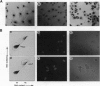
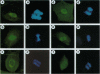
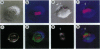
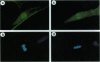
Abstract
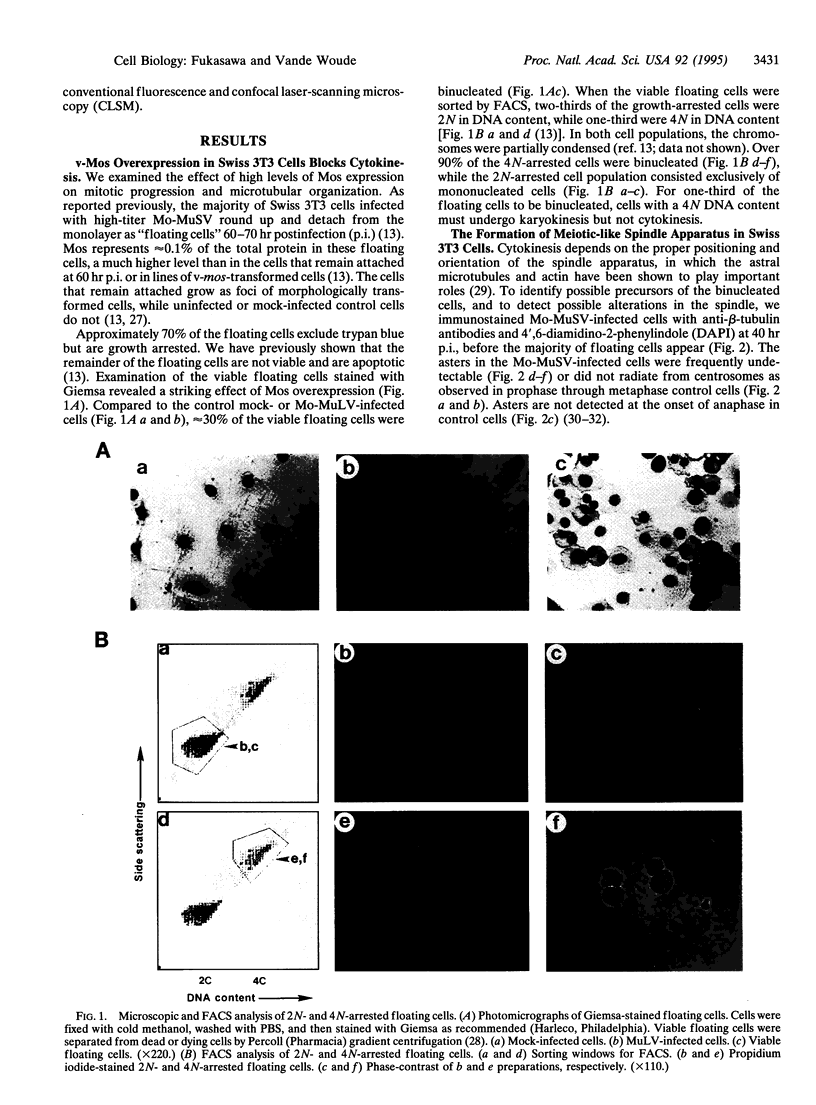
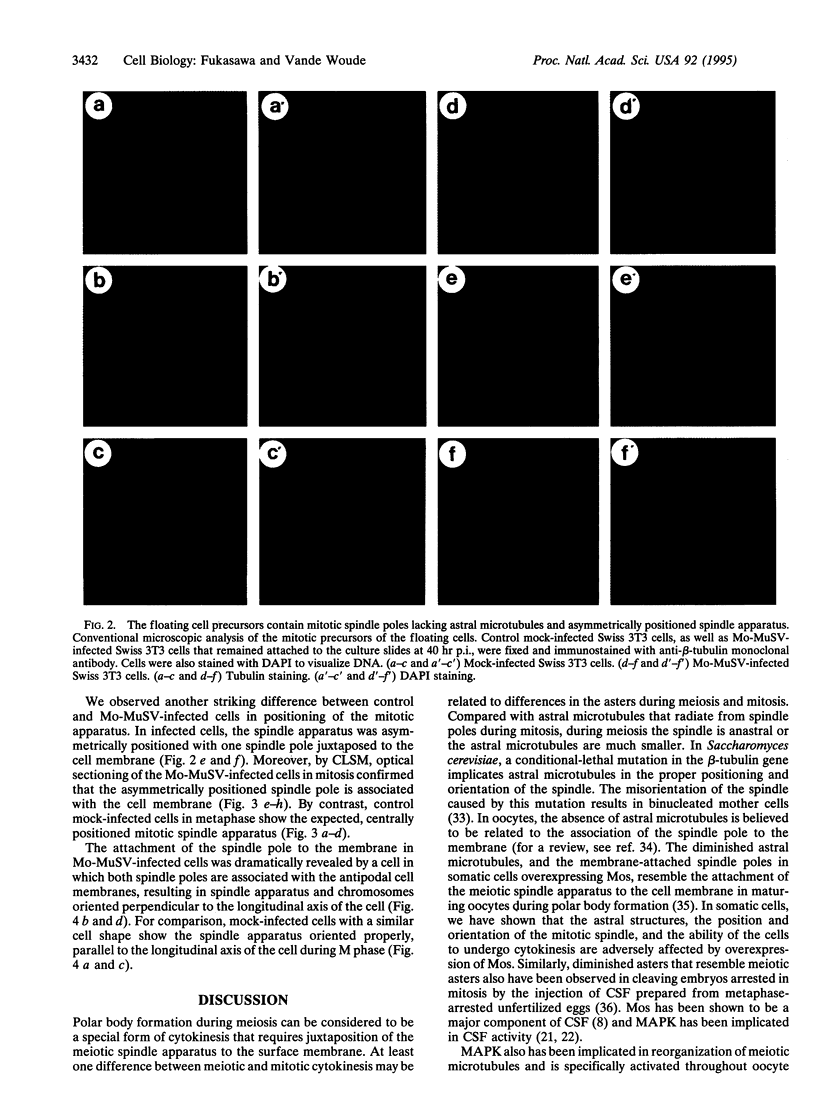
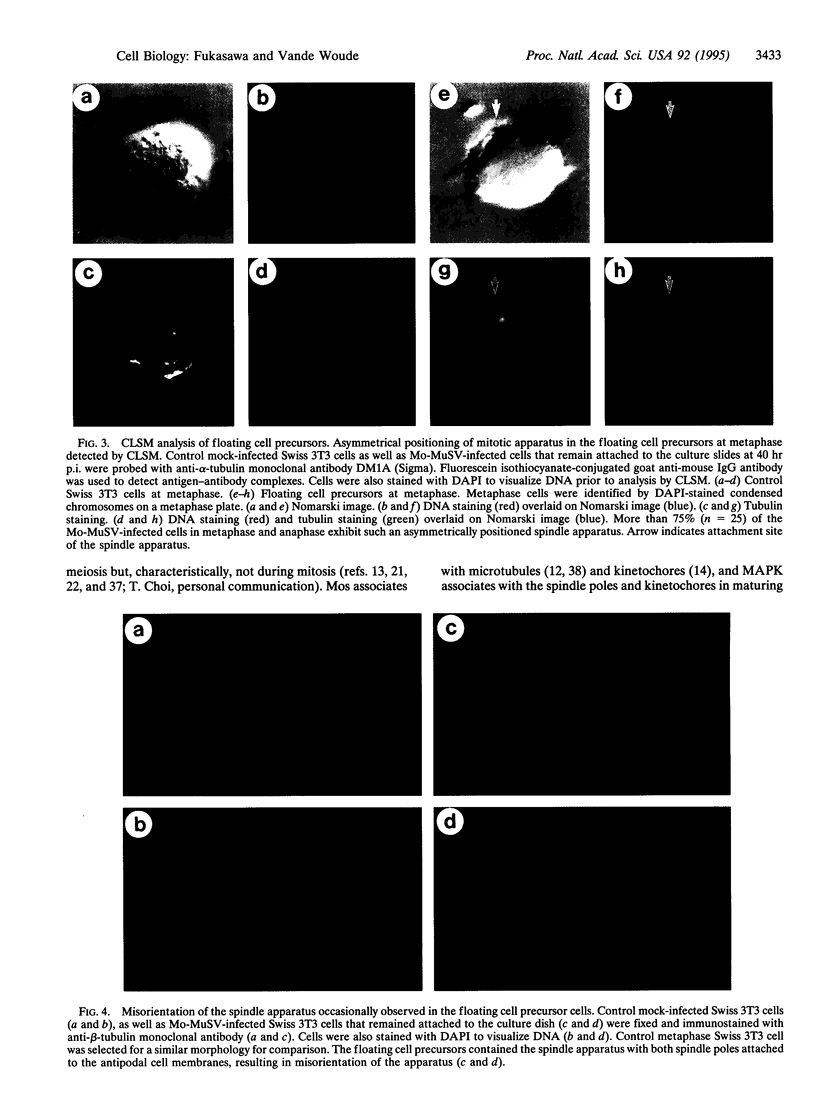
High levels of mos protooncogene product are expressed during oocyte meiotic maturation and Mos has been implicated in formation of the spindle and spindle pole. Here, we show that in Swiss 3T3 cells with 4N DNA content, high levels of Mos lead to the production of binucleated cells. The Swiss 3T3 cells in mitosis, before binucleation occurs, are anastral and the spindle poles are juxtaposed to the cell membrane. These phenotypes may be related to the meiotic process of attachment of the spindle pole to the oocyte membrane during polar body formation. The production of binucleated somatic cells could result from attachment of the altered mitotic spindle pole to the cell membrane that interferes with cytokinesis but not karyokinesis. This can explain at least one form of genetic instability that leads to altered DNA content in tumor cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bai W., Singh B., Yang Y., Ramagli L. S., Nash M., Herzog N. K., Arlinghaus R. B. The physical interactions between p37env-mos and tubulin structures. Oncogene. 1992 Mar;7(3):493–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball J., McCarter J. A., Sunderland S. M. Evidence for helper independent murine sarcoma virus. I. Segregation of replication-defective and transformation-defective viruses. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):268–284. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90305-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett C. B., Schroetke R. M., Van der Hoorn F. A., Nordeen S. K., Maller J. L. Ha-rasVal-12,Thr-59 activates S6 kinase and p34cdc2 kinase in Xenopus oocytes: evidence for c-mosxe-dependent and -independent pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):310–315. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colledge W. H., Carlton M. B., Udy G. B., Evans M. J. Disruption of c-mos causes parthenogenetic development of unfertilized mouse eggs. Nature. 1994 Jul 7;370(6484):65–68. doi: 10.1038/370065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dan K., Tanaka Y. Attachment of one spindle pole to the cortex in unequal cleavage. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;582:108–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb21672.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Wu M., Gerhart J. C., Martin G. S. Cell cycle tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc2 and a microtubule-associated protein kinase homolog in Xenopus oocytes and eggs. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1965–1971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischinger P. J., Haapala D. K. Quantitative interactions of feline leukaemia virus and its pseudotype of murine sarcoma virus in cat cells: requirement for DNA synthesis. J Gen Virol. 1971 Nov;13(2):203–214. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-13-2-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. S., Pickham K. M., Kanki J. P., Lee B. A., Pena S. V., Donoghue D. J. Xenopus homolog of the mos protooncogene transforms mammalian fibroblasts and induces maturation of Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5805–5809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukasawa K., Murakami M. S., Blair D. G., Kuriyama R., Hunt T., Fischinger P., Vande Woude G. F. Similarities between somatic cells overexpressing the mos oncogene and oocytes during meiotic interphase. Cell Growth Differ. 1994 Oct;5(10):1093–1103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Matsuda S., Shiina N., Kosako H., Shiokawa K., Akiyama T., Ohta K., Sakai H. In vitro effects on microtubule dynamics of purified Xenopus M phase-activated MAP kinase. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):251–254. doi: 10.1038/349251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haccard O., Sarcevic B., Lewellyn A., Hartley R., Roy L., Izumi T., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Induction of metaphase arrest in cleaving Xenopus embryos by MAP kinase. Science. 1993 Nov 19;262(5137):1262–1265. doi: 10.1126/science.8235656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto N., Watanabe N., Furuta Y., Tamemoto H., Sagata N., Yokoyama M., Okazaki K., Nagayoshi M., Takeda N., Ikawa Y. Parthenogenetic activation of oocytes in c-mos-deficient mice. Nature. 1994 Jul 7;370(6484):68–71. doi: 10.1038/370068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosako H., Gotoh Y., Nishida E. Requirement for the MAP kinase kinase/MAP kinase cascade in Xenopus oocyte maturation. EMBO J. 1994 May 1;13(9):2131–2138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. J., Matten W. T., Hermann A. S., Candia J. M., Rong S., Fukasawa K., Vande Woude G. F., Ahn N. G. Transformation of mammalian cells by constitutively active MAP kinase kinase. Science. 1994 Aug 12;265(5174):966–970. doi: 10.1126/science.8052857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Sun H., Tonks N. K., Murray A. W. A MAP kinase-dependent spindle assembly checkpoint in Xenopus egg extracts. Cell. 1994 Nov 4;79(3):475–486. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin synthesis drives the early embryonic cell cycle. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):275–280. doi: 10.1038/339275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebreda A. R., Hunt T. The c-mos proto-oncogene protein kinase turns on and maintains the activity of MAP kinase, but not MPF, in cell-free extracts of Xenopus oocytes and eggs. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1979–1986. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05847.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe S. J., Wolfes H., Kiessling A. A., Cooper G. M. Microinjection of antisense c-mos oligonucleotides prevents meiosis II in the maturing mouse egg. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7038–7042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. E., Sullivan D. S., Huffaker T., Koshland D. Role of astral microtubules and actin in spindle orientation and migration in the budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):583–593. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paules R. S., Buccione R., Moschel R. C., Vande Woude G. F., Eppig J. J. Mouse Mos protooncogene product is present and functions during oogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5395–5399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perk K., Moloney J. B. Pathogenesis of a virus-induced rhabdomyosarcoma in mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1966 Nov;37(5):581–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada J., Yew N., Ahn N. G., Vande Woude G. F., Cooper J. A. Mos stimulates MAP kinase in Xenopus oocytes and activates a MAP kinase kinase in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2546–2553. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS E., GONATAS N. K. THE ULTRASTRUCTURE OF A MAMMALIAN CELL DURING THE MITOTIC CYCLE. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jun;21:429–463. doi: 10.1083/jcb.21.3.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport R. Establishment of the mechanism of cytokinesis in animal cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1986;105:245–281. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins E., Jentzsch G. Ultrastructural changes in the mitotic apparatus at the metaphase-to-anaphase transition. J Cell Biol. 1969 Mar;40(3):678–691. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.3.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Daar I., Oskarsson M., Showalter S. D., Vande Woude G. F. The product of the mos proto-oncogene as a candidate "initiator" for oocyte maturation. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):643–646. doi: 10.1126/science.2474853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Oskarsson M., Copeland T., Brumbaugh J., Vande Woude G. F. Function of c-mos proto-oncogene product in meiotic maturation in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):519–525. doi: 10.1038/335519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya E. K., Masui Y. Stabilization and enhancement of primary cytostatic factor (CSF) by ATP and NaF in amphibian egg cytosols. Dev Biol. 1988 Sep;129(1):253–264. