Abstract
Relapse of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is triggered by stem cells with a reconstituting capacity similar to that of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and CML stem cells are a source of resistance in drug therapy with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). Ecotropic viral integration site 1 (EVI1), a key transcription factor in HSC regulation, is known to predict poor outcomes in myeloid malignancies, however, incapability of prospective isolation of EVI1-high leukemic cells precludes the functional evaluation of intraindividual EVI1-high cells. Introduction of CML into Evi1-internal ribosomal entry site (IRES)-green fluorescent protein (GFP) knock-in mice, a versatile HSC-reporter strain, enables us to separate Evi1-high CML cells from the individual. Evi1-IRES-GFP allele models of CML in chronic phase (CML-CP), by retroviral overexpression of BCR–ABL and by crossing BCR–ABL transgenic mice, revealed that Evi1 is predominantly enriched in the stem cell fraction and associated with an enhanced proliferative as well as a leukemia-initiating capacity and that Evi1-high CML-CP cells exhibit resistance to TKIs. Overexpressing BCR–ABL and NUP98–HOXA9 in Evi1-IRES-GFP knock-in mice to model CML in blast crisis (CML-BC), in which Evi1-high cells turned to be a major population as opposed to a minor population in CML-CP models, showed that Evi1-high CML-BC cells have a greater potential to recapitulate the disease and appear resistant to TKIs. Furthermore, given that Evi1 heterozygosity ameliorates CML-CP and CML-BC development and that the combination of Evi1 and BCR–ABL causes acute myeloid leukemia resembling CML-BC, Evi1 could regulate CML development as a potent driver. In addition, in human CML-CP cases, we show that EVI1 is highly expressed in stem cell-enriched CD34+CD38–CD90+ fraction at single-cell level. This is the first report to clarify directly that Evi1-high leukemic cells themselves possess the superior potential to Evi1-low cells in oncogenic self-renewal, which highlights the role of Evi1 as a valuable and a functional marker of CML stem cells.
Introduction
As multipotent hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) reside at the apex of hematopoietic hierarchy, leukemic progeny from leukemic stem cells (LSCs) shape the bulk of the tumor with intact capacity of LSCs to self-renew. Physiological and biological similarities of LSCs to those of HSCs are supposed to be the main causes of the difficulties in establishment of LSC-targeted therapy.1,2
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a myeloproliferative disorder by BCR–ABL, which can transform HSCs into LSCs with a limitless capacity for self-renewal, whereas LSCs of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) are mainly composed of more differentiated progenitor cells.3, 4, 5 The relentless march of CML from chronic phase (CP) to blast crisis (BC) phase can result in fatal survival outcomes.6 Despite substantial prognostic improvement of CML by a specific debulking of tumor burden with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) targeting ABL kinase, imatinib-treated CP patients can relapse and progress to BC because of the remnant CML stem cells.7, 8, 9, 10 Although recent findings have started to unveil the biological nature of CML stem cells,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 further elucidation of the mechanisms controlling the self-renewal of these cells is still needed.
Defects in the molecular components that control hematopoiesis severely perturb normal development, one of which is ecotropic viral integration site 1 (Evi1), a predictor of poor outcomes in myeloid malignancies such as AML, myelodysplastic syndrome and CML-BC.17, 18, 19, 20, 21 In normal hematopoiesis, Evi1 is restricted to embryonic and adult HSCs22 and cumulative data have placed Evi1 as one of ‘stemness' genes.23, 24, 25 The recent gene expression profiling of bulk samples or selective populations have shown that EVI1 is one of LSC signature genes in AML and that stem cell-enriched CML CD34+ cells have high EVI1, underlining the relevance of EVI1 and LSCs.26,27 As EVI1 is an oncogenic transcription factor,28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34 prospective isolation of EVI1-high leukemic cells from clinical patients is unfeasible, so is the functional assessment of EVI1-high cells compared with EVI1-low cells intraindividually.
In this study, we aimed to cover in depth the regulation of CML stem cells by Evi1. Our single-cell analysis of primitive or differentiated subsets from primary CML-CP samples show that EVI1 is highly expressed in stem cell-enriched CD34+CD38–CD90+ cells. Furthermore, we have established multiple CML mice model with Evi1-Internal Ribosomal Entry Site (IRES)-green fluorescent protein (GFP) knock-in allele, in which Evi1-high CML cells can be separated directly and prospectively using a single GFP35 to evaluate their capacity for leukemia development. Evi1-IRES-GFP allele leukemia animals provide us for the first time with a more definite hierarchical map in CML hematopoiesis and, through loss- and gain-of-function studies we could evaluate the functional role of Evi1 in CML. This study could also determine whether Evi1-high CML cells could have resistance to TKI therapy.
Results
EVI1 is highly expressed in human CML-CP stem cells
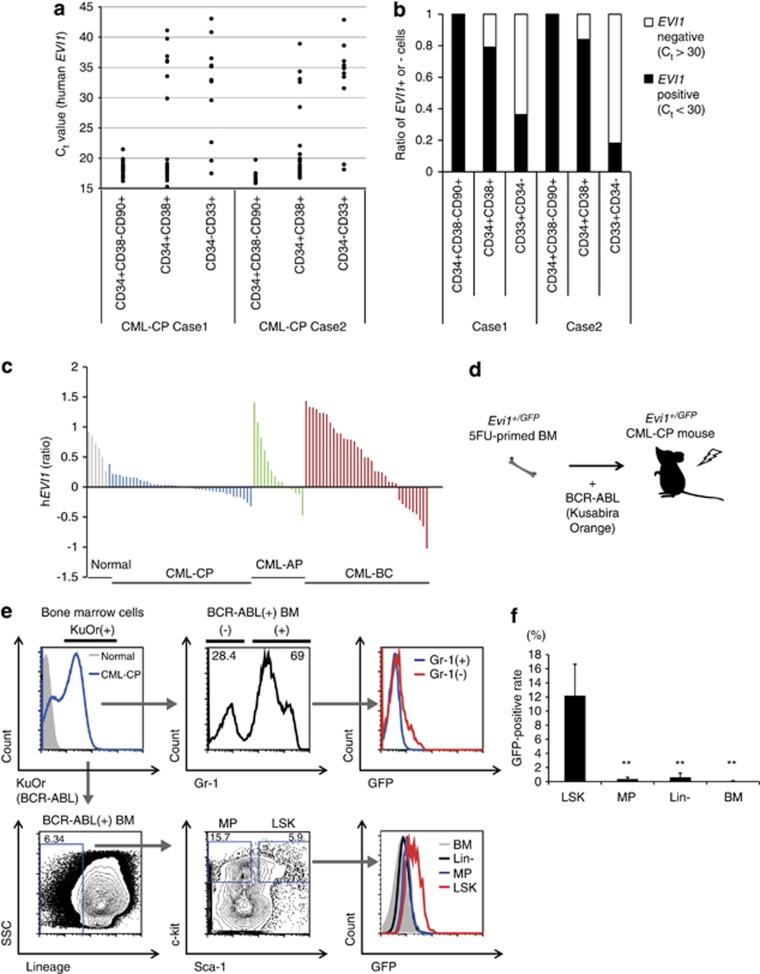
To ask whether CML-CP stem cells have high EVI1, we performed gene expression analysis in single primary CML-CP cells prospectively isolated from bone marrow (BM) samples of two newly diagnosed CML-CP patients (Supplementary Table S1). A total of 120 single cells (21 and 16 stem (CD34+CD38–CD90+) cells, 31 and 25 progenitor (CD34+CD38+) cells, 14 and 13 differentiated (CD34–CD33+) cells in cases 1 and 2, respectively) were subjected to single-cell gene expression analysis of housekeeping genes (beta-actin and gapdh), BCR–ABL and EVI1 (Supplementary Figure S1). As CML-CP cells could be distinguished by their positive expression of BCR–ABL from normal BM cells, it was revealed that, among CML-CP cells, CD34+CD38–CD90+ cells showed lower Ct values of EVI1 than CD34+CD38+ cells or CD34–CD33+ cells intraindividually, implying the highest EVI1 in CML-CP stem cells (Figure 1a). When Ct=30 was set as a threshold of EVI1 positivity, all CD34+CD38–CD90+ cells were EVI1 positive (Ct<30; n=21/21 for case 1, n=12/12 for case 2), while one-fifth of CD34+CD38+ cells (n=5/24 (20.8%), n=4/25 (16%), respectively) or three to four-fifths of CD34–CD33+ cells (n=7/11 (63.8%), n=9/11 (81.8%), respectively) were EVI1 negative (Ct>30) (Figure 1b). Microarray data from Radich et al.1 revealed that EVI1 in the whole BM is upregulated in advanced phase (accelerated phase (AP) and BC) of CML compared with CML-CP, possibly implying the limited EVI1 in CML-CP stem cells and the extended EVI1 in BM of CML-AP and CML-BC (Figure 1c). These clinical data indicate a potential role of EVI1 as a valuable marker of CML-CP stem cells.
