Abstract
Traits that mediate intraspecific social interactions may overlap in closely related sympatric species, resulting in costly between-species interactions. Such interactions have principally interested investigators studying the evolution of reproductive isolation via reproductive character displacement (RCD) or reinforcement, yet in addition to reproductive interference, interspecific trait overlap can lead to costly between-species aggression. Previous research on rubyspot damselflies (Hetaerina spp.) demonstrated that sympatric shifts in male wing colour patterns and competitor recognition reduce interspecific aggression, supporting the hypothesis that agonistic character displacement (ACD) drove trait shifts. However, a recent theoretical model shows that RCD overshadows ACD if the same male trait is used for both female mate recognition and male competitor recognition. To determine whether female mate recognition is based on male wing coloration in Hetaerina, we conducted a phenotype manipulation experiment. Compared to control males, male H. americana with wings manipulated to resemble a sympatric congener (H. titia) suffered no reduction in mating success. Thus, female mate recognition is not based on species differences in male wing coloration. Experimental males did, however, experience higher interspecific fighting rates and reduced survival compared to controls. These results greatly strengthen the case for ACD and highlight the mechanistic distinction between ACD and RCD.
Keywords: agonistic character displacement, competitor recognition, mate recognition, interspecific aggression, species recognition
1. Introduction
When closely related species come into secondary contact, they may overlap in traits used as intraspecific social signals, resulting in costly interactions between species. Evolutionary biologists have focused primarily on the ways in which selection acts to reduce the occurrence of costly reproductive interactions between heterospecific males and females in the context of reproductive character displacement (RCD) and reinforcement [1–7]. Interference competition between species, which in animals usually takes the form of aggressive interactions, is also very common [8], yet agonistic character displacement (ACD), a process whereby natural selection acts on traits that mediate the occurrence or outcome of interspecific aggression, remains relatively understudied [9,10]. While RCD and ACD can result in the same geographical patterns, the processes are conceptually distinct, because interspecific interference competition need not be related to competition for mates [10], and the dynamics of trait evolution can proceed quite differently [9,10]. As such, studies of selection on traits that mediate interspecific social interactions should distinguish between these two processes when drawing conclusions about the evolutionary history of such traits.
Many phenotypic traits function as signals in both mating and competitive contexts [11] (see table 1 in [12]), and, in some cases, the same character displacement patterns (e.g. sympatric shifts in phenotypes) have been attributed to both ACD and RCD. In the best-known example, male pied flycatchers (Ficedula hypoleuca) have black dorsal plumage in allopatry, but in sympatry with the dominant collared flycatcher (Ficedula albicollis), most male pied flycatchers have dull, brown plumage, which resembles female collared flycatchers [13] and reduces territorial aggression from male collared flycatchers [14–16]. The same plumage shift also reduces the rate of cross-species mating and hybridization because female pied flycatchers prefer males with brown plumage in sympatry, which represents a reversal of the preference for black males in allopatry [17]. In another well-studied example, male Calopteryx splendens damselflies have blue-black wing spots that are larger in allopatry than in sympatry with C. virgo, which have fully blue–black wings [18,19]. Moreover, C. virgo males are more aggressive to C. splendens males with relatively larger wing spots in sympatry, which consequently affects male fitness [18,20,21], yet female mate recognition is also influenced by male wing coloration and shifts in sympatry in a manner consistent with RCD [22,23].
In a recent theoretical study, Okamoto & Grether [12] set out to understand whether ACD and RCD can act synergistically to drive evolutionary divergence, or whether one process has priority over the other. They constructed an individual-based theoretical model based on territorial damselflies to explore how RCD and ACD interact when female mate recognition and male competitor recognition are based on the same male trait. The male trait closely tracked the evolution of the mate recognition function, regardless of the relative strength of selection against interspecific mating and interspecific fighting. Even in the absence of selection against cross-species mating, a trait on which female mate recognition is based cannot diverge through ACD in this model. The basic reason is that mutations that reduce interspecific aggression by causing a male's phenotype to deviate from the mean of the other species also reduce his ability to attract conspecific females, and thus have a net negative effect on fitness. Okamoto & Grether's [12] model also showed that sympatric shifts in competitor recognition, which previously were thought to constitute de facto evidence for ACD, can arise as a byproduct of trait divergence caused by RCD. This is because males still need to recognize conspecific males as competitors, as the trait diverges though RCD. In short, RCD completely dominates ACD in this model. Therefore, to conclude that ACD is responsible for an observed character displacement pattern, RCD needs to be ruled out as an alternative explanation.
Previous research on two species pairs of rubyspot damselflies (Hetaerina spp.) showed that male competitor recognition is based on wing coloration [24,25] and that competitor recognition and male wing coloration in these species pairs diverge in sympatric populations [24,26]. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that ACD has acted in these species pairs. Based on Okamoto & Grether's [12] findings, however, these trait shifts cannot be taken as compelling evidence for ACD unless females do not use male wing coloration for species recognition. While attempts to detect female mate choice based on male coloration within species of Hetaerina have yielded no such evidence [27,28], whether females use male coloration for species discrimination is unknown.
