Abstract
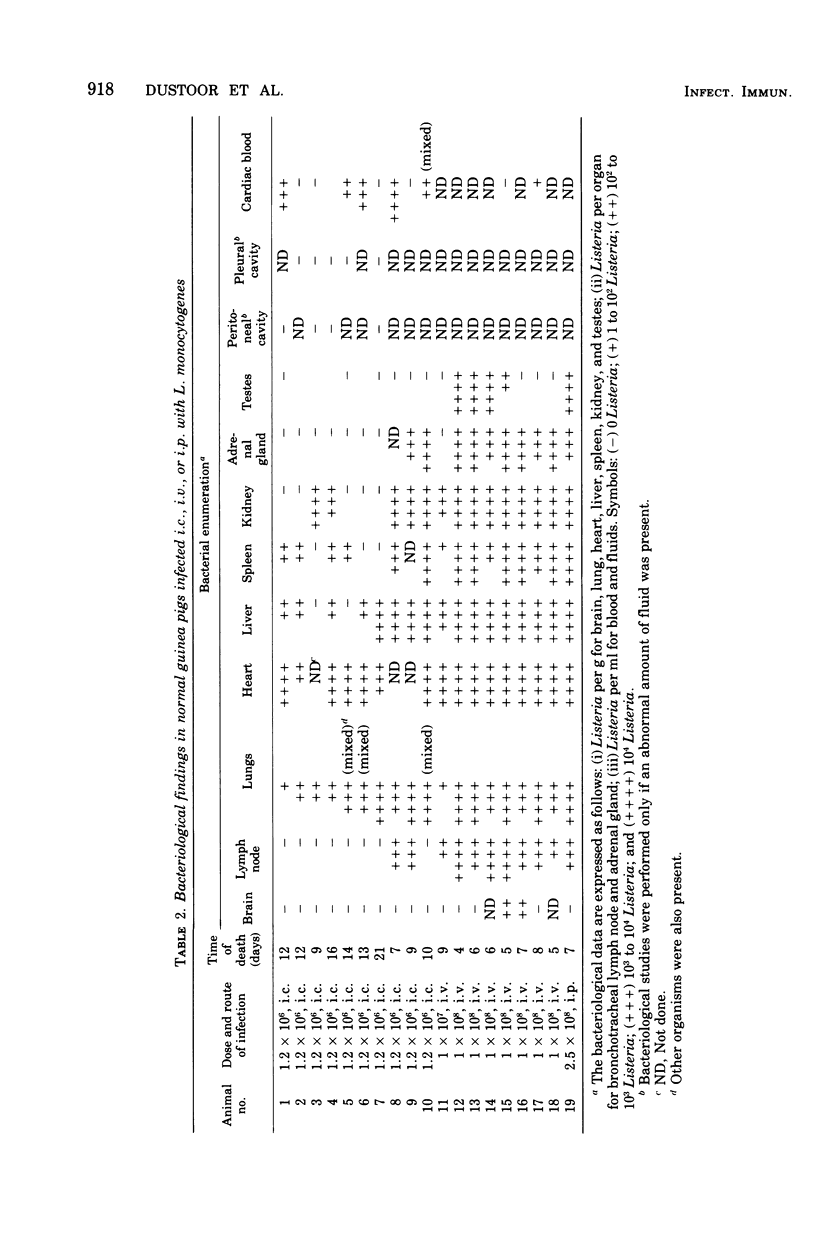
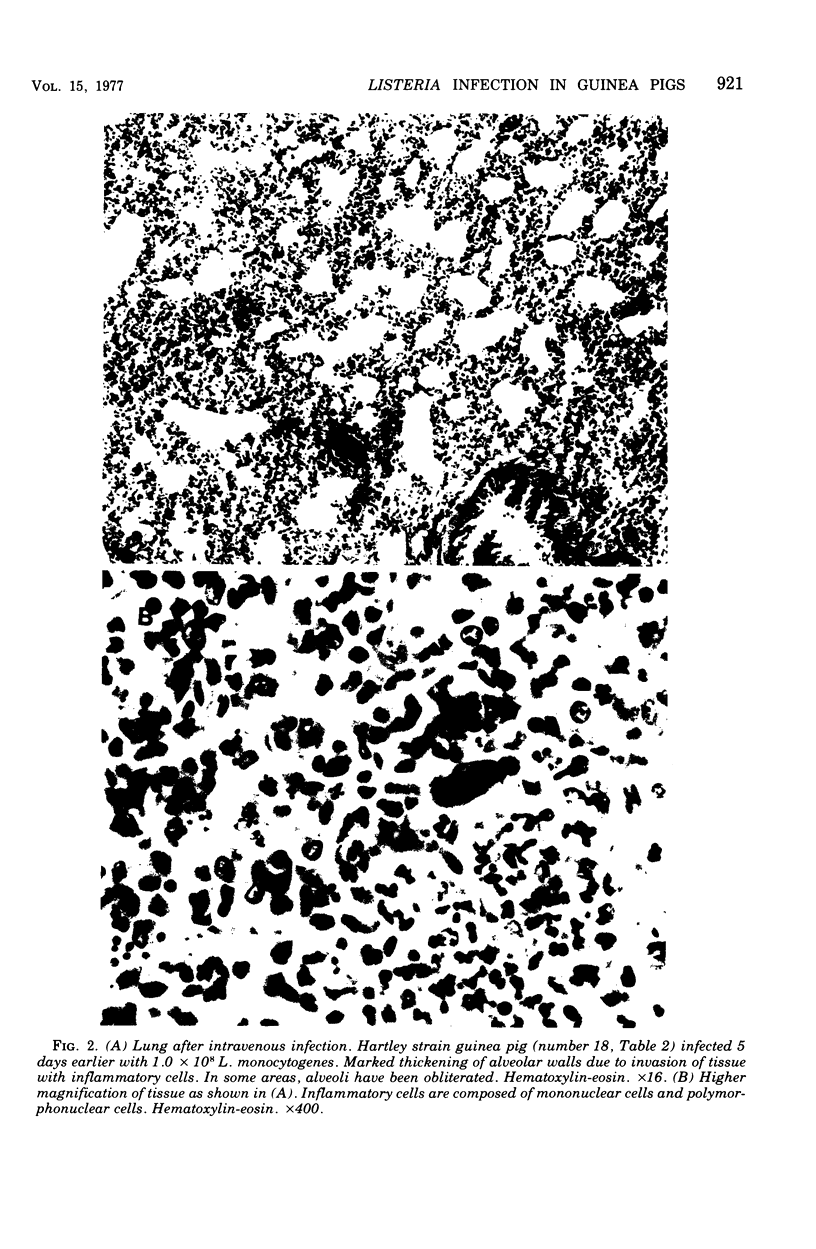
Randomly bred guinea pigs were infected with Listeria monocytogenes using the intracardial, intravenous and intraperitoneal routes of infection. Doses of Listeria ranged from 5 to 1,000 x the 50% lethal dose based on the 50% lethal dose for intracardially injected Listeria. A complete necropsy was performed on all animals that died after infection. Gross and microscopic examination of tissues revealed major pathological features which include myocarditis, edema and congestion with interstitial pneumonitis present in the lungs, and fatty hepatic changes with focal necrosis. For all or a majority of the animals, large numbers of Listeria were likewise recovered from these organs and from lymph nodes, spleen, kidneys, and adrenal gland tissue. Of the three routes of infection used, guinea pigs were most susceptible to Listeria injected via the intracardial route. The relatively high lethal dose of listeric for the quinea pig, however, suggests that the organism is a low-grade pathogen for this species.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bast R. C., Jr, Zbar B., Mackaness G. B., Rapp H. J. Antitumor activity of bacterial infection. I. Effect of Listeria monocytogenes on growth of a murine fibrosarcoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Mar;54(3):749–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bast R. C., Jr, Zbar B., Miller T. E., Mackaness G. B., Rapp H. J. Antitumor activity of bacterial infection. II. effect of Listeria monocytogenes on growth of a guinea pig hepatoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Mar;54(3):757–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft W. A., Bryan G. T. Production of urinary bladder carcinomas in male hamsters by N-(4-(5-nitro-2-furyl)-2-thiazolyl)formamide, N-(4-(5-nitro-2-furyl)-2-thiazolyl)-acetamide, or formic acid 2-(4-(5-nitro-2-furyl)-2-thiazolyl)hydrazide. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Sep;51(3):941–949. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.3.941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton A. M., Dustoor M. M., Kasinski J. E., Blazkovec A. A. Blastogenesis as an in vitro correlate of delayed hypersensitivity in guinea pigs infected with Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):647–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.647-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliburton B. L., Blazkovec A. A. Delayed hypersensitivity and acquired cellular resistance in guinea pigs infected with Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.1-7.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUTTER D. A., SILVERMAN S. J., ROESSLER W. G., DRAWDY J. F. Virulence of Listeria monocytogenes for experimental animals. J Infect Dis. 1963 Mar-Apr;112:167–180. doi: 10.1093/infdis/112.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. A., Seaman A., Woodbine M. Proceedings: The pathogenicity of Listeria monocytogenes. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1972;19(4):421–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youdim S., Moser M., Stutman O. Nonspecific suppression of tumor growth by an immune reaction to Listeria monocytogenes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Jan;52(1):193–198. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.1.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youdim S. Resistance to tumor growth mediated by Listeria monocytogenes. Destruction of experimental malignant melanoma by LM-activated peritoneal and lymphoid cells. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):579–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]