Abstract
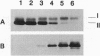
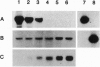
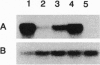
NADPH-protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase (POR; EC 1.6.99.1) catalyzes the only known light-dependent step in chlorophyll synthesis of higher plants, the reduction of protochlorophyllide (Pchlide) to chlorophyllide. In barley, two distinct immunoreactive POR proteins were identified. In contrast to the light-sensitive POR enzyme studied thus far (POR-A), levels of the second POR protein remained constant in seedlings during the transition from dark growth to the light and in green plants. The existence of a second POR-related protein was verified by isolating and sequencing cDNAs that encode a second POR polypeptide (POR-B) with an amino acid sequence identity of 75% to the POR-A. In the presence of NADPH and Pchlide, the in vitro-synthesized POR-A and POR-B proteins could be reconstituted to ternary enzymatically active complexes that reduced Pchlide to chlorophyllide only after illumination. Even though the in vitro activities of the two enzymes were similar, the expression of their genes during the light-induced transformation of etiolated to green seedlings was distinct. While the POR-A mRNA rapidly declined during illumination of dark-grown seedlings and soon disappeared, POR-B mRNA remained at an approximately constant level in dark-grown and green seedlings. Thus these results suggest that chlorophyll synthesis is controlled by two light-dependent POR enzymes, one that is active only transiently in etiolated seedlings at the beginning of illumination and the other that also operates in green plants.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apel K., Kloppstech K. The plastid membranes of barley (Hordeum vulgare). Light-induced appearance of mRNA coding for the apoprotein of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):581–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apel K. Phytochrome-induced appearance of mRNA activity for the apoprotein of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein of barley (Hordeum vulgare). Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun;97(1):183–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13101.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apel K., Santel H. J., Redlinger T. E., Falk H. The protochlorophyllide holochrome of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Isolation and characterization of the NADPH:protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(1):251–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batschauer A., Apel K. An inverse control by phytochrome of the expression of two nuclear genes in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Eur J Biochem. 1984 Sep 17;143(3):593–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benli M., Schulz R., Apel K. Effect of light on the NADPH-protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Apr;16(4):615–625. doi: 10.1007/BF00023426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broglie R., Bellemare G., Bartlett S. G., Chua N. H., Cashmore A. R. Cloned DNA sequences complementary to mRNAs encoding precursors to the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase and a chlorophyll a/b binding polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7304–7308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darrah P. M., Kay S. A., Teakle G. R., Griffiths W. T. Cloning and sequencing of protochlorophyllide reductase. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):789–798. doi: 10.1042/bj2650789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esen A. A simple method for quantitative, semiquantitative, and qualitative assay of protein. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):264–273. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90749-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forde B. G., Kreis M., Bahramian M. B., Matthews J. A., Miflin B. J., Thompson R. D., Bartels D., Flavell R. B. Molecular cloning and analysis of cDNA sequences derived from poly A+ RNA from barley endosperm: identification of B hordein related clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6689–6707. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forreiter C., Apel K. Light-independent and light-dependent protochlorophyllide-reducing activities and two distinct NADPH-protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase polypeptides in mountain pine (Pinus mugo). Planta. 1993;190(4):536–545. doi: 10.1007/BF00224793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franck F., Strzalka K. Detection of the photoactive protochlorophyllide-protein complex in the light during the greening of barley. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 31;309(1):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80742-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths W. T. Reconstitution of chlorophyllide formation by isolated etioplast membranes. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 15;174(3):681–692. doi: 10.1042/bj1740681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häuser I., Dehesh K., Apel K. The proteolytic degradation in vitro of the NADPH-protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Feb 1;228(2):577–586. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSKI V. M., FRENCH C. S., SMITH J. H. C. The action spectrum for the transformation of protochlorophyll to chlorophyll a in normal and albino corn seedlings. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Mar;31(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90178-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay S. A., Griffiths W. T. Light-Induced Breakdown of NADPH-Protochlorophyllide Oxidoreductase In Vitro. Plant Physiol. 1983 May;72(1):229–236. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.1.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawetz S. A., Pon R. T., Dixon G. H. Increased efficiency of the Taq polymerase catalyzed polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):819–819. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapleston R. E., Griffiths W. T. Light modulation of the activity of protochlorophyllide reductase. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 1;189(1):125–133. doi: 10.1042/bj1890125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santel H. J., Apel K. The protochlorophyllide holochrome of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). The effect of light on the NADPH:protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(1):95–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz R., Steinmüller K., Klaas M., Forreiter C., Rasmussen S., Hiller C., Apel K. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA coding for the NADPH-protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase (PCR) of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) and its expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):355–361. doi: 10.1007/BF02464904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spano A. J., He Z., Michel H., Hunt D. F., Timko M. P. Molecular cloning, nuclear gene structure, and developmental expression of NADPH: protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Mar;18(5):967–972. doi: 10.1007/BF00019210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spano A. J., He Z., Timko M. P. NADPH: protochlorophyllide oxidoreductases in white pine (Pinus strobus) and loblolly pine (P. taeda). Evidence for light and developmental regulation of expression and conservation in gene organization and protein structure between angiosperms and gymnosperms. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Dec;236(1):86–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teakle G. R., Griffiths W. T. Cloning, characterization and import studies on protochlorophyllide reductase from wheat (Triticum aestivum). Biochem J. 1993 Nov 15;296(Pt 1):225–230. doi: 10.1042/bj2960225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]