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90179-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen M., Scherdin U., Vértes I., Boecker W., Dietel M., Hölzel F. Karyotype instability and altered differentiation of rat sarcoma cells after retroviral infection. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1992 Jan;4(1):46–57. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870040107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan D. S., Huffaker T. C. Astral microtubules are not required for anaphase B in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(2):379–388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verlhac M. H., Kubiak J. Z., Clarke H. J., Maro B. Microtubule and chromatin behavior follow MAP kinase activity but not MPF activity during meiosis in mouse oocytes. Development. 1994 Apr;120(4):1017–1025. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.4.1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verlhac M. H., de Pennart H., Maro B., Cobb M. H., Clarke H. J. MAP kinase becomes stably activated at metaphase and is associated with microtubule-organizing centers during meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes. Dev Biol. 1993 Aug;158(2):330–340. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorobjev I. A., Chentsov Y. S. The dynamics of reconstitution of microtubules around the cell center after cooling. Eur J Cell Biol. 1983 May;30(2):149–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. M., Yew N., Peloquin J. G., Vande Woude G. F., Borisy G. G. Mos oncogene product associates with kinetochores in mammalian somatic cells and disrupts mitotic progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 30;91(18):8329–8333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.18.8329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yew N., Mellini M. L., Vande Woude G. F. Meiotic initiation by the mos protein in Xenopus. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):649–652. doi: 10.1038/355649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yew N., Strobel M., Vande Woude G. F. Mos and the cell cycle: the molecular basis of the transformed phenotype. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Feb;3(1):19–25. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80336-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao X., Singh B., Batten B. E. The role of c-mos proto-oncoprotein in mammalian meiotic maturation. Oncogene. 1991 Jan;6(1):43–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou R. P., Oskarsson M., Paules R. S., Schulz N., Cleveland D., Vande Woude G. F. Ability of the c-mos product to associate with and phosphorylate tubulin. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):671–675. doi: 10.1126/science.1825142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]