Abstract
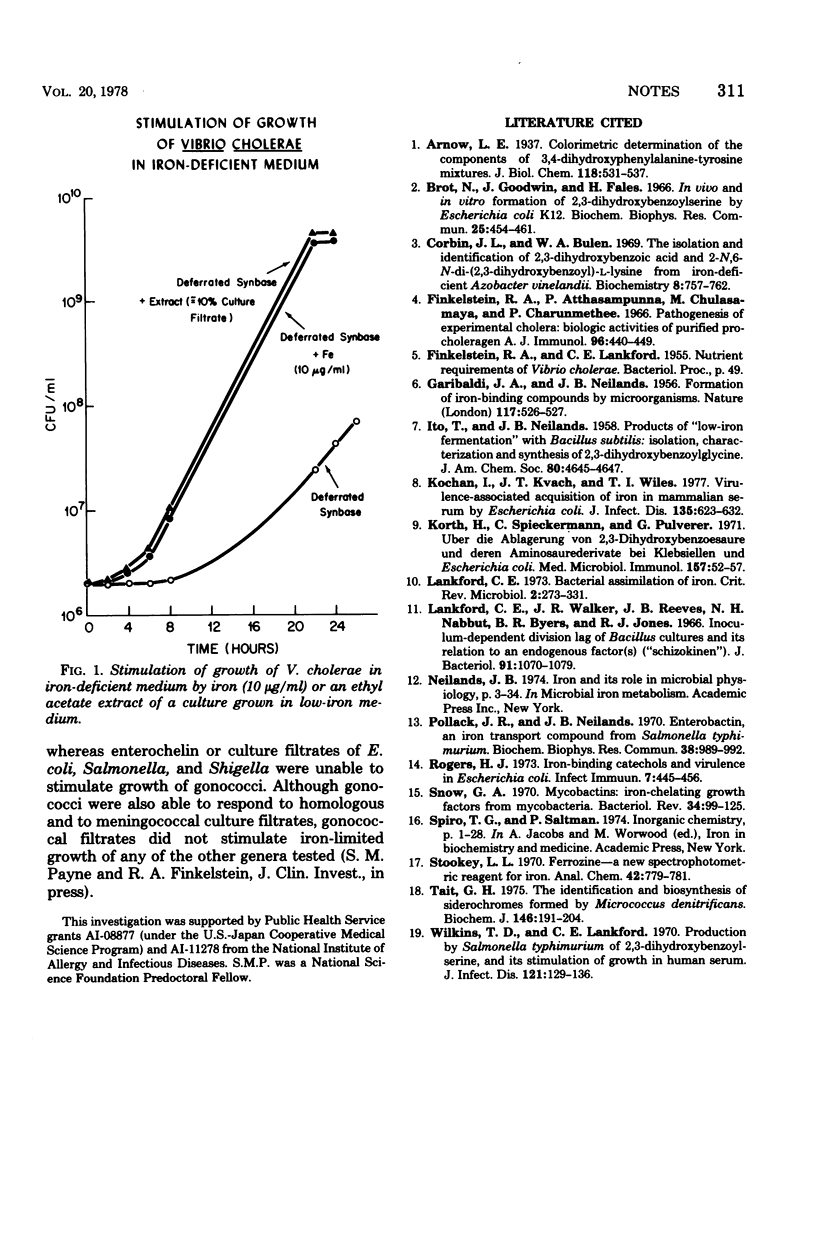
Vibrio cholerae produces a phenolate-type siderophore that stimulates growth of the organism in low-iron medium. This compound is similar, but not identical, to enterochelin, the siderophore produced by Salmonella and Escherichia coli.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brot N., Goodwin J., Fales H. In vivo and in vitro formation of 2,3-dihydroxybenzoylserine by Escherichia coli K12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Nov 22;25(4):454–461. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90227-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. L., Bulen W. A. The isolation and identification of 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid and 2-N,6-N-di-92,3-dihydroxybenzoyl)-L-lysine formed by iron-deficient Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochemistry. 1969 Mar;8(3):757–762. doi: 10.1021/bi00831a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Atthasampunna P., Chulasamaya M., Charunmethee P. Pathogenesis of experimental cholera: biologic ativities of purified procholeragen A. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):440–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARIBALDI J. A., NEILANDS J. B. Formation of iron-binding compounds by micro-organisms. Nature. 1956 Mar 17;177(4507):526–527. doi: 10.1038/177526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochan I., Kvach J. T., Wiles T. I. Virulence-associated acquisition of iron in mammalian serum by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1977 Apr;135(4):623–632. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.4.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korth H., Spieckermann C., Pulverer G. Uber die Ablagerung von 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoesäure und deren Aminosäurederivate bei Klebsiellen und Escherichia coli. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1971;157(1):52–57. doi: 10.1007/BF02121291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lankford C. E., Walker J. R., Reeves J. B., Nabbut N. H., Byers B. R., Jones R. J. Inoculum-dependent division lag of Bacillus cultures and its relation to an endogenous factor(s) ("schizokinen"). J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1070–1079. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1070-1079.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. R., Neilands J. B. Enterobactin, an iron transport compound from Salmonella typhimurium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Mar 12;38(5):989–992. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90819-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Iron-Binding Catechols and Virulence in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):445–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.445-456.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow G. A. Mycobactins: iron-chelating growth factors from mycobacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Jun;34(2):99–125. doi: 10.1128/br.34.2.99-125.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait G. H. The identification and biosynthesis of siderochromes formed by Micrococcus denitrificans. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):191–204. doi: 10.1042/bj1460191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins T. D., Lankford C. E. Production by Salmonella typhimurium of 2,3-dihydroxybenzoylserine, and its stimulation of growth in human serum. J Infect Dis. 1970 Feb;121(2):129–136. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.2.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


