Abstract
The study of animal behaviour is important for both ecology and ecotoxicology, yet research in these two fields is currently developing independently. Here, we synthesize the available knowledge on drug-induced behavioural alterations in fish, discuss potential ecological consequences and report results from an experiment in which we quantify both uptake and behavioural impact of a psychiatric drug on a predatory fish (Perca fluviatilis) and its invertebrate prey (Coenagrion hastulatum). We show that perch became more active while damselfly behaviour was unaffected, illustrating that behavioural effects of pharmaceuticals can differ between species. Furthermore, we demonstrate that prey consumption can be an important exposure route as on average 46% of the pharmaceutical in ingested prey accumulated in the predator. This suggests that investigations of exposure through bioconcentration, where trophic interactions and subsequent bioaccumulation of exposed individuals are ignored, underestimate exposure. Wildlife may therefore be exposed to higher levels of behaviourally altering pharmaceuticals than predictions based on commonly used exposure assays and pharmaceutical concentrations found in environmental monitoring programmes.
Keywords: benzodiazepines, bioconcentration, contaminants, behaviour, ecological effects, Perca fluviatilis
1. Introduction
There is a growing awareness among ecologists that behavioural variation and alterations are important for individual performance [1,2], ecosystem function [3] and species evolution [4]. In ecotoxicology it has been recognized that such behavioural alterations may be caused by contaminants found in natural systems [5]. However, despite this common interest in behaviour, and even though both ecology and ecotoxicology often use the same species and similar endpoints, limited cross-citation suggests that these fields are developing independently. An independent development could be the reason why standardized ecotoxicological tests (e.g. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development protocols) rarely consider ecologically important behaviours or effects on ecosystem processes, food webs and ecosystem functioning. The advantage of combining these two research fields is evident, as many pharmaceuticals found in the environment are designed to modify ecologically important behaviours. Hence, the use of standardized behavioural assays in ecotoxicological studies, especially those including behaviours known to be of direct and indirect ecological importance (table 1), would probably improve our understanding of pharmaceutical effects on wildlife.
Table 1.
Ecologically important behavioural traits central for assessing sub-lethal effects of pharmaceutical exposure, and potential subsequent ecological effects (direct or indirect). Every indirect effect can potentially arise as a result of changes in any of the direct effects.
| behavioural traits | ecological effects |
|
|---|---|---|
| direct | indirect | |
| activity | cooperationb,e | community structure |
| aggression | dispersal/migrationa,c,d,e | cross-boundary effects |
| boldness | feeding ratea,b,c,d | ecosystem function |
| exploration | mating successb,e | feedbacks |
| sociality | parental careb,e | population dynamics |
| predator avoidancea,c,e | trophic cascades | |
aActivity.
bAggression.
cBoldness.
dExploration.
eSociality.
Examples of behaviours with obvious direct ecological importance are feeding rate, mating success and parental care, and changes in these have consequences for individual fitness (i.e. an individual's future reproductive output) [6,7]. There are also other behaviours where alterations have less obvious, but still direct, effects on fitness (table 1). For example, in most animal species, predator avoidance is crucial, and individuals often adjust their behaviour in accordance with perceived predation risk [8,9]. Typically, predator avoidance involves reduced activity to minimize encounter rates with potential predators, but an activity reduction often means less feeding and growth and, hence, reduced fitness. On the other hand, underestimating predation risk by remaining active will generally also result in reduced fitness, via increased predation, despite maintained food intake and growth [10]. The ability of potential prey to correctly assess predation risk is therefore crucial for fitness. Dispersal and migration are also examples of behaviours that have direct importance for population persistence, especially in the face of rapid environmental change [11], as individuals that express more active, bold and/or asocial behaviours tend to be more prone to disperse or migrate [12–15]. Lastly, among fish, schooling—a behaviour tightly linked to sociality—is directly important [16], as it confuses the predator and thereby increases each schooling individual's chance of survival [17]. As such, several different behaviours are of direct importance for individual fitness throughout an animal's lifetime. These behaviours and the behavioural reactions to different stimuli have been fine-tuned over evolutionary history. Therefore, extrinsic factors, such as pharmaceutical contamination, that alter selection pressures or introduce new ones will probably have both individual- and ecosystem-level consequences.
In this paper, we merge findings from studies in ecology and ecotoxicology, in a context that should be of interest to researchers active in either (or both) research field. We do this by presenting: (a) an overview of pharmaceutical contamination in freshwater systems, (b) a comprehensive review of the literature on pharmaceutical effects on fish behaviour and (c) discuss potential ecological effects of pharmaceuticals via behavioural alterations in fish. As a compliment to existing literature, largely lacking information on how pharmaceutical uptake and potential subsequent behavioural alterations in prey affect pharmaceutical exposure in predatory fish, we present novel findings on the uptake and behavioural effects of a psychiatric pharmaceutical (oxazepam) on an invertebrate species (the northern damselfly, Coenagrion hastulatum) and its common predator (Eurasian perch, Perca fluviatilis). Here, we distinguish between pharmaceutical uptake via water (i.e. bioconcentration) and food (i.e. bioaccumulation), as the latter is rarely considered in exposure studies [18]. If bioaccumulation contributes importantly to the net uptake of pharmaceuticals, pharmaceutical concentrations found in monitoring programmes may inaccurately reflect realized exposure levels of wildlife.
(a). Pharmaceuticals in freshwater systems
Pharmaceuticals have been found in aquatic systems globally, due to a combination of worldwide usage and low removal efficiency in sewage treatment plants (STPs) or a lack of STPs [19–23]. In surface waters, concentrations of pharmaceuticals usually range from low ng l−1 to low µg l−1, and are correlated to human population density in the drainage area, volume of the receiving water body and technologies used in STPs [21,24,25], but certain point sources, such as pharmaceutical production and manufacturing facilities, can result in concentrations as high as mg l−1 in receiving surface waters [25–27]. A wide range of pharmaceuticals has been found in freshwater systems [21,28,29]. Most of these pharmaceuticals are designed to quickly medicate and then leave the human body without degrading, resulting in them entering freshwater systems still pharmacologically active. Even though detected concentrations of these pharmaceuticals in surface waters usually are much lower than known levels of toxicity [21,25,30], sub-lethal effects at environmentally relevant concentrations have been found in aquatic organisms [31–33]. Consequently, pharmaceuticals may be a ‘neglected source of behavioural variation’ in natural systems [34]. Clearly, this is of concern, as several studies conclude that ecological endpoints, such as behaviours, are more sensitive to pharmaceuticals than more commonly used toxicological endpoints [35–38]. Pharmaceuticals known to affect fish behaviour are listed in table 2 and include antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), hormones, antihistamines and various psychiatric drugs.
Table 2.