Figure 1.
Both human and mouse CML-CP stem cells show high Evi1 expression. (a) BM cells from two CML-CP patients were single-cell sorted into CD34+CD38–CD90+ (n=21 for case 1, n=12 for case 2), CD34+CD38+ (n=24 for case 1, n=25 for case 2) and CD34–CD33+ fractions (n=11 for both cases) and EVI1 was evaluated by quantitative real-time–PCR. Ct value was shown. (b) Ratio of EVI1-positive or -negative cells in each fraction from two CML cases. Ct=30 was set as a threshold value of EVI1 positivity. (c) Relative EVI1 expression found to be upreguated in BM samples from advanced phase (AP, BC) disease compared with those from CP of CML. Microarray data from Radich et al.1 (n=6 for normal samples, n=42 for CML-CP, n=15 for CML-AP and n=36 for CML-BC). (d) Experimental design of Evi1-reporter CML-CP mice. 5FU-primed Evi1+/GFP BM cells with retroviral BCR–ABL were transplanted into lethally irradiated recipient mice. (e) Representative FCM data of BM cells from Evi1-reporter CML-CP mice. In BCR–ABL (KuOr)-positive BM cells, Gr-1– CML cells had GFP-positive population, while almost Gr-1+ CML cells showed low GFP intensity (upper). When BCR–ABL (KuOr)-positive BM cells were analyzed with lineage markers, Sca-1 and c-kit, LSK population showed the highest GFP intensity (lower). (f) GFP-positive rates of stem/progenitor fractions and BM cells in Evi1-reporter CML-CP mice were shown (n=5). Data are mean±s.d. **P<0.001.
Evi1-high CML-CP cells have LSK phenotype in murine CML model
To elucidate the in vivo expression pattern of Evi1 in CML-CP, 5-fluorouracil (5FU)-primed BM cells from heterozygous Evi1-IRES-GFP (Evi1+/GFP) knock-in mice were retrovirally transduced with BCR–ABL (detected with Kusabira Orange (KuOr) fluorescent protein) and injected into lethally irradiated recipient mice to generate ‘Evi1-reporter' CML-CP mice (Figure 1d). Within BCR–ABL-positive (KuOr+) BM cells from moribund Evi1-reporter CML-CP mice (3-4 weeks after transplantation), the flow cytometry (FCM) analysis showed that immature (Gr-1-negative) CML cells have a higher GFP-positive rate than mature (Gr-1-positive) CML cells. GFP-positive rates of sub-populations in these mice revealed that Lineage-Sca-1+c-kit+ (LSK) fraction is the highest compared with myeloid progenitor (MP; Lineage-Sca-1-c-kit+) fraction, Lineage– (Lin–) fraction and whole BM cells (Figures 1e and f,Supplementary Figure S2a). Evi1-high KuOr+ cells comprised only 0.065% in the BM, were mostly Gr-1-, and about 90% of these cells showed LSK immunophenotype (Supplementary Figure S2b). The enlarged spleens from these mice also contained Evi1-high cells, which were the most abundant in LSK (Supplementary Figure S2c). Collectively, our data from human CML-CP samples and CML-CP mice revealed that Evi1 is highly expressed in the stem cell fraction.
Evi1-high CML-CP LSK cells have a higher proliferative potential
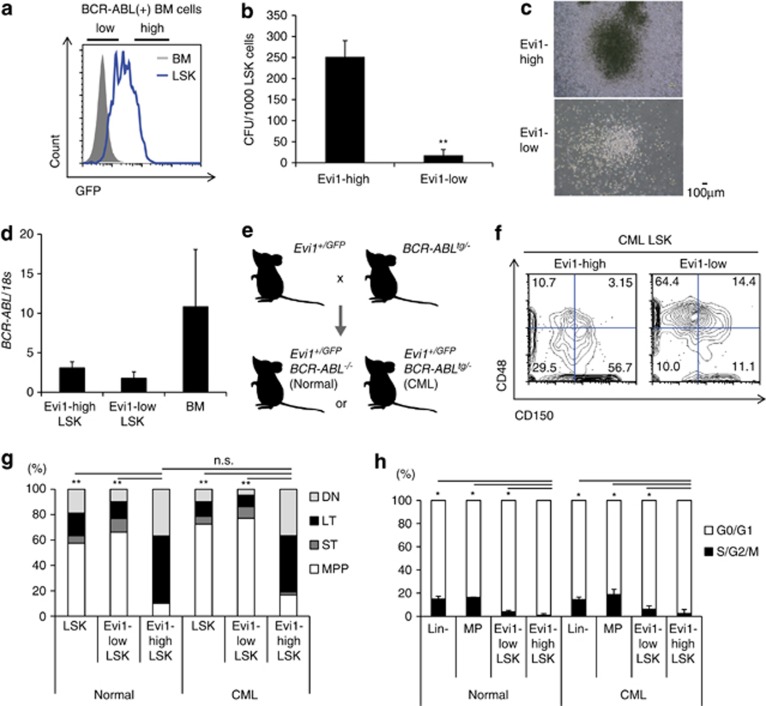
As LSK cells showed a heterogeneous pattern of Evi1 in BM of Evi1-reporter CML-CP mice, we sorted the Evi1-high or Evi1-low fractions from KuOr+ LSK cells (Figure 2a). Evi1-high LSK cells showed a higher colony-forming potential in vitro, the sizes of which were larger than those from Evi1-low cells (Figures 2b and c). Co-culture of LSK cells with OP-9 cells revealed a higher clonogenic potential of Evi1-high LSK cells (Supplementary Figure S2e). Transcripts of BCR–ABL were comparable between Evi1-high and Evi1-low LSK populations (Figure 2d), suggesting little relevance of BCR–ABL to the enhanced proliferation of Evi1-high CML cells. These results suggest that Evi1-high CML-CP LSK cells have the proliferative advantage.
Figure 2.
Evi1-high CML-CP LSK cells possess a higher clonogenic potential. (a) FCM panel of BM and LSK cells in Evi1-reporter CML-CP mice. The gate of Evi1 (GFP)-high fraction for separation was depicted. (b) Semisolid colony assay was done with 1000 Evi1-high or Evi1-low CML-CP LSK cells (n=7). (c) Images of colonies derived from Evi1-high (upper) or Evi1-low (lower) CML-CP LSK cells. (d) BCR–ABL mRNA expression was measured for each population from CML-CP mice (n=6). (e) Schematic abstract of Evi1-reporter CML transgenic mice. Evi1+/GFP BCR–ABLtg/− mice were used as CML model and Evi1+/GFP BCR–ABL−/− as normal controls. (f) Representative FCM data from Evi1-reporter CML transgenic mice. Within CML LSK cells, Evi1-high cells showed greater proportion of CD150+CD48- immunophenotype. (g) Immunophenotypic analyses of LSK cells with CD150 and CD48. Both Evi1-high normal and CML LSK cells mainly comprises CD150+CD48- (long-term HSC; LT) and CD150-CD48- (double negative; DN) fraction. CD150+CD48+ (short-term HSC; ST) and CD150-CD48+ (multipotent progenitor; MPP) fractions were commonly seen in Evi1-low LSK cells (n=7 mice per group). The differences between the proportions of LT in LSK cells were statistically evaluated. (h) Cell cycle status of each stem or progenitor fraction from normal or CML mice. Hoechst 33342 was measured by FCM (normal; n=3, CML; n=4). Data are mean±s.d. *P<0.01, **P<0.001, n.s., not significant.
Evi1-high CML LSK cells have SLAM LSK marker profile with CML-initiating potential and TKI resistance
Generating primary CML-CP mice by BCR–ABL retrovirus with irradiated recipients inevitably leads to damaged BM microenvironment and likely overestimation of extramedullary hematopoiesis. To clarify the precise behavior of Evi1-high CML LSK cells in vivo, we crossed Evi1+/GFP mice with p210 BCR–ABL transgenic mice (BCR–ABLtg/−),36 which develop a CML-like disease (Supplementary Figure S3a), to analyze undamaged BM of CML-CP (Figure 2e). Evi1+/GFP BCR–ABLtg/− (CML) mice showed myeloid cell expansion in BM with mild splenomegaly (Supplementary Figures S3b and c) representing a myeloproliferative disorder phenotype of this model. The median survival of Evi1+/GFP BCR–ABLtg/− mice in our experiments was 287 days, consistent with the previous report,36 which revealed that Evi1-IRES-GFP allele had no unforeseen effect on CML development. In addition to the expanded bulk of CML BM cells, Evi1+/GFP BCR–ABLtg/− mice showed an increase in GFP intensity and the number of LSK cells (Supplementary Figures S2a and S3c). Evi1-high cells in the BM of these mice only amounted to 0.05% with negative marker profiles of Gr-1, B220, CD4, CD8, TER-119 and intermediate Mac-1, while almost all Evi1-low cells were Gr-1+Mac-1+. In Lin– cells, the majority of Evi1-high cells resided in Sca-1+c-kit+ fraction, consistent with the profile of a retroviral CML-CP model bearing Evi1+/GFP allele (Supplementary Figure S3d). Strikingly, analysis of CD150/signaling lymphocyte activation molecule (SLAM) markers in LSK cells of Evi1+/GFP BCR–ABLtg/− mice clearly showed that Evi1-high LSK cells had a higher percentage of CD150+CD48– cells, a well-established marker phenotype of long-term stem cells (Figures 2f and g). Evi1-high CML LSK cells were the most in G0/G1 phase (quiescent) in CML setting, similar to the trend of sub-populations from normal Evi1+/GFP mice (Figure 2h). Colony-forming assay showed the advantageous phenotype of Evi1-high CML LSK cells to proliferate in vitro (Supplementary Figure S3e). From these data, Evi1-high Evi1+/GFP BCR–ABLtg/− LSK cells had the most immature immunophenotype.