Here we test for effects of male wing coloration on female mate recognition in H. americana in a population sympatric with H. titia, which is one of the species pairs in which sympatric divergence in male coloration and competitor recognition has been detected. Male H. americana have large basal red wing spots and otherwise clear wings (figure 1a), while male H. titia have smaller basal red wing spots and variable amounts of black wing pigmentation (figure 1b; electronic supplementary material, figure S1). To test whether female H. americana use the species difference in male wing coloration to avoid mating with heterospecific males, we conducted a field experiment in which a portion of H. americana males in the study area were manipulated to resemble H. titia males with black ink. We then tracked naturally occurring mating events, territorial fights, changes in territory ownership and survival on a continuous basis for five weeks.
Figure 1.
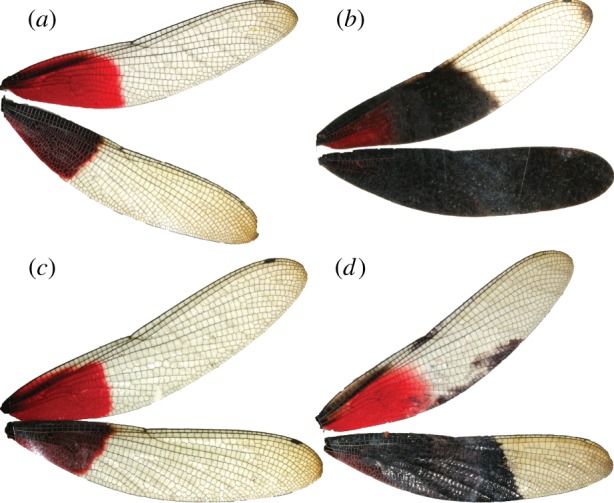
Photographs of a representative (a) unmanipulated Hetaerina americana male, (b) a H. titia male and H. americana males with (c) clear ink and (d) black ink on their hindwings. All males shown here were photographed during the course of the experiment. (Online version in colour.)
2. Material and methods
(a). Study site and species
We carried out this study on two transects (approx. 100 m each) marked at 1 m intervals along the Medina River in Castroville, TX, USA (29.371797°, −98.896444°; 29.374733°, −98.896769°) from 23 May to 23 June 2013. To minimize dispersal, the study transects were located such that long pools (more than 100 m), which are not suitable as breeding habitat, were located both up and downstream. Every individual American rubyspot (H. americana) and smoky rubyspot (H. titia) damselfly encountered along these transects was captured with an aerial net and marked on its abdomen with a unique combination of DecoColor paint pens [24,29]. Hetaerina perch with their wings folded above their bodies, so abdomen marks are usually clearly visible to observers.
(b). Experimental wing manipulation
When we captured mature H. americana males, we assigned them to one of three treatments: (i) unmanipulated control (figure 1a), (ii) clear control: clear ink on the outer surface of the hindwings from the base to halfway between the nodus and the tip using a Prismacolor marker (clear, PM-121, figure 1c) or (iii) blackened: black ink on the same part of the hindwings (black, PM-98, figure 1d), following the protocol of Anderson & Grether [25] (see [30] for a similar approach to phenotype manipulation). To maximize the statistical power to detect effects of the experimental treatment, half of the males were assigned to the blackened treatment and 25% were assigned to each of the control groups. We restricted the experimental blackening to hindwings to prevent males' wings from sticking together. Although some H. titia males have extensive black pigmentation on their forewings, many do not ([31,32]; see also the electronic supplementary material, figure S1), so our experimental manipulation was biologically realistic. Throughout the study, mature H. americana males were marked and assigned to a treatment group as they appeared or reached maturity on the transects (mature males have brilliant red forewing spots while immature males have pink to light red forewing spots [33]).
(c). Behavioural observations
During each day of the study, three to five observers, typically four, continuously walked along the transects from approximately 9.00 to 18.00 h, systematically recording the location to the nearest 0.1 m and ID of each individual encountered, with priority given to recording tandem (mating) pairs and fighting individuals. We strived to record all matings, which is quite feasible because tandem pairs are conspicuous and stay together for several minutes.
Hetaerina mating sequences do not include courtship, instead they begin when a male clasps a female's prothorax (intersternite), at which point the pair is in tandem [34]. From here, the tandem pair either breaks up without proceeding, which we considered a failed mating attempt, or continues on to form the characteristic copulatory wheel of odonates. In H. americana, after the copulatory wheel breaks, the tandem pair exhibits a jerking motion before the female submerges to oviposit in underwater vegetation [35]. When we encountered a mating pair, we recorded the IDs of both individuals and followed them until the mating was either successful (i.e. we saw a copulatory wheel, jerking or submersion) or the tandem broke. When possible, we recorded the entire length of time the pair was in the copulatory wheel. We also recorded instances where we observed a male pursue and fail to grasp a female and considered these to be failed mating attempts.
When an observer witnessed a fight, the location, species involved, ID of individuals (if marked) and escalation level were recorded; we considered two-way circle chases or back-and-forth chases [27,32] to be ‘escalated’ in subsequent analyses.
