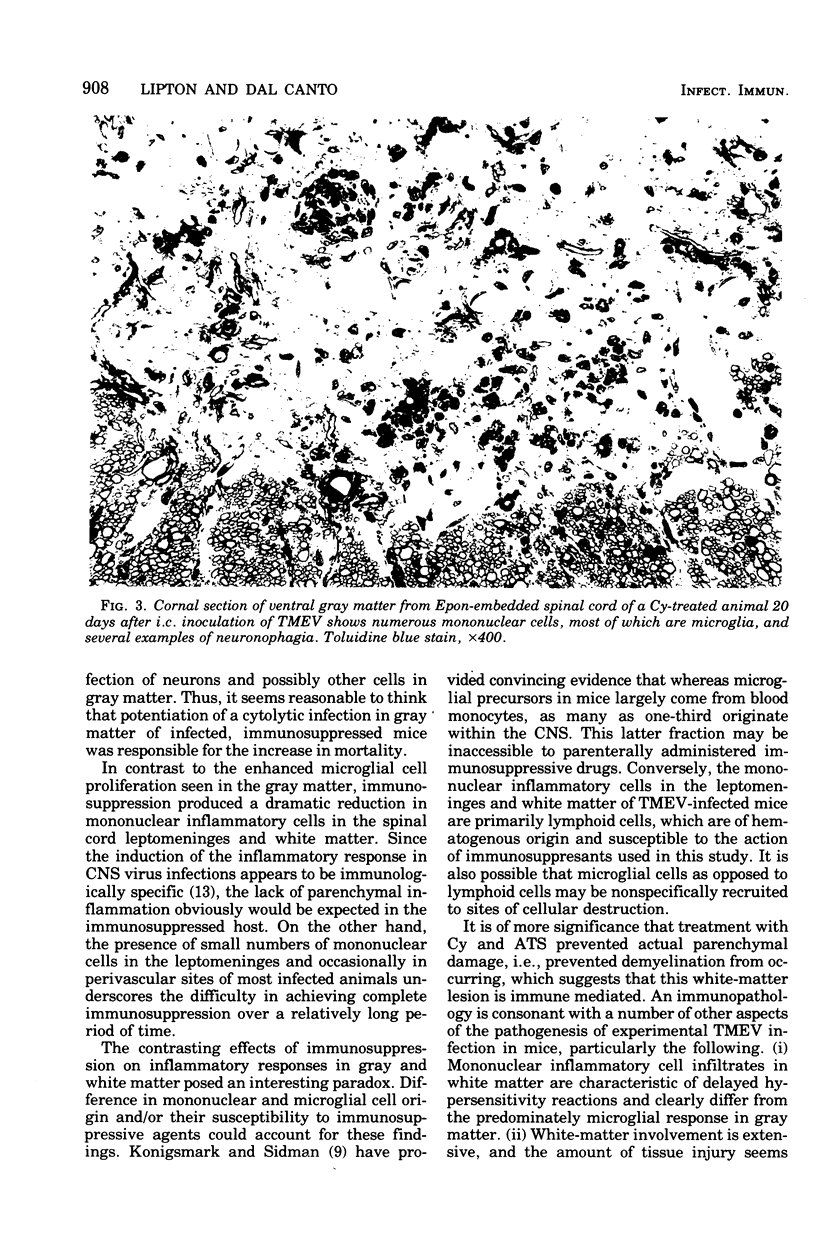
Abstract
In the present study, cyclophosphamide and rabbit anti-mouse thymocyte serum were used to immunosuppress SJL/J mice infected with Theiler's mouse encephalomyelitis virus (TMEV) in order to delineate the potential mechanism(s) of virus-induced cellular injury in this infection. Whereas both immunosuppressive agents produced a significant increase in mortality, this treatment had differing effects on the pathological involvement of gray and white-matter structures in the central nervous system. The central nervous system of immunosuppressed TMEV-infected mice had increased microglial cell proliferation and neuronal necrosis, longer maintenance of high virus levels and spread of virus antigen to involve the neocortex and hippocampal complex. These observations indicate that TMEV causes a cytolotic infection of neurons and possibly other cells in gray matter. In contrast, immunosuppression produced a dramatic reduction in mononuclear inflammatory cells in the leptomeninges and spinal cord white matter of infected mice and prevented demyelination. Further, virus antigen was not detected in the leptomeninges and white matter of immunosuppressed and infected mice. These findings suggest that demyelination of TMEV infection is immune mediated.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brier A. M., Wohlenberg C., Rosenthal J., Mage M., Notkins A. L. Inhibition or enhancement of immunological injury of virus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3073–3077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns W., Billups L. C., Notkins A. L. Thymus dependence of viral antigens. Nature. 1975 Aug 21;256(5519):654–656. doi: 10.1038/256654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEAN D. J. Mouse encephalomyelitis; immunologic studies of a non-infected colony. J Immunol. 1951 Mar;66(3):347–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dal Canto M. C., Lipton H. L. Primary demyelination in Theiler's virus infection. An ultrastructural study. Lab Invest. 1975 Dec;33(6):626–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Zinkernagel R. M. H-2 compatibility is required for T-cell-mediated lysis of target cells infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):502–507. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Cole G. A., Nathanson N. Immunopathogenesis of acute central nervous system disease produced by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. II. Adoptive immunization of virus carriers. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):874–889. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm G., Perlmann P. Cytotoxic potential of stimulated human lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1967 Apr 1;125(4):721–736. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.4.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONIGSMARK B. W., SIDMAN R. L. ORIGIN OF BRAIN MACROPHAGES IN THE MOUSE. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1963 Oct;22:643–676. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196310000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koszinowski U., Ertl H. Lysis mediated by T cells and restricted by H-2 antigen of target cells infected with vaccinia virus. Nature. 1975 Jun 12;255(5509):552–554. doi: 10.1038/255552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L., Dal Canto M. C. Chronic neurologic disease in Theiler's virus infection of SJL/J mice. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Nov;30(1):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90267-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L., Dal Canto M. C. Theiler's virus-induced demyelination: prevention by immunosuppression. Science. 1976 Apr 2;192(4234):62–64. doi: 10.1126/science.176726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L. Theiler's virus infection in mice: an unusual biphasic disease process leading to demyelination. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1147–1155. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1147-1155.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland H. F., Griffin D. E., Johnson R. T. Specificity of the inflammatory response in viral encephalitis. I. Adoptive immunization of immunosuppressed mice infected with Sindbis virus. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):216–226. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Pathogenesis of chronic disease associated with persistent lymphocytic choriomeningitis viral infection. I. Relationship of antibody production to disease in neonatally infected mice. J Exp Med. 1969 Mar 1;129(3):483–505. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.3.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rager-Zisman B., Grose C., Bloom B. R. Mechanism of selective nonspecific cell-mediated cytotoxicity of virus-infected cells. Nature. 1976 Mar 25;260(5549):369–370. doi: 10.1038/260369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. L., Black C. M., Melewicz F. M., Wood P. A., Nahmias A. J. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity to target cells infected with type 1 and type 2 herpes simplex virus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):194–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER D. L. THE VIRAL CARRIER STATE IN ANIMAL CELL CULTURES. Prog Med Virol. 1964;6:111–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M. Virus-specific T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity across the H-2 barrier to virus-altered alloantigen. Nature. 1976 May 13;261(5556):139–141. doi: 10.1038/261139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