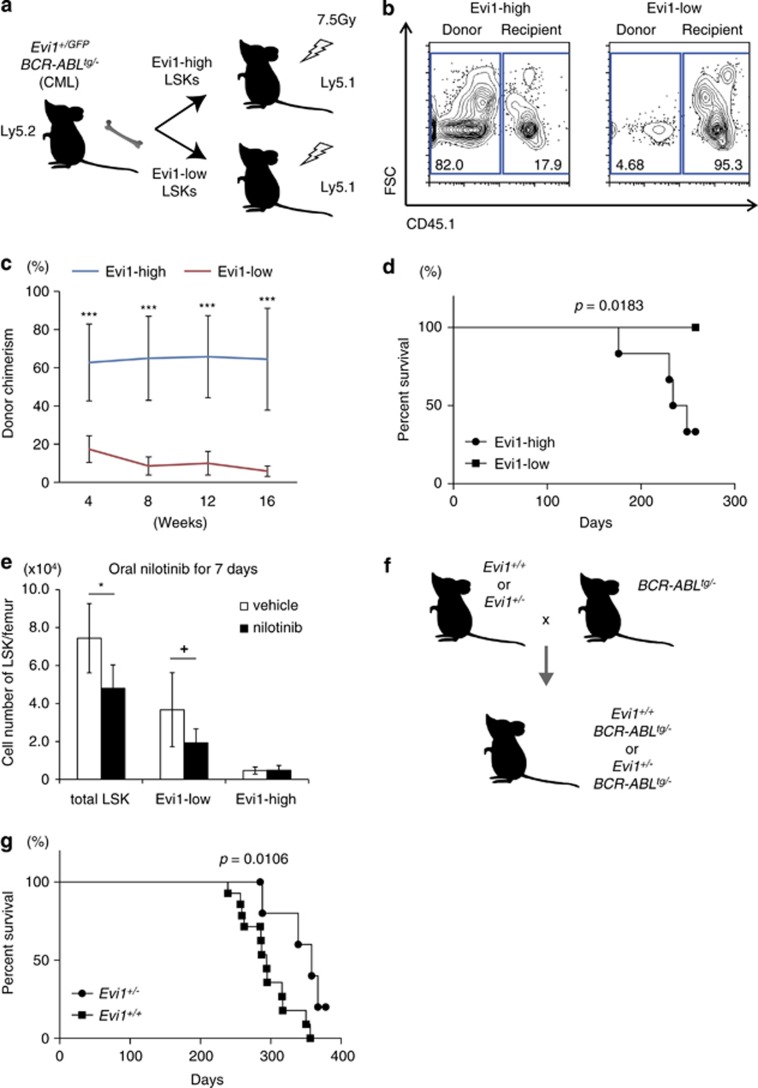
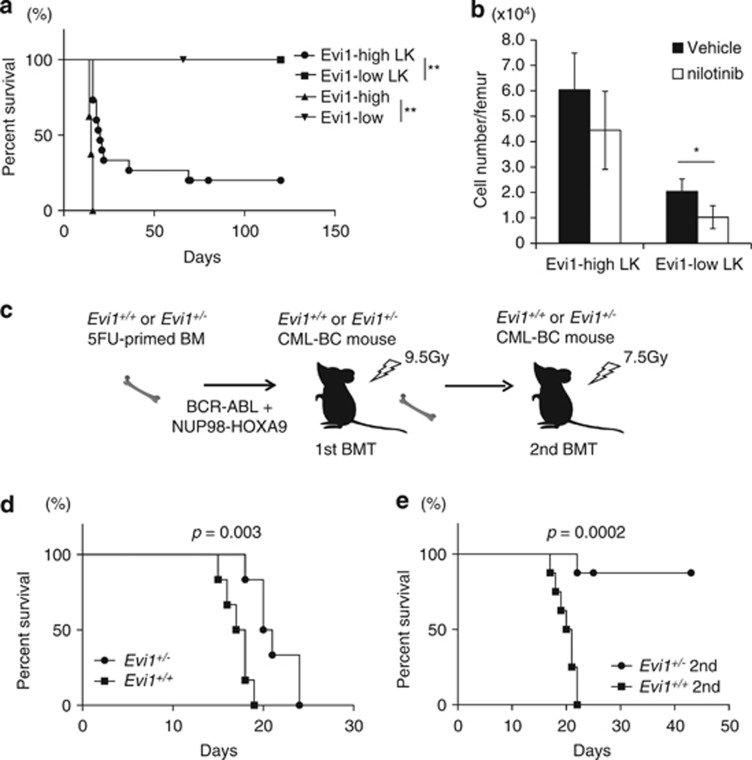
To evaluate the stem cell activity of Evi1-high CML LSK cells in vivo, we next performed BM transplantation (BMT) experiments, in which 5 × 103 Evi1-high or Evi1-low LSK cells were injected intravenously into sublethally irradiated recipients (Figure 3a). FCM analyses of peripheral blood (PB) in recipients revealed the efficient engraftment of donor cells from Evi1-high LSK-transplanted cohort as contrasted with recipients of Evi1-low LSK cells (Figure 3b). The successive engraftment and multilineage reconstitution up to 16 weeks after BMT clearly indicated the higher repopulating capacity of Evi1-high LSK cells (Figure 3c, Supplementary Figure S3f). With such a prolonged engraftment, recipients with Evi1-high LSK cells died of CML (4 deaths per 6 mice), while those with Evi1-low LSK cells had no incidence of CML (0 death per 6 mice), revealing high CML-initiating potential of Evi1-high CML LSK cells (Figure 3d).
Figure 3.
Evi1-high CML-CP cells show CML engraftment capacity and TKI resistance in vivo. (a) Design of non-competitive repopulation assay with Evi1-high or Evi1-low LSK cells from Evi1+/GFP BCR–ABLtg/− mice. (b) Representative FCM data of PB from recipients 16 weeks after BMT were shown to distinguish donor cells (CD45.2+CD45.1–) from recipient cells (CD45.2-CD45.1+). (c) Serial assessments of PB from recipients as for donor chimerism were done every 4 weeks after BMT (n=8 mice per group). (d) Kaplan–Meier plot of the survival of recipient mice transplanted with 5000 Evi1-high or Evi1-low LSK cells from Evi1+/GFP BCR–ABLtg/− mice (n=6 mice per group, P=0.0183). (e) Vehicle or nilotinib (75 mg/kg daily) were administered orally to Evi1+/GFP BCR–ABLtg/− mice for a week just after the CML development and the number of the residual LSK cells in femur were calculated (CML: with vehicle; CML nilo: with nilotinib; n=6 mice per group). (f) Schematic abstract of Evi1 knock-out CML transgenic mice. Evi1+/+ or Evi1+/− mice were crossed with BCR–ABLtg/− mice to generate Evi1+/+ BCR–ABLtg/− or Evi1+/− BCR–ABLtg/− mice. (g) Kaplan–Meier plot of the survival of Evi1+/− BCR–ABLtg/− or Evi1+/+ BCR–ABLtg/− mice (n=7 for Evi1+/− BCR–ABLtg/− mice and n=14 for Evi1+/+ BCR–ABLtg/− mice, P=0.0106). Data are mean±s.d. +P<0.05, *P<0.01, ***P<0.0001.
