Abstract
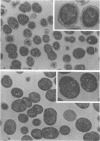
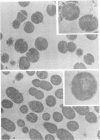
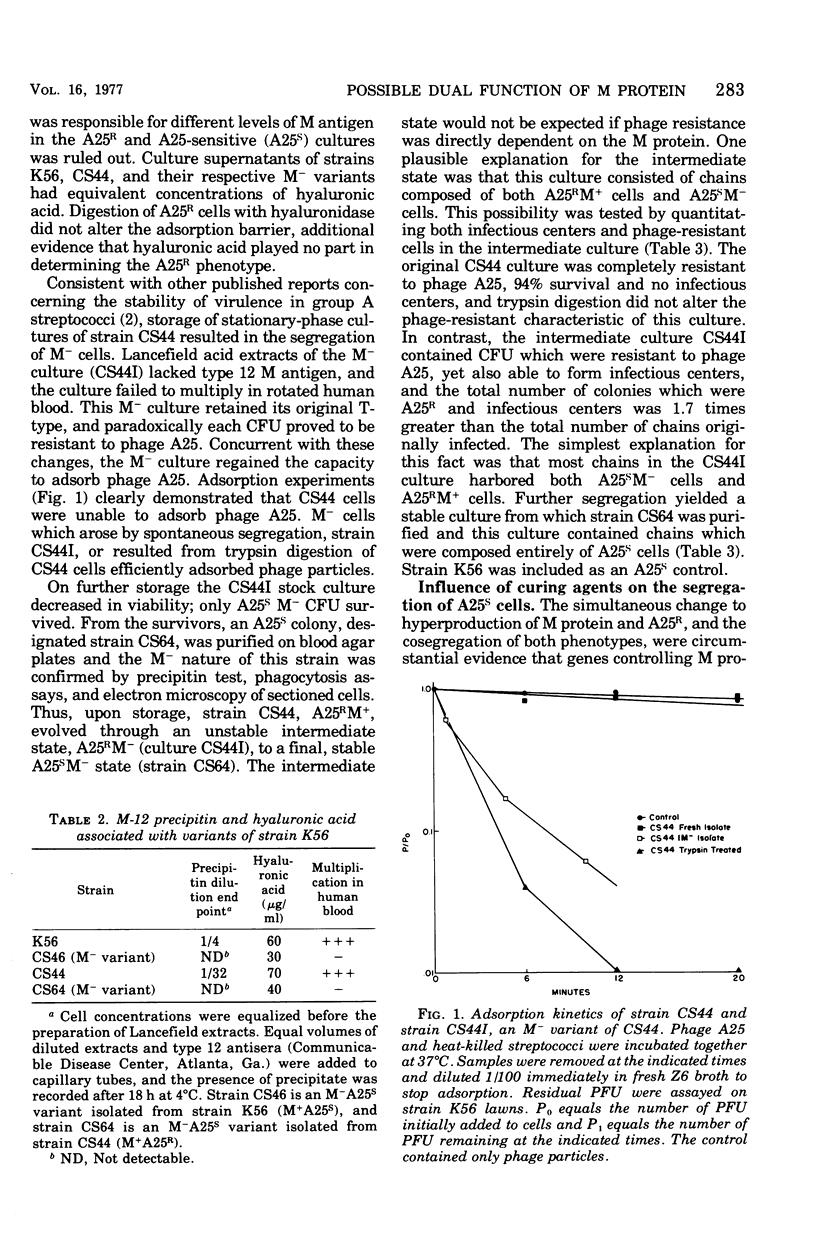
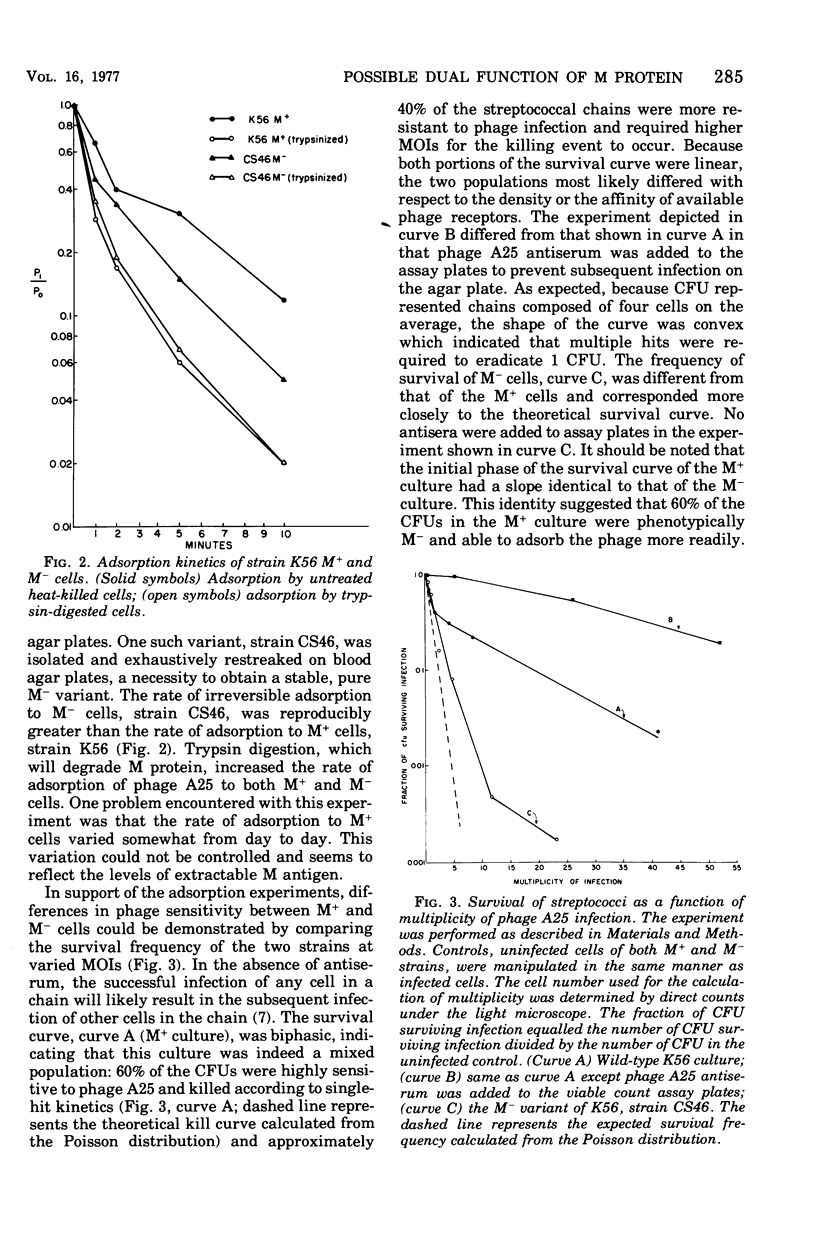
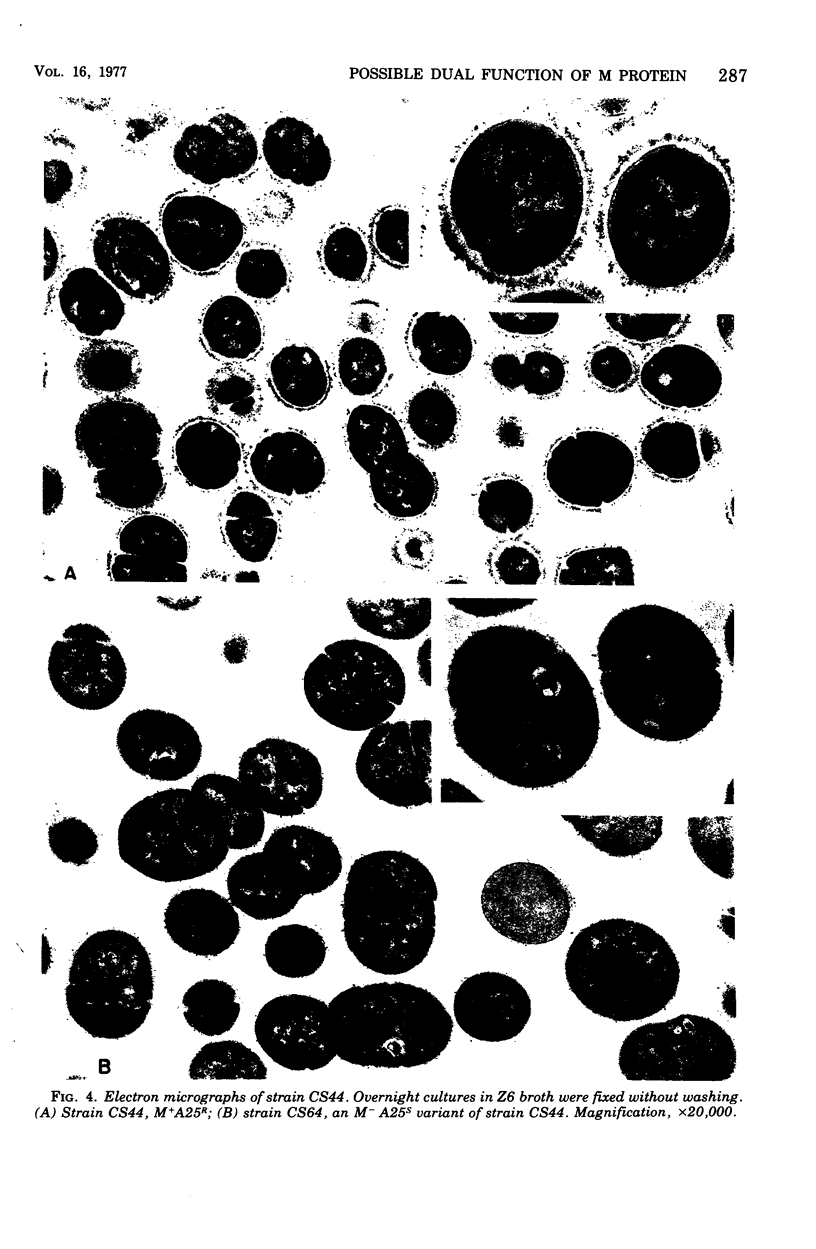
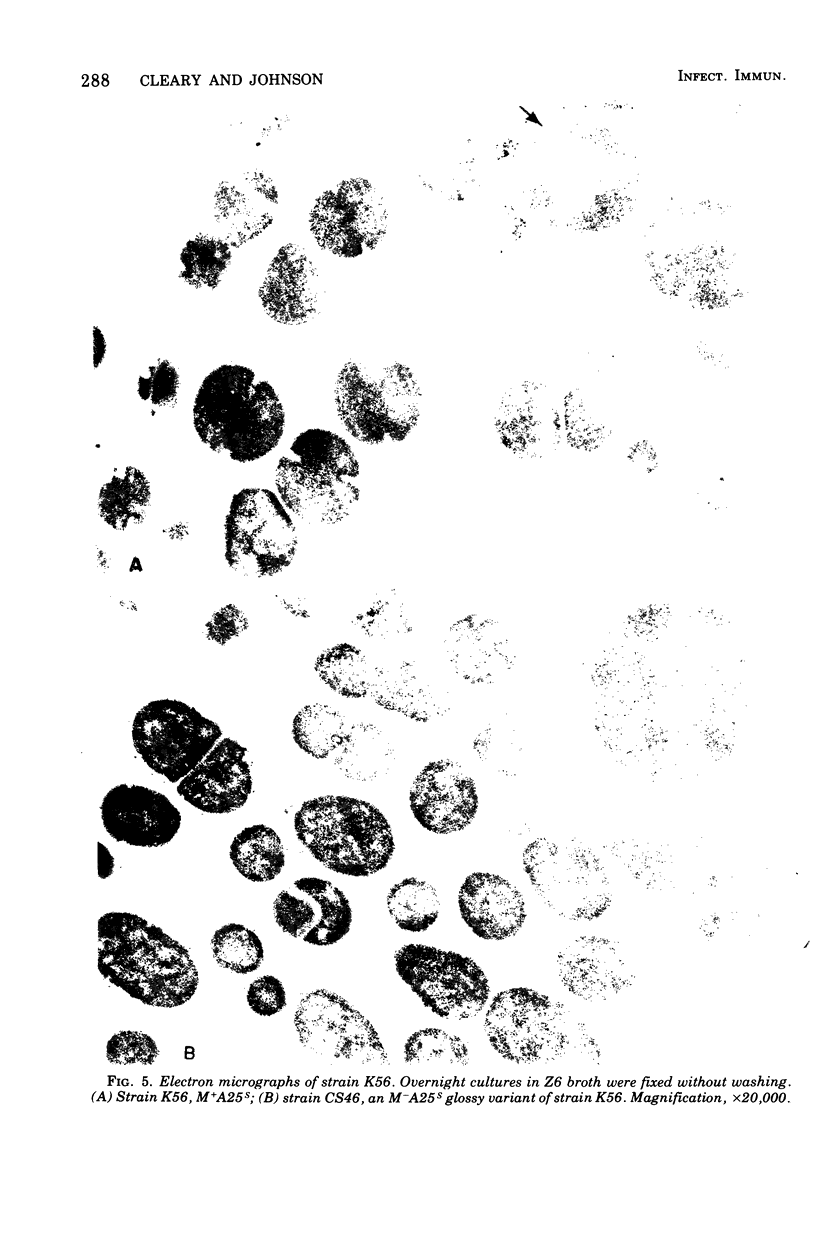
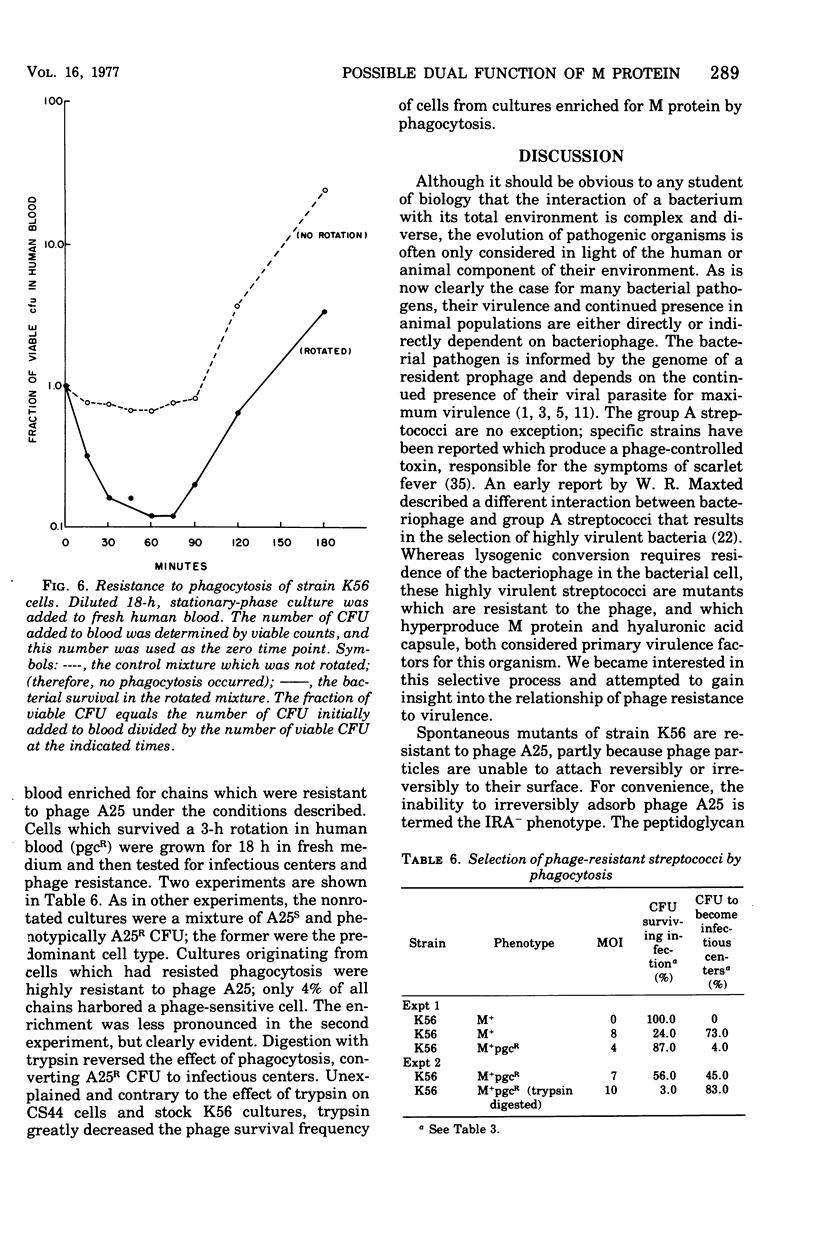
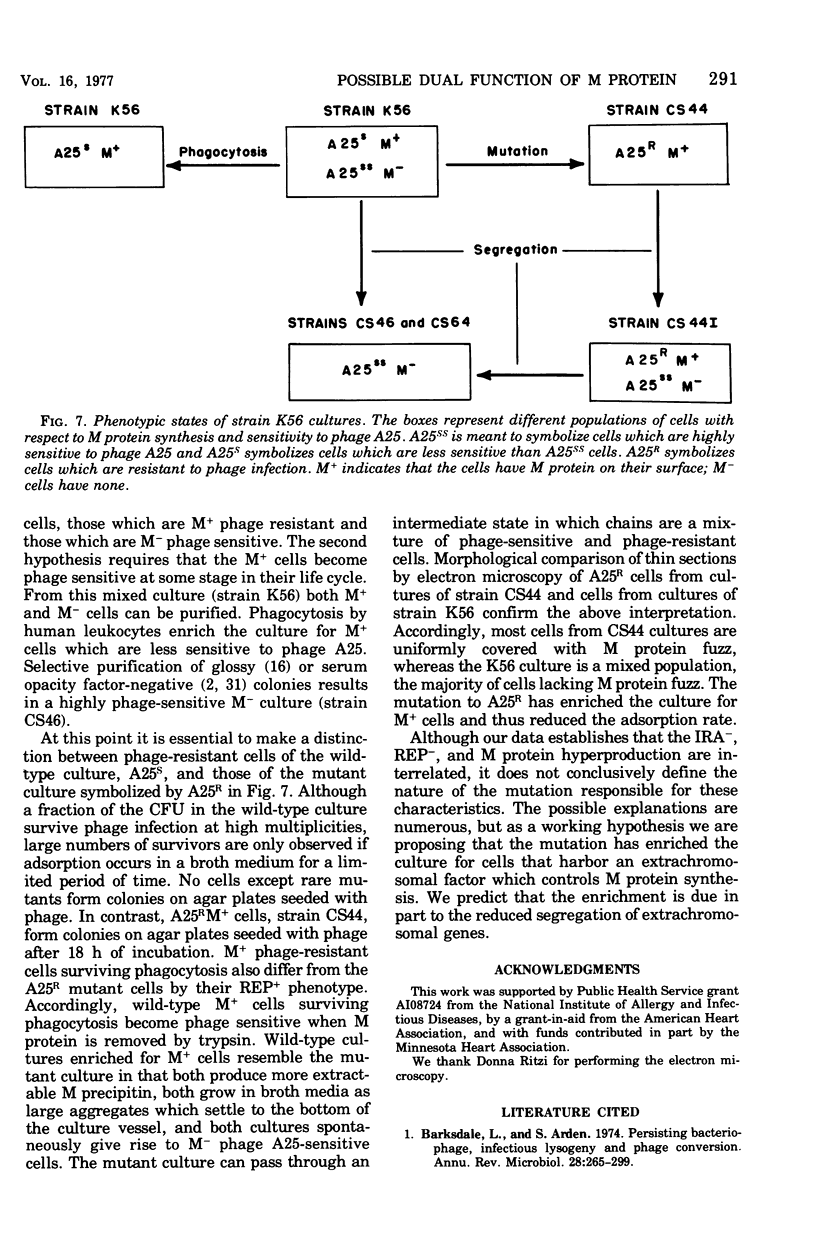
Spontaneous phage A25-resistant (A25R) mutants of group A streptococci, strain K56, were isolated. The mutant cultures were unable to adsorb phage particles and hyperproduced M protein. Trypsin-digested A25R cells regained the ability to adsorb phage particles, but failed to become infectious centers. This failure indicated that the mutation created a double barrier to phage growth: (i) receptors were masked by M protein; (ii) irreversibly adsorbed phage were unable to multiply. Spontaneous variants of one A25R mutant, shown to be M negative (M−) by electron microscopy, serological tests, and sensitivity to phagocytosis, rapidly adsorbed phage and were able to become infectious centers. Therefore, it was concluded that the mutant phenotype, A25R, arose by a single mutation and genes coding for this trait and M protein synthesis were either genetically linked, controlled by a common gene or were biochemically interdependent. The A25R phenotype was unstable and, as expected for plasmid-coded properties, acridine orange induced segregation of this phenotype. The parental M+, A25-sensitive (A25S) cultures