(d). Female mating analyses
Females may make post-copulatory decisions that bias paternity, since subsequent mates can remove previous mates' sperm from females' sperm storage organs [36,37]. To test for this possibility, we analysed (i) the treatments of females' first and last mates during each day and (ii) whether males' treatments influenced whether females remated or the treatment of subsequent mates. Nearly all females' mating bouts (N consecutive days observed in a mated pair) lasted for 3 days or fewer, so to test for the possibility that sperm removal influenced male mating success, we analysed female remating (i) within each day and (ii) across a 3-day window.
(e). Data analyses
In several analyses, we partitioned the reproductive career of individual males into territorial and non-territorial episodes in order to distinguish between the effects of male–male interactions and male–female interactions [27]. The territorial status of a given male on a given day was assessed based only on the male's resighting and fighting record and without knowledge of his treatment group or mating success. We considered males to be holding a territory if they were resighted consistently on a low perch near the bank of the river within a 3 m radius for at least 2 consecutive days [24]. Additionally, we took fighting and resights in the same area near the stream over a period of several hours to be evidence that a male was holding a territory.
To analyse fighting rates, we took three approaches: (i) treating all recorded fights between the same two males as a single fight (as in [25]), (ii) treating fights between the same two males on N different days as N different fights (i.e. one fight recorded per dyad per day) and (iii) treating all fights as unique whether they were between the same or different males (i.e. all fights recorded per dyad per day). Hetaerina titia male densities were not consistent along the entire length of the transect. Because the wing blackening treatment was only expected to affect males that interacted with H. titia males, we restricted some analyses to males that were observed within close proximity (less than or equal to 4 m), of a H. titia territory holder. The 4 m criterion was chosen, a priori, based on the observation that the reaction distance of territory holders to conspecific male intruders is less than or equal to 2 m and that adjacent territories are typically less than or equal to 2 m apart, as reported previously [25].
Because the opportunity for males to fight and mate depended on the number of days they were present in the study, we analysed the data using count models with exposure terms of the logarithm of the number of days that a male was resighted. For analyses partitioned into territorial and non-territorial episodes, the exposure term was the number of days males held or did not hold territories during the study.
To include repeated measurements on individuals when available, we used mixed-effect models with random intercepts for individual IDs. We used R [38] to conduct all statistical analyses, using the packages MASS [39] for negative binomial regression, survival [40,41] for survival analyses, glmmADMB [42,43] and lme4 [44] for mixed-effect GLMs, pscl for zero-inflation models [45,46] and ggplot2 [47] for figures.
3. Results
(a). Sample sizes and preliminary results
We marked and included 146 H. americana males in the experiment, recorded 444 unique H. americana mating events involving marked males (82 failed mating attempts; 362 successful matings; mean number of successful matings per male = 3.26, s.d. = 4.74) and made 1207 observations of fights involving at least one H. americana male. We resighted 111 males, or 76.03% of the number marked, at least 1 day after marking, and resighted males' locations were recorded an average of 12.1 times per day. Among these resighted males, the median number of days resighted was 6, and most were resighted every day prior to their final disappearance (mean proportion of days on which males were resighted = 0.93). We witnessed five failed mating attempts of H. americana males with H. titia females; a tandem was successfully formed in three of these cases but broke prior to copulation. In no cases did the sham (clear) and unmanipulated control groups differ significantly from each other (see the electronic supplementary material), and thus the control groups were pooled for comparison to the experimental (blackened) group.
(b). Female mate recognition
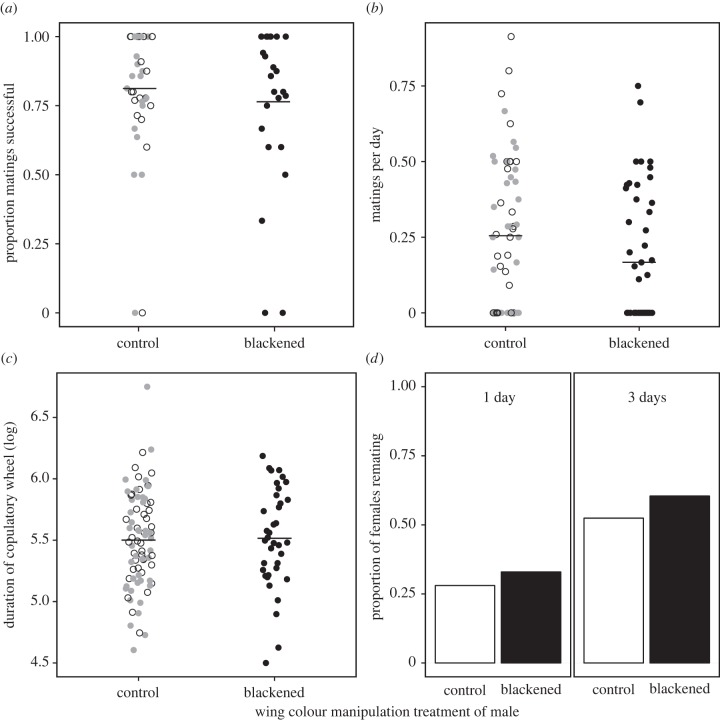
There was no overall effect of the wing blackening treatment on: (i) the proportion of attempted tandems that resulted in a successful mating (figure 2a, mixed-effect binomial model of tandems (success = 1, failure = 0) with a random intercept for male IDs, treatment n = 444, z = −0.14, p = 0.89), (ii) the rate of successful matings (figure 2b, negative binomial model of the count of matings with an offset term for the log of the total number of days resighted, treatment d.f. = 110, z = −1.02, p = 0.31) or (iii) the duration of copulatory wheels (figure 2c, mixed-effect model of the logarithm of the duration of copulatory wheels with a random intercept for male IDs, treatment n = 119, z = 0.26, p = 0.8).
