Abstract
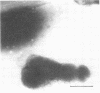
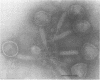
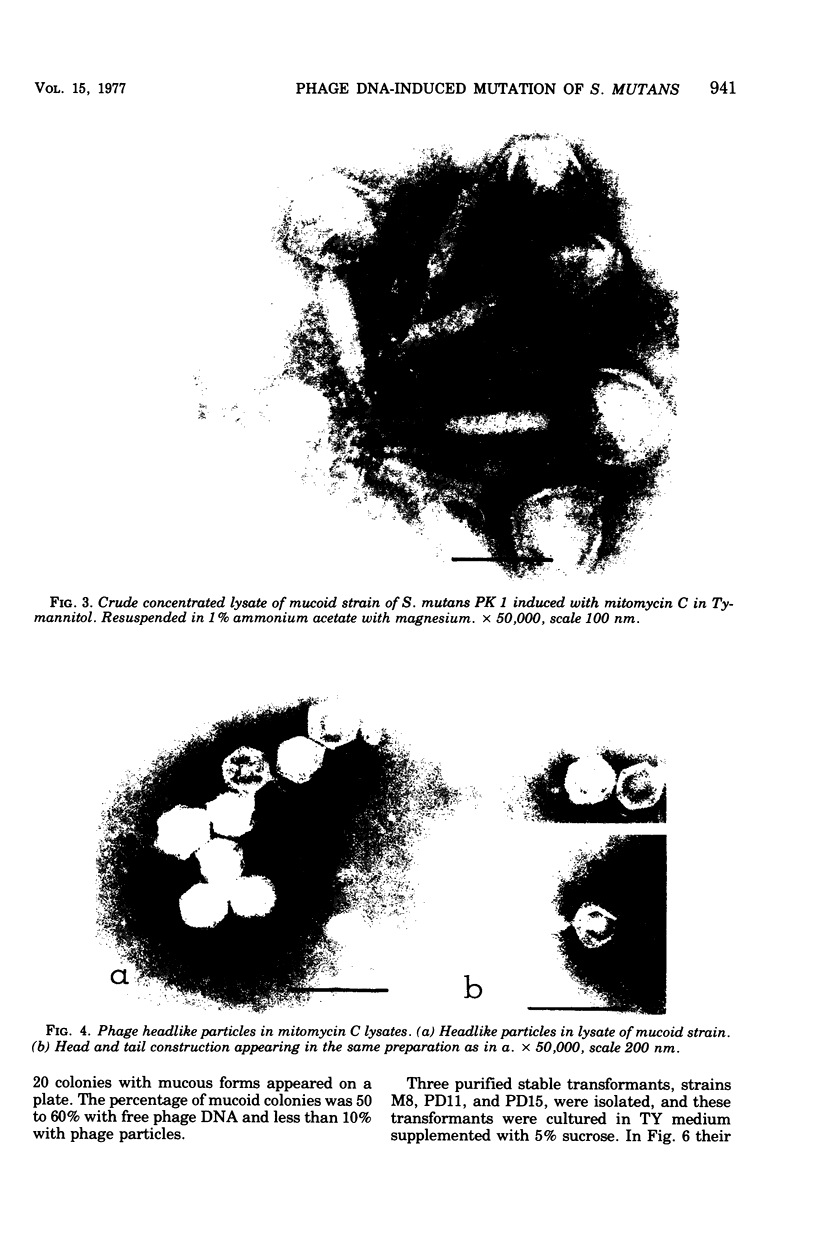
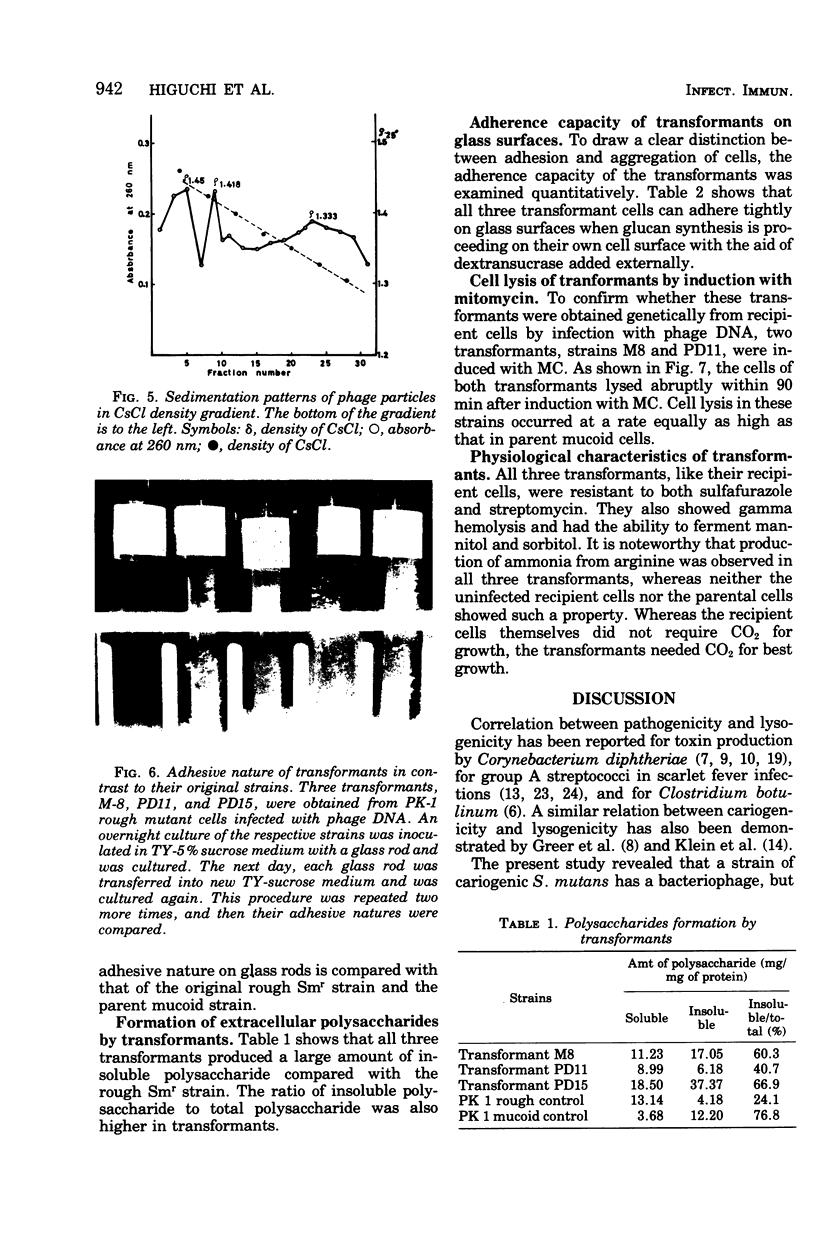
A cariogenic strain, Streptococcus mutans PK 1, has been demonstrated to have prophage by observation of phage particles with an electron microscope and by induction with mitomycin C. The phage particles could not be detected in a mutant strain which lost the characteristic adhesive nature on glass surfaces and exhibited diminished ability to synthesize insoluble polysaccharide. By infecting the mutant cells with the phages or with free phage deoxyribonucleic acid isolated from the parent strain of S. mutans PK1, the mutant cells were transformed to the cariogenic strain with adhesive nature. The transformants retained the general characteristics of S. mutans PK 1, but in addition all transformants showed a new character; namely, the transformant cell could produce ammonia from arginine, whereas neither the parent nor mutant strains of S. mutans PK 1 had such a property;
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eklund M. W., Poysky F. T., Boatman E. S. Bacteriophages of Clostridium botulinum types A, B, E, and F and nontoxigenic strains resembling type E. J Virol. 1969 Feb;3(2):270–274. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.2.270-274.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN V. J. Studies on the virulence of bacteriophage-infected strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol. 1951 Jun;61(6):675–688. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.6.675-688.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROMAN N. B. Evidence for the active role of bacteriophage in the conversion of nontoxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae to toxin production. J Bacteriol. 1955 Jan;69(1):9–15. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.1.9-15.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer S. B., Hsiang W., Musil G., Zinner D. D. Viruses of cariogenic streptococci. J Dent Res. 1971 Nov-Dec;50(6):1594–1604. doi: 10.1177/00220345710500064101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEWITT L. F. Diphtheria bacteriophages and their relation to the development of bacterial variants. J Gen Microbiol. 1952 Nov;7(3-4):362–371. doi: 10.1099/00221287-7-3-4-362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi M., Araya S., Higuchi M. Plasmid DNA satellite bands seen in lysates of Streptococcus mutans that form insoluble extracellular polysaccharides. J Dent Res. 1976 Mar-Apr;55(2):266–271. doi: 10.1177/00220345760550021801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi M., Endo K., Hoshino E., Araya S. Preferential induction of rough variants in Streptococcus