Abstract
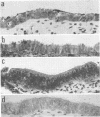
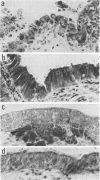
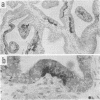
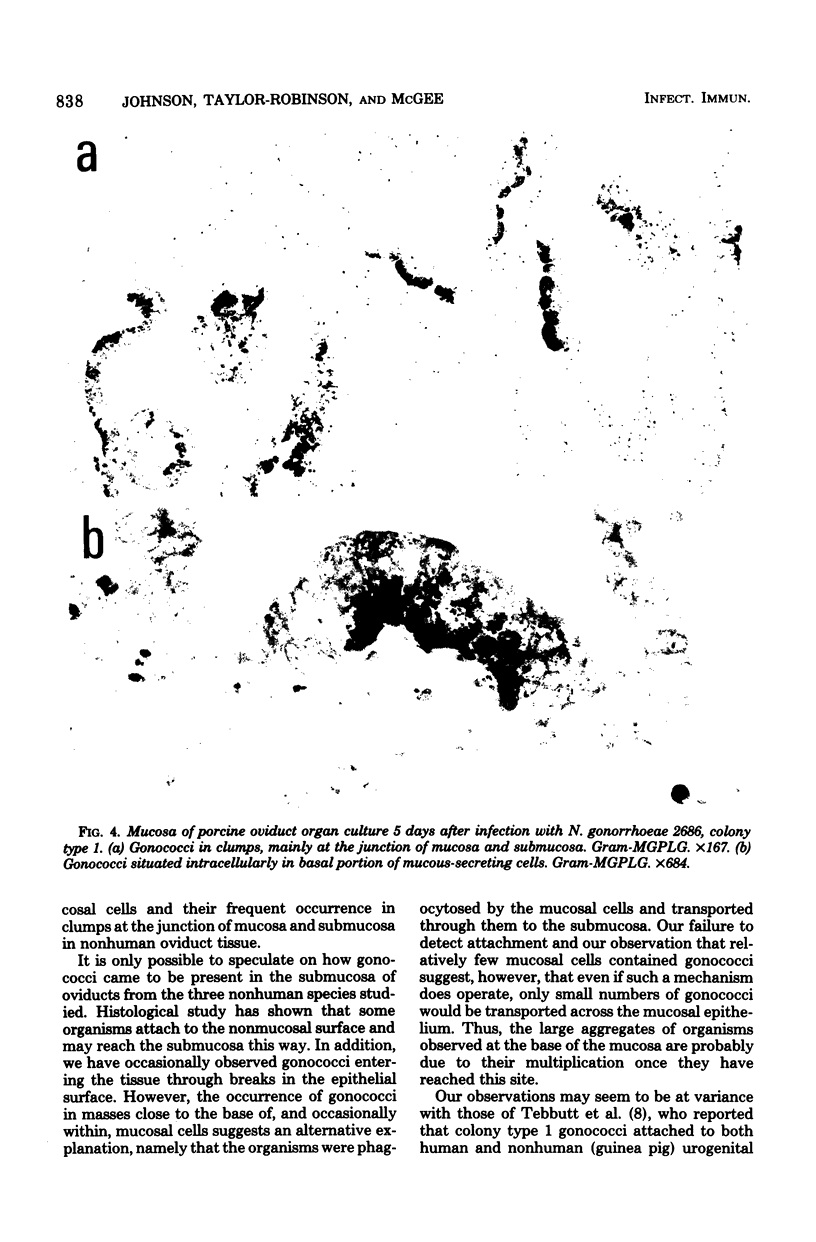
Neisseria gonorrhoeae colony type 1 were inoculated into organ cultures of oviducts obtained from various animal species. Gonococci rapidly attached to extensive areas of the mucosa of human oviducts (fallopian tubes), entered the mucous-secreting cells, and caused histological damage to the tissues. In addition, 2 to 4 days after infection there was complete loss of ciliary activity. In contrast, gonococci attached very scantily or not at all to the mucosa of rabbit, porcine, or bovine oviducts. However, the organisms multiplied in the medium of these organ cultures and were located sometimes in the base of mucosal cells and in large numbers in the submucosa. Despit this, there was no histological evidence of damage, and at least 7 days after infection ciliary activity was maintained equally as well as it was in uninfected control cultures. The host specificity of N. gonorrhoeae appears to be determined, at least in part, by a markedly diminished ability of the organisms to attach to and damage the genital mucosa of nonhuman species.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carney F. E., Jr, Taylor-Robinson D. Growth and effect of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in organ cultures. Br J Vener Dis. 1973 Oct;49(5):435–440. doi: 10.1136/sti.49.5.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler F. W., Jr, Kraus S. J. Animal model of human disease. Gonorrhea. Am J Pathol. 1976 Feb;82(2):437–440. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas C. T., Chandler F., Jr, Martin J. E., Jr, Schmale J. D. Transfer of gonococcal urethritis from man to chimpanzee. An animal model for gonorrhea. JAMA. 1971 Jun 7;216(10):1612–1614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee Z. A., Gross J., Dourmashkin R. R., Taylor-Robinson D. Nonpilar surface appendages of colony type 1 and colony type 4 gonococci. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):266–270. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.266-270.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee Z. A., Johnson A. P., Taylor-Robinson D. Human fallopian tubes in organ culture: preparation, maintenance, and quantitation of damage by pathogenic microorganisms. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):608–618. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.608-618.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowter C., McGEE Z. A. Evaluation of a new technique for the demonstration of gonococci and other micro-organisms in host cells. J Clin Pathol. 1976 May;29(5):433–437. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.5.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Whytock S., Green C. J., Carney F. E., Jr Effect of Neisseria gonorrhoeae on human and rabbit oviducts. Br J Vener Dis. 1974 Aug;50(4):279–288. doi: 10.1136/sti.50.4.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tebbutt G. M., Veale D. R., Hutchison J. G., Smith H. The adherence of pilate and non-pilate strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to human and guinea-pig epithelial tissues. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Aug;9(3):263–273. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-3-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E., Watt P. J., Robertson J. N. The human fallopian tube: a laboratory model for gonococcal infection. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jun;129(6):650–659. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.6.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]