Figure 2.
Lack of an effect of the experimental treatment on overall male mating success, measured either as (a) the proportion of successful tandems, (b) the mating rates of males, (c) the length of the copulatory wheel or (d) the probability of a female remating within 1 or 3 days. In panels (a–c), black dots indicate blackened males, grey dots indicate males with clear ink, empty circles indicate unmanipulated males and horizontal lines represent group means. In panel (d), black bars represent blackened males and empty bars represent control males.
In H. americana, holding a territory is not essential for mating but males generally mate more often when they hold a territory [27]. Thus, a male's mating rate is influenced by the proportion of his life spent holding a territory. In this experiment, males mated 2.1 times more frequently when they held a territory than when they did not (zero-inflated negative binomial model of the count of successful matings with a random intercept for male ID, n = 180, z = 5.03, p < 0.001). To separate effects of territory competition from female choice, we partitioned males' careers into territorial and non-territorial episodes to further examine the effect of the experimental treatment on male mating success [27]. In other words, differences in mating success between treatments could be a result of males of one treatment being unable to hold territories, a phenomenon independent of female mate recognition. When males held territories, neither the proportion of attempted tandems that resulted in a successful mating (mixed-effect binomial model of tandems (success = 1, failure = 0) with a random intercept for male IDs, n = 353, treatment z = −0.50, p = 0.62) nor the mating rate (negative binomial model of the count of matings with an offset term for the log of the total number of days territorial, treatment d.f. = 71, z = −1.69, p = 0.092) were influenced by the experimental treatment. Likewise, when males did not hold territories, the proportion of successful tandems did not depend on treatment (mixed-effect binomial model of tandems (success = 1, failure = 0) with a random intercept for male IDs, n = 91, treatment z = 0.89, p = 0.37). However, the mating rate of non-territory holding blackened males was 1.74 times higher than that of controls (negative binomial model of the count of matings with an offset term for the log of the total number of days non-territorial, treatment d.f. = 107, z = −1.992, p = 0.046).
The post-copulatory behaviour of females did not distinguish among males based on their treatments. Neither a female's first nor last mate of the day depended on the male's treatment group (estimated from intercept of a mixed-effect model of first or last male treatment with a random intercept for female ID, both p > 0.05, see the electronic supplementary material). Similarly, the treatment of a female's mates did not influence her probability of remating within 1 day (figure 2d, blackened versus control in a binomial mixed-effect model of remating with a random intercept for female ID, n = 255, z = 0.82, p = 0.41) or within 3 days (figure 2d, blackened versus control in a binomial mixed-effect model of remating with a random intercept for female ID, n = 255, z = 1.28, p = 0.20). Furthermore, the treatment of the male with which a female remated was not influenced by the treatment of her previous mate, whether analysed within 1 day (binomial lag model with a lag variable for the subsequent mate treatment used as a predictor with a random intercept for female/1 day, n = 76, z = −0.811, p = 0.42) or over a 3 day period (binomial lag model with a lag variable for the subsequent mate treatment used as a predictor with a random intercept for female/3 day, n = 141, z = −0.784, p = 0.43).
(c). Treatment effects on fighting, disappearance, and territory tenure
Compared to controls, blackened H. americana males were more likely to fight with H. titia males, with an increasing effect of treatment in escalated fights and for males who were resighted within 4 m of H. titia territory holders (table 1). We found little evidence for an effect of the experimental treatment on intraspecific fighting rates (table 1). In the analysis for which we reduced all fights between the same two males to a single observation, there was a marginally significant trend for blackened males to be involved in more intraspecific fights than control males, but this effect disappeared when the analysis was restricted to escalated fights, and there was no such trend in the other two datasets (table 1; electronic supplementary material, figure S2).
Table 1.
