Abstract
NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase (CPR; NADPH:ferrihemoprotein reductase, EC 1.6.2.4) catalyzes the transfer of electrons to all known microsomal cytochromes P450. CPR is unique in that it is one of only two mammalian enzymes known to contain both flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) and flavin mononucleotide (FMN), the other being the various isoforms of nitric oxide synthase. Similarities in amino acid sequence and in functional domain arrangement with other key flavoproteins, including nitric oxide synthase, make CPR an excellent prototype for studies of interactions between two flavin cofactors. We have obtained diffraction-quality crystals of rat liver CPR, expressed in Escherichia coli and solubilized by limited proteolysis with trypsin. The crystals were grown in Hepes buffer (pH 7.0), containing polyethylene glycol 4500 and NaCl. The crystals belong to the orthorhombic space group P2(1)2(1)2(1), with unit cell dimensions a = 103.3 A, b = 116.1 A, and c = 120.4 A. If we assume that there are two molecules of the 72-kDa CPR polypeptide per asymmetric unit, the calculated value of Vm is 2.54 A3/Da.
Full text
PDF

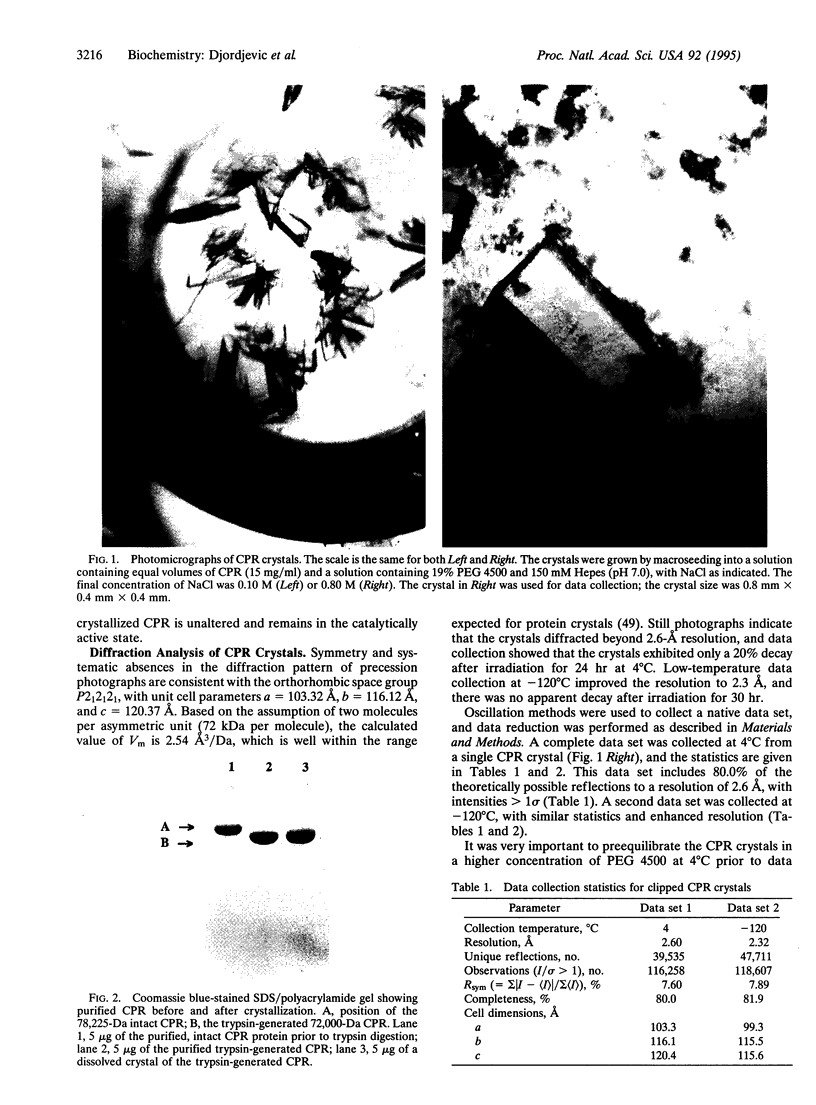

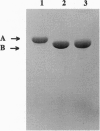
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews S. C., Shipley D., Keen J. N., Findlay J. B., Harrison P. M., Guest J. R. The haemoglobin-like protein (HMP) of Escherichia coli has ferrisiderophore reductase activity and its C-terminal domain shares homology with ferredoxin NADP+ reductases. FEBS Lett. 1992 May 18;302(3):247–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80452-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastiaens P. I., Bonants P. J., Müller F., Visser A. J. Time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy of NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase: demonstration of energy transfer between the two prosthetic groups. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8416–8425. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black S. D., Coon M. J. Structural features of liver microsomal NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase. Hydrophobic domain, hydrophilic domain, and connecting region. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5929–5938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonants P. J., Müller F., Vervoort J., Edmondson D. E. A 31P-nuclear-magnetic-resonance study of NADPH-cytochrome-P-450 reductase and of the Azotobacter flavodoxin/ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase complex. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 5;190(3):531–537. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15606.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C. W., Jr, Carter C. W. Protein crystallization using incomplete factorial experiments. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):12219–12223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correll C. C., Batie C. J., Ballou D. P., Ludwig M. L. Phthalate dioxygenase reductase: a modular structure for electron transfer from pyridine nucleotides to [2Fe-2S]. Science. 1992 Dec 4;258(5088):1604–1610. doi: 10.1126/science.1280857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffaud G. D., March P. E., Inouye M. Expression and secretion of foreign proteins in Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:492–507. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch H. G., Strittmatter P. Cytochrome b5 reduction by NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8976–8981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P. Oxidation-reduction properties of rat liver cytochromes P-450 and NADPH-cytochrome p-450 reductase related to catalysis in reconstituted systems. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 7;22(12):2811–2820. doi: 10.1021/bi00281a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniu M., McManus M. E., Birkett D. J., Lee T. D., Shively J. E. Structural and functional analysis of NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase from human liver: complete sequence of human enzyme and NADPH-binding sites. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8639–8645. