Abstract
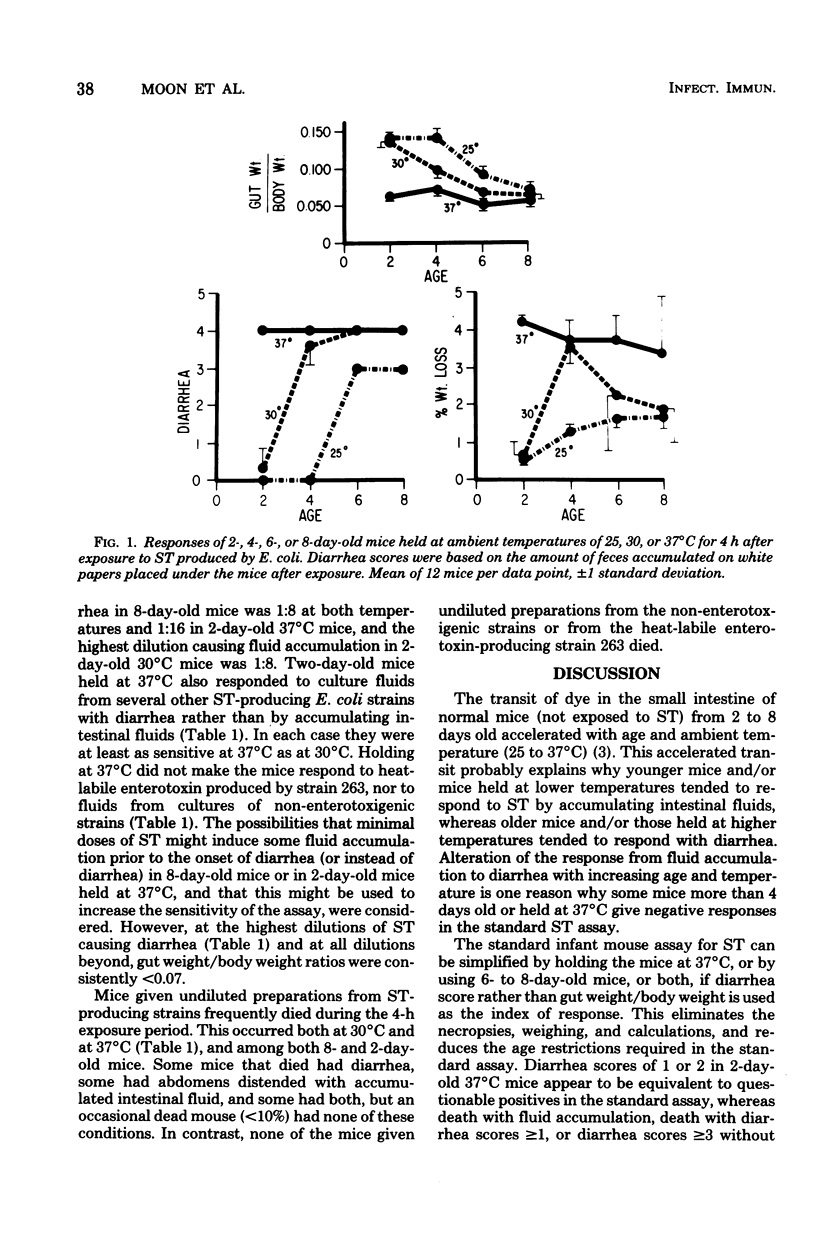
The response of infant mice to heat-stable enterotoxin from Escherichia coli was affected by the age of the mice (2, 4, 6, and 8 days) and by the ambient temperature (25, 30, and 37 degrees C) after exposure to the enterotoxin. The younger mice and/or mice held at lower temperatures tended to accumulate intestinal fluid (high gut weight/body weight ratios), but older mice and/or mice held at higher temperatures tended to respond with diarrhea and low gut weight/body weight ratios. The standard infant mouse assay forheat-stable E. coli enterotoxin can be simplified, without loss of sensitivity or reliability, by holding the mice at 37 degrees C after exposure and using diarrhea as the index of response. Diarrhea can be detected easily by incorporating dye in the inocula and (at the end of the assay) checking for dye mixed with feces on the rear quarters of the mice or on a sheet of white paper placed under them during incubation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Suckling mouse model for detection of heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin: characteristics of the model. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):95–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.95-99.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Skartvedt S. M. Etiologic diagnosis of diarrheal disease of calves: frequency and methods for detecting enterotoxin and K99 antigen production by Escherichia cola. Am J Vet Res. 1976 Sep;37(9):1025–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp S. C., Moon H. W., Lyon N. C. Heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin production in vivo. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):240–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.240-244.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