Effects of the experimental treatment on intraspecific and interspecific fighting rates. Statistical tests compare blackened and control males. Datasets correspond to those described in the main text. Analyses presented in italics restrict males to those seen within 4 m of a territorial H. titia male. The ratios of blackened male interspecific fighting rates to control male interspecific fighting rates are presented in parentheses.
| dataset | intraspecific fights (H. americana versus H. americana) |
interspecific fights (H. americana versus H. titia) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| all fight types | only escalated fights | all fight types | only escalated fights | |
| (1) one fight per dyada | n = 666, χ2 =4.17, p = 0.041 | n = 374, χ2 = 0.22, p = 0.64 | n = 115, χ2 = 4.69, p = 0.00099 | n = 82, χ2 = 11.66, p = 0.00064 |
| (2) one fight per dyad per dayb | d.f. = 81, z = 1.07, p = 0.28 | d.f. = 81, z = 0.18, p = 0.86 | d.f. = 81, z = 2.38, p = 0.017, (1.94) d.f. = 55, z = 3.01, p = 0.0026, (2.25) |
d.f. = 81, z = 2.92, p = 0.0035, (2.5) d.f. = 55, z = 3.53, p = 0.00043, (2.96) |
| (3) all fight observationsb | d.f. = 81, z = 0.18, p = 0.86 | d.f. = 81, z = –0.48, p = 0.63 | d.f. = 81, z = 2.82, p = 0.0049, (2.36), d.f. = 55, z = 3.38, p = 0.00072, (2.75) | d.f. = 81, z = 3.02, p = 0.0026, (2.76), d.f. = 55, z = 3.52, p = 0.00043, (3.26) |
aChi-squared goodness-of-fit test of count of fights, comparing experimental versus control to a null expectation of fights based on the resighting record (see the electronic supplementary material).
bNegative binomial model of the number of interspecific fights, offset by the log of the number of days territorial or fighting (if larger).
The rate at which blackened males disappeared from the study transects was 1.57 times higher than that of controls (Cox proportional hazard treatment coefficient = 0.4541, n = 146, z = 2.549, p = 0.011; limiting analysis to clear and blackened treatments, Cox proportional hazard treatment coefficient = 0.474, n = 110, z = 2.12, p = 0.034). Among all males that were resighted at least once, however, there was no difference in the disappearance rate of blackened males and controls (Cox proportional hazard treatment coefficient = 0.3531, n = 111, z = 1.694, p = 0.09; limiting analysis to clear and black ink treatments, Cox proportional hazard treatment coefficient = 0.432, n = 80, z = 1.65, p = 0.10).
Experimentally blackened males were just as likely as control males to perch and defend territories near heterospecifics (see the electronic supplementary material). However, blackened males suffered a survival cost from interacting with H. titia males; blackened males whose median perch locations were ever within 4 m of H. titia males had 1.9 times higher disappearance rates than control males (figure 3, Cox proportional hazard treatment coefficient = 0.643, n = 62, z = 2.154, p = 0.031; limiting analysis to clear and black ink treatments, Cox proportional hazard treatment coefficient = 0.992, n = 42, z = 2.37, p = 0.018). Experimentally blackened males also held territories for fewer days than control males when they were ever within 4 m of H. titia males, but experienced no such difference when they were never within 4 m of H. titia males (negative binomial model of territorial days with offset term for the log number of total days resighted, treatment × proximity d.f. = 110, z = −2.427, p = 0.015).
Figure 3.
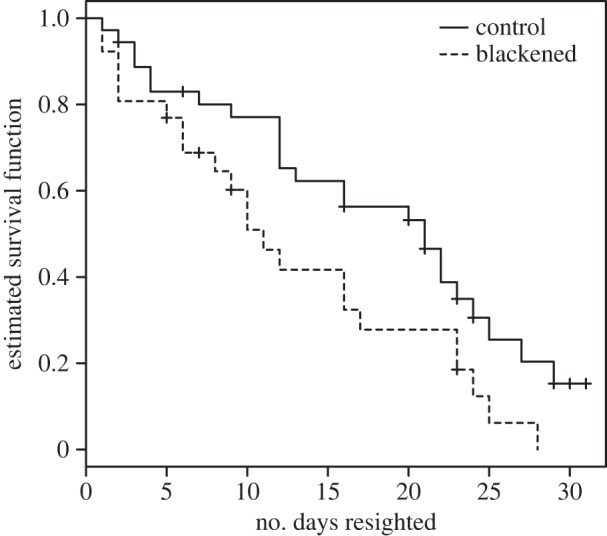
Effects of the experimental treatment on survival of males seen in close proximity to H. titia males. Kaplan–Meier plot, crosshatches indicate censored data points.
4. Discussion
Female mate recognition appeared to be unaffected by the species difference in male wing coloration. Manipulating H. americana male wings to appear similar to those of H. titia males had no discernable effect on mating—females neither rejected experimentally blackened males more often after being clasped nor mated leszs often with experimentally blackened males (figure 2a,b). The only hint of an effect of the experimental treatment on female responses was opposite to the predicted direction: among non-territory holders, blackened males mated at a marginally significantly higher rate than controls. Mating rates in this study are similar to those measured previously in H. americana [35].
