Abstract
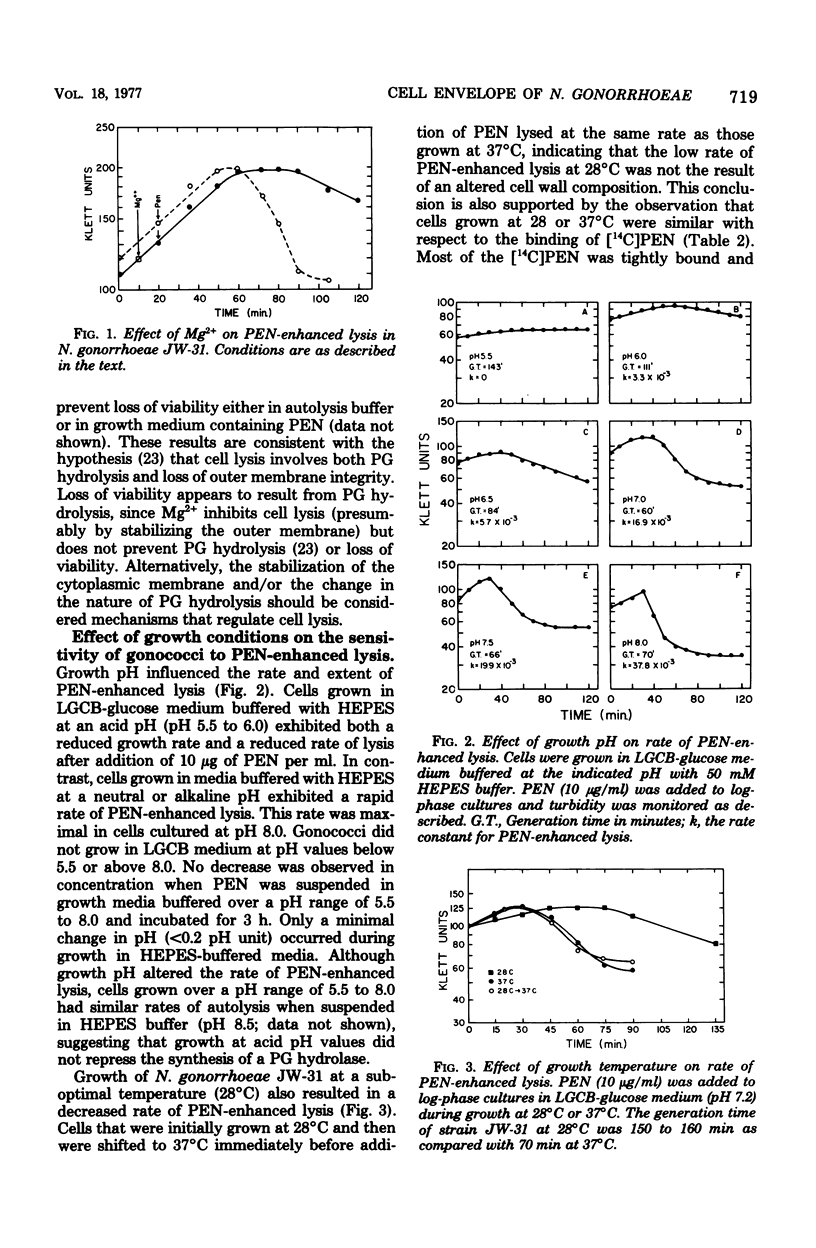
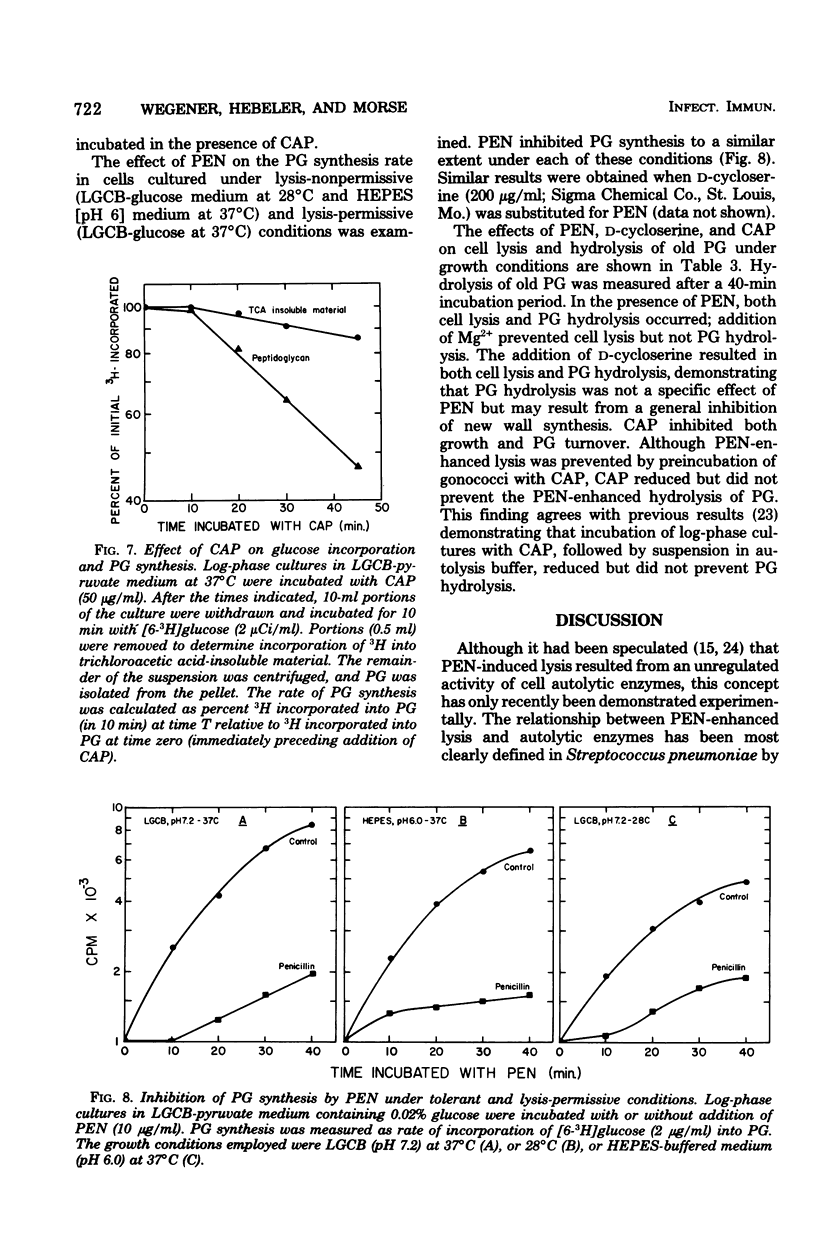
The addition of 10 microgram of penicillin G per ml to log-phase cultures of Neisseria gonorrhoeae JW-31 (minimum inhibitory concentration for penicillin G, less than 0.007 microgram/ml) resulted in cellular lysis after a lag of 30 min. Penicillin markedly decreased the rate of peptidoglycan synthesis and enhanced the rate of hydrolysis of existing peptidoglycan. Hydrolysis was initiated immediately after addition of penicillin; cellular lysis did not occur until a considerable percentage of the peptidoglycan had been degraded. Cellular lysis was not due to penicillin per se but resulted from inhibition of cell wall synthesis. When cells were grown in media buffered with N-2-hydroxyethyl piperazine-N'-2-ethanesulfonic acid at pH 6, penicillin did not cause lysis; however, at this pH, peptidoglycan hydrolysis occurred and cells lost viability at the same rate as in the control (pH 7.2). We suggest that the stability of gonococci grown at pH 6 is related to increased stability of the outer membrane. The penicillin-enhanced rate of peptidoglycan hydrolysis decreased approximately 50% at pH 6.0. Penicillin-enhanced lysis, peptidoglycan hydrolysis, and loss of viability were also markedly reduced in cells grown at 28 degrees C.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Elwell L. P., Roberts M., Mayer L. W., Falkow S. Plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase production in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):528–533. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W., Lopez R., Tomasz A. Suppression of lytic effect of beta lactams on Escherichia coli and other bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3293–3297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guymon L. F., Sparling P. F. Altered crystal violet permeability and lytic behavior in antibiotic-resistant and -sensitive mutants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):757–763. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.757-763.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebeler B. H., Morse S. A. Physiology and metabolism of pathogenic neisseria: tricarboxylic acid cycle activity in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):192–201. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.192-201.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebeler B. H., Young F. E. Chemical composition and turnover of peptidoglycan in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1180–1185. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1180-1185.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebeler B. H., Young F. E. Mechanism of autolysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1186–1193. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1186-1193.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne D., Tomasz A. Tolerant response of Streptococcus sanguis to beta-lactams and other cell wall inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 May;11(5):888–896. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.5.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tomasz A. Lipoteichoic acid: a specific inhibitor of autolysin activity in Pneumococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1690–1694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tomasz A. Purification of the pneumococcal N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase to biochemical homogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4199–4207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. The barrier function of the gram-negative envelope. