Abstract
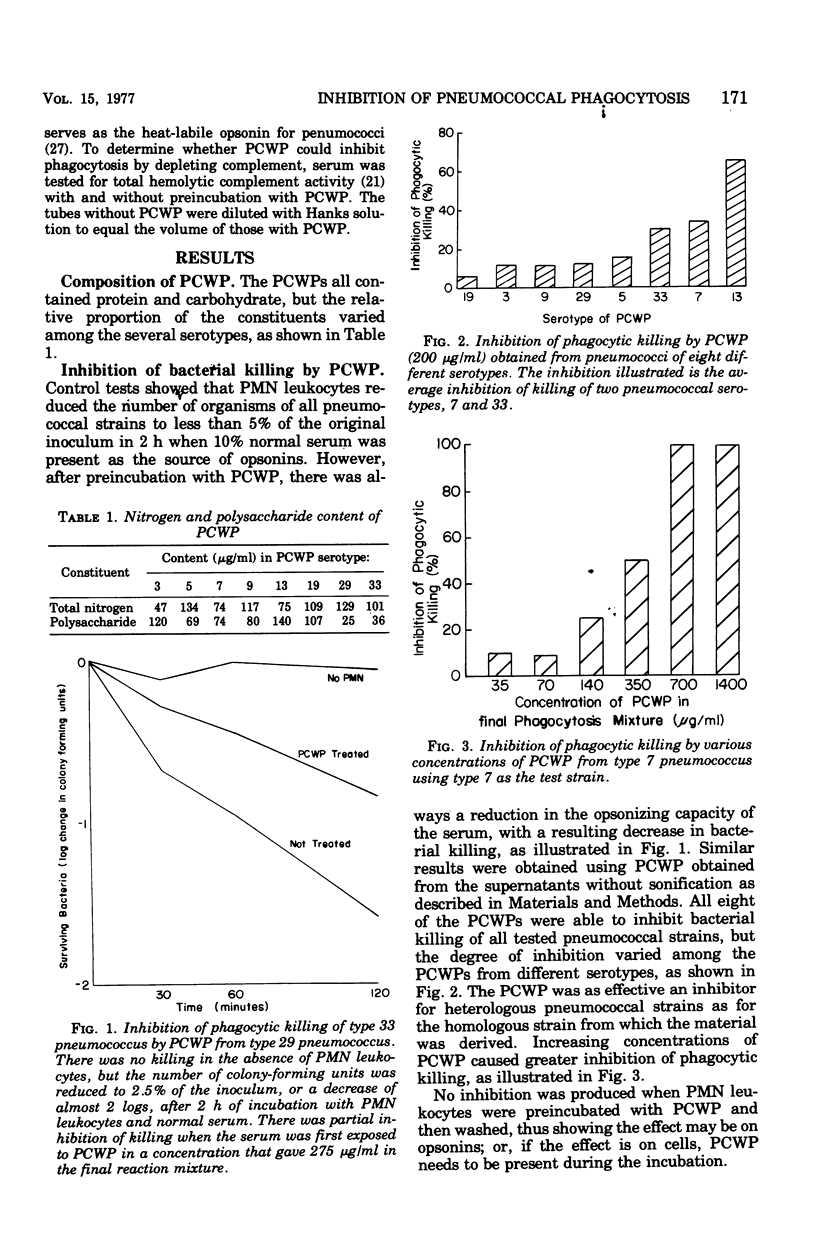
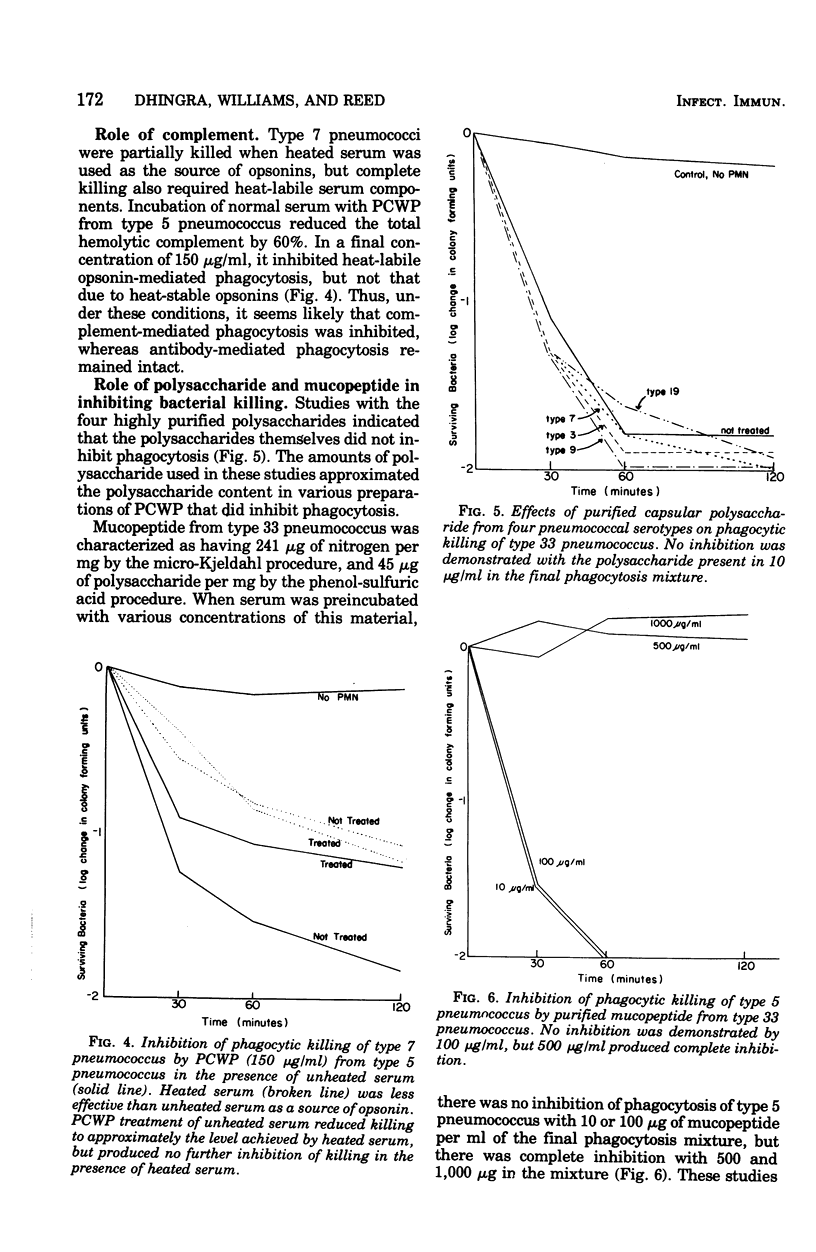
Pneumoccal cell wall and capsular products from eight serotypes were tested for their ability to inhibit polymorphonuclear neutrophil killing of the same eight pneumococcal strains. Crude pneumococcal cell wall preparations from all serotypes inhibited phagocytic killing of several pneumococcal serotypes, and were just as effective with heterologous as with homologous strains. Phagocytosis dependent on heat-labile serum factors was inhibited, whereas phagocytosis not dependent on heat-labile factors was not significantly affected. These findings were compatible with inhibition of complement consumption. The inhibitory activity was found in a purified cell wall mucopeptide, whereas purified capsular polysaccharides failed to inhibit phagocytosis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUSTRIAN R., GOLD J. PNEUMOCOCCAL BACTEREMIA WITH ESPECIAL REFERENCE TO BACTEREMIC PNEUMOCOCCAL PNEUMONIA. Ann Intern Med. 1964 May;60:759–776. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-60-5-759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abdulla E. M., Schwab J. H. Biological properties of streptococcal cell-wall particles. 3. Dermonecrotic reaction to cell-wall mucopeptides. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):374–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.374-383.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger R., Hadding U., Schorlemmer H. U., Brade V., Bitter-Suermann D. Dextran sulphate: a synthetic activator of C3 via the alternative pathway. I. Influence of molecular size and degree of sulphation on the activation potency. Immunology. 1975 Sep;29(3):549–554. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROMARTIE W. J., SCHWAB J. H., CRADDOCK J. G. The effect of a toxic cellular component of group A streptococci on connective tissue. Am J Pathol. 1960 Jul;37:79–99. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. H., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Quantitative studies of the specificity of anti-pneumococcal polysaccharide antibodies, types 3 and 8. I. Isolation of oligosaccharides from acid and from enzymatic hydrolysates of S3 and S8. Immunochemistry. 1966 May;3(3):195–212. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(66)90184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coonrod J. D., Leach R. P. Antigenemia in fulminant pneumococcemia. Ann Intern Med. 1976 May;84(5):561–563. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-5-561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Quie P. G. Effects of staphylococcal protein A on heat labile opsonins. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):1177–1180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J. G., STRAUSS B. STUDIES ON HEAT-LABILE OPSONIN IN RABBIT SERUM. J Immunol. 