mutans by ethidium bromide. J Dent Res. 1973 Sep-Oct;52(5):1070–1075. doi: 10.1177/00220345730520051401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KJEMS E. Studies on streptococcal bacteriophages. I. Technique of isolating phage-producing strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1955;36(5):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. P., Frank R. M. Mise en évidence de virus dans les bactéries cariogénes de la plaque dentaire. J Biol Buccale. 1973 Mar;1(1):79–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Mechanism of adherence of Streptococcus mutans to smooth surfaces. I. Roles of insoluble dextran-levan synthetase enzymes and cell wall polysaccharide antigen in plaque formation. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):555–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.555-562.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Mechanism of the Adherence of Streptococcus mutans to Smooth Surfaces III. Purification and Properties of the Enzyme Complex Responsible for Adherence. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1135–1145. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1135-1145.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARSONS E. I., FROBISHER M., Jr Effect of bacteriophage on virulence of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Dec;78(3):746–747. doi: 10.3181/00379727-78-19204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR A. L. BACTERIOPHAGE-INDUCED MUTATION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1043–1051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., HARRISON J. S. Studies on yeast metabolism. 7. Yeast carbohydrate fractions. Separation from nucleic acid, analysis, and behaviour during anaerobic fermentation. Biochem J. 1956 May;63(1):23–33. doi: 10.1042/bj0630023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer J. M., Freedman M. L., Fitzgerald R. J., Larson R. H. Diminished virulence of glucan synthesis-defective mutants of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):197–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.197-203.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZABRISKIE J. B. THE ROLE OF TEMPERATE BACTERIOPHAGE IN THE PRODUCTION OF ERYTHROGENIC TOXIN BY GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI. J Exp Med. 1964 May 1;119:761–780. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.5.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Stoppelaar J. D., König K. G., Plasschaert A. J., van der Hoeven J. S. Decreased cariogenicity of a mutant of Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1971 Aug;16(8):971–975. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(71)90186-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]