Abstract
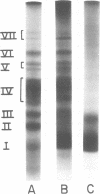
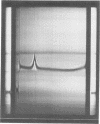
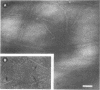
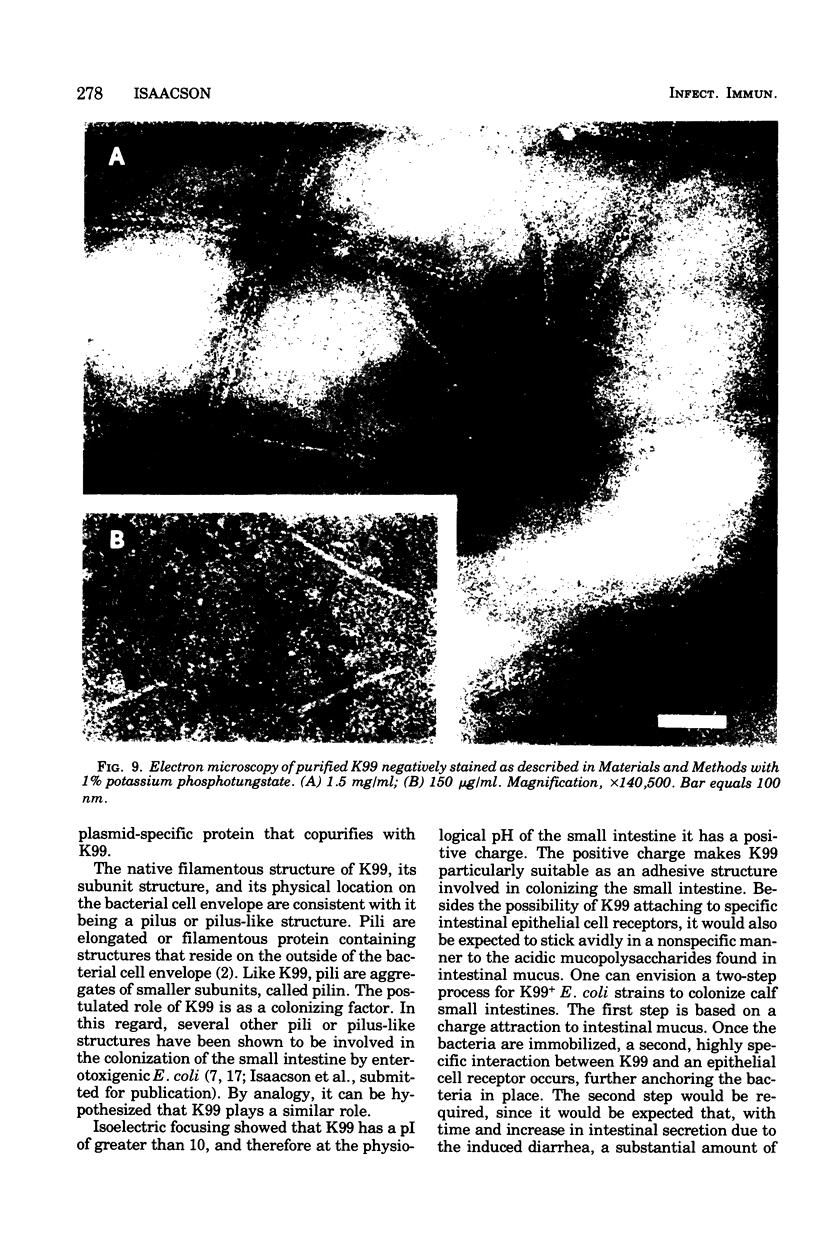
K99, a presumed colonizing factor of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of calf origin, has been purified. K99 was removed from K99+ bacteria by salt extraction and subsequently purified by ammonium sulfate precipitation and column chromatography on diethylaminoethyl-Sephadex. The purified material was homogenous in size, having an s20,w of 13 to 15 S. It was composed of two subunits: a major component with a molecular weight of 22,500 and a minor component of 29,500. When observed in the electron microscope, K99 appeared to be rod-shaped, with a strong tendency for self-aggregation. At concentrations where aggregation was minimized, individual rods were observed with diameters of 8.4 nm and mean lengths of 130 nm. Based on the subunit structure, exterior location, and rod-like shape of K99, it is concluded that K99 is a pilus or pilus-like structure. Chemically, K99 is composed primarily of protein and has an isoelectric point of greater than 10. Purified K99 did not hemagglutinate guinea pig erythrocytes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Silver R. P., Evans D. J., Jr, Chase D. G., Gorbach S. L. Plasmid-controlled colonization factor associated with virulence in Esherichia coli enterotoxigenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):656–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.656-667.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinée P. A., Jansen W. H., Agterberg C. M. Detection of the K99 antigen by means of agglutination and immunoelectrophoresis in Escherichia coli isolates from calves and its correlation with entertoxigenicity. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1369–1377. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1369-1377.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. The association of K88 antigen with haemagglutinating activity in porcine strains of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):135–144. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Skartvedt S. M. Etiologic diagnosis of diarrheal disease of calves: frequency and methods for detecting enterotoxin and K99 antigen production by Escherichia cola. Am J Vet Res. 1976 Sep;37(9):1025–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L., Guinée P. A. Occurrence and characteristics of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from calves with diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1117–1119. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1117-1119.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Smith H. W., Sojka W. J. The establishment of K99, a thermolabile, transmissible escherichia coli K antigen, previously called "Kco", possessed by calf and lamb enteropathogenic strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Feb;83(1):31–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Linggood M. A. Further observations on Escherichia coli enterotoxins with particular regard to those produced by atypical piglet strains and by calf and lamb strains: the transmissible nature of these enterotoxins and of a K antigen possessed by calf and lamb strains. J Med Microbiol. 1972 May;5(2):243–250. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirm S., Orskov F., Orskov I., Birch-Andersen A. Episome-carried surface antigen K88 of Escherichia coli. 3. Morphology. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):740–748. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.740-748.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]