Abstract
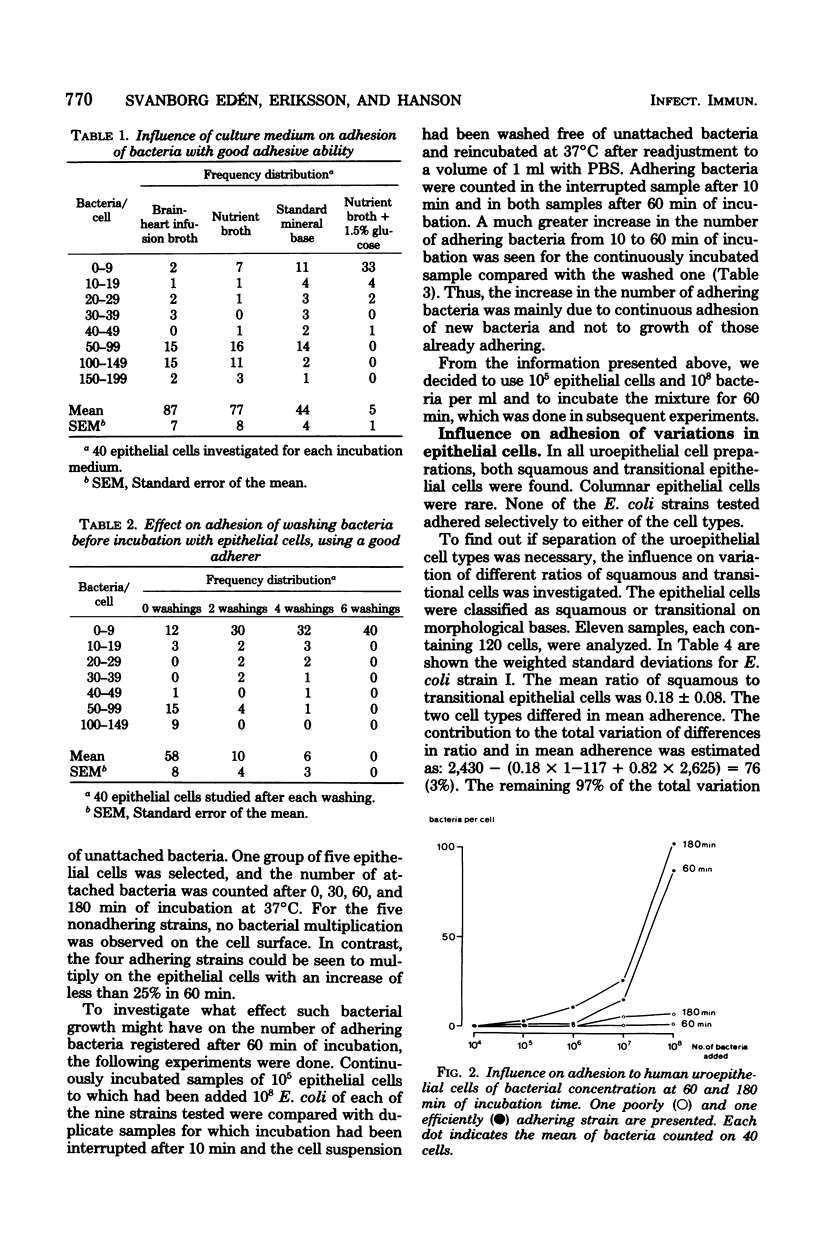
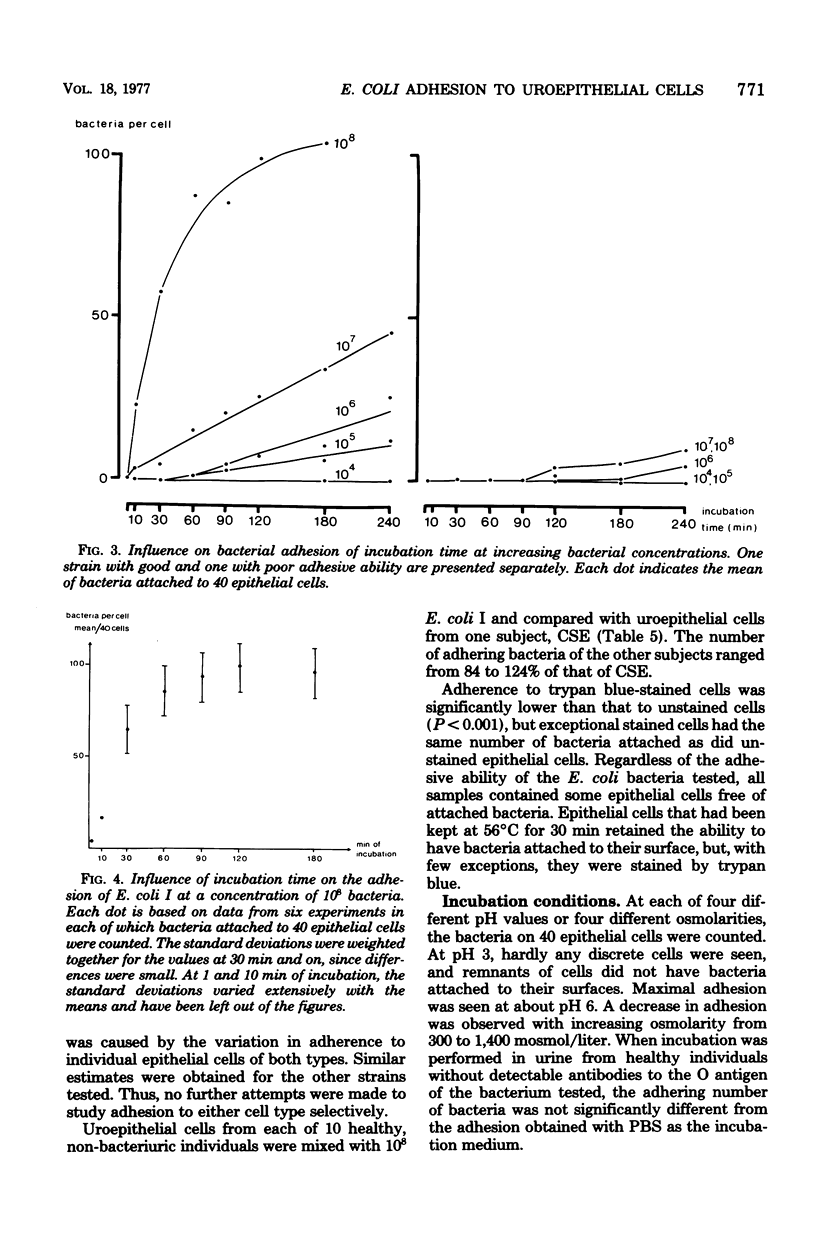
Optimal conditions for in vitro adherence of Escherichia coli to uroepithelial cells, previously shown to more efficient for strains causing acute symptomatic than that for strains causing "asymptomatic" urinary tract infections, were investigated. Uroepithelial cells from fresh morning urine of healthy individuals and E. coli bacteria from patients with various forms of urinary tract infeciton were used. Adhesion was found to vary, between individuals and epithelial cell types, with epithelial cell viability, bacterial cultivation medium and growth phase, number of bacteria added to the epithelial cells, and incubation time and temperature. Adhesion was also influenced by variations in pH and osmolarity. Optimal test conditions were obtained with post-log-phase bacterial cultures grown on nutrient broth when 10(8) bacteria were added to 10(5) epithelial cells and incubated for 60 min. Considerable variation was found between experiments done on different days, whereas the variation between duplicates was small. The method described may provide a useful tool in the study of the host-parasite relationship in urinary tract infections.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Hanson L. A., Jodal U., Lindberg U., Akerlund A. S. Variable adherence to normal human urinary-tract epithelial cells of Escherichia coli strains associated with various forms of urinary-tract infection. Lancet. 1976 Sep 4;1(7984):490–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Gibbons R. J. Parameters affecting the adherence and tissue tropisms of Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):85–91. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.85-91.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans H. M., Schulemann W. THE ACTION OF VITAL STAINS BELONGING TO THE BENZIDINE GROUP. Science. 1914 Mar 27;39(1004):443–454. doi: 10.1126/science.39.1004.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R., Jones G. W. Adhesive properties of Vibrio cholerae: nature of the interaction with intact mucosal surfaces. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):246–256. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.246-256.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Houte J. V. Bacterial adherence in oral microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:19–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson L. A., Ahlstedt S., Fasth A., Jodal U., Kaijser B., Larsson P., Lindberg U., Olling S., Sohl-Akerlund A., Svanborg-Edén C. Antigens of Escherichia coli, human immune response, and the pathogenesis of urinary tract infections. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S144–S149. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann A., Wilson M. R. Adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to intestinal epithelium in vivo. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):866–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.866-880.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Abrams G. D., Freter R. Adhesive properties of Vibrio cholerae: adhesion to isolated rabbit brush border membranes and hemagglutinating activity. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):232–239. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.232-239.