Drug resistance is one of critical characteristics of LSCs, which motivated us to conduct in vivo therapeutical interventions to Evi1+/GFP BCR–ABLtg/− mice. Oral administration of nilotinib, a potent BCR–ABL inhibitor, to Evi1+/GFP BCR–ABLtg/− mice for 7 days resulted in amelioration of BM cellularity and splenomegaly, which underlay the efficacy of the drug (Supplementary Figure S3c). In LSK fraction, although nilotinib-treated Evi1+/GFP BCR–ABLtg/− mice showed the reduced number of Evi1-low LSK cells in BM compared with vehicle-treated Evi1+/GFP BCR–ABLtg/− mice, that of Evi1-high LSK cells had no change irrespective of nilotinib treatment, which implied nilotinib resistance of Evi1-high CML cells (Figure 3e). The relatively nilotinib-resistant aspect of these cells was confirmed by in vitro colony-forming assay (Supplementary Figure S3g). FCM analysis of the residual cells in BM and spleen of nilotinib-treated Evi1+/GFP BCR–ABLtg/− mice revealed a marked increase in the percentage of CD150+CD48– fraction of Evi1-high LSK cells (Supplementary Figure S3h). The treatment had no impact on normal Evi1+/GFP mice as to Evi1-positive rate (data not shown). These data of Evi1+/GFP BCR–ABLtg/− mice revealed CML stem cell activity and nilotinib resistance of Evi1-high cells.
Evi1 heterozygosity impairs CML development
Based on these findings, we next crossed Evi1 heterozygous knock-out (Evi1+/−) mice with BCR–ABLtg/− mice to clarify whether loss of Evi1 would affect CML development (Figure 3f). Surprisingly, 1-year follow-up revealed a significantly prolonged survival of Evi1+/− BCR–ABLtg/− mice (4 deaths per 7 cases), with an obvious contrast to the high lethality of Evi1+/+ BCR–ABLtg/− mice (12 deaths per 14 cases; Figure 3g, P=0.0106). All dead mice in both cohorts had granulocytosis and mild splenoegaly (data not shown). Given that Evi1+/− mice are fertile with no sign of BM failure over a year,25 these data suggest that Evi1 has a distinctive role in CML development.
BCR–ABL and NUP98–HOXA9 induce myeloid BC of CML with Evi1 upregulation
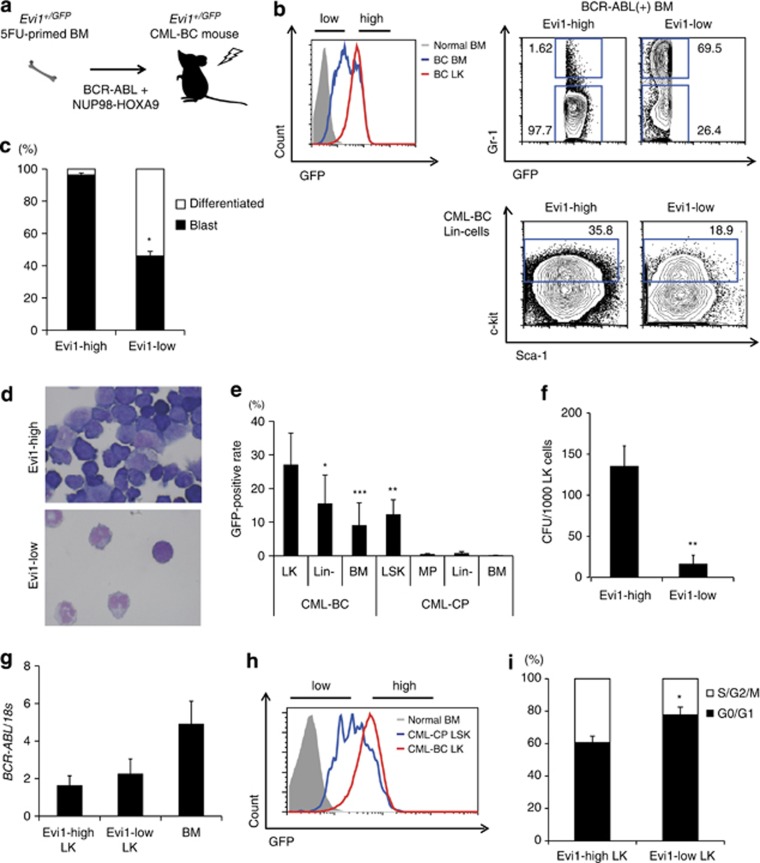
The BC phase of CML is characterized by high mortality and resistance to both TKI therapy and conventional chemotherapy, with HSC transplantation being the only therapy providing appreciable efficacy. Among CML-BC cases with high EVI1, there exist not only 3q-rearranged cases but also cases without 3q rearrangement, possibly suggesting unknown EVI1 regulation. To evaluate a leukemogenic function of Evi1-high cells in CML-BC, BCR–ABL and NUP98–HOXA9 were co-transduced37 into 5FU-primed BM of Evi1+/GFP mice to establish Evi1-reporter CML-BC mice (Figure 4a). Evi1-reporter CML-BC mice had an obviously high level of Evi1-positive cells in the BM compared with Evi1-reporter CML-CP mice (Figures 4b and e). Evi1-reporter CML-BC mice died at 14 days after BMT and showed emergence of blast cells in PB as well as in BM and spleen, a AML-like phenotype, which was markedly different from that of CML-CP model.
Figure 4.
BCR–ABL with NUP98–HOXA9 augments Evi1 expression to cause CML-BC in vivo. (a) Experimental scheme of Evi1-reporter CML-BC mice. 5FU-primed Evi1+/GFP BM cells with retroviral BCR–ABL and NUP98–HOXA9 were transplanted into lethally irradiated recipient mice. (b) GFP intensities of LK cells and BM cells from Evi1-reporter CML-BC mice were analyzed by FCM (upper left). The difference of Gr-1-positive rate in BCR–ABL (+) BM cells (upper right) and that of c-kit-positive rate in BCR–ABL (+) Lin– BM cells (lower) were shown. (c) The proportion of leukemic blasts in Evi1-high or Evi1-low CML-BC BM cells was shown (n=3). (d) Evi1-high or Evi1-low cells from CML-BC BM cells were sorted, cytospun and subjected to Wright–Giemsa staining. (e) GFP-positive rates of stem/progenitor fractions and BM cells in Evi1-reporter CML-BC or CP mouse were shown (n=13 for CML-BC mice, n=5 for CML-CP mice). (f) Semisolid colony assay was done with 1000 Evi1-high or Evi1-low CML-BC LK cells (n=5). (g) BCR–ABL mRNA expression was measured for each subset from CML-BC mice (n=3). (h) Representative FCM plot of LK cells from CML-BC mice (red) and LSK cells from CML-CP mice (blue). GFP intensity of normal BM cells is shown in solid gray. (i) Cell cycle status of Evi1-high or Evi1-low LK cells of CML-BC mice. Hoechst 33342 was measured by FCM (n=3). Data are mean±s.d. *P<0.01, **P<0.001, ***P<0.0001.
Evi1-high CML-BC cells are enriched in the progenitor fraction
The morphological analyses of BM in Evi1-reporter CML-BC mice showed that Evi1-high cells mostly comprises leukemic blasts, while more than half of Evi1-low cells were differentiated cells (Figures 4c and d). From FCM analyses, most of Evi1-high CML-BC cells were negative for Gr-1, as opposed to Gr-1+ immunophenotype of Evi1-low cells. In Lin– cells of these mice, Evi1-high cells had a higher percentage of c-kit (Figure 4b). Totally, Evi1-high cells were rich in Lin-c-kit+ (LK) fraction of myeloid progenitor immunophenotype, the level of which was apparently higher than that of CML-CP (Figure 4e). Evi1-high LK cells had higher colony-forming capacity, indicating their proliferative advantage (Figure 4f, Supplementary Figure S4a). Transcripts of BCR–ABL and HOXA9 were comparable between Evi1-high and Evi1-low LK populations (Figure 4g, Supplementary Figure S4b), reflecting little relevance of BCR–ABL or NUP98–HOXA9 dosage to the enhanced proliferation of Evi1-high cells. The majority of CML-BC LK cells showed higher Evi1 than CML-CP LSK cells, whereas CML-CP LSK cells had a wide range of Evi1, suggesting Evi1 upregulation in CML-BC model (Figure 4h). Cell cycle analysis revealed that Evi1-high LK cells were more in S/G2/M phase than their Evi1-low counterpart, possibly reflecting their higher proliferating potential (Figure 4i).
Evi1-high CML-BC cells have higher leukemogenic potential and TKI resistance
To assess the leukemogenic potential of Evi1-high CML-BC cells in vivo, we performed serial BMT experiments. Recipients with 5 × 104 Evi1-high CML-BC cells recapitulated the disease, while recipeints with Evi1-low cells showed no leukemia incidence. When 1 × 103 LK cells were transplanted, leukemia-initiating cells were found to be enriched in the Evi1-high fraction with the frequency of 1/62 cells (1.6%), indicative of high leukemogenicity, whereas Evi1-low cells even in LK fraction had no potential for CML-BC development (Figure 5a, Supplementary Table S4). Under in vitro nilotinib treatment, Evi1-high LK cells showed a relatively higher proliferative capacity than Evi1-low cells (Supplementary Figure S4c). Seven-day in vivo nilotinib treatment resulted in the significant improvement of hepatosplenomegaly and only Evi1-low LK cells showed a significant decrease in number, indicating that Evi1-high LK cells are more resistant to TKI than the Evi1-low counterpart (Figure 5b,Supplementary Figure S4d). Even residual Evi1-high LK cells in BM after nilotinib still possessed leukemogenic potential (Supplementary Figure S4e). All of CML-BC mice treated with nilotinib relapsed with the expansion of Evi1-high cells after the drug cessation, reflecting a limited role of TKI for CML-BC (data not shown).