Post-copulatory means of discrimination are possible in calopterygid damselflies, where there is extensive evidence that males remove stored sperm from females during copulation [37,48,49]. If the amount of time spent in copula is under female control (but see [50–52]), females may be able to control how much sperm from previous mates is removed by her current mate, the amount of sperm that the male is able to transfer, or the amount of time she spends with the current male at the expense of time for future matings [36,53,54]. Yet, in our study, copulation duration was also unaffected by the experimental treatment. Since females are sometimes clasped by different males after emerging from ovipositing, cryptic female choice may take the form of females biasing either first or last matings towards particular males, remating more often after mating with a non-preferred male [36,55], or similarly, biasing remating towards a particular treatment, yet none of these indicators of cryptic female choice occurred in our experiment, whether we analysed single days or 3 day windows for each female (given the possibility of sperm storage across days of a female's reproductive bout). We did not test the possibility that females discriminated between the treatments via some other cryptic choice mechanism such as biasing paternity sperm storage [36,55,56] or manipulating fecundity [57,58].
Hetaerina americana females may use traits other than wing coloration to differentiate between conspecific and heterospecific males. In Enallagma damselflies, the appendages that males use to clasp females (cerci) have evolved in a correlated fashion with the corresponding structures on females—consistent with the hypothesis that these structures are involved in species recognition [59,60]. Female Hetaerina may also use tactile information from male cerci and/or paraprocts (i.e. inferior and superior clasping appendages), as these structures are highly variable and species specific [34].
In agreement with previous research [25], manipulating the wings of H. americana males to resemble those of H. titia males increased the occurrence of interspecific fighting. We further documented effects of the experimental manipulation on the rate and intensity of interspecific fights and the proportion of a male's life during which he held a territory. Moreover, blackened H. americana males in our study close in proximity to H. titia males suffered reduced survival compared to control males, probably resulting from the increase in fights with heterospecific males. We also documented an immediate effect of the phenotype manipulation: a reduction in the probability that blackened males were resighted. Whether this early attrition of blackened males reflects mortality or dispersal is not clear, but if weaker/lower quality males were more likely to be lost from the study, this might account for the relatively high non-territorial mating rates of the remaining blackened males.
Together, our results strengthen the hypothesis that previously documented shifts in both competitor recognition and male wing coloration [24–26] have resulted from ACD. One previous study documented a pattern of character displacement in male breeding coloration of benthic and limnetic forms of three-spined sticklebacks (Gasterosteus aculeatus) [61] that cannot be explained by a shift in female preferences or colour sensitivity [62,63], effectively ruling out RCD as a potential explanation for the observed shift. Nevertheless, to the best of our knowledge, the current study is the first to experimentally demonstrate that a target of male competitor recognition is not also a target of female mate recognition and thus the first to support ACD over RCD as the cause of a character displacement pattern. Although some investigators have grouped character displacement influencing interspecific aggression under RCD [2], this study highlights the mechanistic distinction between RCD and ACD: our phenotype manipulation experiment confirmed that the species difference H. americana male wing coloration influences interspecific aggression but does not influence female mate recognition. Based on these results, we can reject the hypothesis that previously documented sympatric shifts in male traits are by-products of RCD.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We thank Simone Giovanetti, Sara Hu and Linnea Karlen for field assistance, Cynthia Gonzalez for help with data processing, and Andy Lin at UCLA Stats Consulting for statistical help. Adrea Gonzales-Karlsson, Kathryn Peiman, Thomas B. Smith, Erik Svensson and an anonymous reviewer provided helpful feedback on the manuscript.
Data accessibility
Datasets used in our analyses are available at Dryad (dryad.org): doi:10.5061/dryad.158pj.
Funding statement
J.P.D. received an NSF Graduate Research Fellowship and fellowship support from the UCLA Graduate Division and Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology. This research was funded by NSF DEB-1020586 to G.F.G.
References
- 1.Brown WL, Wilson EO. 1956. Character displacement. Syst. Zool. 5, 49–64. ( 10.2307/2411924) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pfennig KS, Pfennig DW. 2009. Character displacement: ecological and reproductive responses to a common evolutionary problem. Q. Rev. Biol. 84, 253–276. ( 10.1086/605079) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wallace AR. 1889. Darwinism. 2007 facsi New York, NY: Cosimo, Inc. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dobzhansky T. 1937. Genetics and the origin of species. 1982 Reprint New York, NY: Columbia University Press. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dobzhansky T. 1940. Speciation as a stage in evolutionary divergence. Am. Nat. 74, 312–321. ( 10.1086/282871) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Coyne J, Orr H. 2004. Speciation. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates, Inc. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gröning J, Hochkirch A. 2008. Reproductive interference between animal species. Q. Rev. Biol. 83, 257–282. ( 10.1086/590510) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Peiman K, Robinson B. 2010. Ecology and evolution of resource-related heterospecific aggression. Q. Rev. Biol. 85, 133–158. ( 10.1086/652374) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Grether GF, Losin N, Anderson CN, Okamoto K. 2009. The role of interspecific interference competition in character displacement and the evolution of competitor recognition. Biol. Rev. 84, 617–635. ( 10.1111/j.1469-185X.2009.00089.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Grether G, Anderson C, Drury JP, Losin N, Peiman K, Okamoto K. 2013. The evolutionary consequences of interspecific aggression. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1289, 48–68. ( 10.1111/nyas.12082) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Berglund A, Bisazza A, Pilastro A. 1996. Armaments and ornaments: an evolutionary explanation of traits of dual utility. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 58, 385–399. ( 10.1111/j.1095-8312.1996.tb01442.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Okamoto K, Grether GF. 2013. The evolution of species recognition in competitive and mating contexts: the relative efficacy of alternative mechanisms of character displacement. Ecol. Lett. 16, 670–678. ( 10.1111/ele.12100) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Calhim S, Adamik P, Järvistö P, Leskinen P, Török J, Wakamatsu K, Laaksonen T. 2014. Heterospecific female mimicry in Ficedula flycatchers. J. Evol. Biol. 27, 660–666. ( 10.1111/jeb.12328) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Král M, Järvi T, Bicik V. 1988. Inter-specific aggression between the collared flycatcher and the pied flycatcher: the selective agent for the evolution of light-coloured male pied flycatcher populations? Ornis Scand. 19, 287–289. ( 10.2307/3676723) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sætre G-P, Král M, Bicik V. 1993. Experimental evidence for interspecific female mimicry in sympatric Ficedula flycatchers. Evolution (N. Y). 47, 939–945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Alatalo RV, Gustafsson L, Lundberg A. 1994. Male coloration and species recognition in sympatric flycatchers. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 256, 113–118. ( 10.1098/rspb.1994.0057) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sætre G-P, Moum T, Stanislav B, Král M, Adamjan M, Moreno J. 1997. A sexually selected character displacement in flycatchers reinforces premating isolation. Nature 387, 1995–1998. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tynkkynen K, Rantala MJ, Suhonen J. 2004. Interspecific aggression and character displacement in the damselfly Calopteryx splendens. J. Evol. Biol. 17, 759–767. ( 10.1111/j.1420-9101.2004.00733.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Honkavaara J, Dunn DW, Ilvonen S, Suhonen J. 2010. Sympatric shift in a male sexual ornament in the damselfly Calopteryx splendens. J. Evol. Biol. 24, 139–145. ( 10.1111/j.1420-9101.2010.02146.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tynkkynen K, Kotiaho JS, Luojumäki M, Suhonen J. 2006. Interspecific territoriality in Calopteryx damselflies: the role of secondary sexual characters. Anim. Behav. 71, 299–306. ( 10.1016/j.anbehav.2005.03.042) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tynkkynen K, Kotiaho JS, Luojumäki M, Suhonen J. 2005. Interspecific aggression causes negative selection on sexual characters. Evolution (N. Y). 59, 1838–1843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Svensson EI, Karlsson K, Friberg M, Eroukhmanoff F. 2007. Gender differences in species recognition and the evolution of asymmetric sexual isolation. Curr. Biol. 17, 1943–7. ( 10.1016/j.cub.2007.09.038) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Svensson EI, Eroukhmanoff F, Karlsson K, Runemark A, Brodin A. 2010. A role for learning in population divergence of mate preferences. Evolution (N. Y). 64, 3101–13. ( 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2010.01085.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Anderson CN, Grether GF. 2010. Interspecific aggression and character displacement of competitor recognition in Hetaerina damselflies. Proc. R. Soc. B 277, 549–555. ( 10.1098/rspb.2009.1371) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Anderson CN, Grether GF. 2011. Multiple routes to reduced interspecific territorial fighting in Hetaerina damselflies. Behav. Ecol. 22, 527–534. ( 10.1093/beheco/arr013) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Anderson CN, Grether GF. 2010. Character displacement in the fighting colours of Hetaerina damselflies. Proc. R. Soc. B 277, 3669–3675. ( 10.1098/rspb.2010.0935) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Grether GF. 1996. Intrasexual competition alone favors a sexually dimorphic ornament in the rubyspot damselfly Hetaerina americana. Evolution (N. Y). 50, 1949–1957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Córdoba-Aguilar A, Raihani G, Serrano-Meneses A, Contreras-Garduño J. 2009. The lek mating system of Hetaerina damselflies (Insecta: Calopterygidae). Behaviour 146, 189–207. ( 10.1163/156853909X410739) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Anderson CN, Córdoba-Aguilar A, Drury JP, Grether GF. 2011. An assessment of marking techniques for odonates in the family Calopterygidae. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 141, 258–261. ( 10.1111/j.1570-7458.2011.01185.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kemp DJ, Jones D, Macedonia JM, Krockenberger AK. 2014. Female mating preferences and male signal variation in iridescent Hypolimnas butterflies. Anim. Behav. 87, 221–229. ( 10.1016/j.anbehav.2013.11.001) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Calvert PP. 1908. Odonata In Biologia Centrali Americana: Insecta Neuroptera. London: RH Porter and Dulau Co. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Johnson C. 1963. Interspecific territoriality in Hetaerina americana (Fabricius) and H. titia (Drury)(Odonata: Calopterygidae) with a preliminary analysis of the wing color pattern variation. Can. Entomol. 95, 575–582. ( 10.4039/Ent95575-6) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Grether GF. 1995. Natural and sexual selection on wing coloration in the rubyspot damselfly Hetaerina americana. PhD dissertation, University of California, Davis, USA. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Garrison RW. 1990. A synopsis of the genus Hetaerina with descriptions of four new species. Trans. Am. Entomol. Soc. 116, 175–259. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Grether G. 1996. Sexual selection and survival selection on wing coloration and body size in the rubyspot damselfly Hetaerina americana. Evolution (N. Y). 50, 1939–1948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Eberhard WG. 1996. Female control: Sexual selection by cryptic female choice. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Waage JK. 1979. Dual function of the damselfly penis: sperm removal and transfer. Science 203, 916 ( 10.1126/science.203.4383.916) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.R Core Team. 2013. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; See http://www.R-project.org/. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Venables WN, Ripley BD. 2002. Modern applied statistics with S. Fourth. New York, NY: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Therneau T, Grambsch P. 2000. Modeling survival data: extending the cox model. New York, NY: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Therneau T. 2013. A package for survival analysis in S (R package version 2.37–4) See http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survival.