Studies of pharmaceutical effects on behaviour of fish, including type of pharmaceutical substance, study species, type of behaviour studied (endpoint), concentration at which effects were observed and the reference. Concentrations are given in µg l−1 (or in µg g−1 body tissue, if stated). If no pharmaceutical effect on behaviour was observed, the highest concentration tested is presented in brackets. Species names: A. dispar, Aphanius dispar (Arabian killifish); B. splendens, Betta splendens (Siamese fighting fish); C. auratus, Carassius auratus (goldfish); D. rerio, Danio rerio (zebrafish); L. gibbosus, Lepomis gibbosus (pumpkinseed sunfish); M. chrysops, Morone chrysops (white bass); M. saxatilis, Morone saxatilis (striped bass); M. saxatilis × M. chrysops, Morone saxatilis × Morone chrysops (hybrid striped bass); O. mykiss, Oncorhynchus mykiss (rainbow trout); P. fluviatilis, Perca fluviatilis (Eurasian perch); P. promelas, Pimephales promelas (fathead minnow); O. latipes, Oryzias latipes (Japanese medaka fish); T. bifasciatum, Thalassoma bifasciatum (bluehead wrasse).
| pharmaceutical | species | endpoint | concentration µg l−1 | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| anticholinesterasic drugs | ||||
| neostigmine | L. gibbosus | boldness | (100 000) | [39] |
| pyridostigmine | L. gibbosus | boldness | (100 000) | [39] |
| antidepressants | ||||
| citalopram | O. mykiss | aggression | (100 000) | [40] |
| bupropion | P. promelas | reproductive behaviour | (0.057) | [41] |
| fluoxetine | A. dispar | activity, aggression, sociality | 0.3 | [42] |
| fluoxetine | B. splendens | activity, aggression | 3 000 | [43] |
| fluoxetine | B. splendens | activity, aggression | 350 | [44] |
| fluoxetine | B. splendens | aggression | 0.5–0.008a | [45] |
| fluoxetine | C. auratus | feeding rate | 54 000 | [46] |
| fluoxetine |
M. saxatilis × M. chrysops |
feeding rate | 23 000 | [47] |
| fluoxetine | P. promelas | feeding rate | 3.7 | [35] |
| fluoxetine | P. promelas | reproductive behaviour | (0.028) | [41] |
| fluoxetine | T. bifasciatum | aggression | 6000 μg kg−1 | [48] |
| sertraline | P. promelas | reproductive behaviour | (0.0052) | [41] |
| sertraline | P. promelas | boldness | 3.0 | [49] |
| sertraline | P. fluviatilis | feeding rate | 89a | [50] |
| venlafaxine | P. promelas | reproductive behaviour | (1.1) | [41] |
| venlafaxine | M. saxatilis × M. chrysops | feeding rate | 36 | [51] |
| antiepileptic drugs | ||||
| carbamazepine | O. latipes | activity, feeding rate | 6100 | [52] |
| antihistamines | ||||
| diphenhydramine | P. promelas | feeding rate | 5.6 | [37] |
| beta blockers | ||||
| propranolol | P. promelas | reproductive behaviour | (4.0) | [53] |
| propranolol | D. rerio | activity | 3000 | [54] |
| NSAIDb | ||||
| diclofenac | O. latipes | feeding | 1000 | [52] |
| psychiatric drugs | ||||
| bromazepam | D. rerio | activity | 1500 | [54] |
| buspirone | D. rerio | activity | 3000 | [54] |
| clonazepam | D. rerio | activity | 300 | [54] |
| diazepam | D. rerio | activity | 273 | [55] |
| diazepam | D. rerio | activity | 160 | [54] |
| diazepam | D. rerio | boldness | 5000 | [56] |
| diazepam | L. gibbosus | activity | 266 | [57] |
| haloperidol | P. promelas | aggression | 50 | [58] |
| oxazepam | P. fluviatilis | activity, sociality, feeding rate | 1.8 | [33] |
aNominal concentration.
bNon-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
(b). Pharmaceutical effects on fish behaviour
(i). Antidepressants
The most commonly used antidepressants, SSRIs and serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), act via the serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake transporters and interact with other parts of the serotonin system, but no clear relationship between the clinical efficacy and plasma concentrations has been found [59]. Serotonin levels influence both physiology [60] and behaviour in a wide range of organisms, including fish [61,62], and play a pivotal role in activity, aggression and reproductive behaviours [62–64], which has been shown, for example, by a negative correlation between serotonin levels and levels of aggression [65,66]. It is therefore intuitive to use behavioural endpoints when studying effects of SSRIs and SNRIs, and several studies have evaluated impacts on various behaviours in fish (table 2). Subsequently, antidepressants have been shown to reduce territorial aggression in coral reef fish [48] and locomotion and aggression in Siamese fighting fish [44]. Rainbow trout were, however, unaffected by another SSRI, citalopram, even at concentrations a thousand times higher than in the previous studies [40], highlighting substance-specific effects of, and species-specific responses to, SSRIs (table 2). Besides treating depression, SSRIs are also used to treat obesity in humans, as serotonin is important for controlling appetite [67], suggesting that SSRI exposure could lead to changed feeding behaviour. Accordingly, it has been shown that fluoxetine reduces the feeding rate in both white and striped bass [47], as well as in goldfish [46] (table 2). While these effects were found at rather high concentrations, more than 1 mg l−1, studies have also found that fathead minnow [35] and hybrid striped bass [51] experienced reduced feeding rates after exposure to 3.7 and 250 µg l−1 of fluoxetine and venlafaxine, respectively. Lastly, serotonin plays an important role in modulating motor output and may either increase or decrease locomotion [64]. In a short-term exposure experiment, Arabian killifish showed reduced activity when exposed to low µg l−1 levels of fluoxetine [42], and a similar effect was observed for Siamese fighting fish [43–45] (table 2).
In addition to the effects reported on aggression, feeding rate and activity, several studies have investigated how SSRIs and SNRIs affect other behaviours such as courting, schooling and shelter seeking (table 2). In one study, the reproductive behaviour of male fathead minnows was unaffected by the antidepressants bupropion, fluoxetine, sertraline and venlafaxine, individually or as a mixture [41] (table 2). In contrast, Arabian killifish exhibited increased sociality after exposure to fluoxetine, and fathead minnows showed increased boldness after exposure to sertraline [49]. The exposed fish in the latter study also obtained higher plasma concentrations of sertraline than human therapeutic plasma concentrations, which clearly links the response in fish to the human pharmacological response [49]. As such, although the use of behavioural endpoints is promising, the contrasting results from studies of antidepressants illustrate the problems associated with generalizing behavioural effects across species even within classes of pharmaceuticals. In addition, the contrasting results highlight the importance of monitoring several key behaviours when assessing the risk of ecological effects of pharmaceuticals.
(ii). Psychiatric drugs
Several psychiatric pharmaceuticals have behavioural endpoints in human medicine, suggesting comparable effects in exposed wildlife. One group of pharmaceuticals that has received increasing attention is benzodiazepines that act via the γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor, a highly conserved entity, found in a wide range of vertebrate species [61,68]. Benzodiazepines depress the central nervous system, and are used to treat anxiety, insomnia and muscle spasms [69]. One of the most commonly used benzodiazepines, diazepam, has been shown to increase activity in zebrafish [55] and pumpkinseed sunfish [57] at μg l−1 concentrations, and exposure to mg l−1 diazepam increased boldness in larval zebrafish [56] (table 2). Similar effects, that is, increased activity and affinity towards light, were shown for zebrafish exposed to three benzodiazepines [54] (table 2). Further, haloperidol, a pharmaceutical that is used to treat acute psychosis, aggression and acute delirium, was found to increase dominance in male fathead minnows [58]. While most investigations of pharmaceutical effects on fish have used laboratory populations, a recent study on perch from a natural population found increased activity and decreased sociality after exposure to low μg l−1 of the benzodiazepine oxazepam and increased boldness at high μg l−1 [33] (table 2). Further, these observed behavioural changes resulted in a direct ecological effect—an increased feeding rate on zooplankton—after exposure [33].
