Awareness and use of e-cigarettes have increased rapidly, and the products now represent a billion-dollar industry in the US.[1,2] Public health concerns about e-cigarettes center on their potential appeal to the youth market,[3] lack of scientific evidence regarding their impact on individual and population health,[4] and inconsistent product standards, including variations in nicotine content within and across brands.[5–7] While some US cities have extended public smoking bans to cover e-cigarettes or taken other restrictive measures [8–9], the products remain unregulated at the federal level. Globally, there is significant variation in how products are treated with some countries including Canada and Australia taking a more restrictive approach. [10] A recent proliferation of e-cigarette marketing—including ads in media where traditional tobacco advertising has long been prohibited, such as television [1]—likely plays a key role in the exponential growth of the products’ popularity. With some exceptions,[11–12] reports of e-cigarette marketing to-date have been mainly anecdotal; surveillance and tracking of the quantity and content of such marketing is much-needed.
The goal of this Industry Watch is to examine and systematically track marketing expenditures for e-cigarette products. The data source was Kantar Media, which tracks US advertising across media channels including television, print, radio, and Internet, and then estimates expenditures based on market rate data. Kantar organizes advertising expenditures data by both product name and category. Because e-cigarettes are referenced in a variety of ways in the Kantar system, we searched product names for a series of more than 100 keywords identified through monitoring online e-cigarette forums and social media, and brand-level sales data. Keywords encompassed generic terms for e-cigarettes and component parts (e.g. e-cig, ecig, e-juice), slang terms (e.g. vape), and numerous brand names. For Kantar product categories that we deemed highly likely to include e-cigarette products, such as “smoking materials and accessories,” we manually reviewed each product for relevance. Expenditures were available from the beginning of 2008 and were broken down by media channel.
After grouping by brand (e.g. Njoy includes Njoy King) and combining in the case of duplicates, we identified 131 unique brands for which Kantar captured advertising expenditures between January 1, 2008 and June 30, 2012. Most were e-cigarette brands (e.g., Blu), although we also captured some retailer brands (e.g., Vaporium). We found that promotional spending was minimal through mid-2010, and has since rapidly increased, reaching $12 million in 2011 and $22 million in 2012 (figure 1). For the second quarter of 2013 alone, expenditures reached $28 million, over eight times more than spending in the second quarter of 2012. Print was the dominant channel, followed by television. Over 60% of 2013 expenditures were for Blu (figure 2). The remaining top five most promoted brands we identified in 2013 were Njoy, Fin, Mistic, and 21st Century Smoke. Television comprised the majority of 2013 expenditures for Njoy and 21st Century Smoke, while print media comprised the majority of expenditures for the other top brands. Mistic was the only top brand without television campaign expenditures.
Figure 1.
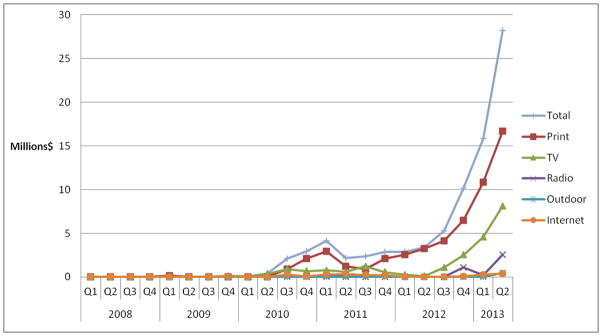
Quarterly promotional expenditures by media, 2008–2013
Figure 2.
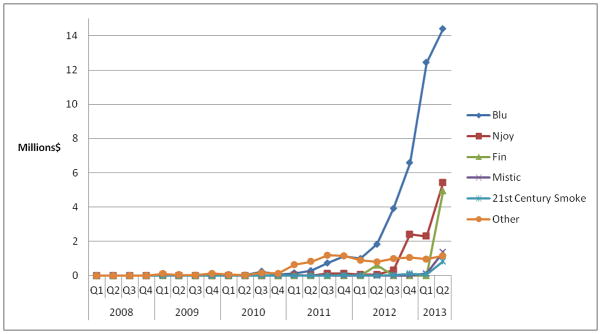
Quarterly spending for top-promoted brands, 2008–2013
Our analysis indicates that e-cigarette promotional spending is rapidly increasing, with expenditures for the first and second quarters of 2013 already representing more than double the expenditures for year 2012. Levels of television advertising are likely to further increase as tobacco companies acquire an increasing share of the market, with Vuse (R.J. Reynolds) and MarkTen (Phillip Morris) recently launching television campaigns.[13,14] Evidence suggests that e-cigarette marketers are borrowing from the tobacco industry playbook,[15,16] a matter of public health concern as the products might be marketed in a way that ultimately promotes smoking, especially in the context of the increasing tobacco industry market share.[12] This research is limited by the fact that Kantar’s media audit is not comprehensive; thus these figures likely underestimate the true extent of e-cigarette advertising. Furthermore, media channels like Internet promotion are relatively cheap but may nonetheless be associated with substantial exposure. Social media promotion and sponsored events—not included in this analysis—may also represent an important component of e-cigarette promotional strategy. The exponential increase in e-cigarette marketing may carry public health risks due to its potential to increase youth awareness and use of the products in the context of current uncertainty about their long-term health impact. Continued surveillance and monitoring of e-cigarette marketing expenditures is needed to guide product regulation and policy. In addition, further research on the content of e-cigarette promotional messages across different media platforms is urgently needed in order to assess the implied and explicit claims made and how these messages may affect consumers’ attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors.
