Abstract
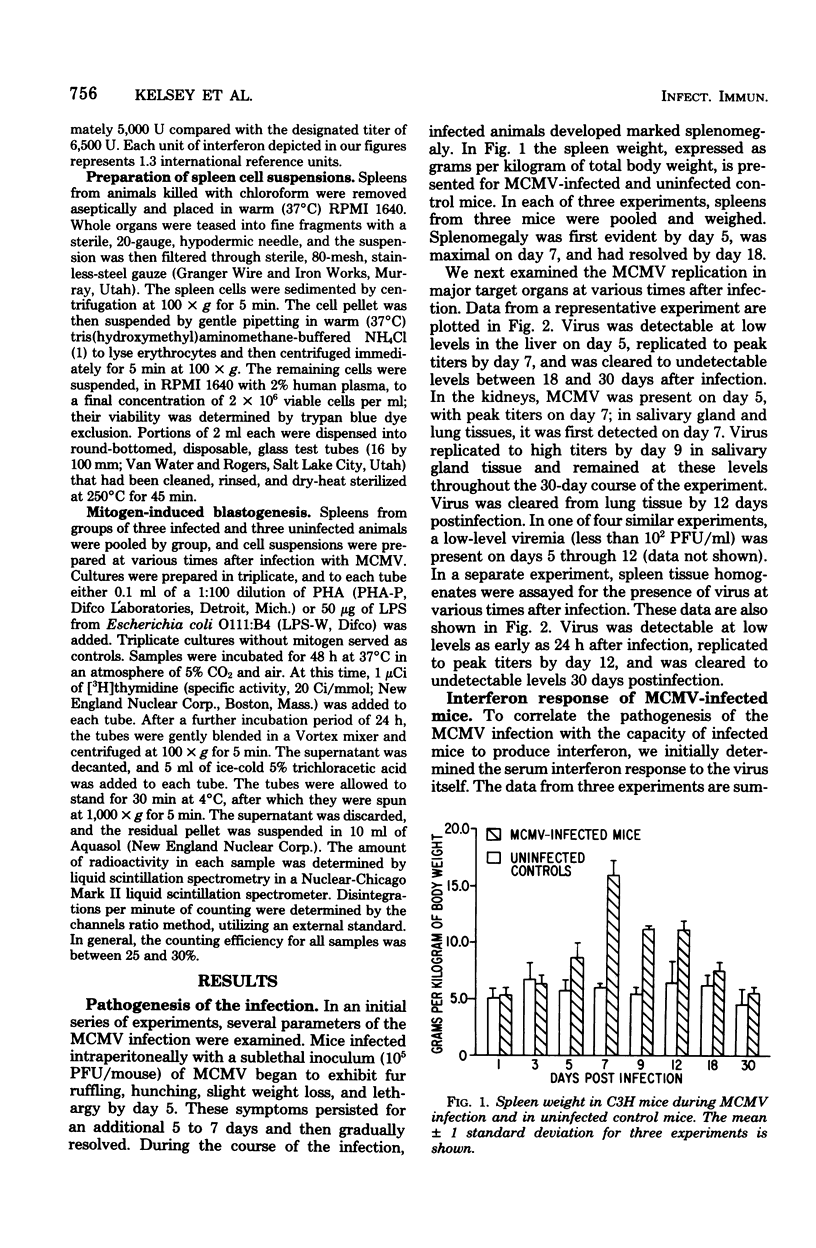
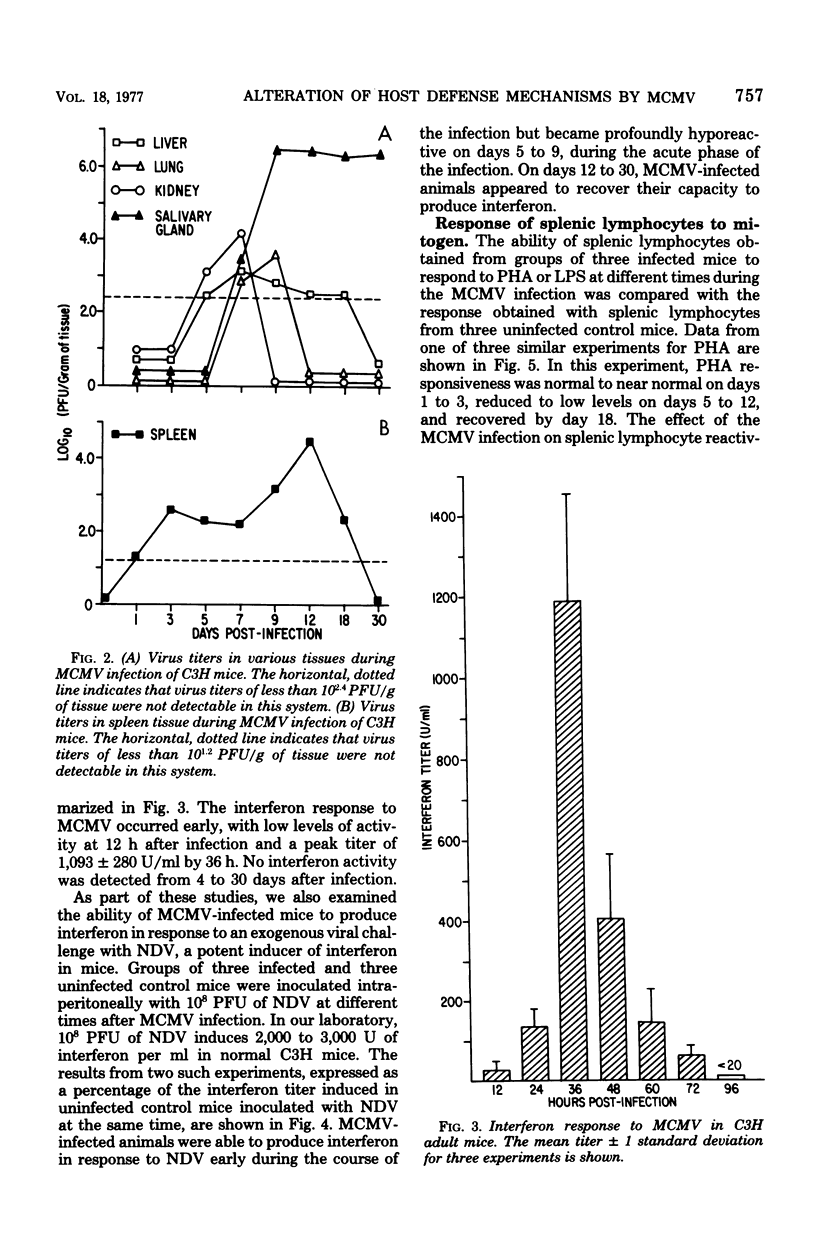
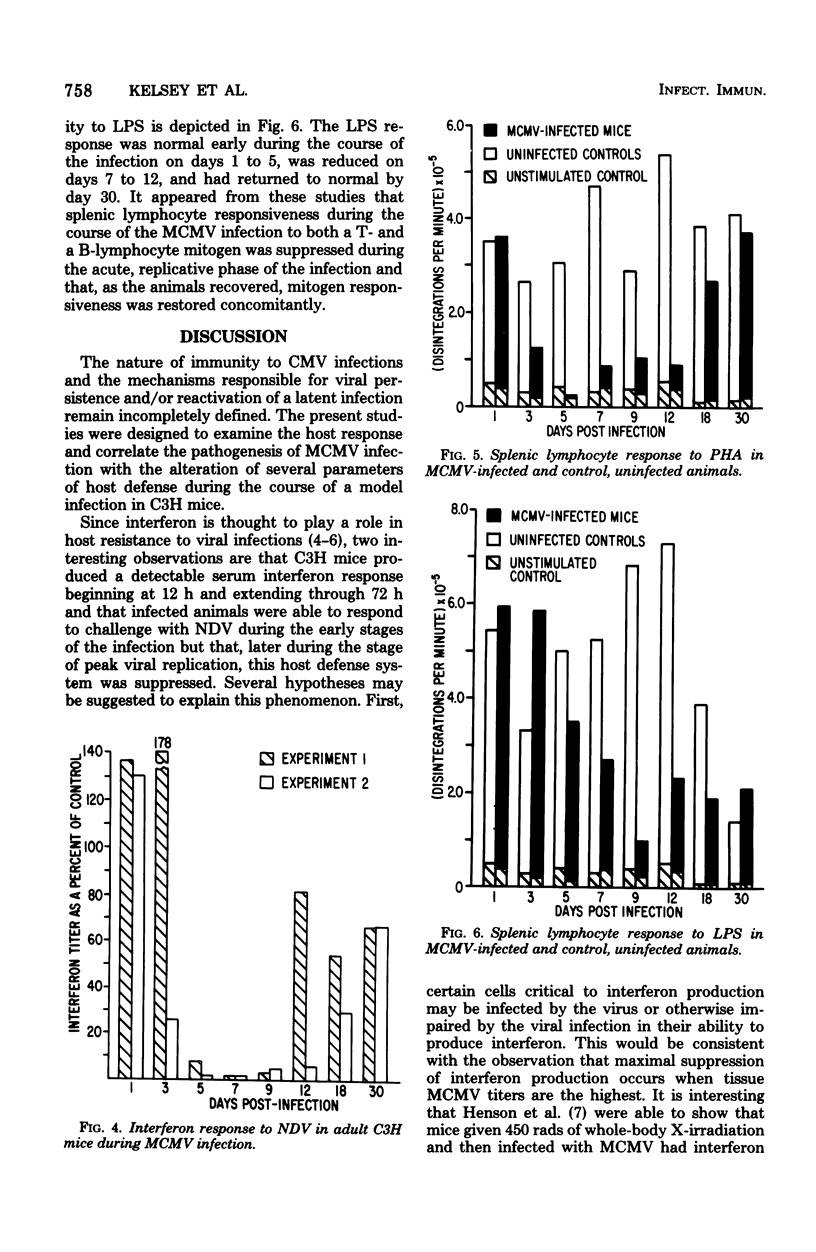
An animal model of a sublethal infection, utilizing murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV), was developed to determine whether immunological factors could contribute to the establishment of a persistent viral infection. Adult female C3H mice inoculated intraperitoneally with 10(5) plaque-forming units of MCMV developed splenomegaly 5 to 12 days after infection. Virus replicated to peak titers (10(3) to 10(6) plaque-forming units per g of tissue) in liver, spleen, lung, kidney, and salivary gland tissue during the acute phase of the infection (3 to 12 days); it then decreased to undetectable levels in all tissues except salivary gland. Serum interferon was detected as early as 12 h after infection, peaked at 36 h (1,093 U/ml), and was undetectable by 4 days after infection. MCMV-infected animals were hyporeactive to interferon induction with New castle disease virus on days 5 to 9 of the infection. Splenic lymphocyte reactivity to phytohemagglutinin and lipopolysaccharide was normal early during the course of the infection, was suppressed during the acute phase of the infection, and had returned to normal by day 18. These data indicate that several parameters of host defense are transiently suppressed during the course of a MCMV infection. The capacity of cytomegaloviruses to alter host resistance may be one factor that contributes to the establishment of a persistent infection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyle W. An extension of the 51Cr-release assay for the estimation of mouse cytotoxins. Transplantation. 1968 Sep;6(6):761–764. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196809000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diosi P., Moldovan E., Tomescu N. Latent cytomegalovirus infection in blood donors. Br Med J. 1969 Dec 13;4(5684):660–662. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5684.