(iii). Other pharmaceuticals
Effects of other types of pharmaceuticals on fish behaviour have also been studied (table 2), as they have the potential to influence wildlife behaviour. For example, beta blockers, used to treat hypertension, act antagonistically on the β-receptors and prevent effects of adrenaline and noradrenaline, resulting in lower stress and fight-or-flight response [70]. However, studies have failed to find effects of beta blockers on fish activity, boldness and reproductive behaviour [53,54] (table 2). Another group of pharmaceuticals with the potential to affect wildlife behaviour is antihistamines. They primarily reduce allergic responses, but some can also influence serotonin levels and act as an anticholinergic agent [71]. Consequently, fathead minnows were found to reduce their feeding rate after exposure to μg l−1 of diphenhydramine [36] (table 2), and this response was attributed to diphenhydramine's effect on serotonin levels [36]. Similarly, exposure to carbamazepine, an antiepileptic drug, and diclofenac, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, separately reduced the feeding rate and/or activity in Japanese medaka fish [52] (table 2). Lastly, exposure to high mg l−1 neostigmine or pyrostigmine, cholinesterase inhibitors used to treat neuromuscular junction disorders, did not affect boldness in pumpkinseed sunfish [39], but the authors do not provide any mechanistic explanations for how these pharmaceuticals potentially could influence behaviour [39,52]. Another important group of pharmaceuticals found to affect aquatic communities are those with endocrine disrupting properties [37,72,73]. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs) include a diverse group of chemicals, in addition to pharmaceutical compounds, and in the light of recent comprehensive publications covering effects of EDCs [37,72,73], including those in this theme issue [74–76], addressing them here is not warranted.
(c). Potential ecological effects of pharmaceuticals via behavioural changes
Effects of pharmaceutical on behaviour are of direct ecological importance, as behaviours are tightly linked to individual fitness and population persistence [2,77]. Yet, whether, or how, pharmaceuticals alter wildlife behaviour remains poorly studied. For example, despite boldness being crucial for anti-predator response as well as the tendency to disperse or migrate [14,78], the consequence of changed boldness after exposure to dilute pharmaceutical concentrations has so far not been studied. Further, some pharmaceuticals have the potential to alter sociality [33], and thereby schooling tendency. However, despite the potential impact of pharmaceuticals on wildlife behaviour, and the demonstrated importance of animal behaviour for fitness, population dynamics and ecosystem functioning, few studies have investigated the ecological implications of pharmaceutically induced behavioural modifications (but see [32,33,45]).
It is a fact that certain behaviours directly affect fitness, and it is therefore probable that pharmaceuticals designed to alter behaviour will influence the fitness of exposed individuals. However, besides these direct effects, changes in individual fitness may also produce indirect ecological effects (table 1). Such indirect effects occur via changed species interactions, such as predation or competition [79]. For example, as individual behaviours change, a number of trade-offs (e.g. to eat or being eaten) affecting individual fitness also change, resulting in population increase, decrease, or even local extinction [80,81]. Obviously, extinction has consequences for the remaining community, but changes in population size may also have effects, albeit more subtle. Examples of such subtle effects are changes in population dynamics or food-web cascades following, for example, an increase or decrease in feeding efficiency of a species exposed to pharmaceuticals. Nevertheless, both extinctions and novel population dynamics will influence both higher and/or lower trophic levels, and the initial impact probably depends on at what trophic level the first major change occurs. For example, if pharmaceutical exposure increases feeding rates of a secondary consumer [33], primary consumers are likely to be suppressed, with positive consequences for primary producers via predation release. Conversely, an increased feeding rate (i.e. activity) among intermediate consumers may make them more vulnerable to top predators, resulting in a population reduction and, subsequently, an increase in primary consumers. Such cascading effects may, however, be transient, and over time (e.g. via feedbacks, such as promoted algal growth leading to anoxic conditions), other impacts on the system and its organisms may arise.
Other indirect ecological effects of pharmaceutical exposure in aquatic systems may arise through changed population sizes (especially extinctions) and subsequently altered community composition and species richness, as these are known to influence ecosystem functioning [75,82]. Such effects may be especially probable if different taxa respond differently to the exposure. Further, as aquatic systems are intimately connected with adjacent terrestrial systems via cross-boundary resource flows (e.g. emergent aquatic insects) [83], and because these flows are probably indirectly (and maybe directly [84]) altered if pharmaceuticals induce behavioural changes in aquatic consumer organisms, pharmaceutical impacts on aquatic systems may also influence adjacent terrestrial food webs [85–88]. This largely unexplored route of pharmaceutical transfer from aquatic to terrestrial systems has been demonstrated in bats feeding on emerging insects at wastewater treatment plants [89,90].
(d). Bioaccumulation—an overlooked uptake variable
So far, most risk-assessment studies have focused on uptake of pharmaceuticals in organisms as a function of water concentrations, that is, bioconcentration [18]. None of the exposure studies listed in table 2 considered additional uptake via consumption of exposed prey that, in themselves, bioconcentrate pharmaceutical substances [88,91]. If this uptake, referred to as bioaccumulation, is important, consumers may be exposed to higher levels of pharmaceuticals than those found in the water. In addition, pharmaceuticals that increase feeding rates may result in a positive feedback loop between behavioural change and bioaccumulation, as individuals exhibiting higher feeding rates [33] are exposed to increasing levels of the pharmaceutical. Consequently, if bioaccumulation and biomagnification are prevalent, pharmaceutical concentrations found in water may not reflect exposure levels as experienced by wildlife. Because very little is known about this potentially important exposure route of pharmaceuticals for aquatic wildlife, we experimentally quantified the relative importance of bioconcentration and bioaccumulation for pharmaceutical (oxazepam) exposure in an aquatic secondary consumer (Eurasian perch). Our hypotheses were: (i) insect prey bioconcentrate oxazepam, (ii) secondary consumers bioconcentrate oxazepam, (iii) secondary consumers feeding on exposed prey bioaccumulate oxazepam and therefore obtain higher tissue concentrations than those feeding on non-exposed prey. In addition, we compared how oxazepam affects two ecologically important behaviours, activity and boldness, of fish and damselfly larvae, and discuss the ecological implications of the results.
2. Material and methods
(a). Experimental setup
We measured the bioconcentration and bioaccumulation of an anxiolytic pharmaceutical (oxazepam) in 1-year-old perch exposed to four different treatments: the pharmaceutical administered through (i) water, (ii) live food, (iii) a combination of both food and water and (iv) a control without the pharmaceutical. Perch were kept in a single tank with oxygenated aged tap water and fed ad libitum with frozen chironomidae larvae for 21 days before they were moved to individual aquariums and exposed to one of the four treatments. Exposure lasted 7 days, and was carried out in August 2013 in a climate chamber (+20.4°C) with a 15 : 9 L : D regime to mimic natural conditions.
Larvae of the damselfly C. hastulatum were chosen as live food. Two thousand individuals were captured with a sweep net in lake Nydalasjön, Umeå, northern Sweden, 6 days prior to the start of the experiment. In the laboratory, the damselfly larvae were kept in groups of 50 individuals in containers each filled with 5 l of aged tap water. The damselfly larvae were fed twice daily with zooplankton cultivated at Umeå University. Oxazepam was added to 20 randomly chosen containers, to obtain a concentration of 2 µg l−1, while the other 20 containers were kept clean of pharmaceuticals. Treated and untreated water was sampled 30 min after oxazepam addition and after 7 days (at termination), when also 20 damselfly individuals, with a mean individual biomass of 7.30 ± 1.06 mg, were collected to measure bioconcentration. After collection, all water and damselfly samples were frozen for later analysis.