- 42.Fournier D, Skaug H, Ancheta J, Ianelli J, Magnusson A, Maunder M, Nielsen A, Sibert J. 2012. AD model builder: using automatic differentiation for statistical inference of highly parameterized complex nonlinear models. Optim. Methods Softw. 27, 233–249. ( 10.1080/10556788.2011.597854) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Skaug H, Fournier D, Nielsen A, Magnusson A, Bolker B. 2012. Generalized linear mixed models using AD model builder (R package version 0.7.2.12) See http://glmmadmb.r-forge.r-project.org/.
- 44.Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B. 2012. lme4: Linear mixed-effects models using S4 classes R package version 1.1-6 See http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=lme4.
- 45.Jackman S. 2012. pscl: classes and methods for R developed in the Political Science Computational Laboratory, Stanford University R package version 1.4.6 See http://pscl.stanford.edu/.
- 46.Zeileis A, Kleiber C, Jackman S. 2008. Regression models for count data in R. J. Stat. Softw. 27, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wickham H. 2009. ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis. New York, NY: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Siva-Jothy MT, Hooper RE. 1995. The disposition and genetic diversity of stored sperm in females of the damselfly Calopteryx splendens xanthostoma (Charpentier). Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 259, 313–318. ( 10.1098/rspb.1995.0046) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Córdoba-Aguilar A. 1999. Male copulatory sensory stimulation induces female ejection of rival sperm in a damselfly. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 266, 779–784. ( 10.1098/rspb.1999.0705) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Miller P. 1987. An examination of the prolonged copulations of Ischnura elegans (Vander Linden) (Zygoptera: Coenagrionidae). Odonatologica 16, 37–56. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Siva-Jothy M, Tsubaki Y. 1989. Variation in copulation duration in Mnais pruinosa pruinosa Selys (Odonata: Calopterygidae): 2. Causal factors. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 25, 261–267. ( 10.1007/BF00300052) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Fincke OM. 1997. Conflict resolution in the Odonata: implications for understanding female mating patterns and female choice. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 60, 201–220. ( 10.1111/j.1095-8312.1997.tb01492.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Michiels NK. 1992. Consequences and adaptive significance of variation in copulation duration in the dragonfly Sympetrum danae. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 29, 429–435. ( 10.1007/BF00170173) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Andrés J, Cordero-Rivera A. 2000. Copulation duration and fertilization success in a damselfly: an example of cryptic female choice? Anim. Behav. 59, 695–703. ( 10.1006/anbe.1999.1372) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Eberhard WG. 2000. Criteria for demonstrating postcopulatory female choice. Evolution 54, 1047–1050. ( 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2000.tb00105.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Siva-Jothy M, Hooper R. 1996. Differential use of stored sperm during oviposition in the damselfly Calopteryx splendens xanthostoma (Charpentier). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 39, 389–393. ( 10.1007/s002650050305) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Burley N. 1988. The differential-allocation hypothesis: an experimental test. Am. Nat. 132, 611–628. ( 10.1086/284877) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Gowaty PA, Anderson WW, Bluhm CK, Drickamer LC, Kim Y-K, Moore AJ. 2007. The hypothesis of reproductive compensation and its assumptions about mate preferences and offspring viability. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 15 023–15 027. ( 10.1073/pnas.0706622104) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.McPeek MA, Shen L, Torrey JZ, Farid H. 2008. The tempo and mode of three-dimensional morphological evolution in male reproductive structures. Am. Nat. 171, E158–E178. ( 10.1086/587076) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.McPeek MA, Shen L, Farid H. 2009. The correlated evolution of three-dimensional reproductive structures between male and female damselflies. Evolution (N. Y). 63, 73–83. ( 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2008.00527.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Albert AYK, Millar NP, Schluter D. 2007. Character displacement of male nuptial colour in threespine sticklebacks (Gasterosteus aculeatus). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 91, 37–48. ( 10.1111/j.1095-8312.2007.00777.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Boughman JW. 2001. Divergent sexual selection enhances reproductive isolation in sticklebacks. Nature 411, 944–948. ( 10.1038/35082064) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Boughman J, Rundle H, Schluter D. 2005. Parallel evolution of sexual isolation in sticklebacks. Evolution (N. Y). 59, 361–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Datasets used in our analyses are available at Dryad (dryad.org): doi:10.5061/dryad.158pj.