1964 Jan;92:145–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Glynn A. A. The virulence for mice of strains of Escherichia coli related to the effects of K antigens on their resistance to phagocytosis and killing by complement. Immunology. 1971 May;20(5):767–777. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. M., Schwab J. H. Effects of streptococcal cell wall fragments on phagocytosis and tissue culture cells. Infect Immun. 1970 Mar;1(3):232–242. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.3.232-242.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E., Wentworth B. B., Beasley R. P., Foy H. M. Correlation of circulating capsular polysaccharide with bacteremia in pneumococcal pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):431–437. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.431-437.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohanian S. H., Schwab J. H., Cromartie W. J. Relation of rheumatic-like cardiac lesions of the mouse to localization of group A streptococcal cell walls. J Exp Med. 1969 Jan 1;129(1):37–49. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. P., Davidson M. S., Williams R. C., Jr Complement system in pneumococcal infections. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1120–1125. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1120-1125.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. P., Drach G. W., Williams R. C., Jr Antigens common to human and bacterial cells. IV. Studies of human pneumococcal disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Apr;83(4):599–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rytel M. W., Dee T. H., Ferstenfeld J. E., Hensley G. T. Possible pathogenetic role of capsular antigens in fulminant pneumococcal disease with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Am J Med. 1974 Dec;57(6):889–896. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. H., Ohanian S. H. Degradation of streptococcal cell wall antigens in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1346–1352. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1346-1352.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shayegani M., Hisatsune K., Mudd S. Cell Wall Component Which Affects the Ability of Serum to Promote Phagocytosis and Killing of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1970 Dec;2(6):750–756. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.6.750-756.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber J. W., Polley M. J., Zabriskie J. B. Nonspecific complement activation by streptococcal structures. II. Properdin-independent initiation of the alternate pathway. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1352–1366. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelstein J. A., Shin H. S., Wood W. B., Jr Heat labile opsonins to Pneumococcus. 3. The participation of immunoglobulin and of the alternate pathway of C3 activation. J Immunol. 1972 Jun;108(6):1681–1689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