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):109–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez R., Ronda-Lain C., Tapia A., Waks S. B., Tomasz A. Suppression of the lytic and bactericidal effects of cell wallinhibitory antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):697–706. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Bartenstein L. Factors affecting autolysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Apr;145(4):1418–1421. doi: 10.3181/00379727-145-38025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Stein S., Hines J. Glucose metabolism in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):702–714. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.702-714.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez W., Saz A. K. Possible mechanism of decreased susceptibility of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jun;7(6):788–792. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.6.788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarubbi F. A., Jr, Sparling P. F., Blackman E., Lewis E. Loss of low-level antibiotic resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae due to env mutations. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):750–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.750-756.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senff L. M., Wegener W. S., Brooks G. F., Finnerty W. R., Makula R. A. Phospholipid composition and phospholipase A activity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):874–880. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.874-880.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F., Sarubbi F. A., Jr, Blackman E. Inheritance of low-level resistance to penicillin, tetracycline, and chloramphenicol in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):740–749. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.740-749.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Waks S. Mechanism of action of penicillin: triggering of the pneumococcal autolytic enzyme by inhibitors of cell wall synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4162–4166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., PELZER H. BAGSHAPED MACROMOLECULES--A NEW OUTLOOK ON BACTERIAL CELL WALLS. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1964;26:193–232. doi: 10.1002/9780470122716.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener W. S., Hebeler B. H., Morse S. A. Cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: relationship between autolysis in buffer and the hydrolysis of peptidoglycan. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):210–219. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.210-219.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westling-Häggström B., Elmros T., Normark S., Winblad B. Growth pattern and cell division in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):333–342. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.333-342.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Lipoteichoic acids: a new class of bacterial antigen. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1161–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.46620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