Figure 5.
Evi1-high CML-BC cells possess leukemogenic potential and TKI resistance in vivo. (a) Kaplan–Meier plot of the survival of sublethally irradiated recipient mice receiving Evi1-high or Evi1-low CML-BC BM cells (n=8 mice per group) or mice with Evi1-high or Evi1-low LK cells of CML-BC (n=15 for Evi1-high CML-BC LK cells, n=9 for Evi1-low CML-BC LK cells). (b) Vehicle or nilotinib (75 mg/kg daily) were administered orally to Evi1-reporter CML-BC mice for a week from day 10 after BMT and the number of residual Evi1-high or Evi1-low CML-BC LK cells per femur were calculated (n=5). (c) Experimental scheme of generating Evi1+/+ or Evi1+/− CML-BC mice. 5FU-primed Evi1+/+ or Evi1+/− BM cells with retroviral BCR–ABL and NUP98–HOXA9 were transplanted into lethally irradiated recipient mice (1st BMT). BM cells from primary transplants were inoculated into sublethally irradiated recipient mice (2nd BMT). (d) Kaplan–Meier plot of the survival of primary transplants receiving 5FU-primed Evi1+/+ or Evi1+/− BM cells transduced with BCR–ABL and NUP98–HOXA9 (n=6 mice per group). (e) Kaplan–Meier plot of the survival of secondary transplants with Evi1+/+ or Evi1+/− CML-BC BM cells (n=8 mice per group). Data are mean±s.d. *P<0.01, **P<0.001.
We next tested whether loss of Evi1 would affect the development of CML-BC. 5FU-primed Evi1+/+ or Evi1+/− BM cells transduced with BCR–ABL and NUP98–HOXA9 were injected into lethally irradiated recipients (Figure 5c). All of the primary recipients developed CML-BC regardless of Evi1 dosage, with a slight delayed onset in Evi1+/− cohort (Figure 5d). In the secondary recipients receiving 5 × 104 CML-BC BM cells, however, Evi1+/− CML-BC cells showed a significantly attenuated leukemogenic potential, whereas Evi1+/+ CML-BC retained the full capacity (Figure 5e). These results indicate that the development of CML-BC is dependent on Evi1 dosage.
Combination of BCR–ABL and Evi1 induces AML
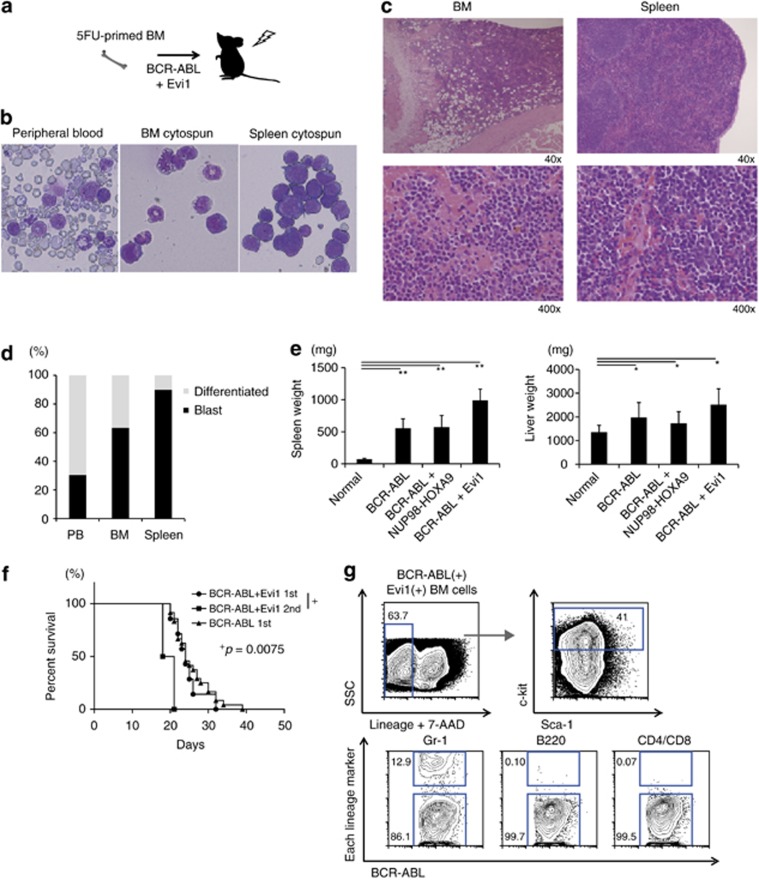
Having established that Evi1 was upregulated in vivo by BCR–ABL and NUP98–HOXA9, we analyzed a role for Evi1 as a direct driver in CML-BC. Co-transduction of BCR–ABL and Evi1 caused lethality in transplanted mice (median survival: 24 days after BMT, Figures 6a and f). These recipients showed marked predominance of leukemic blasts in BM, spleen and PB, with a neutrophilic component, hypercellular BM and hepatosplenomegaly (Figures 6b–d). Splenomegaly was more obvious in the recipients of BCR–ABL plus Evi1 than those of either BCR–ABL alone or BCR–ABL plus NUP98–HOXA9, whereas liver sizes were comparable (Figure 6e). The disease was transplantable with the shorter latency and BM cells of the recipients with BCR–ABL and Evi1 were skewed to the myeloid lineage (Gr-1+) and Lin-c-kit+ cells were dominant in the primitive fractions (Figures 6f and g). Based on the criteria of Bethesda proposals,38 the disease was finally diagnosed as ‘Myeloid leukemia with maturation'. Thus, even without NUP98–HOXA9, activation of Evi1 can induce AML, resembling myeloid BC in CML, in collaboration with BCR–ABL in mice. Given that the duration of CML-CP development by BCR–ABL retrovirus is about 3–4 weeks, and Evi1 alone could induce myelodysplastic syndrome/AML in mice after 6 months or more,39,40 these results indicate that Evi1 can have a causative role in blastic transformation of CML.
Figure 6.
BCR–ABL cooperates with Evi1 to induce AML (CML-BC-like disease) in vivo. (a) Experimental scheme of BMT mice with BCR–ABL and Evi1 overexpression. 5FU-primed C57BL/6 BM cells with retroviral BCR–ABL and Evi1 were transplanted into lethally irradiated recipient mice. (b) Wright–Giemsa staining of PB, BM and spleen from BCR–ABL and Evi1 overexpressing mice. (c) HE staining of BM (upper) and spleen (lower) from BCR–ABL and Evi1 overexpressing mice with low (left) and high (right) magnitude. (d) The proportion of blasts in PB, BM and spleen from BCR–ABL and Evi1 overexpressing mice (n=3). (e) The weight of spleen and liver from normal (n=13), BCR–ABL (n=27), BCR–ABL+NUP98–HOXA9 (n=29) or BCR–ABL+Evi1 mice (n=3). (f) Kaplan–Meier plot of the survival of primary or secondary recipient mice transplanted with BCR–ABL and Evi1 overexpressing cells (n=7 for primary transplants and n=4 for secondary transplants) and primary recipient mice transplanted with BCR–ABL overexpressing cells (n=24). (g) Representative FCM data of BM cells from BCR–ABL and Evi1 overexpressing mice. In BCR–ABL(+) Evi1(+) BM cells, most cells were Lin– (upper left) and about 40% of Lin– cells had c-kit expression (upper right). Mostly BCR–ABL(+) Evi1(+) BM cells were Gr-1+, B220- and CD4/CD8− (lower). Data are mean±s.d. *P<0.01, **P<0.001.
