Abstract
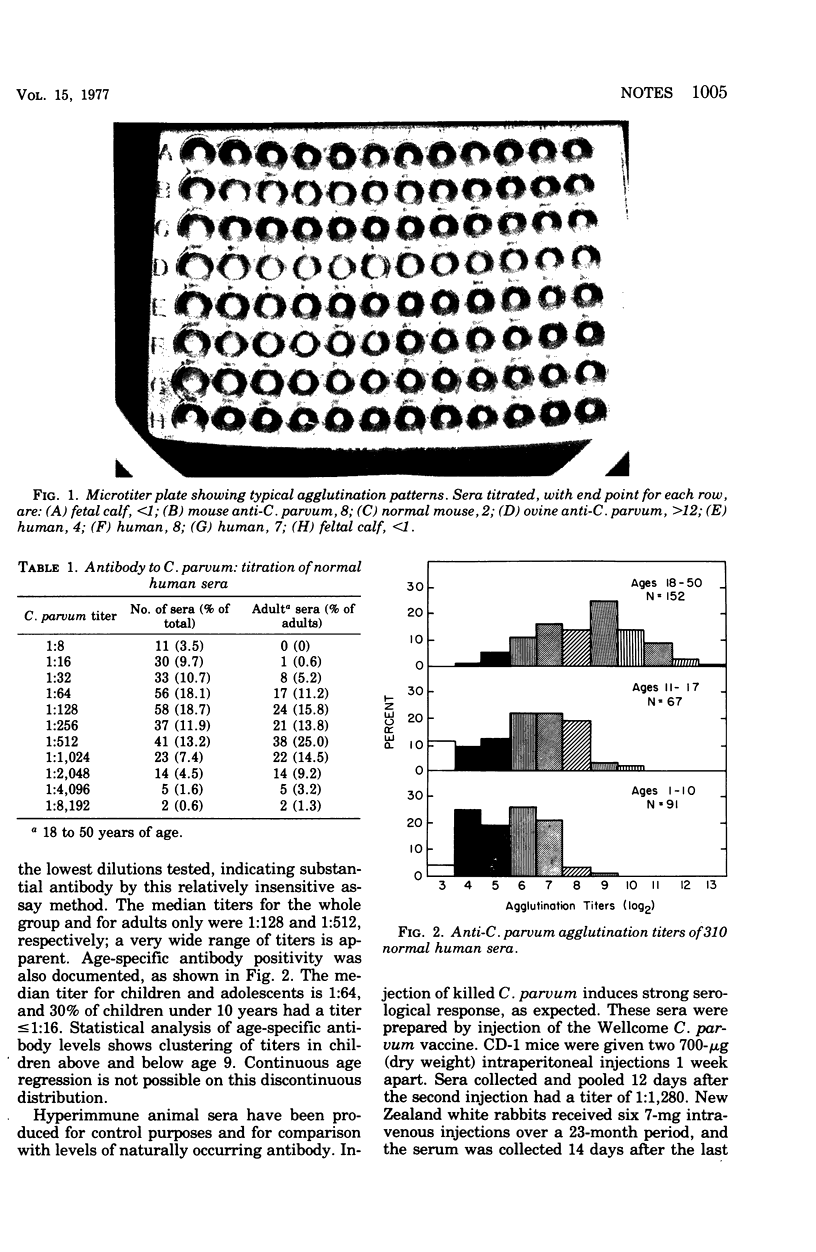
Using a microtiter bacterial agglutination test, we have estimated antibodies to Corynebacterium parvum in "normal" human and "normal" and immune animal sera. Widely differing levels of C. parvum antibodies were found in the normal human sera. The median titer for all 310 human sera was 1:128, whereas that for the 1- to 17-year and 18- to 50-year subgroups was 1:64 and 1:512, respectively. Antibody titers in the various animal species were generally much lower.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheng V. S., Suit H. D., Wang C. C., Cummings C. Nonspecific immunotherapy by Corynebacterium parvum: phase I toxicity study in 12 patients with advanced cancer. Cancer. 1976 Apr;37(4):1687–1695. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197604)37:4<1687::aid-cncr2820370412>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins C. S., Johnson J. L. Corynebacterium parvum: a synonym for Propionibacterium acnes? J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Feb;80(2):433–442. doi: 10.1099/00221287-80-2-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher B., Rubin H., Sartiano G., Ennis L., Wolmark N. Observations following Corynebacterium parvum administration to patients with advanced malignancy. a phase I study. Cancer. 1976 Jul;38(1):119–130. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197607)38:1<119::aid-cncr2820380121>3.0.co;2-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori T., Mori A. Bacteriological survey of anaerobic Corynebacterium in human bone marrow and blood. Gan. 1973 Feb;64(1):7–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James K., Clunie G. J., Woodruff M. F., McBride W. H., Stimson W. H., Drew R., Catty D. The effect of Corynebacterium parvum therapy on immunoglobulin class and IgG subclass levels in cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 1975 Sep;32(3):310–322. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1975.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan K., Weinstein L. Diphtheroid infections of man. Ann Intern Med. 1969 May;70(5):919–929. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-5-919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., Parke J. C., Jr, Schneerson R., Whisnant J. K. Quantitative measurement of "natural" and immunization-induced Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide antibodies. Pediatr Res. 1973 Mar;7(3):103–110. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197303000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. T. Corynebacterium parvum as an immunotherapeutic anticancer agent. Semin Oncol. 1974 Dec;1(4):367–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuster S. Biological purpose of acne. Lancet. 1976 Jun 19;1(7973):1328–1329. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92657-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville D. A., Murphy C. T. Quantitation of Corynebacterium acnes on healthy human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1973 Apr;60(4):231–233. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12724525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttle R. L., North R. J. Mchanisms of antitumor action of Corynebacterium parvum: nonspecific tumor cell destruction at site of immunologically mediated sensitivity reaction to C. parvum. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Dec;55(6):1403–1411. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.6.1403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteside J. A., Voss J. G. Incidence and lipolytic activity of Propionibacterium acnes (Corynebacterium acnes group I) and P. granulosum (C. acnes group II) in acne and in normal skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1973 Feb;60(2):94–97. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12724177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff M. F., McBride W. H., Dunbar N. Tumour growth, phagocytic activity and antibody response in Corynebacterium parvum-treated mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jul;17(3):509–518. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]