Abstract
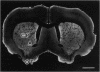
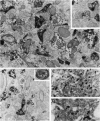
Protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) is a highly conserved enzyme that has been implicated in diverse biological processes in the brain as well as in nonneuronal tissues. The present study used light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry to characterize the distribution of two PP1 isoforms, PP1 alpha and PP1 gamma 1, in the rat neostriatum. Both isoforms are heterogeneously distributed in brain with the highest immunoreactivity being found in the neostriatum and hippocampal formation. Further, both isoforms are highly and specifically concentrated in dendritic spines. Weak immunoreactivity is present in dendrites, axons, and some axon terminals. Immunoreactivity for PP1 alpha is also present in the perikaryal cytoplasm and nuclei of most medium- and large-sized neostriatal neurons. The specific localization of PP1 in dendritic spines is consistent with a central role for this enzyme in signal transduction. The data support the concept that, in the course of evolution, spines developed as specialized signal transduction organelles enabling neurons to integrate diverse inputs from multiple afferent nerve terminals.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken A., Bilham T., Cohen P., Aswad D., Greengard P. A specific substrate from rabbit cerebellum for guanosine-3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. III. Amino acid sequences at the two phosphorylation sites. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3501–3506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alberts A. S., Montminy M., Shenolikar S., Feramisco J. R. Expression of a peptide inhibitor of protein phosphatase 1 increases phosphorylation and activity of CREB in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4398–4407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alberts A. S., Thorburn A. M., Shenolikar S., Mumby M. C., Feramisco J. R. Regulation of cell cycle progression and nuclear affinity of the retinoblastoma protein by protein phosphatases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):388–392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axton J. M., Dombrádi V., Cohen P. T., Glover D. M. One of the protein phosphatase 1 isoenzymes in Drosophila is essential for mitosis. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):33–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90286-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beullens M., Van Eynde A., Bollen M., Stalmans W. Inactivation of nuclear inhibitory polypeptides of protein phosphatase-1 (NIPP-1) by protein kinase A. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13172–13177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brautigan D. L., Sunwoo J., Labbé J. C., Fernandez A., Lamb N. J. Cell cycle oscillation of phosphatase inhibitor-2 in rat fibroblasts coincident with p34cdc2 restriction. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):74–78. doi: 10.1038/344074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Pozzo Miller L. D., Petrozzino J., Müller W. Calcium signaling in dendritic spines of hippocampal neurons. J Neurobiol. 1994 Mar;25(3):234–242. doi: 10.1002/neu.480250304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Ueda T., Bloom F. E., Battenberg E., Greengard P. Widespread distribution of protein I in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5977–5981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P., Lavoinne A., Nakielny S., Caudwell F. B., Watt P., Cohen P. The molecular mechanism by which insulin stimulates glycogen synthesis in mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):302–308. doi: 10.1038/348302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detre J. A., Nairn A. C., Aswad D. W., Greengard P. Localization in mammalian brain of G-substrate, a specific substrate for guanosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Neurosci. 1984 Nov;4(11):2843–2849. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-11-02843.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohadwala M., da Cruz e Silva E. F., Hall F. L., Williams R. T., Carbonaro-Hall D. A., Nairn A. C., Greengard P., Berndt N. Phosphorylation and inactivation of protein phosphatase 1 by cyclin-dependent kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6408–6412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombrádi V., Axton J. M., Brewis N. D., da Cruz e Silva E. F., Alphey L., Cohen P. T. Drosophila contains three genes that encode distinct isoforms of protein phosphatase 1. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 27;194(3):739–745. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19464.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doonan J. H., Morris N. R. The bimG gene of Aspergillus nidulans, required for completion of anaphase, encodes a homolog of mammalian phosphoprotein phosphatase 1. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):987–996. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90337-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dosemeci A., Reese T. S. Inhibition of endogenous phosphatase in a postsynaptic density fraction allows extensive phosphorylation of the major postsynaptic density protein. J Neurochem. 1993 Aug;61(2):550–555. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb02158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez A., Brautigan D. L., Lamb N. J. Protein phosphatase type 1 in mammalian cell mitosis: chromosomal localization and involvement in mitotic exit. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(6):1421–1430. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.6.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francisco L., Wang W., Chan C. S. Type 1 protein phosphatase acts in opposition to IpL1 protein kinase in regulating yeast chromosome segregation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4731–4740. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson E. L., Girault J. A., Hemmings H. C., Jr, Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Immunocytochemical localization of phosphatase inhibitor-1 in rat brain. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Aug 8;310(2):170–188. doi: 10.1002/cne.903100204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie P. B., Segal M., Kater S. B. Independent regulation of calcium revealed by imaging dendritic spines. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):76–80. doi: 10.1038/354076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara M., Alberts A., Brindle P., Meinkoth J., Feramisco J., Deng T., Karin M., Shenolikar S., Montminy M. Transcriptional attenuation following cAMP induction requires PP-1-mediated dephosphorylation of CREB. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90537-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpain S., Girault J. A., Greengard P. Activation of NMDA receptors induces dephosphorylation of DARPP-32 in rat striatal slices. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):369–372. doi: 10.1038/343369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings B. A., Resink T. J., Cohen P. Reconstitution of a Mg-ATP-dependent protein phosphatase and its activation through a phosphorylation mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 27;150(2):319–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80760-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings H. C., Jr, Greengard P., Tung H. Y., Cohen P. DARPP-32, a dopamine-regulated neuronal phosphoprotein, is a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase-1. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):503–505. doi: 10.1038/310503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang F. L., Glinsmann W. H. Separation and characterization of two phosphorylase phosphatase inhibitors from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 15;70(2):419–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C., Zador A. The function of dendritic spines: devices subserving biochemical rather than electrical compartmentalization. J Neurosci. 1993 Feb;13(2):413–422. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00413.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuret J., Bell H., Cohen P. Identification of high levels of protein phosphatase-1 in rat liver nuclei. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 28;203(2):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80741-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisman J. A mechanism for the Hebb and the anti-Hebb processes underlying learning and memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9574–9578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malenka R. C. Synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus: LTP and LTD. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):535–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90517-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin L. J., Blackstone C. D., Levey A. I., Huganir R. L., Price D. L. AMPA glutamate receptor subunits are differentially distributed in rat brain. Neuroscience. 1993 Mar;53(2):327–358. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90199-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulkey R. M., Endo S., Shenolikar S., Malenka R. C. Involvement of a calcineurin/inhibitor-1 phosphatase cascade in hippocampal long-term depression. Nature. 1994 Jun 9;369(6480):486–488. doi: 10.1038/369486a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkura H., Kinoshita N., Miyatani S., Toda T., Yanagida M. The fission yeast dis2+ gene required for chromosome disjoining encodes one of two putative type 1 protein phosphatases. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):997–1007. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouimet C. C., Miller P. E., Hemmings H. C., Jr, Walaas S. I., Greengard P. DARPP-32, a dopamine- and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. III. Immunocytochemical localization. J Neurosci. 1984 Jan;4(1):111–124. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-01-00111.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei J. J., Sersen E., Iqbal K., Grundke-Iqbal I. Expression of protein phosphatases (PP-1, PP-2A, PP-2B and PTP-1B) and protein kinases (MAP kinase and P34cdc2) in the hippocampus of patients with Alzheimer disease and normal aged individuals. Brain Res. 1994 Aug 29;655(1-2):70–76. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)91598-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenolikar S., Nairn A. C. Protein phosphatases: recent progress. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1991;23:1–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields S. M., Ingebritsen T. S., Kelly P. T. Identification of protein phosphatase 1 in synaptic junctions: dephosphorylation of endogenous calmodulin-dependent kinase II and synapse-enriched phosphoproteins. J Neurosci. 1985 Dec;5(12):3414–3422. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-12-03414.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley J. F., Levey A. I., Ciliax B. J., Goldman-Rakic P. S. D1 dopamine receptor immunoreactivity in human and monkey cerebral cortex: predominant and extrasynaptic localization in dendritic spines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5720–5724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder G. L., Fisone G., Greengard P. Phosphorylation of DARPP-32 is regulated by GABA in rat striatum and substantia nigra. J Neurochem. 1994 Nov;63(5):1766–1771. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63051766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas S. I., Aswad D. W., Greengard P. A dopamine- and cyclic AMP-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):69–71. doi: 10.1038/301069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas S. I., Greengard P. DARPP-32, a dopamine- and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. I. Regional and cellular distribution in the rat brain. J Neurosci. 1984 Jan;4(1):84–98. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-01-00084.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas S. I., Greengard P. Protein phosphorylation and neuronal function. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Sep;43(3):299–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]