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Inouye M. Up-promoter mutations in the lpp gene of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3101–3110. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyanagi T., Makino R., Anan F. K. Studies on the microsomal mixed-function oxidase system: mechanism of action of hepatic NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 31;20(7):1722–1730. doi: 10.1021/bi00510a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyanagi T., Mason H. S. Some properties of hepatic reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-cytochrome c reductase. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 5;12(12):2297–2308. doi: 10.1021/bi00736a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karplus P. A., Daniels M. J., Herriott J. R. Atomic structure of ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase: prototype for a structurally novel flavoenzyme family. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):60–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper C. B. Biochemical distinctions between the nuclear and microsomal membranes from rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):577–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri M., Murakami H., Yabusaki Y., Sugiyama T., Okamoto M., Yamano T., Ohkawa H. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of full-length cDNA for rabbit liver NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase mRNA. J Biochem. 1986 Oct;100(4):945–954. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters B. S., Bilimoria M. H., Kamin H., Gibson Q. H. The mechanism of 1- and 2-electron transfers catalyzed by reduced triphosphopyridine nucleotide-cytochrome c reductase. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):4081–4088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters B. S., Okita R. T. The history, properties, and function of NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase. Pharmacol Ther. 1980;9(2):227–244. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(80)80020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W. Solvent content of protein crystals. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):491–497. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90205-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanasami R., Otvos J. D., Kasper C. B., Shen A., Rajagopalan J., McCabe T. J., Okita J. R., Hanahan D. J., Masters B. S. 31P NMR spectroscopic studies on purified, native and cloned, expressed forms of NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase. Biochemistry. 1992 May 5;31(17):4210–4218. doi: 10.1021/bi00132a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otvos J. D., Krum D. P., Masters B. S. Localization of the free radical on the flavin mononucleotide of the air-stable semiquinone state of NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase using 31P NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):7220–7228. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS A. H., LANGDON R. G. Hepatic triphosphopyridine nucleotide-cytochrome c reductase: isolation, characterization, and kinetic studies. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2652–2660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter T. D., Kasper C. B. Coding nucleotide sequence of rat NADPH-cytochrome P-450 oxidoreductase cDNA and identification of flavin-binding domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):973–977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter T. D., Kasper C. B. NADPH-cytochrome P-450 oxidoreductase: flavin mononucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide domains evolved from different flavoproteins. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 8;25(7):1682–1687. doi: 10.1021/bi00355a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter T. D., Wilson T. E., Kasper C. B. Expression of a functional 78,000 dalton mammalian flavoprotein, NADPH-cytochrome P-450 oxidoreductase, in Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Apr;254(1):353–367. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90111-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacter B. A., Nelson E. B., Marver H. S., Masters B. S. Immunochemical evidence for an association of heme oxygenase with the microsomal electron transport system. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3601–3607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sem D. S., Kasper C. B. Geometric relationship between the nicotinamide and isoalloxazine rings in NADPH-cytochrome P-450 oxidoreductase: implications for the classification of evolutionarily and functionally related flavoproteins. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 7;31(13):3391–3398. doi: 10.1021/bi00128a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sem D. S., Kasper C. B. Interaction with arginine 597 of NADPH-cytochrome P-450 oxidoreductase is a primary source of the uniform binding energy used to discriminate between NADPH and NADH. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 2;32(43):11548–11558. doi: 10.1021/bi00094a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen A. L., Porter T. D., Wilson T. E., Kasper C. B. Structural analysis of the FMN binding domain of NADPH-cytochrome P-450 oxidoreductase by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7584–7589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. C., Tew D. G., Wolf C. R. Dissection of NADPH-cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase into distinct functional domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 30;91(18):8710–8714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.18.8710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel H. W., Dignam J. D. Purification and properties of NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase. Methods Enzymol. 1978;52:89–96. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)52009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Nisimoto Y., Mason H. S., Loehr T. M. Flavins of NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase: evidence for structural alteration of flavins in their one-electron-reduced semiquinone states from resonance Raman spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 4;24(12):3012–3019. doi: 10.1021/bi00333a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urenjak J., Linder D., Lumper L. Structural comparison between the trout and mammalian hydrophilic domain of NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase. J Chromatogr. 1987 Jun 26;397:123–136. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)84995-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermilion J. L., Ballou D. P., Massey V., Coon M. J. Separate roles for FMN and FAD in catalysis by liver microsomal NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):266–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel F., Lumper L. Complete structure of the hydrophilic domain in the porcine NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 15;236(3):871–878. doi: 10.1042/bj2360871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS C. H., Jr, KAMIN H. Microsomal triphosphopyridine nucleotide-cytochrome c reductase of liver. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:587–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabusaki Y., Murakami H., Ohkawa H. Primary structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase deduced from nucleotide sequence of its cloned gene. J Biochem. 1988 Jun;103(6):1004–1010. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamano S., Aoyama T., McBride O. W., Hardwick J. P., Gelboin H. V., Gonzalez F. J. Human NADPH-P450 oxidoreductase: complementary DNA cloning, sequence and vaccinia virus-mediated expression and localization of the CYPOR gene to chromosome 7. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):83–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasukochi Y., Masters B. S. Some properties of a detergent-solubilized NADPH-cytochrome c(cytochrome P-450) reductase purified by biospecific affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5337–5344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasukochi Y., Peterson J. A., Masters B. S. NADPH-cytochrome c (P-450) reductase. Spectrophotometric and stopped flow kinetic studies on the formation of reduced flavoprotein intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7097–7104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]