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Krüger J., Spiesel S. Z. Stimulation of B-lymphocytes by endotoxin. Reactions of thymus-deprived mice and karyotypic analysis of dividing cells in mice bearing T 6 T 6 thymus grafts. J Immunol. 1972 Apr;108(4):1088–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow L. A. Cellular immunity in host resistance to viral infections. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Jul;126(1):125–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Tovey M. G., Bandu M. E., Maury C., Brouty-Boyé D. Role of interferon in the pathogenesis of virus diseases in mice as demonstrated by the use of anti-interferon serum. I. Rapid evolution of encephalomyocarditis virus infection. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1305–1315. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Tovey M. G., Maury C., Bandu M. T. Role of interferon in the pathogenesis of virus diseases in mice as demonstrated by the use of anti-interferon serum. II. Studies with herpes simplex, Moloney sarcoma, vesicular stomatitis, Newcastle disease, and influenza viruses. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1316–1323. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson D., Smith R. D., Gehrke J. Non-fatal mouse cytomegalovirus hepatitis. Combined morphologic, virologic and immunologic observations. Am J Pathol. 1966 Nov;49(5):871–888. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson D., Strano A. J., Slotnik M., Goodheart C. Mouse cytomegalovirus: isolation from spleen and lymph nodes of chronically infected mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Jul;140(3):802–806. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M., Suwansirikul S., Dowling J. N., Youngblood L. A., Armstrong J. A. The transplanted kidney as a source of cytomegalovirus infection. N Engl J Med. 1975 Nov 27;293(22):1109–1112. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197511272932201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Miller J., Najarian J. S. Cytomegalovirus-induced immune suppression. II. Cell-mediated immunity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):119–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Greaves M. F. Lymphocyte activation. I. Response of T and B lymphocytes to phytomitogens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Oct;9(4):483–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey D. K., Kern E. R., Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Effect of cytosine arabinoside and 5-iodo-2'-deoxyuridine on a cytomegalovirus infection in newborn mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):458–464. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner H., Herberman R. B., Glaser M., Lavrin D. H. Suppression of in vitro lymphocyte stimulation in mice bearing primary Moloney sarcoma virus-induced tumors. Cell Immunol. 1974 Jul;13(1):32–40. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90224-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olding L. B., Jensen F. C., Oldstone M. B. Pathogenesis of of cytomegalovirus infection. I. Activation of virus from bone marrow-derived lymphocytes by in vitro allogenic reaction. J Exp Med. 1975 Mar 1;141(3):561–572. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Blazkovec A. A., Walker D. L. Immunosuppression during acute murine cytomegalovirus infection. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):835–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Medearis D. N., Jr Studies of relationship between mouse cytomegalovirus and interferon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Mar;121(3):819–824. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D. W., Stagno S., Hosty T. S., Tiller M., Alford C. A., Jr Maternal cytomegalovirus excretion and perinatal infection. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jul 5;289(1):1–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197307052890101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royston I., Sullivan J. L., Periman P. O., Perlin E. Cell-mediated immunity to Epstein-Barr-virus-transformed lymphoblastoid cells in acute infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1975 Dec 4;293(23):1159–1163. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197512042932301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selgrade M. K., Ahmed A., Sell K. W., Gershwin M. E., Steinberg A. D. Effect of murine cytomegalovirus on the in vitro responses of T and B cells to mitogens. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1459–1465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr J. G., Gold E. Prevalence and duration of postnatally acquired human cytomegalovirus infection. J Chronic Dis. 1970 Feb;22(8):603–607. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(70)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringfellow D. A., Glasgow L. A. Hyporeactivity due to infection: recognition of a transferable hyporeactive factor in the serum of encephalomyocarditis virus-infected mice. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1337–1342. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1337-1342.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringfellow D. A., Glasgow L. A. Tilorone hydrochloride: an oral interferon-inducing agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Aug;2(2):73–78. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.2.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringfellow D. A., Kern E. R., Kelsey D. K., Glasgow L. A. Suppressed response to interferon inducation in mice infected with encephalomyocarditis virus, Semliki forest virus, influenza A2 virus, Herpesvirus hominis type 2, or murine cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1977 Apr;135(4):540–551. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.4.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Lactic dehydrogenase activity in blood. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):210–213. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. B., French L. Plaque assay of cytomegalovirus strains of human origin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Nov;135(2):253–258. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


