Abstract
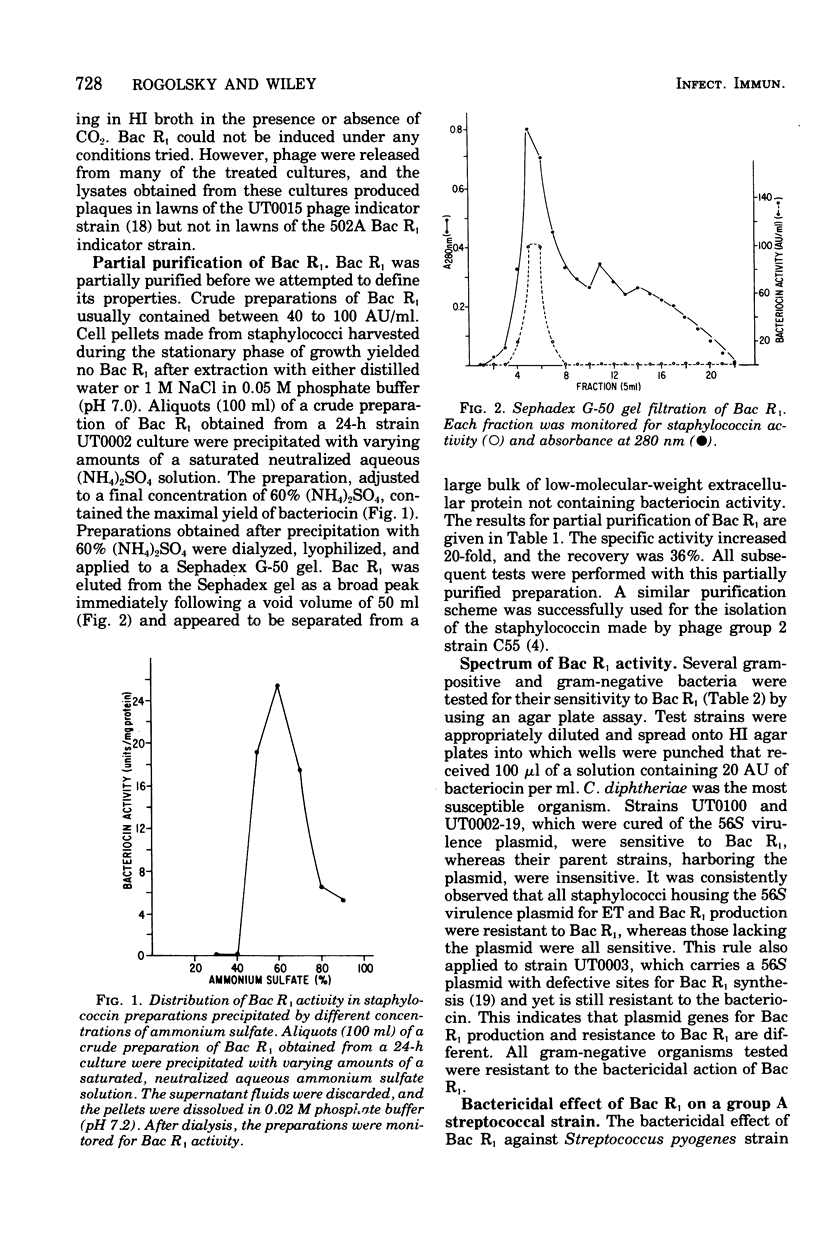
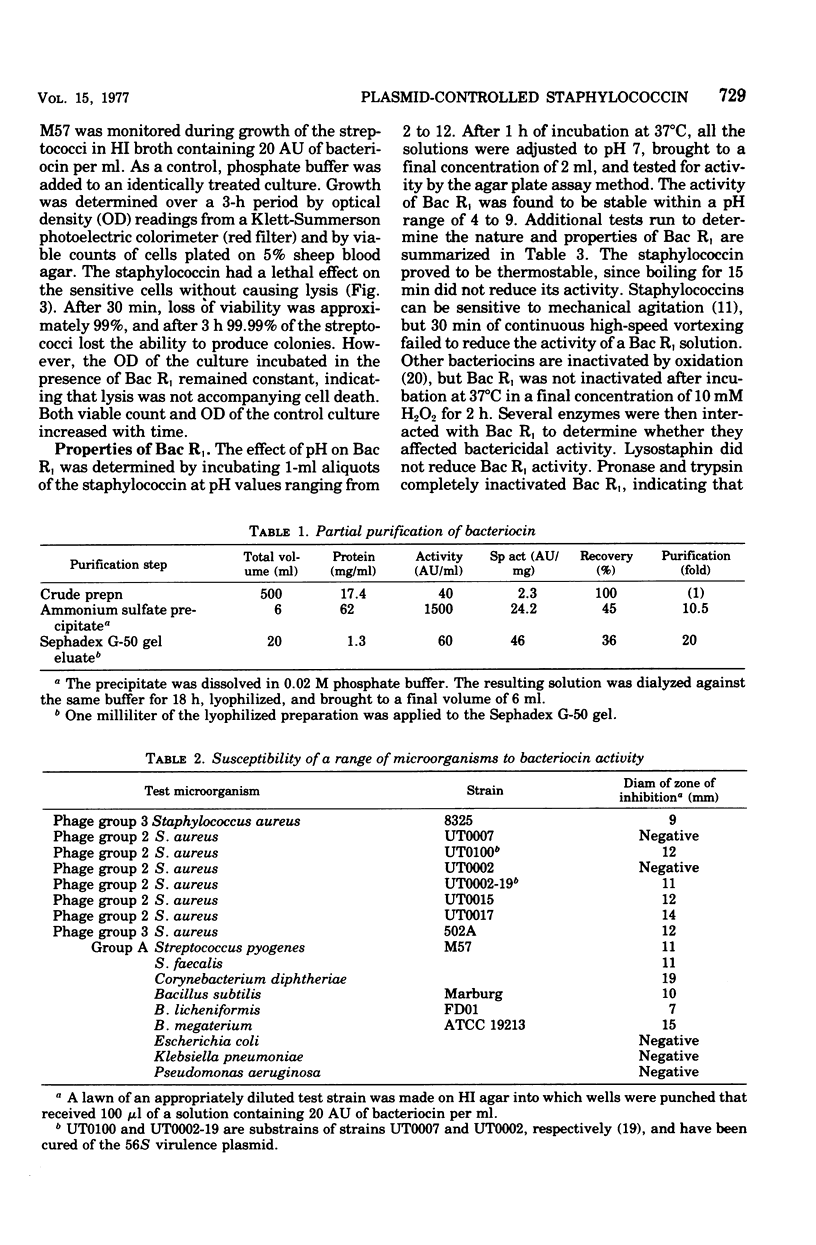
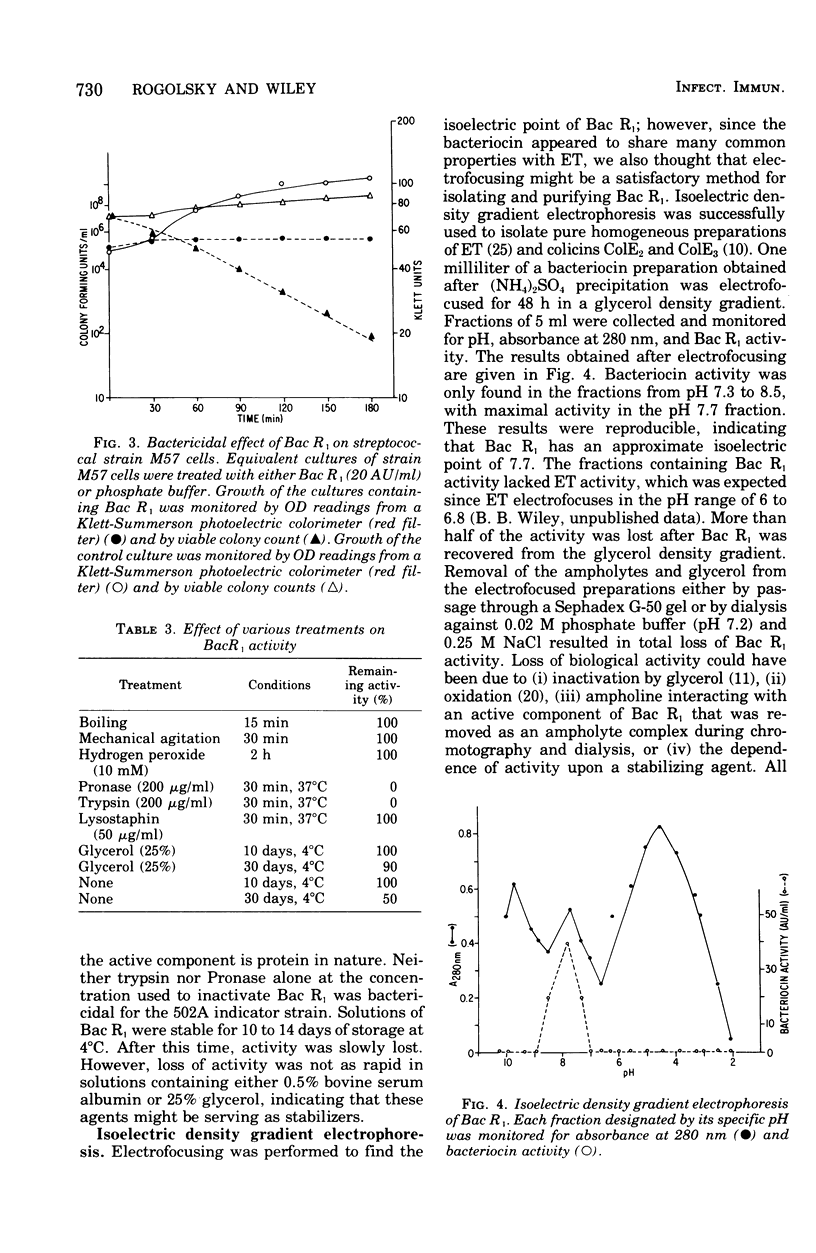
Previous data from this laboratory showed that certain phage group 2 staphylococci contain a large 56S virulence plasmid containing genes that code for both exfoliative toxin (ET) and a specific staphylococcin. Optimal cultural conditions for bacteriocin production were similar to those found for ET production. The bacteriocin is an extracellular product produced in small quantities that can be neither extracted from cell pellets with 1 M NaCl nor induced with mitomycin C. The staphylococcin is active against a wide variety of gram-positive organisms and also against group 2 staphylococcal strains that have been cured of the plasmid carrying the staphylococcin marker. The bacteriocin is not inactivated by oxidation, mechanical agitation, or boiling for 15 min. It is sensitive to the action of trypsin and Pronase but not lysostaphin and is stable within a pH range of 4 to 9. It has an isoelectric point of approximately 7.7. Removal of the ampholytes and glycerol from electrofocused staphylococcin preparations resulted in total loss of bacteriocin activity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony B. F., Giuliano D. M., Oh W. Nursery outbreak of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. Rapid identification of the epidemic bacterial strain. Am J Dis Child. 1972 Jul;124(1):41–44. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1972.02110130043006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Gray E. D., Wannamaker L. W. Bactericidal substance from Staphylococcus aureus. Biological properties. J Exp Med. 1970 May 1;131(5):1004–1015. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.5.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Gray E. D., Wannamaker L. W. Effect of Bactericidal Substance from Staphylococcus aureus on Group A Streptococci I. Biochemical Alterations. Infect Immun. 1970 May;1(5):485–490. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.5.485-490.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Taube Z. Plasmid-mediated production of staphylococcin in bacteriophage type 71 Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jun;5(6):594–598. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.6.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Demonstration of a bactericidal substance against beta-hemolytic streptococci in supernatant fluids of staphylococcal cultures. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):985–991. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.985-991.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimond R. L., Wuepper K. D. Purification and characterization of a staphylococcal epidermolytic toxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):627–633. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.627-633.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagliano V. J., Hinsdill R. D. Characterization of a Staphylococcus aureus bacteriocin. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):117–125. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.117-125.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschman H. R., Helinski D. R. Purification and characterization of colicin E2 and colicin E3. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5360–5368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Vogels G. D. Nature and properties of a Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteriocin. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):243–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.243-250.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Vogels G. D., de Windt F. Production and purification of a Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteriocin. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):235–242. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.235-242.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Metzger J. F., Spero L. Production, purification, and chemical characterization of Staphylococcus aureus exfoliative toxin. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1206–1210. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1206-1210.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A., Miller M. M. Product of Staphylococcus aureus responsible for the scalded-skin syndrome. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):541–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.541-545.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo I., Sakurai S., Sarai Y. Purification of exfoliatin produced by Staphylococcus aureus of bacteriophage group 2 and its physicochemical properties. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):156–164. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.156-164.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melish M. E., Glasgow L. A. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome: the expanded clinical syndrome. J Pediatr. 1971 Jun;78(6):958–967. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogolsky M., Warren R., Wiley B. B., Nakamura H. T., Glasgow L. A. Nature of the genetic determinant controlling exfoliative toxin production in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):157–165. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.157-165.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogolsky M., Wiley B. B., Glasgow L. A. Phage group II staphylococcal strains with chromosomal and extrachromosomal genes for exfoliative toxin production. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):44–52. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.44-52.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J. A., de Klerk H. C., Coetzee J. N. Properties of a Proteus morganii bacteriocin. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Nov;54(1):67–75. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-1-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiffler P. W., Sweeney H. M., Cohen S. Absence of circular plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid attributable to a genetic determinant for methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):771–777. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.771-777.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Bacteriocins of gram-positive bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):722–756. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.722-756.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R., Rogolsky M., Wiley B. B., Glasgow L. A. Effect of ethidium bromide on elimination of exfoliative toxin and bacteriocin production in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):980–985. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.980-985.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R., Rogolsky M., Wiley B. B., Glasgow L. A. Isolation of extrachromosomal deoxyribonucleic acid for exfoliative toxin production from phage group II Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):99–105. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.99-105.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley B. B., Glasgow L. A., Rogolsky M. Staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome: development of a primary binding assay for human antibody to the exfoliative toxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):513–520. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.513-520.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