Discussion
Discovery strategies aimed to identify novel driver oncogenic lesions have succeeded in enrichment of the catalog of therapeutic targets, the most striking of which is BCR–ABL where TKI therapy has conferred tremendous benefits to CML patients with a sustained debulking of tumor burden. Even in the era of TKI treatment in CML, blastic transformation can occur with the translocation involving EVI1 locus,41,42 which is crucial because the clinical outcomes of CML plummet from CP (80%) to BC (20%).43,44 Allogeneic HSC transplantation is so far the only potential remedy for high EVI1 cases of CML-BC as well as AML, emphasizing the need for new therapy targeting EVI1.18,21,45,46
Our hypothesis stems from the fact that EVI1 is a valuable prognostic factor of myeloid malignancies as well as a critical regulator of HSCs. To overcome the incapability of prospective separation of intraindividual EVI1-high cells in human leukemias, we used our original Evi1+/GFP mice, developing two types of CML-CP model to show that Evi1 is a valuable marker for CML stem cells. Both in retrovirally developed CML-CP mice and BCR–ABLtg/− mice, Evi1 is restricted to a small population with primitive immunophenotypic markers, especially in the latter, the most primitive profile like SLAM-LSK represents Evi1-high cells. When seen against previous studies,47, 48, 49 the novelty of this study lies in that high Evi1 could distinguish CML-CP stem cells even from SLAM-LSK cells or non-SLAM-LSK cells. This point can be translated to human CML cases like that high EVI1 means the increasing number of CML stem cells. Evi1-high CML LSK cells have a superior proliferative potential in vitro, a superior leukemia-initiating capacity in vivo and nilotinib resistance. The resistant aspect of Evi1-high cells to nilotinib would fit into clinical data that high EVI1 is related to TKI resistance.17 The in vivo quiescent status of Evi1-high CML-CP cells, which could proliferate aggressively in vitro, may be controlled by hypoxic BM niche microenvironment.50,51 In line with less dependence of CML stem cells on BCR–ABL,2,52,53 Evi1-high CML-CP LSK cells showed a comparable BCR–ABL to their Evi1-low counterpart, reflecting little addiction to BCR–ABL (Figure 2d).
In accordance with Evi1-reporter CML-CP model, our single-cell analysis of clinical CML-CP cases revealed the highest EVI1 in stem cell-enriched CD34+CD38–CD90+ cells, reflecting CML-CP as a stem cell disease (Figure 1a). Using BCR–ABL-specific primers, we could effectively distinguish CML-CP cells (BCR–ABL+) from remnant normal cells (BCR–ABL–). These human data could reinforce the value of murine CML data.
We also examined retroviral Evi1-reporter CML-BC mice and showed that a sizable fraction of LK cells have distinct Evi1 expression in sharp contrast to the CML-CP model. CML-BC stem cells are exclusively enriched in Evi1-high LK cells with resistance to nilotinib. The impact of combining the CML-BC with Evi1 upregulation is in strong contrast to that of the simple BCR–ABL BMT model, which only leads to CML-CP in mice 3–4 weeks after inoculation (Figure 4h). Taken together, this is the first report that visualizes Evi1 upregulation in in vivo leukemia models. The finding is consistent with the previous report that showed the transcriptional regulation of Evi1 by NUP98–HOXA9 in vitro.54 In our CML-BC model, HOXA9 showed no difference between Evi1-high and Evi1-low LK cells, eliminating the possible dependence of Evi1-high cells on NUP98–HOXA9 (Supplementary Figure S4b).
In our Evi1 knock-out studies of CML-CP and BC mice, Evi1 heterozygosity alleviated the disease (Figures 3g and 5e), highlighting a functional role of Evi1 in CML pathogenesis. Although complete loss of Evi1 causes embryonic lethality in mice,25,55 Evi1+/− mice have no sign of BM failure over a year and are fertile with a decreased size and function of HSCs.25,35 EVI1 has been reported to be relevant to BCR–ABL tyrosine kinase activity.27 Collectively, it is supposed that Evi1 reduction may permit the reversal of CML at the partial expense of HSCs.
We extended this study to establish a new model of AML by BCR–ABL and Evi1. It is meaningful that overexpression of Evi1 itself is the driver in blastic transformation of CML not only by Evi1-related fusions. Cuenco et al.56 have previously reported that EVI1 with BCR–ABL induces not leukemias but a fatal myeloproliferative disorder in mice. In contrast to the usage of human EVI1 complementary DNA (in MSCV retroviral vector) in murine BMT model of Cuenco's study, we utilized murine Evi1 for Evi1 overexpression. Murine Evi1 especially in pMYs vector is suitable for establishing myeloid leukemia in mouse BMT model (Jones et al.42 and unpublished), which resulted in a new AML model by Evi1 plus BCR–ABL. These findings can remind us of the importance of controlling Evi1 to impair CML-BC development by BCR–ABL and NUP98–HOXA9. As authentic Evi1 targets,22,33,34 such as Gata2, Pten and Pbx1, showed no difference in expression levels between Evi1-high and Evi1-low CML cells (data not shown), the further exploration of CML-specific Evi1 targets would be warranted.
As opposed to Evi1-reporter CML models, in AML model by MLL-ENL retrovirus, Evi1-high MLL-ENL leukemic cells showed no advantage in leukemia initiation compared with Evi1-low cells (Supplementary Figure S5). Other Evi1-reporter AML models by MOZ-TIF2 and TP+AE never generated Evi1-high fraction, suggesting the high affinity of Evi1 for stem cell disease such as CML. Although Evi1 could not enrich MLL-ENL AML LSCs in our model, it is possible that Evi1 reduction in the bulk leukemia cells would be a key in amelioration of MLL-related leukemia as previously investigated.25 Exact introduction of these oncogenes to HSCs by different approaches such as via a transgene or a knocking-in technology could unravel the relation between AML stem cells and Evi1.
In conclusion, high Evi1 can define the population of CML stem cells that are resistant to nilotinib. This is the first report that uncovers the importance of leukemia cells with high Evi1 intraindividually. Combinatorial analyses of Evi1-IRES-GFP allele CML animals and single cells from primary CML-CP patients covered in depth the critical regulation of CML stem cells by Evi1. To elucidate the complex cellular circuits involving Evi1, a further genetic and epigenetic investigation of Evi1-high cells would unveil precise mechanisms of the phenotype in leukemias.
Materials and methods
Single-cell gene expression analysis
Primary BM samples of CML-CP patients were stained with anti-CD34, anti-CD38, anti-CD33 and anti-CD90 (Supplementary Table S2), and single-cell sorted by FACSAriaII (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) gating on each population excluding cell duplets directly into individual wells of 96-well plates filled with 5 μl RT/Specific Target Amplification master mix solution (Fluidigm, San Francisco, CA, USA) immediately followed by reverse transcription and gene-specific pre-amplification with CellsDirect One-Step qRT-PCR kit (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) in the same plates. Each complementary DNA was subjected to quantitative real-time PCR by LightCycler 480 (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) using SYBR Green (TAKARA, Otsu, Japan) with the primers inside of the pre-amplified complementary DNA. Gene-specific primers were listed in Supplementary Table S3. Only samples with a specific product peak in the melting curve analysis of housekeeping genes were taken for further analysis. This study was approved by ethical committee of the University of Tokyo.
Population quantitative real-time–PCR
Target gene expression for bulk samples or sorted populations was evaluated by LightCycler 480 as described previously.35 All assays were performed in triplicate and expression levels relative to 18s ribosomal RNA were determined. Primer sequences are listed in Supplementary Table S3.
Mice
Evi1-IRES-GFP knock-in (Evi1+/GFP) mice, Evi1 knock-out (Evi1+/−) mice and p210 BCR–ABL transgenic (BCR–ABLtg/−) mice on a C57BL/6 (Ly5.2) background were used and genotyped as previously described.25,35,57 CML development of BCR–ABLtg/− mice was confirmed by leukocyte elevation (>10 000 cells/μl) and >80% increase of Gr-1+ cells in PB. Ly5.1 mice were purchased from SRL Inc. (Tokyo, Japan). All mice were kept at the Animal Center for Biomedical Research of the University of Tokyo.
Flow cytometry
FACSAriaII was used for cell sorting of stained cells and LSRII (BD Biosciences) was used for other analyses. Data were analyzed with FlowJo (TreeStar, Ashland, OR, USA). In experiments with the Evi1-IRES-GFP knock-in mouse, a ‘fluorescence minus one' littermate control was analyzed in parallel to set GFP gates.35 Antibodies are listed in Supplementary Table S2.
Retrovirally developed leukemia model mice
Plat-E packaging cells58 were transiently transfected with retroviral constructs by FuGENE6 (Roche). 5FU-primed BM cells were incubated in RPMI1640 medium (Wako, Osaka, Japan) with cytokines (50 ng/ml stem cell factor, 50 ng/ml thrombopoietin, 10 ng/ml interleukin-6) for 24 h as previously described,25,35 and cultured cells were infected with retrovirus on RetroNectin (TAKARA)-coated plate. The combination of donor cells and retroviruses is as follows; Evi1+/GFP BM with pGCDNsam/BCR–ABL/IRES-KuOr for Evi1+/GFP CML-CP, Evi1+/GFP BM with pGCDNsam/BCR–ABL/IRES-KuOr and pMSCVpuro/NUP98–HOXA9 for Evi1+/GFP CML-BC, Evi1+/GFP BM with pGCDNsam/MLL-ENL/IRES-KuOr or pGCDNsam/MOZ-TIF2/IRES-KuOr or pMSCV/TEL-PDGFR/IRES/AML1-ETO for Evi1+/GFP AML, and C57BL/6 (Ly5.2) BM with pGCDNsam/BCR–ABL/IRES-GFP and pGCDNsam/Evi1/IRES-KuOr for a new AML model. The infected cells were harvested 48 h after retrovirus infection, and injected into lethally (9.5 Gy) irradiated recipient mice in competition with 2 × 105 unfractionated BM cells from congenic mice. BCR–ABL-positive CML cells were distinguished by each fluorescent protein.
