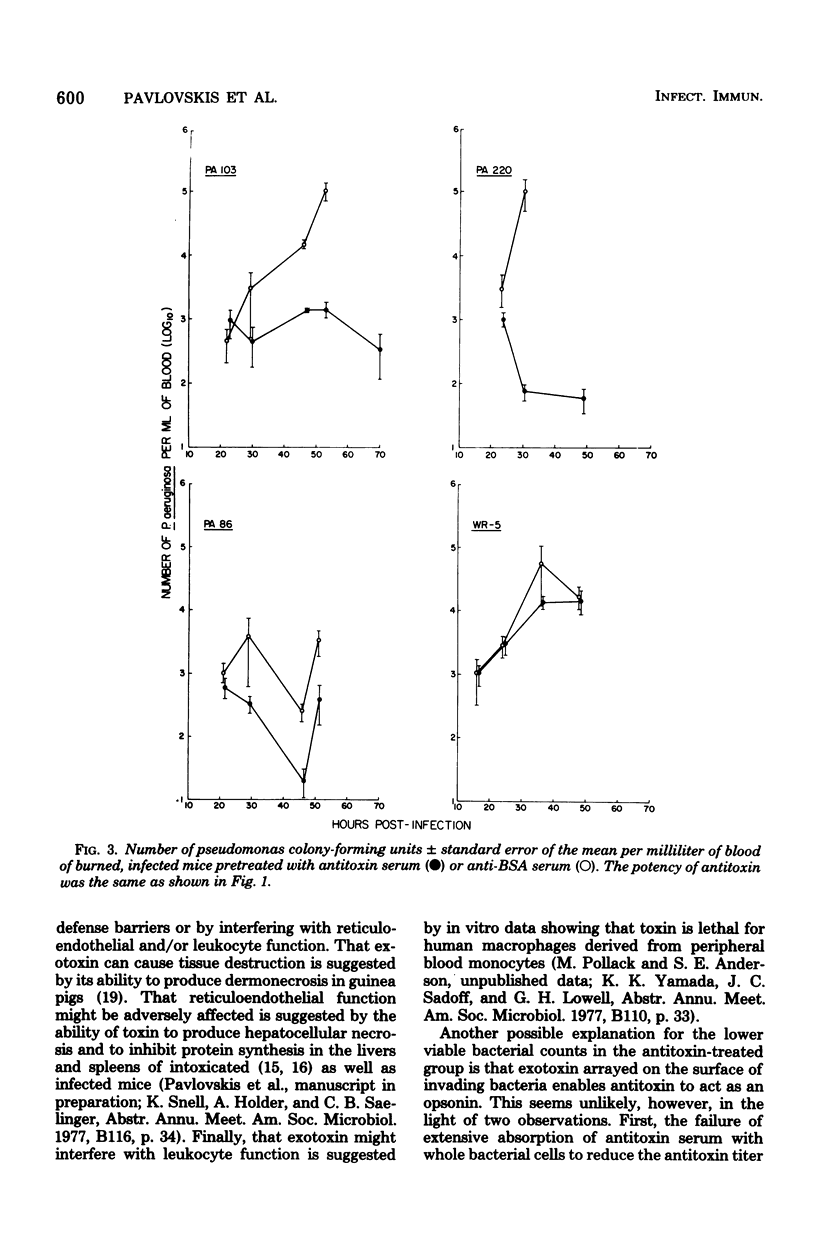
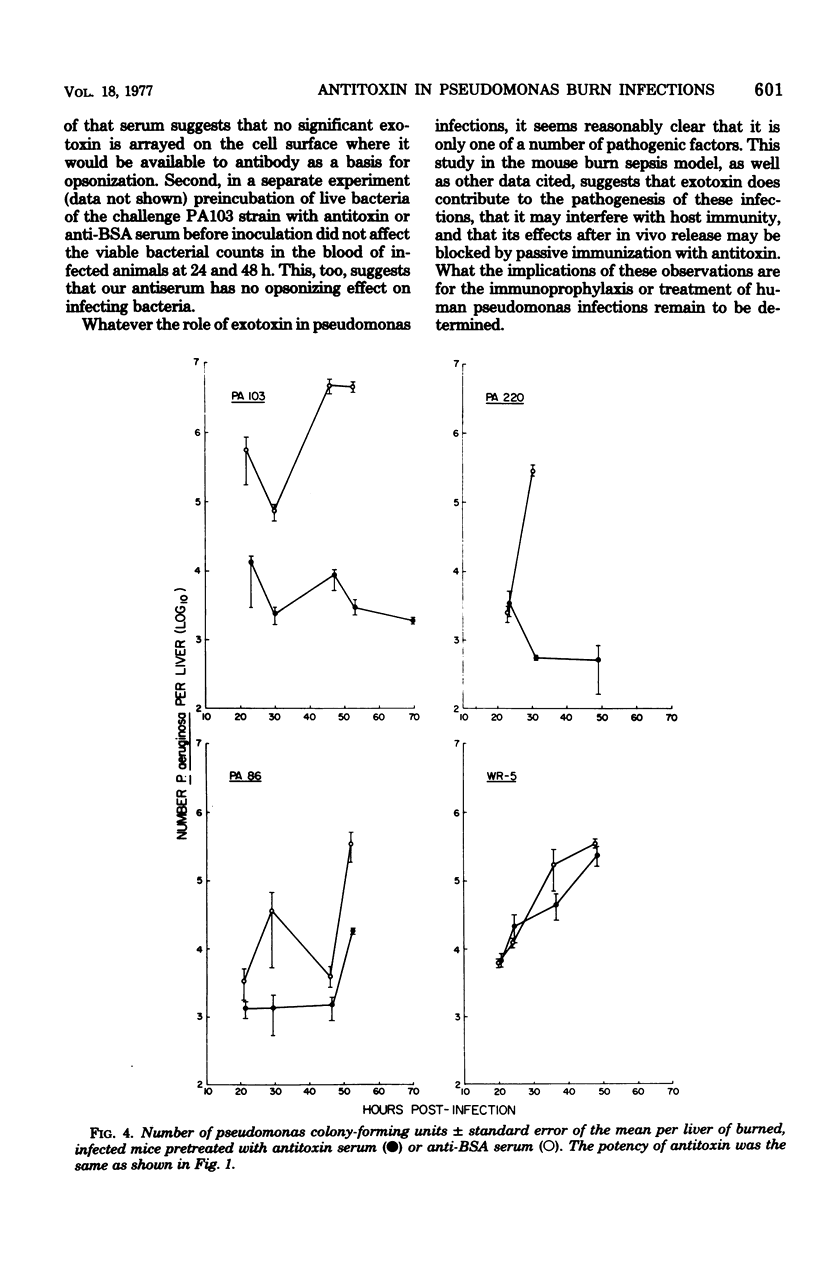
The protective effect of intravenously administered rabbit antitoxin serum was studied in lethal Pseudomonas aeruginosa burn infections in mice. Survival after infection with 2 median lethal doses of a toxigenic, low-protease-producing strain (PA103) was enhanced in antitoxin-treated mice, as compared with controls that had received anti-bovine serum albumin serum (P = 0.0004). Survival time was prolonged in other antitoxin-treated mice infected with toxigenic, high-protease-producing strains (PA86 and PA220, P = 0.0003 and P = 0.01, respectively). In contrast, antitoxin had no protective effect in mice challenged with a nontoxigenic strain (WR 5, P = 0.57). There were fewer viable bacteria in blood and liver of antitoxin-treated mice than in those of anti-bovine serum albumin-treated controls after infection with toxigenic organisms, whereas there were no significant differences between the two groups after challenge with the nontoxigenic strain. These data suggest that P. aeruginosa exotoxin A contributes to lethality in this burn infection model, and this effect is diminished by passive immunization with antitoxin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atik M., Liu P. V., Hanson B. A., Amini S., Rosenberg C. F. Pseudomonas exotoxin shock. A preliminary report of studies in dogs. JAMA. 1968 Jul 15;205(3):134–140. doi: 10.1001/jama.205.3.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorn M. J., Vasil M. L., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H. Incidence of exotoxin production by Pseudomonas species. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):362–366. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.362-366.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan L. T., 3rd Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin: purification by preparative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and the development of a highly specific antitoxin serum. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.55-61.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan L. T., 3rd Purification and characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):113–118. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.113-118.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Liu P. V., Kabat D. Mechanism of action of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin Aiadenosine diphosphate-ribosylation of mammalian elongation factor 2 in vitro and in vivo. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.138-144.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. Extracellular toxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130 (Suppl)(0):S94–S99. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.supplement.s94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V., Hsieh H. Exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 3. Characteristics of antitoxin A. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):520–526. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. 3. Identity of the lethal toxins produced in vitro and in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1966 Oct;116(4):481–489. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.4.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V., Yoshii S., Hsieh H. Exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. II. Concentration, purification, and characterization of exotoxin A. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):514–519. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B. Response of cultured mammalian cells to the exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Corynebacterium diphtheriae: differential cytotoxicity. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Feb;23(2):183–189. doi: 10.1139/m77-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Gordon F. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin: effect on cell cultures. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):631–636. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Shackelford A. H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin in mice: localization and effect on protein synthesis. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):540–546. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.540-546.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Voelker F. A., Shackelford A. H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin in mice: histopathology and serum enzyme changes. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133(3):253–259. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.3.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Callahan L. T., 3rd, Taylor N. S. Neutralizing antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin in human sera: evidence for in vivo toxin production during infection. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):942–947. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.942-947.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Taylor N. S., Callahan L. T., 3rd Exotoxin production by clinical isolates of pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):776–780. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.776-780.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Taylor N. S. Serum antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin measured by a passive hemagglutination assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jul;6(1):58–61. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.1.58-61.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieritz D. D., Holder I. A. Experimental studies of the pathogenesis of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: description of a burned mouse model. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jun;131(6):688–691. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.6.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