Acknowledgments
Funding statement: This work was supported by the National Cancer Institute grant number U01CA154254 and by the National Institutes of Health grant number P50-CA-179546-01. The funding bodies did not play any role in study design; in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the article for publication.
The authors would like to thank Anne Buffington for her excellent research assistance.
Footnotes
The opinions expressed here are those of the authors, and do not necessarily reflect those of the sponsors.
Competing Interests Statement: None of the authors have any competing interests to disclose.
Contributorship Statement:
Conceived and designed the study: SE, JH, RK, LV; Acquired and managed the data: RK, SE; Analyzed the data: RK, JH, SE; Wrote the paper: RK, JH, LV; Supervised the research: SE
References
- 1.Elliott SE. Cigarette Makers’ Ads Echo Tobacco’s Heyday. [accessed September 2013];N Y Times. 2013 Aug 29; at http://www.nytimes.com/2013/08/30/business/media/e-cigarette-makers-ads-echo-tobaccos-heyday.html.
- 2.Bruell A. E-Cigarette Brands Spend More on Advertising and Keep Careful Watch on Health Claims. Advert Age. 2012 Jan 2;:29. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. E-cigarette use more than doubles among U.S. middle and high school students from 2011–2012. MMWR. 2013;62(35):729. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Etter J-F, Bullen C, Flouris AD, et al. Electronic nicotine delivery systems: a research agenda. Tob Control. 2011;20:243–248. doi: 10.1136/tc.2010.042168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cameron JM, Howell DN, White JR, et al. Variable and potentially fatal amounts of nicotine in e-cigarette nicotine solutions. Tob Control. 2014;23:77–78. doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2012-050604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Goniewicz ML, Kuma T, Gawron M, Knysak J, Kosmider L. Nicotine levels in electronic cigarettes. Nicotine & Tobacco Research. 2013;15(1):158–166. doi: 10.1093/ntr/nts103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Goniewicz ML, Hajek P, McRobbie H. Nicotine content of electronic cigarettes, its release in vapour and its consistency across batches: regulatory implications. Addiction. 2014 doi: 10.1111/add.12410. n/a–n/a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gregory A. New York Council Votes to Ban Foam Food Containers and to Curb E-Cigarette Smoking. [accessed March 2014];NY Times. 2013 Dec 19; at http://www.nytimes.com/2013/12/20/nyregion/new-york-council-votes-to-ban-foam-food-containers-and-to-curb-e-cigarette-smoking.html.
- 9.Zahniser D. Los Angeles approves sweeping e-cigarette restrictions. [accessed March 2014];LA Times. 2014 Mar 4; at http://www.latimes.com/local/lanow/la-me-ln-los-angeles-ecigarettes-ban-20140304,0,4359853.story#axzz2wLeu5WQ3.
- 10.Saitta D, Ferro GA, Polosa R. Achieving appropriate regulations for electronic cigarettes. Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease. 2014;5(2):50–61. doi: 10.1177/2040622314521271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Andrade MD, Hastings G, Angus K, Dixon D, Purves R. Cancer Research UK. University of Stirling; 2013. [accessed March 2014]. The marketing of electronic cigarettes in the UK. Retrieved from https://dspace.stir.ac.uk/bitstream/1893/17889/1/deAndradeetale-cigsreport.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Andrade MD, Hastings G, Angus K. Promotion of electronic cigarettes: Tobacco marketing reinvented? BMJ. 2013;347:f7473. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f7473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chudgar S. Altria to Launch MarkTen E-Cigarette in Indiana. [accessed October 2013];Advert Age. 2013 Jun 11; at http://adage.com/article/news/altria-launches-markten-e-cigarette-indiana/242043/
- 14.Sebastian M. See the First Vuse E-Cig Commercial, Reynolds American’s Return to TV. [accessed October 2013];AdAge Media News. 2013 Aug 28; at http://adage.com/article/media/watch-reynolds-american-s-e-cig-commercial/243856/
- 15.Associated Press. Old Tobacco Playbook Gets New Use by E-cigarettes. [accessed September 2013];Patriot News – PennLivecom. 2013 Aug 3; at http://www.pennlive.com/midstate/index.ssf/2013/08/electronic_cigarettes_marketin.html.
- 16.Campaign for Tobacco-free Kids. 7 Ways E-cigarette Companies are Copying Big Tobacco’s Playbook. [accessed January 2014];Tob Unfiltered Blog. 2013 Oct 2; at http://www.tobaccofreekids.org/tobacco_unfiltered/post/2013_10_02_ecigarettes.