A total of 40 1-year-old perch were individually hosted in plastic containers filled with 2 l of aged tap water. Ten individuals (N = 10) were allocated to each of the four treatments and were fed 0.06 g of damselfly larvae (approximately 3% of perch body weight) daily. At the end of the experiment, the perch were euthanized with MS222, measured, weighed (mean individual biomass of 1.77 ± 0.06 g, N = 39), and then stored frozen for later analyses. Five samples were lost during sampling pretreatment ending up with a total of 34 perch samples.
To investigate whether behaviour of perch and damselfly larvae changed following oxazepam exposure, 30 perch and 23 damselfly larvae were assayed for activity and boldness both before and after exposure. Perch activity was assayed in an aquarium (30 cm high × 30 cm wide × 50 cm long) filled with aged tap water to a depth of 12 cm. The focal individual was introduced to the centre of the aquarium and allowed to acclimate for 5 min, followed by a 600 s video recording of its movements from above. The recorded movements were analysed using the software Observer 2.01 and activity was measured as the number of individual locomotor activities (during 600 s), defined as swimming bouts resulting in movement exceeding half a body length (3.5 cm). When the activity assay was complete, perch were returned to their individual home aquarium for 1 h. Individual fish were then gently introduced to an initial refuge (an 8 × 8 × 20 cm opaque, covered chamber) in a novel environment: a well-lit, opaque, white plastic tank (50 cm high × 40 cm wide × 72 cm long), filled with 8 cm of aged tap water. After 5 min, a 4 cm-wide door of the initial refuge was remotely opened, allowing fish access to the experimental arena. Individual boldness was scored as latency to enter the arena; bolder fish enter the open area faster than shy [14,33].
Damselfly larvae had all grown to instar F-5 or F-6 (F-1 denotes last instar before emerging and F-2 second to the last and so on) when the behavioural trials were carried out. To quantify boldness, we followed the protocol of Brodin (2009) where the larva is exposed to tactile stimulus at the lamellae, simulating predator disturbance [91]. This generates two complementary measures of boldness. First, latency for the damselfly larva to stop moving after being disturbed: bold individuals stop moving sooner than shy ones after the initial escape behaviour. The second measure of boldness is the latency for a damselfly larva to start moving again, after initial escape response and subsequent freezing behaviour. A bold individual would start moving sooner rather than later compared to a shy one, after being disturbed by a potential predator. We scored larval activity levels following the protocols developed by Stoks [92] and later repeatedly validated [93,94]. Activity assays were carried out in aquaria (25 × 25 × 8 cm, filled with 1.2 l aged tap water) with a coordinate grid (1 × 1 cm) drawn on the bottom. Each larva, placed individually in the aquarium, was observed once every 10 min, for 120 min, and the position of the larva was recorded. A move was recorded when the larva had moved its head from one grid square to another. This widely used procedure generated an activity score for each larva ranging from 0 (inactive) to 12 (very active). The individuals used in behavioural assays were not the same as were used for tissue concentration analyses, to avoid dilution of tissue concentrations as all behavioural assays were done in unexposed water.
(b). Water and tissue analyses
To obtain tissue concentrations, full body of the damselflies and 0.1 g from the perch dorsal muscle were analysed. Samples were dried; internal standard was added (50 ng of D5-oxazepam); then extracted sequentially with 1.5 ml acetonitrile twice. Samples were homogenized for 4 min at 42 000 oscillations per minute, using a Mini Beadbeater (Biospec. Bartlesville, USA) with zirconium beads and then centrifuged at 14 000 r.p.m. for 10 min. Both supernatants were combined, evaporated to 20 µl and reconstituted in 100 ml methanol. Oxazepam concentrations in water and biota samples were determined by chemical analysis using an in-line solid phase extraction column coupled to liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, as described in Brodin et al. [33]. In short, a triple stage quadrupole MS/MS TSQ Quantum Ultra EMR (Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Jose, CA, USA) coupled with an Accela and a Surveyor LC pump (Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Jose, CA, USA) and a PAL HTC autosampler (CTC Analytics AG, Zwingen, Switzerland) were used as analytical system. Absolute recoveries of oxazepam in the damselfly and fish muscle extraction were 104% (RSD 7%, N = 6) and 100% (RSD 12%, N = 6), respectively. Limit of quantification was 0.5 µg kg−1. Bioconcentration factors (BCFs) were estimated by dividing individual full body concentrations with measured water concentration in the corresponding individual aquarium.
(c). Statistical analyses
Potential difference in oxazepam concentration of exposure water before and after the experiment was tested by one-way ANOVA. To test whether mean concentrations of oxazepam in perch differed significantly between treatments, t-tests were performed and simple linear regression was used to assess relationships between individual biomass and tissue concentrations of oxazepam. To test whether a mean concentration was significantly different from zero, 95% CI was used. The data on damselfly boldness and activity and perch activity were normally distributed and hence analysed using a two-way ANOVA. In contrast, perch boldness was not normally distributed and was analysed using the non-parametric Mann–Whitney test. All statistical tests were carried out in IBM SPSS Statistics v. 22.
3. Results
The average oxazepam concentration in treated water was 2.1 µg l−1 (table 3) and remained unchanged over the course of the experiment (F = 1.1, d.f. = 36, p = 0.30). Across treatments, the survival of damselfly larvae and perch was 90% and 98%, respectively. Only surviving individuals were used in subsequent tissue analyses, resulting in a slight loss of replicates (table 3).
Table 3.
Concentrations of a benzodiazepine (oxazepam) in water, damselfly tissue and fish tissue after seven days of exposure (±1 s.e.), bioconcentration factor (BCF) for exposed damselfly and fish tissue, and bioaccumulation factor (BAF) for exposed and unexposed fish eating exposed prey. LOQ, below limit of quantification.
| measure | N | oxazepam | BCF | BAF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| water (µg l−1) | 37 | 2.1 ± 0.04 | — | — |
| damselfly tissue (µg kg−1) | 18 | 5.8 ± 2.0 | 3 | — |
| unexposed fish, unexposed prey (µg kg−1) | 9 | LOQ | LOQ | LOQ |
| unexposed fish, exposed prey (µg kg−1) | 10 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | — | 0.3 |
| exposed fish, unexposed prey (µg kg−1) | 6 | 25.7 ± 1.5 | 12 | — |
| exposed fish, exposed prey (µg kg−1) | 9 | 27.6 ± 2.0 | — | 13 |
After 7 days of exposure, damselfly larvae contained on average 5.8 µg of oxazepam kg−1 body tissue resulting in a mean BCF of 3 (table 3). There was no significant correlation between damselfly bioconcentration of oxazepam and damselfly individual biomass (R2 = 0.11, N = 18, p > 0.05). Perch contained significantly higher concentrations of oxazepam (t = 5.6, d.f. = 22, p < 0.001) than the damselfly larvae, with a BCF of 12 (table 3). For exposed perch that were fed unexposed prey, there was a marginally significant negative correlation between individual biomass and tissue concentration (R2 = 0.79, N = 6, p = 0.06), while the individual biomass of perch that were fed exposed prey showed no such correlation (R2 = 0.11, N = 9, p > 0.05). This suggests that individual biomass (i.e. surface-to-volume ratio) in fish can influence bioconcentrations of pharmaceuticals, but also that this influence might be offset through the ingestion of contaminated prey.