In vivo transplantation assay
For secondary BMT assay of BCR–ABL and NUP98–HOXA9 overexpressing mice and BCR–ABL and Evi1 overexpressing mice, sublethally irradiated (7.5 Gy) mice (Ly5.2) were injected with the indicated subsets from these mice (Ly5.2). Reconstitution of donor-derived cells was monitored by GFP or KuOr. For BMT assay of BCR–ABLtg/− mice, sublethally irradiated mice (Ly5.1) were injected with the indicated subsets from Evi1+/GFP BCR–ABLtg/− mice (Ly5.2). Reconstitution was monitored by Ly5.1, CD4, CD8, B220, TER-119, Mac-1 and Gr-1.
Nilotinib treatment
For in vivo treatment, nilotinib (AMN107-AA) was diluted at 10 mg/ml in 10% 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA), 90% polyethylenglycol 300 (Sigma-Aldrich) and administered by oral gavage at 75 mg/kg once a day for a week. A mixture without nilotinib was used as vehicle. For in vitro treatment, nilotinib diluted in dimethylsulphoxide (Sigma-Aldrich) was used at the final concentration of 1 or 5 μmol/l.
Colony-forming assay
Cells (1 × 103) were plated into MethoCult GF M3434 (StemCell Technologies, Vancouver, BC, Canada) as described previously.59 The number of colonies was counted at day 7. Images were taken with a Nikon Eclipse TE2000-U (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan).
Hoechst 33342 staining
Cells were incubated with 5 ng/ml Hoechst 33342 (Invitrogen/Life Technologies) and 25 μg/ml verapamil at 37 °C for 45 min.35
OP-9 co-culture
OP-9 cells were pre-seeded on 24-well plates at day –1.59,60 One hundred LSK cells from Evi1-reporter CML-CP mice were cultured from day 0 in alpha-minimum essential medium with 20% fetal calf serum, 1% penicillin+streptomycin, 2 μmol/l L-glutamine (Gibco/Invitrogen/Life Technologies), 1 μmol/l sodium pyruvate and 50 μmol/l 2-mercaptoethanol (Sigma-Aldrich). Culture medium was replaced every 4 days and images were taken at day 10.
Statistical analysis
Statistical significance of differences between parameters was assessed by a two-tailed unpaired t-test. The overall survival of mice was analyzed with a Mantel–Cox test according to the Kaplan–Meier method.
Acknowledgments
We thank Takuro Nakamura for NUP98–HOXA9; Issay Kitabayashi for MOZ-TIF2; Michael Tomasson for TEL-PDGFR/IRES/AML1-ETO; Novartis for nilotinib. We appreciate expert technical supports by Yoshi Shimamura, Yuko Sawamoto and Rumi Takizawa-Toyama. We express our heartfelt sorrow over Yuko Sawamoto's sudden passing away. This work was carried out at the Joint Usage/Research Center (RIRBM), Hiroshima University, and supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and by Health.
MK is a member of the advisory committees of Bristol-Myers and Novartis, and has also received research funding and honoraria from the two companies. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary Material
References
- Radich JP, Dai H, Mao M, Oehler V, Schelter J, Druker B, et al. Gene expression changes associated with progression and response in chronic myeloid leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:2794–2799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510423103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y, Swerdlow S, Duffy TM, Weinmann R, Lee FY, Li S. Targeting multiple kinase pathways in leukemic progenitors and stem cells is essential for improved treatment of Ph+ leukemia in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:16870–16875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0606509103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81683-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huntly BJ, Shigematsu H, Deguchi K, Lee BH, Mizuno S, Duclos N, et al. MOZ-TIF2, but not BCR-ABL, confers properties of leukemic stem cells to committed murine hematopoietic progenitors. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:587–596. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2004.10.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguer-Satta V, Petzer AL, Eaves AC, Eaves CJ. BCR-ABL expression in different subpopulations of functionally characterized Ph+ CD34+ cells from patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 1996;88:1796–1804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radich JP. The Biology of CML blast crisis. Hematology. 2007. pp. 384–391. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chomel JC, Bonnet ML, Sorel N, Bertrand A, Meunier MC, Fichelson S, et al. Leukemic stem cell persistence in chronic myeloid leukemia patients with sustained undetectable molecular residual disease. Blood. 2011;118:3657–3660. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-02-335497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu S, McDonald T, Lin A, Chakraborty S, Huang Q, Snyder DS, et al. Persistence of leukemia stem cells in chronic myelogenous leukemia patients in prolonged remission with imatinib treatment. Blood. 2011;118:5565–5572. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-12-327437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham SM, Jorgensen HG, Allan E, Pearson C, Alcorn MJ, Richmond L, et al. Primitive, quiescent, Philadelphia-positive stem cells from patients with chronic myeloid leukemia are insensitive to STI571 in vitro. Blood. 2002;99:319–325. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.1.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X, Zhao Y, Smith C, Gasparetto M, Turhan A, Eaves A, et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells possess multiple unique features of resistance to BCR-ABL targeted therapies. Leukemia. 2007;21:926–935. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2404609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naka K, Hoshii T, Muraguchi T, Tadokoro Y, Ooshio T, Kondo Y, et al. TGF-beta-FOXO signalling maintains leukaemia-initiating cells in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 2010;463:676–680. doi: 10.1038/nature08734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao C, Blum J, Chen A, Kwon HY, Jung SH, Cook JM, et al. Loss of beta-catenin impairs the renewal of normal and CML stem cells in vivo. Cancer Cell. 2007;12:528–541. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2007.11.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao C, Chen A, Jamieson CH, Fereshteh M, Abrahamsson A, Blum J, et al. Hedgehog signalling is essential for maintenance of cancer stem cells in myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 2009;458:776–779. doi: 10.1038/nature07737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H, Peng C, Hu Y, Li H, Sheng Z, Chen Y, et al. The Blk pathway functions as a tumor suppressor in chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells. Nat Genet. 2012;44:861–871. doi: 10.1038/ng.2350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y, Hu Y, Zhang H, Peng C, Li S. Loss of the Alox5 gene impairs leukemia stem cells and prevents chronic myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet. 2009;41:783–792. doi: 10.1038/ng.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neviani P, Santhanam R, Trotta R, Notari M, Blaser BW, Liu S, et al. The tumor suppressor PP2A is functionally inactivated in blast crisis CML through the inhibitory activity of the BCR/ABL-regulated SET protein. Cancer Cell. 2005;8:355–368. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2005.10.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daghistani M, Marin D, Khorashad JS, Wang L, May PC, Paliompeis C, et al. EVI-1 oncogene expression predicts survival in chronic-phase CML patients resistant to imatinib treated with second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Blood. 2010;116:6014–6017. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-01-264234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groschel S, Lugthart S, Schlenk RF, Valk PJ, Eiwen K, Goudswaard C, et al. High EVI1 expression predicts outcome in younger adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia and is associated with distinct cytogenetic abnormalities. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:2101–2107. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.26.0646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa S, Kurokawa M, Tanaka T, Tanaka K, Hangaishi A, Mitani K, et al. Increased Evi-1 expression is frequently observed in blastic crisis of chronic myelocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 1996;10:788–794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M, Thompson F, Spier C, Taetle R. Expression of the EVI1 gene in chronic myelogenous leukemia in blast crisis. Leukemia. 1993;7:1654–1657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valk PJ, Verhaak RG, Beijen MA, Erpelinck CA, Barjesteh van Waalwijk van Doorn-Khosrovani S, Boer JM, et al. Prognostically useful gene-expression profiles in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1617–1628. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa040465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuasa H, Oike Y, Iwama A, Nishikata I, Sugiyama D, Perkins A, et al. Oncogenic transcription factor Evi1 regulates hematopoietic stem cell proliferation through GATA-2 expression. EMBO J. 2005;24:1976–1987. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg EC, Passegue E, Prohaska SS, Wagers AJ, Koeva M, Stuart JM, et al. Molecular signatures of quiescent, mobilized and leukemia-initiating hematopoietic stem cells. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e8785. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chitteti BR, Liu Y, Srour EF. Genomic and proteomic analysis of the impact of mitotic quiescence on the engraftment of human CD34+ cells. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e17498. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyama S, Yamamoto G, Shimabe M, Sato T, Ichikawa M, Ogawa S, et al. Evi-1 is a critical regulator for hematopoietic stem cells and transformed leukemic cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3:207–220. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2008.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppert K, Takenaka K, Lechman ER, Waldron L, Nilsson B, van Galen P, et al. Stem cell gene expression programs influence clinical outcome in human leukemia. Nat Med. 2011;17:1086–1093. doi: 10.1038/nm.2415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S, Jorgensen HG, Roy P, Abed El Baky M, Melo JV, Strathdee G, et al. BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase sustained MECOM expression in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2012;157:446–456. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2012.09078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai S, Yoshimi A, Shimabe M, Ichikawa M, Nakagawa M, Imai Y, et al. Evi-1 is a transcriptional target of mixed-lineage leukemia oncoproteins in hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 2011;117:6304–6314. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-234310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyama S, Nitta E, Yoshino T, Kako S, Watanabe-Okochi N, Shimabe M, et al. EVI-1 interacts with histone methyltransferases SUV39H1 and G9a for transcriptional repression and bone marrow immortalization. Leukemia. 2010;24:81–88. doi: 10.1038/leu.2009.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izutsu K, Kurokawa M, Imai Y, Maki K, Mitani K, Hirai H. The corepressor CtBP interacts with Evi-1 to repress transforming growth factor beta signaling. Blood. 2001;97:2815–2822. doi: 10.1182/blood.v97.9.2815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa M, Mitani K, Yamagata T, Takahashi T, Izutsu K, Ogawa S, et al. The evi-1 oncoprotein inhibits c-Jun N-terminal kinase and prevents stress-induced cell death. EMBO J. 2000;19:2958–2968. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.12.2958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa M, Mitani K, Irie K, Matsuyama T, Takahashi T, Chiba S, et al. The oncoprotein Evi-1 represses TGF-beta signalling by inhibiting Smad3. Nature. 1998;394:92–96. doi: 10.1038/27945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimabe M, Goyama S, Watanabe-Okochi N, Yoshimi A, Ichikawa M, Imai Y, et al. Pbx1 is a downstream target of Evi-1 in hematopoietic stem/progenitors and leukemic cells. Oncogene. 2009;28:4364–4374. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimi A, Goyama S, Watanabe-Okochi N, Yoshiki Y, Nannya Y, Nitta E, et al. Evi1 represses PTEN expression and activates PI3K/AKT/mTOR via interactions with polycomb proteins. Blood. 2011;117:3617–3628. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-12-261602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka K, Sato T, Yoshimi A, Goyama S, Tsuruta T, Kobayashi H, et al. Evi1 is essential for hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal, and its expression marks hematopoietic cells with long-term multilineage repopulating activity. J Exp Med. 2011;208:2403–2416. doi: 10.1084/jem.20110447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda H, Oda H, Suzuki T, Takahashi T, Witte ON, Ozawa K, et al. Development of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and myeloproliferative disorder in transgenic mice expressing p210bcr/abl: a novel transgenic model for human Ph1-positive leukemias. Blood. 1998;91:2067–2075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dash AB, Williams IR, Kutok JL, Tomasson MH, Anastasiadou E, Lindahl K, et al. A murine model of CML blast crisis induced by cooperation between BCR/ABL and NUP98/HOXA9. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:7622–7627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.102583199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse HC, 3rd, Anver MR, Fredrickson TN, Haines DC, Harris AW, Harris NL, et al. Bethesda proposals for classification of lymphoid neoplasms in mice. Blood. 2002;100:246–258. doi: 10.1182/blood.v100.1.246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonamici S, Li D, Chi Y, Zhao R, Wang X, Brace L, et al. EVI1 induces myelodysplastic syndrome in mice. J Clin Invest. 2004;114:713–719. doi: 10.1172/JCI21716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe-Okochi N, Yoshimi A, Sato T, Ikeda T, Kumano K, Taoka K, et al. The shortest isoform of C/EBPbeta, liver inhibitory protein (LIP), collaborates with Evi1 to induce AML in a mouse BMT model. Blood. 2013;121:4142–4155. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-07-368654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paquette RL, Nicoll J, Chalukya M, Elashoff D, Shah NP, Sawyers C, et al. Frequent EVI1 translocations in myeloid blast crisis CML that evolves through tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Genet. 2011;204:392–397. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2011.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D, Luthra R, Cortes J, Thomas D, O'Brien S, Bueso-Ramos C, et al. BCR-ABL fusion transcript types and levels and their interaction with secondary genetic changes in determining the phenotype of Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias. Blood. 2008;112:5190–5192. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-04-148791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien SG, Guilhot F, Larson RA, Gathmann I, Baccarani M, Cervantes F, et al. Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:994–1004. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druker BJ, Sawyers CL, Kantarjian H, Resta DJ, Reese SF, Ford JM, et al. Activity of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in the blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia with the Philadelphia chromosome. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1038–1042. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200104053441402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balgobind BV, Lugthart S, Hollink IH, Arentsen-Peters ST, van Wering ER, de Graaf SS, et al. EVI1 overexpression in distinct subtypes of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2010;24:942–949. doi: 10.1038/leu.2010.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugthart S, van Drunen E, van Norden Y, van Hoven A, Erpelinck CA, Valk PJ, et al. High EVI1 levels predict adverse outcome in acute myeloid leukemia: prevalence of EVI1 overexpression and chromosome 3q26 abnormalities underestimated. Blood. 2008;111:4329–4337. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-10-119230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang B, Ho YW, Huang Q, Maeda T, Lin A, Lee SU, et al. Altered microenvironmental regulation of leukemic and normal stem cells in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2012;21:577–592. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.02.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynaud D, Pietras E, Barry-Holson K, Mir A, Binnewies M, Jeanne M, et al. IL-6 controls leukemic multipotent progenitor cell fate and contributes to chronic myelogenous leukemia development. Cancer Cell. 2011;20:661–673. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.10.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schemionek M, Elling C, Steidl U, Baumer N, Hamilton A, Spieker T, et al. BCR-ABL enhances differentiation of long-term repopulating hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 2010;115:3185–3195. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-04-215376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermitte F, Brunet de la Grange P, Belloc F, Praloran V, Ivanovic Z. Very low O2 concentration (0.1%) favors G0 return of dividing CD34+ cells. Stem Cells. 2006;24:65–73. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2004-0351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmar K, Mauch P, Vergilio JA, Sackstein R, Down JD. Distribution of hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow according to regional hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:5431–5436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701152104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton A, Helgason GV, Schemionek M, Zhang B, Myssina S, Allan EK, et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells are not dependent on Bcr-Abl kinase activity for their survival. Blood. 2012;119:1501–1510. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-12-326843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin AS, Agarwal A, Loriaux M, Cortes J, Deininger MW, Druker BJ. Human chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells are insensitive to imatinib despite inhibition of BCR-ABL activity. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:396–409. doi: 10.1172/JCI35721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eguchi-Ishimae M, Eguchi M, Ohyashiki K, Yamagata T, Mitani K. Enhanced expression of the EVI1 gene in NUP98/HOXA-expressing leukemia cells. Int J Hematol. 2009;89:253–256. doi: 10.1007/s12185-009-0267-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt PR, Bartholomew C, Davis AJ, Yutzey K, Gamer LW, Potter SS, et al. The Evi1 proto-oncogene is required at midgestation for neural, heart, and paraxial mesenchyme development. Mech Dev. 1997;65:55–70. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(97)00057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuenco GM, Ren R. Both AML1 and EVI1 oncogenic components are required for the cooperation of AML1/MDS1/EVI1 with BCR/ABL in the induction of acute myelogenous leukemia in mice. Oncogene. 2004;23:569–579. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda H, Ushijima T, Wakazono K, Oda H, Tanaka Y, Aizawa S, et al. Acquired loss of p53 induces blastic transformation in p210(bcr/abl)-expressing hematopoietic cells: a transgenic study for blast crisis of human CML. Blood. 2000;95:1144–1150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura T, Koshino Y, Shibata F, Oki T, Nakajima H, Nosaka T, et al. Retrovirus-mediated gene transfer and expression cloning: powerful tools in functional genomics. Exp hematol. 2003;31:1007–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T, Goyama S, Nitta E, Takeshita M, Yoshimi M, Nakagawa M, et al. Evi-1 promotes para-aortic splanchnopleural hematopoiesis through up-regulation of GATA-2 and repression of TGF-b signaling. Cancer Sci. 2008;99:1407–1413. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyama S, Yamaguchi Y, Imai Y, Kawazu M, Nakagawa M, Asai T, et al. The transcriptionally active form of AML1 is required for hematopoietic rescue of the AML1-deficient embryonic para-aortic splanchnopleural (P-Sp) region. Blood. 2004;104:3558–3564. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-04-1535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.