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Freter R. Adhesive properties of Vibrio cholerae: nature of the interaction with isolated rabbit brush border membranes and human erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):240–245. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.240-245.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING D. W., PAULSON S. R., PUCKETT N. L., KREBS A. T. Cell death. IV. The effect of injury on the entrance of vital dye in Ehrlich tumor cells. Am J Pathol. 1959 Sep-Oct;35:1067–1079. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern W. H. Epithelial cells in urine sediments. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Jul;56(1):67–72. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/56.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeish A. S., Turner P., Fleming J., Evans N. Mucosal adherence of human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Lancet. 1975 Nov 15;2(7942):946–948. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90360-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy B., Moon H. W., Isaacson R. E. Colonization of porcine small intestine by Escherichia coli: ileal colonization and adhesion by pig enteropathogens that lack K88 antigen and by some acapsular mutants. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1214–1220. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1214-1220.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. A., Hu P. C., Wilson M., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Attachment of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to respiratory epithelium. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):959–966. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.959-966.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punsalang A. P., Jr, Sawyer W. D. Role of pili in the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):255–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.255-263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellwood R., Gibbons R. A., Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. Adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to pig intestinal brush borders: the existence of two pig phenotypes. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Aug;8(3):405–411. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-3-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J. Host-parasite interaction in the rat renal pelvis: a possible role for pili in the pathogenesis of pyelonephritis. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1696–1711. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobeslavsky O., Prescott B., Chanock R. M. Adsorption of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to neuraminic acid receptors of various cells and possible role in virulence. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):695–705. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.695-705.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ström J. Cytology of the urine in healthy persons and cytological reactions in acute infections, especially with respect to the presence of inclusion-bearing and giant cells. A study with application of millipore procedure and Papanicolaou staining. Scand J Infect Dis. 1973;5(3):209–228. doi: 10.3109/inf.1973.5.issue-3.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