Perch exposed to oxazepam-treated water that were fed exposed damselfly larvae contained higher concentrations of oxazepam than exposed perch that were fed unexposed prey, but not significantly so (t = −0.7, d.f. = 13, p = 0.51), and displayed a food-dependent BAF of 13 (table 3). The unexposed perch that were fed exposed damselfly larvae showed an average oxazepam concentration that was significantly higher than zero (p < 0.05, i.e. the 95% CI did not overlap with zero), but a low BAF of 0.3 (table 3). Over the 7 days, perch feeding on exposed damselfly larvae received, on average, an additional 0.0024 µg of oxazepam via prey, based on mean damselfly biomass and oxazepam concentration (table 3). In the treatment where unexposed perch fed on exposed damselfly larvae, the average perch contained 0.0011 µg of oxazepam (based on average perch biomass), indicating a food-mediated uptake efficiency of approximately 46% during the experiment.
In accordance with earlier studies, oxazepam exposure affected perch behaviour [33]. Perch became significantly more active (F = 8.0, N = 30, p = 0.007) after oxazepam exposure, while perch activity in the control did not change between before and after as shown by a significant interaction between treatment and time (F = 5.4, N = 30, p = 0.023, figure 1). In addition, perch boldness was unaffected by oxazepam exposure and did not change in either treatments (all p > 0.54). For damselflies, we found no significant effect of oxazepam exposure on larval boldness or activity (all p > 0.80), indicating that invertebrate behaviour, in contrast to perch behaviour, is unaffected by oxazepam exposure at this concentration (figure 1). This means that the effects of oxazepam is asymmetric between the two trophic levels (i.e. secondary and top consumer) and that, as a consequence, ecosystem-scale effects are probable.
Figure 1.
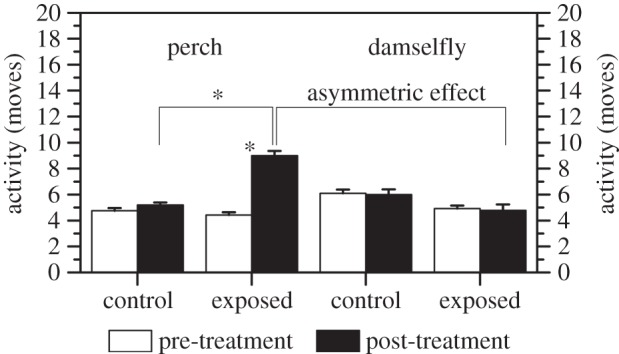
The asymmetrical effect on activity of perch and damselfly larvae exposed to dissolved oxazepam (2.1 µg l−1). Error bars represent ± 1 s.e. and statistically significant differences between the control and exposed treatments are indicated with an asterisk (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
According to the literature reviewed here, it is clear that antidepressants, psychiatric drugs (benzodiazepines) and antihistamines can induce behavioural changes in fish at concentrations ranging from low ng l−1 to low µg l−1 [33,36,42,49], which are close to the concentrations found in natural systems [21,29]. Although this suggests that ecological effects of pharmaceuticals may occur in aquatic systems dominated by wastewater effluent, effects of some pharmaceuticals were found only at higher, not environmentally relevant, concentrations. Hence, the scarcity of studies using behavioural endpoints to study pharmaceutical effects on wildlife makes it hard to draw any general conclusions regarding ecological impact of pharmaceuticals found in aquatic systems. One important step towards more realistic risk assessments of ecological effects of pharmaceuticals would be to incorporate standardized assays of ecologically important behaviours of consistent nature (e.g. activity, boldness and sociality) [95].
Based on the studies in our review, it is apparent that different pharmaceuticals can induce similar behavioural alterations in different species, but both drug- and species-specific effects were also apparent. For example, both activity and feeding rate were influenced by antidepressants, psychiatric drugs and antihistamines, but not necessarily in the same direction between, or even within, species. The results become even more difficult to interpret, synthesize, and extrapolate, given that aquatic wildlife living in contaminated environments is exposed to a wide range of pharmaceuticals that could lead to additive or non-additive effects or even neutralize each other's effects [96]. Therefore, besides the use of standardized behavioural endpoints, studies on effects of mixtures of pharmaceuticals are sorely needed, to obtain a better understanding of ecological effects of exposed wildlife.
Our review highlights that studies on pharmaceutical bioaccumulation are lacking and the results from our experiment illustrates the need to study this route of exposure, as approximately 50% of the ingested pharmaceutical remained in the predator after 7 days. However, firstly, the importance of bioaccumulation for determining level of exposure will depend on to what extent the prey bioconcentrate the substance. Antihistamines, for example, have been reported to generate mean BCF values as high as 2000 in damselfly larvae [84], increasing the significance of bioaccumulation for predators feeding on these prey. Second, ingestion rates will also determine the level of pharmaceutical exposure in predators. In our study, predators were given a relatively low standardized level of prey, just enough to ensure good physiological condition. In natural systems, predators will exhibit much higher ingestion rates, as long as prey are available, and exposure to the pharmaceutical via the ingestion of contaminated prey will therefore be relatively more important. Hence, valuable insights regarding the relative contribution of different exposure routes would be gained from performing long-term exposure experiments. The exposure route via ingestion of exposed prey is particularly interesting, as some pharmaceuticals (e.g. oxazepam) stimulate feeding [33], suggesting the presence of a positive, unexplored, behaviour–bioaccumulation feedback loop. Hence, predicting levels of exposure, its effect on behaviour, and subsequent ecosystem effects based on water concentrations and measured BCFs in the laboratory might lead to underestimations of potential ecological effects.
It is evident from the literature and from our study that pharmaceuticals can affect aquatic species differently. This is a concern, as species-specific effects may disrupt ecological interactions (e.g. predator–prey interactions) with implications for food-web structure and ecosystem function. In a recent meta-study, comparing studies using behavioural endpoints to studies with acute lethality, development or reproduction as endpoints, it was concluded that behavioural studies warrant further attention as tools for assessing the effects of environmental contaminants [38]. However, there are many reasons to further extend the endpoints to also include actual food-web properties (e.g. food-chain length, species richness, species composition) and ecosystem processes (e.g. foraging and growth rates), population and community dynamics, and reproductive success. After all, pharmaceutical impacts on ecosystem properties and functioning are the endpoints of most concern [38]. Thus far, very few studies have investigated how food-web properties might change by pharmaceutical contamination (but see [97]), and even fewer studies have encompassed the full pharmaceutical–behavioural–ecological property chain of potential effects (but see [33]). As reviewed in this article, several groups of pharmaceuticals have been found to influence a range of behaviours that are important for fitness, food-web properties and ecosystem functioning. Hence, aquatic systems exposed to pharmaceuticals may already experience important changes, but how and to what extent is still largely unknown. As pharmaceuticals have been entering natural freshwater systems for at least 50 years, it is about time that we learn more.
Funding statement
Financial support was provided by the Swedish Research Councils Formas (T.B., M.J.) and Vetenskapsrådet (M.J.), C.M. Lerici Foundation (S.P.), the Foundation for Strategic Environmental Research (MISTRA) (J.F.) and the Kempe foundation (T.B., M.H.).
