Abstract
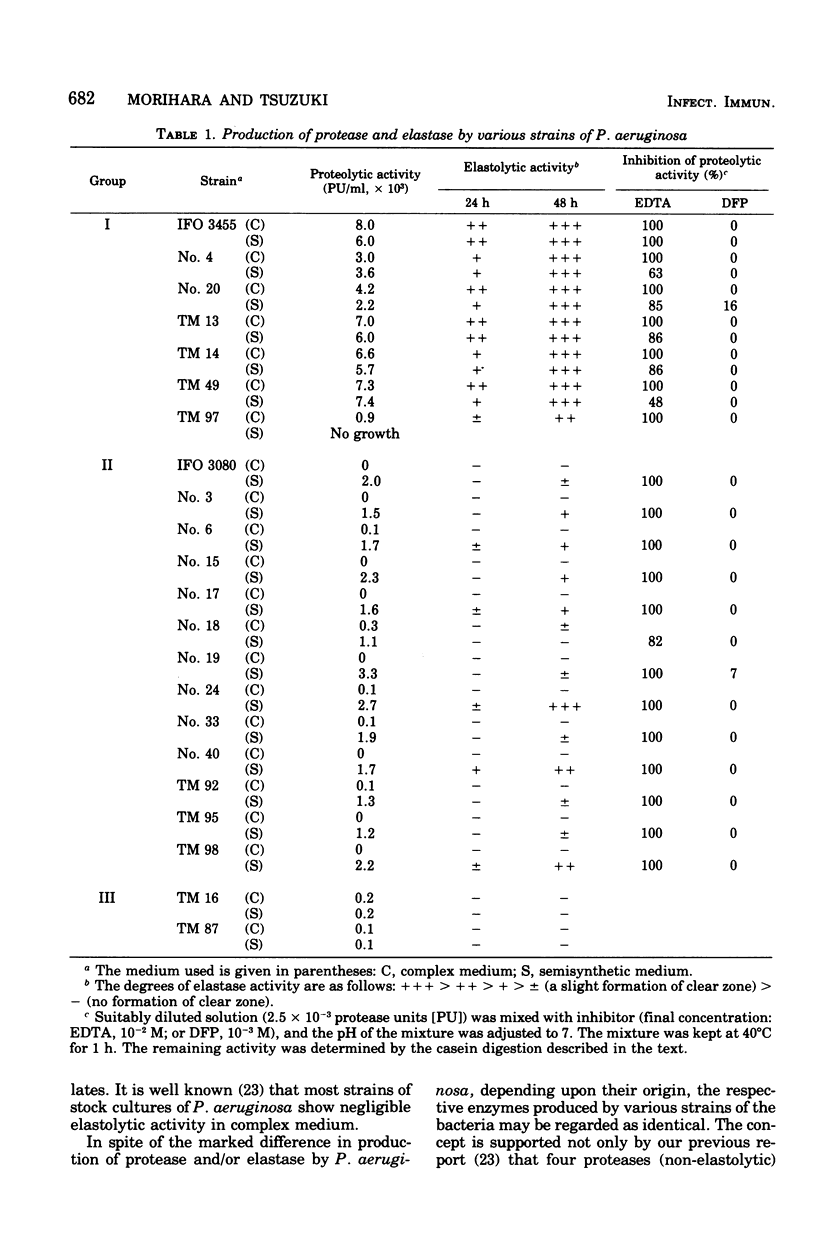
Using 20 strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from patients, production of protease, elastase, and collagenase was determined by shaking culture in either complex or semisynthetic medium. No collagenase was produced by any strain of P. aeruginosa. According to their production of protease and elastase in different media, the P. aeruginosa strains were divided into three groups: the first group can produce elastase in complex medium and both protease and elastase in semisynthetic medium; the second group cannot produce any proteolytic enzymes in complex medium but can produce any proteolytic enzymes in either medium; and the third group cannot produce any proteolytic enzymes in either medium. In spite of the differences in the ability of the strains to produce the enzymes, depending upon the origin of the strains, the protease or elastases produced in different broths were regarded as identical.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balke E., Scharmann W. Untersuchungen an einer Protease (Elastase) aus Pseudomonas aeruginosa, II: Charakterisierung des Enzyms. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1974 Aug;355(8):958–968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrick L., Jr, Berk R. S. Purification and partial characterization of a collagenolytic enzyme from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 24;391(2):422–434. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER E., Jr, ALLEN J. H. Mechanism of corneal destruction by pseudomonas proteases. Am J Ophthalmol. 1958 Nov;46(5 Pt 2):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(58)90804-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetzer A. E., Werner A. S., Hagstrom J. W. Pathologic features of pseudomonal pneumonia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 Dec;96(6):1121–1130. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.96.6.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke J. R., Magliocco M. V. Experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection of the Mouse Cornea. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):209–216. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.209-216.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray L. D., Kreger A. S. Rabbit corneal damage produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):419–432. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.419-432.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma J. Y., Tomiyama T., Sano H., Hirao Y., Saku K. Passive hemagglutination reaction test using formalinized sheep erythrocytes treated with tannic acid and coated with proteast or elastase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1975 Oct;45(5):361–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INOUE H., NAKAGAWA T., MORIHARA K. Pseudomonas aeruginosa proteinase. II. Molecular weight and molecular dimension. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 7;73:125–131. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90427-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. G., Morris J. M., Berk R. S. The extracellular protease from Pseudomonas aeruginosa exhibiting elastase activity. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Jun;13(6):711–719. doi: 10.1139/m67-093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaharajo K., Abe C., Homma J. Y., Kawano M., Goto E. Corneal ulcers caused by protease and elastase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1974 Oct;44(5):435–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaharajo K., Homma J. Y., Aoyama Y., Morihara K. In vivo studies on protease and elastase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1975 Apr;45(2):89–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaharajo K., Homma J. Y., Aoyama Y., Okada K., Morihara K. Effects of protease and elastase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa on skin. Jpn J Exp Med. 1975 Apr;45(2):79–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaharajo K., Homma J. Y. Pathogenesis of the mouse keratitis produced with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1975 Dec;45(6):515–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaharajo K., Homma J. Y. Synergistic effect of immune gamma-globulin fraction on protection by antibiotic against corneal ulcers in experimental mice infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1976 Jun;46(3):155–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S., Griffin O. K. Physicochemical fractionation of extracellular cornea-damaging proteases of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):828–834. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.828-834.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera M., Lysenko O. The mechanism of pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. V. Isolation and properties of the proteinases toxic for larvae of the greater wax moth Galleria mellonella L. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1968;13(4):288–294. doi: 10.1007/BF02909616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. Exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. Factors that influence the production of exotoxin A. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):506–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. Extracellular toxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130 (Suppl)(0):S94–S99. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.supplement.s94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. II. Effects of lecithinase and protease. J Infect Dis. 1966 Feb;116(1):112–116. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.1.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K. PRODUCTION OF ELASTASE AND PROTEINASE BY PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:745–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.745-757.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K., TSUZUKI H., OKA T., INOUE H., EBATA M. PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA ELASTASE. ISOLATION, CRYSTALLIZATION, AND PRELIMINARY CHARACTERIZATION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3295–3304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K., TSUZUKI H. PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA PEPTIDE PEPTIDOHYDROLASE. 3. SOME CHARACTERS AS A CA2+-METALLOENZYME. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Nov 22;92:351–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIHARA K., YOSHIDA N., KURIYAMA K. PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA PEPTIDE PEPTIDOHYDROLASE. IV. OPTICAL ROTATORY DISPERSION AND AMINO ACID COMPOSITION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Nov 22;92:361–366. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90194-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULL J. D., CALLAHAN W. S. ESTIMATION OF ELASTOLYTIC ACTIVITY OF STRAINS OF PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. J Bacteriol. 1963 May;85:1178–1179. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.5.1178-1179.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinke G., Barum J., Rosenberg B., Berk R. In Vivo Studies with the Partially Purified Protease (Elastase) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):583–589. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.583-589.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morihara K. Comparative specificity of microbial proteinases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974;41(0):179–243. doi: 10.1002/9780470122860.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morihara K., Tsuzuki H. Comparative study of various neutral proteinases from microorganisms: specificity with oligopeptides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Sep;146(1):291–296. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(71)80066-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morihara K., Tsuzuki H., Oka T. Comparison of the specificities of various neutral proteinases from microorganisms. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Mar 11;123(3):572–588. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morihara K., Tsuzuki H., Oka T. On the specificity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alkaline proteinase with synthetic peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 6;309(2):414–429. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90040-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morihara K., Tsuzuki H. Substrate specificity of elastolytic and nonelastolytic proteinases from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Apr;114(1):158–165. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90317-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada K., Kawaharajo K., Homma J. Y., Aoyama Y., Kubota Y. Studies on the pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by the use of ligated rabbit intestines (the De test). Jpn J Exp Med. 1976 Aug;46(4):245–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SBARRA A. J., GILFILLAN R. F., BARDAWIL W. A. A plate assay for elastase. Nature. 1960 Oct 22;188:322–323. doi: 10.1038/188322b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharmann W., Balke E. Untersuchungen über eine Protease (Elastase) von Pseudomonas aeruginosa, I. Bildung und Reinigung der Protease. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1974 Apr;355(4):443–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uss R. H., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Muraschi T. F., Miller K. D. Two distinct elastases from different strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Sep 30;191(1):179–181. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90332-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