proved to be a mixed population. Infection at various multiplicities indicated that this culture was composed of phage A25S cells and cells more resistant to infection. Morphological comparison of thin sections of A25R and A25S cells by electron microscopy demonstrated striking differences. The A25R culture was composed entirely of cells uniformly covered with M protein, whereas the A25SM+ wild-type culture was a mixed population, the majority of cells devoid of M protein. Phagocytosis by human blood enriched the culture for the latter cell type, suggesting that differences in phage sensitivity in the wild-type culture were also determined by the presence or absence of M protein. Thus M protein can serve a dual function for the streptococcal cell by allowing it to avoid infection by bacteriophage and ingestion by human leukocytes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barksdale L., Arden S. B. Persisting bacteriophage infections, lysogeny, and phage conversions. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):265–299. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary P. P., Johnson Z., Wannamaker L. Genetic instability of M protein and serum opacity factor of group A streptocci: evidence suggesting extrachromosomal control. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):109–118. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.109-118.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: mode of action and structure. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):54–85. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.54-85.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T., Iwaya M., Larison L. L. The rep mutation. II. Its effect on Escherichia coli and on the replication of bacteriophage phi X174. Virology. 1972 Aug;49(2):486–496. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90500-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EKSTEDT R. D., STOLLERMAN G. H. Factors affecting the chain length of group A streptococci. II. Quantative M-anti-M relationships in the long chain test. J Exp Med. 1960 Oct 1;112:687–698. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.4.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund M. W., Poysky F. T., Meyers J. A., Pelroy G. A. Interspecies conversion of Clostridium botulinum type C to Clostridium novyi type A by bacteriophage. Science. 1974 Nov 1;186(4162):456–458. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4162.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX E. N., KRAMPITZ L. O. Studies on the biosynthesis of the M-protein of group A hemolytic streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1956 Apr;71(4):454–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.4.454-461.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Gotschlich E. C., Siviglia G., Zabriskie J. B. Streptococcal M protein extracted by nonionic detergent. I. Properties of the antiphagocytic and type-specific molecules. J Exp Med. 1976 Jul 1;144(1):32–53. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N. M proteins of group A streptococci. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):57–86. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.57-86.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend P. L., Slade M. D. Characteristics of group A streptococcal bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):148–154. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.148-154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Iida H. Conversion of toxigenicity in Clostridium botulinum type C. Jpn J Microbiol. 1970 Jan;14(1):87–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1970.tb00495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANTOR F. S. FIBRINOGEN PRECIPITATION BY STREPTOCOCCAL M PROTEIN. I. IDENTITY OF THE REACTANTS, AND STOICHIOMETRY OF THE REACTION. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:849–859. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAUSE R. M. SYMPOSIUM ON RELATIONSHIP OF STRUCTURE OF MICROORGANISMS TO THEIR IMMUNOLOGICAL PROPERTIES. IV. ANTIGENIC AND BIOCHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCAL CELL WALLS. Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Dec;27:369–380. doi: 10.1128/br.27.4.369-380.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU T. Y., NEUMANN N. P., ELLIOTT S. D., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. Chemical properties of streptococcal proteinase and its zymogen. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:251–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A. Bacteriophage receptors. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:205–241. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.001225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAXTED W. R. Enhancement of streptococcal bacteriophage lysis by hyaluronidase. Nature. 1952 Dec 13;170(4337):1020–1021. doi: 10.1038/1701020b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAXTED W. R. The influence of bacteriophage on Streptococcus pyogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Jun;12(3):484–495. doi: 10.1099/00221287-12-3-484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström K., Forsgren A. Effect of protein A on adsorption of bacteriophages to Staphylococcus aureus. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):198–202. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.198-202.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotta J., Krause R. M., Lancefield R. C., Everly W., Lackland H. New approaches for the laboratory recognition of M types of group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1971 Nov 1;134(5):1298–1315. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.5.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Hsu K. C., Gotschlich E. C. Electron microscopic studies on streptococci. I. M antigen. J Exp Med. 1969 Nov 1;130(5):1063–1091. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.5.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. E. Laboratory diagnosis of streptococcal infections. Bull World Health Organ. 1958;19(1):153–176. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannamaker L. W., Almquist S., Skjold S. Intergroup phage reactions and transduction between group C and group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1973 Jun 1;137(6):1338–1353. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.6.1338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdowson J. P., Maxted W. R., Grant D. L. The production of opacity in serum by group A streptococci and its relationship withthe presence of M antigen. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Jun;61(3):343–353. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-3-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A., Barzilai N. Isolation and haracterization nonconverting mutants of bacteriophage epsilon 34. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):937–939. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.937-939.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZINDER N. D. Lysogenization and superinfection immunity in Salmonella. Virology. 1958 Apr;5(2):291–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]