References
- 1.Sih A, Bell AM, Johnson JC, Ziemba RE. 2004. Behavioral syndromes: an integrative overview. Q. Rev. Biol. 79, 241–277. ( 10.1086/422893) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Smith BR, Blumstein DT. 2007. Fitness consequences of personality: a meta-analysis. Behav. Ecol. 19, 448–455. ( 10.1093/beheco/arm144) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Woodward G. 2009. Biodiversity, ecosystem functioning and food webs in fresh waters: assembling the jigsaw puzzle. Freshw. Biol. 54, 2171–2187. ( 10.1111/j.1365-2427.2008.02081.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Réale D, Festa-Bianchet M. 2003. Predator-induced natural selection on temperament in bighorn ewes. Anim. Behav. 65, 463–470. ( 10.1006/anbe.2003.2100) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Scott GR, Sloman KA. 2004. The effects of environmental pollutants on complex fish behaviour: integrating behavioural and physiological indicators of toxicity. Aquat. Toxicol. 68, 369–392. ( 10.1016/j.aquatox.2004.03.016) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Werner E, Hall D. 1988. Ontogenetic habitat shifts in bluegill—the foraging rate predation risk trade-off. Ecology 69, 1352–1366. ( 10.2307/1941633) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gross MR. 2005. The evolution of parental care. Q. Rev. Biol. 80, 37–45. ( 10.1086/431023) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Brodin T, Mikolajewski DJ, Johansson F. 2006. Behavioural and life history effects of predator diet cues during ontogeny in damselfly larvae. Oecologia 148, 162–169. ( 10.1007/s00442-005-0334-7) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Keerfoot WC, Sih A. In press Predation: direct and indirect impacts on aquatic communities. Hanover, NH: University Press of New England. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Brodin T, Johansson F. 2004. Conflicting selection pressures on the growth/predation-risk trade-off in a damselfly. Ecology 85, 2927–2932. ( 10.1890/03-3120) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sih A, Ferrari MCO, Harris DJ. 2011. Evolution and behavioural responses to human-induced rapid environmental change. Evol. Appl. 4, 367–387. ( 10.1111/j.1752-4571.2010.00166.x) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fraser DF, Gilliam JF, Daley MJ, Le AN, Skalski GT. 2001. Explaining leptokurtic movement distributions: intrapopulation variation in boldness and exploration. Am. Nat. 158, 124–135. ( 10.1086/321307) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cote J, Fogarty S, Weinersmith K, Brodin T, Sih A. 2010. Personality traits and dispersal tendency in the invasive mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis). Proc. R. Soc. B 277, 1571–1579. ( 10.1098/rspb.2009.2128) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cote J, Fogarty S, Brodin T, Weinersmith K, Sih A. 2010. Personality-dependent dispersal in the invasive mosquitofish: group composition matters. Proc. R. Soc. B 278, 1670–1678. ( 10.1098/rspb.2010.1892) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cote J, Fogarty S, Tymen B, Sih A, Brodin T. 2013. Personality-dependent dispersal cancelled under predation risk. Proc. R. Soc. B 280, 20132349 ( 10.1098/rspb.2013.2349) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Landeau L, Terborgh J. 1986. Oddity and the confusion effect in predation. Anim. Behav. 34, 1372–1380. ( 10.1016/S0003-3472(86)80208-1) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Krause J, Ruxton G. In press. Living in groups. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mogren CL, Walton WE, Parker DR, Trumble JT. 2013. Trophic transfer of arsenic from an aquatic insect to terrestrial insect predators. PLoS ONE 8, e67817 ( 10.1371/journal.pone.0067817) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nikolaou A, Meric S, Fatta D. 2007. Occurrence patterns of pharmaceuticals in water and wastewater environments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 387, 1225–1234. ( 10.1007/s00216-006-1035-8) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Verlicchi P, Al Aukidy M, Zambello E. 2012. Occurrence of pharmaceutical compounds in urban wastewater: removal, mass load and environmental risk after a secondary treatment—a review. Sci. Total Environ. 429, 123–155. ( 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.04.028) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hughes SR, Kay P, Brown LE. 2013. Global synthesis and critical evaluation of pharmaceutical data sets collected from river systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 661–677. ( 10.1021/es3030148) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Loos R, et al. 2013. EU-wide monitoring survey on emerging polar organic contaminants in wastewater treatment plant effluents. Water Res. 47, 6475–6487. ( 10.1016/j.watres.2013.08.024) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lindberg RH, Östman M, Olofsson U, Grabic R, Fick J. 2014. Occurrence and behaviour of 105 active pharmaceutical ingredients in sewage waters of a municipal sewer collection system. Water Res. 58, 221–229. ( 10.1016/j.watres.2014.03.076) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fatta-Kassinos D, Meric S, Nikolaou A. 2011. Pharmaceutical residues in environmental waters and wastewater: current state of knowledge and future research. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 399, 251–275. ( 10.1007/s00216-010-4300-9) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sim W-J, Lee J-W, Lee E-S, Shin S-K, Hwang S-R, Oh J-E. 2011. Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceuticals in wastewater from households, livestock farms, hospitals and pharmaceutical manufactures. Chemosphere 82, 179–186. ( 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.10.026) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Fick J, Söderström H, Lindberg RH, Phan C, Tysklind M, Larsson DG. 2010. Contamination of surface, ground, and drinking water from pharmaceutical production. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 28, 2522–2527. ( 10.1897/09-073.1) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Phillips PJ, Smith SG, Kolpin DW, Zaugg SD, Buxton HT, Furlong ET, Esposito K, Stinson B. 2010. Pharmaceutical formulation facilities as sources of opioids and other pharmaceuticals to wastewater treatment plant effluents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 4910–4916. ( 10.1021/es100356f) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Segura PA, François M, Gagnon C, Sauvé S. 2009. Review of the occurrence of anti-infectives in contaminated wastewaters and natural and drinking waters. Environ. Health Perspect. 117, 675–684. ( 10.1289/ehp.11776) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Loos R, Gawlik BM, Locoro G, Rimaviciute E, Contini S, Bidoglio G. 2009. EU-wide survey of polar organic persistent pollutants in European river waters. Environ. Pollut. 157, 561–568. ( 10.1016/j.envpol.2008.09.020) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Stackelberg PE, Gibs J, Furlong ET, Meyer MT, Zaugg SD, Lippincott RL. 2007. Efficiency of conventional drinking-water-treatment processes in removal of pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. Sci. Total Environ. 377, 255–272. ( 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.01.095) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Palace VP, et al. 2006. Biochemical and histopathological effects in pearl dace (Margariscus margarita) chronically exposed to a synthetic estrogen in a whole lake experiment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 25, 1114–1125. ( 10.1897/04-557R1.1) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kidd KA, Blanchfield PJ, Mills KH, Palace VP, Evans RE, Lazorchak JM, Flick RW. 2007. Collapse of a fish population after exposure to a synthetic estrogen. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 8897–8901. ( 10.1073/pnas.0609568104) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Brodin T, Fick J, Jonsson M, Klaminder J. 2013. Dilute concentrations of a psychiatric drug alter behavior of fish from natural populations. Science 339, 814–815. ( 10.1126/science.1226850) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Montiglio P-O, Royauté R. 2014. Contaminants as a neglected source of behavioural variation. Anim. Behav. 88, 29–35. ( 10.1016/j.anbehav.2013.11.018) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Stanley JK, Ramirez AJ, Chambliss CK, Brooks BW. 2007. Enantiospecific sublethal effects of the antidepressant fluoxetine to a model aquatic vertebrate and invertebrate. Chemosphere 69, 9–16. ( 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.04.080) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Berninger JP, Du B, Connors KA, Eytcheson SA, Kolkmeier MA, Prosser KN, Valenti TW, Chambliss CK, Brooks BW. 2011. Effects of the antihistamine diphenhydramine on selected aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 30, 2065–2072. ( 10.1002/etc.590) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Soeffker M, Tyler CR. 2012. Endocrine disrupting chemicals and sexual behaviors in fish—a critical review on effects and possible consequences. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 42, 653–668. ( 10.3109/10408444.2012.692114) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Melvin SD, Wilson SP. 2013. The utility of behavioral studies for aquatic toxicology testing: a meta-analysis. Chemosphere 93, 2217–2223. ( 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.07.036) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Rodrigues S, Antunes SC, Brandao FP, Castro BB, Goncalves F, Nunes B. 2012. Effects of anticholinesterase drugs on biomarkers and behavior of pumpkinseed, Lepomis gibbosus (Linnaeus, 1758). J. Environ. Monit. 