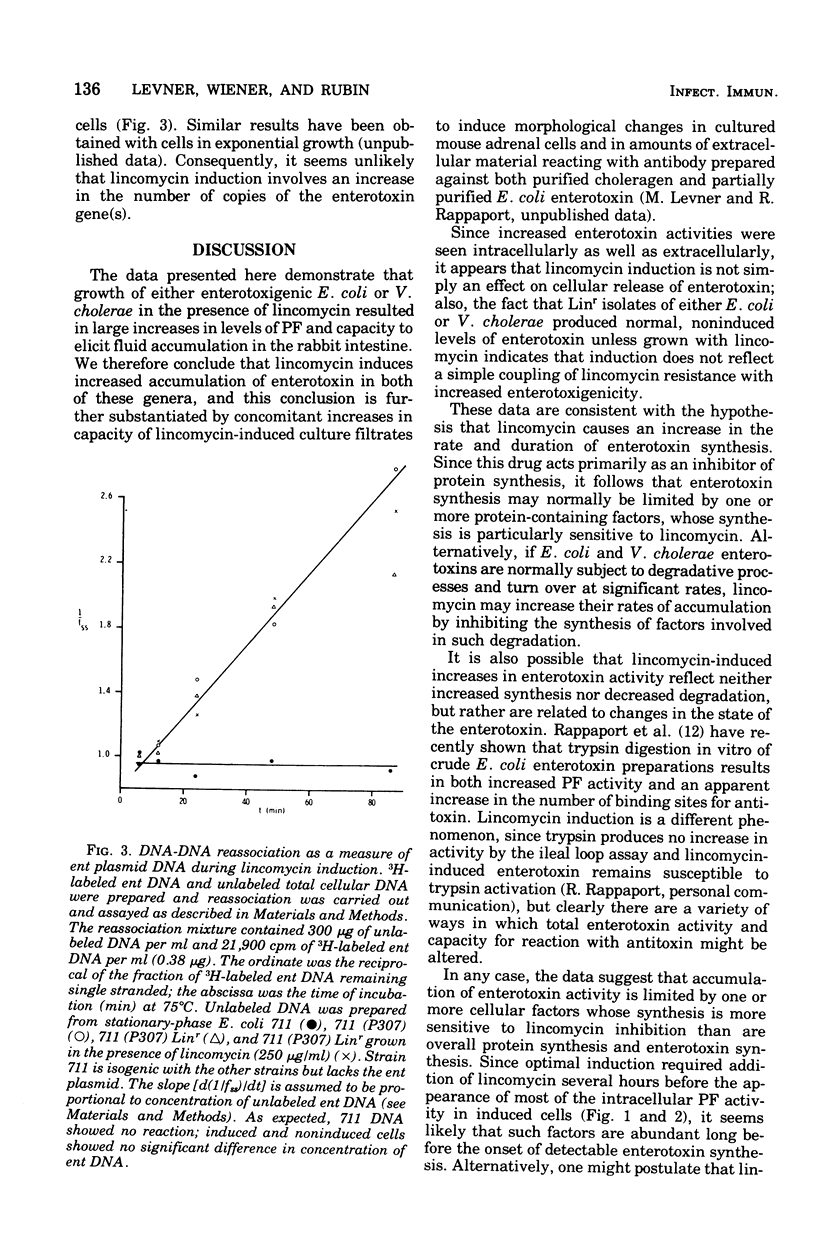
Abstract
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli or Vibrio cholerae 569B (Inaba) grown in the presence of the antibiotic lincomycin, an inhibitor of protein synthesis, produced elevated levels of heat-labile enterotoxin or choleragen, respectively, as assayed by both vascular permeability factor and capacity to elicit fluid accumulation in rabbit ileal loops. This induction of enterotoxin did not reflect either a coupling of lincomycin resistance with increased enterotoxigenicity or an effect of lincomycin on cellular release of enterotoxin, since spontaneously isolated lincomycin-resistant mutants of both E. coli and V. cholerae still required lincomycin for induction, and large increases in E. coli permeability factor activity were found intracellularly as well as extracellularly. After the period of exponential growth, E. coli became refractory to induction by lincomycin, although most of the induced enterotoxin activity appeared only after this period. No increase in copy number of the enterotoxin plasmid in E. coli 711 (P307) was found in induced cells by analysis of deoxyribonucleic acid reassociation kinetics. These and other data suggest that synthesis of enterotoxin, or at least its accumulation, is normally limited by cellular factors whose synthesis is preferentially inhibited by lincomycin. A possible connection between this phenomenon and lincomycin-associated diarrhea is considered.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste R., Yamada T., Davies J. Enzymatic Adenylylation of Streptomycin and Spectinomycin by R-Factor-Resistant Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1970 Jan;1(1):109–119. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.1.109-119.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Kohne D. E. Repeated sequences in DNA. Hundreds of thousands of copies of DNA sequences have been incorporated into the genomes of higher organisms. Science. 1968 Aug 9;161(3841):529–540. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3841.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Sih C. J., Weisblum B. Lincomycin, an inhibitor of aminoacyl sRNA binding to ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Feb;55(2):431–438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.2.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Evans D. G., Gorbach S. L. Polymyxin B-Induced Release of Low-Molecular-Weight, Heat-Labile Enterotoxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1010–1017. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1010-1017.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Gorbach S. L. Production of vascular permeability factor by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from man. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):725–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.725-730.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C., So M., Falkow S. The enterotoxin plasmids of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jul;130(1):40–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman R. B., Schnös M. Partial denaturation of thymine- and 5-bromouracil-containing lambda DNA in alkali. J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 14;49(1):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90378-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Frock J. L., Klainer A. S., Chen S., Gainer R. B., Omar M., Anderson W. The spectrum of colitis associated with lincomycin and clindamycin therapy. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131 (Suppl):S108–S115. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.supplement.s108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos D. S., Palchaudhuri S., Maas W. K. Genetic and physical characteristics of an enterotoxin plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1240–1247. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1240-1247.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerman F. J., Formal S. B., Falkow S. Plasmid-associated enterotoxin production in a strain of Escherichia coli isolated from humans. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):622–624. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.622-624.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil M. L., Holmes R. K., Finkelstein R. A. Conjugal transfer of a chromosomal gene determining production of enterotoxin in vibrio cholerae. Science. 1975 Mar 7;187(4179):849–850. doi: 10.1126/science.1114331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