14, 1638–1644. ( 10.1039/c2em30033h) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Holmberg A, Fogel J, Albertsson E, Fick J, Brown JN, Paxeus N, Forlin L, Johnsson JI, Larsson DGJ. 2011. Does waterborne citalopram affect the aggressive and sexual behaviour of rainbow trout and guppy? J. Hazard. Mater. 187, 596–599. ( 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.01.055) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Schultz MM, Painter MM, Bartell SE, Logue A, Furlong ET, Werner SL, Schoenfuss HL. 2011. Selective uptake and biological consequences of environmentally relevant antidepressant pharmaceutical exposures on male fathead minnows. Aquat. Toxicol. 104, 38–47. ( 10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.03.011) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Barry MJ. 2013. Effects of fluoxetine on the swimming and behavioural responses of the Arabian killifish. Ecotoxicology 22, 425–432. ( 10.1007/s10646-012-1036-7) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lynn SE, Egar JM, Walker BG, Sperry TS, Ramenofsky M. 2007. Fish on Prozac: a simple, noninvasive physiology laboratory investigating the mechanisms of aggressive behavior in Betta splendens. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 31, 358–363. ( 10.1152/advan.00024.2007) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kohlert JG, Mangan BP, Kodra C, Drako L, Long E, Simpson H. 2012. Decreased aggressive and locomotor behaviors in Betta splendens after exposure to fluoxetine. Psychol. Rep. 110, 51–62. ( 10.2466/02.13.PR0.110.1.51-62) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Dzieweczynski TL, Hebert OL. 2012. Fluoxetine alters behavioral consistency of aggression and courtship in male Siamese fighting fish, Betta splendens . Physiol. Behav. 107, 92–97. ( 10.1016/j.physbeh.2012.06.007) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Mennigen JA, Sassine J, Trudeau VL, Moon TW. 2010. Waterborne fluoxetine disrupts feeding and energy metabolism in the goldfish Carassius auratus. Aquat. Toxicol. 100, 128–137. ( 10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.07.022) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gaworecki KM, Klaine SJ. 2008. Behavioral and biochemical responses of hybrid striped bass during and after fluoxetine exposure. Aquat. Toxicol. 88, 207–213. ( 10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.04.011) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Perreault HAN, Semsar K, Godwin J. 2003. Fluoxetine treatment decreases territorial aggression in a coral reef fish. Physiol. Behav. 79, 719–724. ( 10.1016/S0031-9384(03)00211-7) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Valenti TW, Gould GG, Berninger JP, Connors KA, Keele NB, Prosser KN, Brooks BW. 2012. Human therapeutic plasma levels of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) sertraline decrease serotonin reuptake transporter binding and shelter-seeking behavior in adult male fathead minnows. Environ. Sci. Technol. 46, 2427–2435. ( 10.1021/es204164b) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hedgespeth ML, Nilsson PA, Berglund O. 2014. Ecological implications of altered fish foraging after exposure to an antidepressant pharmaceutical. Aquat. Toxicol. 151, 84–87. ( 10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.12.011) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Bisesi JHJ, Bridges W, Klaine SJ. 2014. Effects of the antidepressant venlafaxine on fish brain serotonin and predation behavior. Aquat. Toxicol. 148, 130–138. ( 10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.12.033) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Nassef M, Matsumoto S, Seki M, Khalil F, Kang IJ, Shimasaki Y, Oshima Y, Honjo T. 2010. Acute effects of triclosan, diclofenac and carbamazepine on feeding performance of Japanese medaka fish (Oryzias latipes). Chemosphere 80, 1095–1100. ( 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.04.073) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lorenzi V, Mehinto AC, Denslow ND, Schlenk D. 2012. Effects of exposure to the beta-blocker propranolol on the reproductive behavior and gene expression of the fathead minnow, Pimephales promelas. Aquat. Toxicol. 116, 8–15. ( 10.1016/j.aquatox.2012.03.001) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Gebauer DL, Pagnussat N, Piato AL, Schaefer IC, Bonan CD, Lara DR. 2011. Effects of anxiolytics in zebrafish: similarities and differences between benzodiazepines, buspirone and ethanol. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 99, 480–486. ( 10.1016/j.pbb.2011.04.021) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Oggier DM, Weisbrod CI, Stoller AM, Zenker AK, Fent K. 2010. Effects of diazepam on gene expression and link to physiological effects in different life stages in zebrafish Danio rerio. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 7685–7691. ( 10.1021/es100980r) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Richendrfer H, Pelkowski SD, Colwill RM, Creton R. 2012. On the edge: pharmacological evidence for anxiety-related behavior in zebrafish larvae. Behav. Brain Res. 228, 99–106. ( 10.1016/j.bbr.2011.11.041) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Brandao FP, Rodrigues S, Castro BB, Goncalves F, Antunes SC, Nunes B. 2013. Short-term effects of neuroactive pharmaceutical drugs on a fish species: biochemical and behavioural effects. Aquat. Toxicol. 144–145, 218–229. ( 10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.10.005) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Villeneuve DL, et al. 2010. II: Effects of a dopamine receptor antagonist on fathead minnow dominance behavior and ovarian gene expression in the fathead minnow and zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 73, 478–485. ( 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2009.09.018) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Vaswani M, Linda FK, Ramesh S. 2003. Role of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in psychiatric disorders: a comprehensive review. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 27, 85–102. ( 10.1016/S0278-5846(02)00338-X) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Meston CM, Frohlich PF. 2000. The neurobiology of sexual function. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 57, 1012–1030. ( 10.1001/archpsyc.57.11.1012) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Gunnarsson L, Jauhiainen A, Kristiansson E, Nerman O, Larsson DGJ. 2008. Evolutionary conservation of human drug targets in organisms used for environmental risk assessments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42, 5807–5813. ( 10.1021/es8005173) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kreke N, Dietrich DR. 2008. Physiological endpoints for potential SSRI interactions in fish. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 38, 215–247. ( 10.1080/10408440801891057) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Mennigen JA, Stroud P, Zamora JM, Moon TW, Trudeau VL. 2011. Pharmaceuticals as neuroendocrine disruptors: lessons learned from fish. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B—Crit. Rev. 14, 387–412. ( 10.1080/10937404.2011.578559) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Lillesaar C. 2011. The serotonergic system in fish. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 41, 294–308. ( 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2011.05.009) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Lesch KP, Merschdorf U. 2000. Impulsivity, aggression, and serotonin: a molecular psychobiological perspective. Behav. Sci. Law 18, 581–604. () [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Nelson RJ, Chiavegatto S. 2001. Molecular basis of aggression. Trends Neurosci. 24, 713–719. ( 10.1016/S0166-2236(00)01996-2) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Halford JCG, Harrold JA, Lawton CL, Blundell JE. 2005. Serotonin (5-HT) drugs: effects on appetite expression and use for the treatment of obesity. Curr. Drug Targets 6, 201–213. ( 10.2174/1389450053174550) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Norris DO, Carr JA. 2013. Vertebrate endocrinology. New York, NY: Academic Press. [Google Scholar]
- 69.Tallman J, Paul S, Skolnick P, Gallager D. 1980. Receptors for the age of anxiety—pharmacology of the benzodiazepines. Science 207, 274–281. ( 10.1126/science.6101294) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Small KM, McGraw DW, Liggett SB. 2003. Pharmacology and physiology of human adrenergic receptor polymorphisms. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 43, 381–411. ( 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.43.100901.135823) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Brown N, Roberts LI. In press Histamine, bradykinin, and their antagonists. New York, NY: McGraw Hill. [Google Scholar]
- 72.Colborn T, Saal F, Soto A. 1993. Developmental effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in wildlife and humans. Environ. Health Perspect. 101, 378–384. ( 10.2307/3431890) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Bergman Å, Heindel JJ, Jobling S, Kidd KA, Zoeller RT. 2014. WHO (World Health Organization)/UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme) Global assessment of the state-of-the-science of endocrine disruptors.http://www.who.int/ceh/publications/endocrine/en/index.html.
- 74.Brown AR, Gunnarsson L, Kristiansson E, Tyler CR. 2014. Assessing variation in the potential susceptibility of fish to pharmaceuticals, considering evolutionary differences in their physiology and ecology. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 369, 20130576 ( 10.1098/rstb.2013.0576) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kidd KA, Paterson MJ, Rennie MD, Podemski CL, Findlay DL, Blanchfield PJ, Liber K. 2014. Direct and indirect responses of a freshwater food web to a potent synthetic oestrogen. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 369, 20130578 ( 10.1098/rstb.2013.0578) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Säfholm M, Ribbenstedt A, Fick J, Berg C. 2014. Risks of hormonally active pharmaceuticals to amphibians: a growing concern regarding progestagens. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 369, 20130577 ( 10.1098/rstb.2013.0577) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Fahrig L, Merriam G. 1994. Conservation of fragmented populations. Conserv. Biol. 8, 50–59. ( 10.1046/j.1523-1739.1994.08010050.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Chapman BB, Hulthén K, Blomqvist DR, Hansson L-A, Nilsson J-Å, Brodersen J, Anders Nilsson P, Skov C, Brönmark C. 2011. To boldly go: individual differences in boldness influence migratory tendency. Ecol. Lett. 14, 871–876. ( 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01648.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Brooks JL, Dodson SI. 1965. Predation, body size, and composition of plankton. Science 150, 28–35. ( 10.1126/science.150.3692.28) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Werner EE, Peacor SD. 2003. A review of trait-mediated indirect interactions in ecological communities. Ecology 84, 1083–1100. ( 10.1890/0012-9658(2003)084[1083:AROTII]2.0.CO;2) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Balvanera P, Pfisterer AB, Buchmann N, He J-S, Nakashizuka T, Raffaelli D, Schmid B. 2006. Quantifying the evidence for biodiversity effects on ecosystem functioning and services. Ecol. Lett. 9, 1146–1156. ( 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00963.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Ballinger A, Lake PS. 2006. Energy and nutrient fluxes from rivers and streams into terrestrial food webs. Mar. Freshw. Res. 57, 15–28. ( 10.1071/MF05154) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Knight TM, McCoy MW, Chase JM, McCoy KA, Holt RD. 2005. Trophic cascades across ecosystems. Nature 437, 880–883. ( 10.1038/nature03962) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Jonsson M, Fick J, Klaminder J, Brodin T. 2014. Antihistamines and aquatic insects: bioconcentration and impacts on behavior in damselfly larvae (Zygoptera). Sci. Total Environ. 472, 108–111. ( 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.10.104) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Epanchin PN, Knapp RA, Lawler SP. 2010. Nonnative trout impact an alpine-nesting bird by altering aquatic-insect subsidies. Ecology 91, 2406–2415. ( 10.1890/09-1974.1) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Poulin B, Lefebvre G, Paz L. 2010. Red flag for green spray: adverse trophic effects of Bti on breeding birds. J. Appl. Ecol. 47, 884–889. ( 10.1111/j.1365-2664.2010.01821.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Zenker A, Cicero MR, Prestinaci F, Bottoni P, Carere M. 2014. Bioaccumulation and biomagnification potential of pharmaceuticals with a focus to the aquatic environment. J. Environ. Manage. 133, 378–387. ( 10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.12.017) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Du B, et al. 2014. Bioaccumulation and trophic dilution of human pharmaceuticals across trophic positions of an effluent-dependent wadeable stream. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 369, 20140058 ( 10.1098/rstb.2014.0058) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Park KJ, Cristinacce A. 2006. Use of sewage treatment works as foraging sites by insectivorous bats. Anim. Conserv. 9, 259–268. ( 10.1111/j.1469-1795.2006.00031.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Park KJ, Mueller CT, Markman S, Swinscow-Hall O, Pascoe D, Buchanan KL. 2009. Detection of endocrine disrupting chemicals in aerial invertebrates at sewage treatment works. Chemosphere 77, 1459–1464. ( 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.08.063) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Brodin T. 2009. Behavioral syndrome over the boundaries of life—carryovers from larvae to adult damselfly. Behav. Ecol. 20, 30–37. ( 10.1093/beheco/arn111) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Stoks R. 1998. Effect of lamellae autotomy on survival and foraging success of the damselfly Lestes sponsa (Odonata: Lestidae). Oecologia 117, 443–448. ( 10.1007/s004420050679) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Johansson F, Stoks R, Rowe L, Block MD. 2001. Life history plasticity in a damselfly: effects of combined time and biotic constraints. Ecology 82, 1857 ( 10.2307/2680052) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Mikolajewski DJ, Johansson F, Brodin T. 2004. Condition-dependent behaviour among damselfly populations. Can. J. Zool. 82, 653–659. ( 10.1139/z04-036) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Klaminder J, Jonsson M, Fick J, Sundelin A, Brodin T. 2014. The conceptual imperfection of aquatic risk assessment tests: highlighting the need for tests designed to detect therapeutic effects of pharmaceutical contaminants. Environ. Res. Lett. 9, 084003 ( 10.1088/1748-9326/9/8/084003) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Backhaus T. 2014. Medicines, shaken and stirred: a critical review on the ecotoxicology of pharmaceutical mixtures. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 369, 20130585 ( 10.1098/rstb.2013.0585) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Bundschuh M, Hahn T, Gessner MO, Schulz R. 2009. Antibiotics as a chemical stressor affecting an aquatic decomposer–detritivore system. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 28, 197–203. ( 10.1897/08-075.1) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


