Abstract
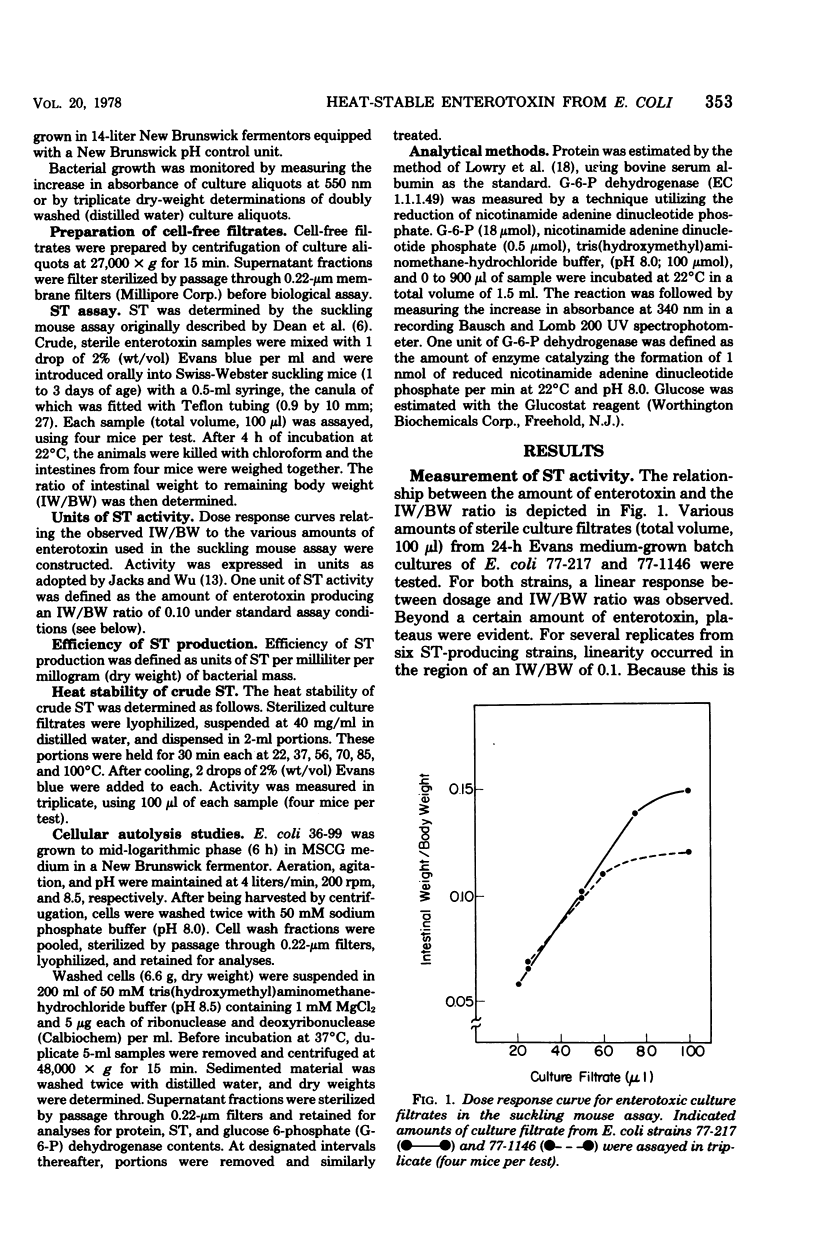
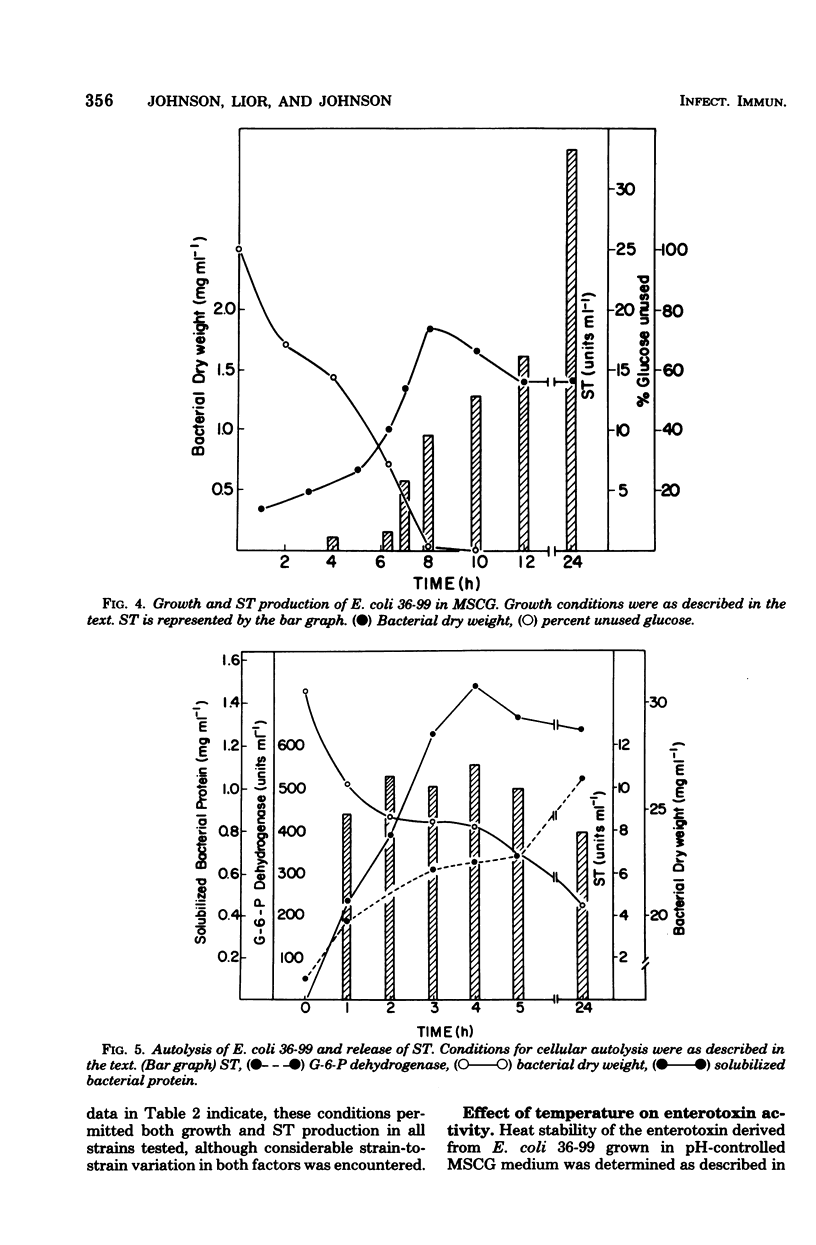
Six enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli produced variable levels of heat-stable enterotoxin (ST) when grown under pH control at 8.5 in a simple synthetic medium containing neither amino acids nor vitamins. Bacterial growth and ST production were at levels as high as or higher than those observed in complex media. ST elaboration was detectable in the early logarithmic phase of growth and appeared to be related to disappearance of glucose in the growth medium. The results of this study did not suggest pH-dependent release of ST. Imposition of pH control in complex media resulted in increased growth rates, earlier detectable ST synthesis, and elevated levels of ST. In synthetic medium, attainment of the stationary growth phase was followed by a significant decrease in culture density and a concomitant increase in ST. Cellular autolysis experiments revealed that as much as 20% of the total ST activity was present in a cell-associated form.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Robertson D. C. Nutrition and enterotoxin synthesis by enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli: defined medium for production of heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):781–788. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.781-788.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Robertson D. C. Repression of heat-stable enterotoxin synthesis in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):629–633. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.629-633.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan L. T., 3rd, Richardson S. H. Biochemistry of Vibrio cholerae virulence. 3. Nutritional requirements for toxin production and the effects of pH on toxin elaboration in chemically defined media. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):567–572. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.567-572.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan L. T., 3rd, Ryder R. C., Richardson S. H. Biochemistry of vibrio cholerae virulence. II. Skin permeability factor-cholera enterotoxin production in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):611–618. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.611-618.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Ingram J. M., Costerton J. W. Release of alkaline phosphatase from cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by manipulation of cation concentration and of pH. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):748–753. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.748-753.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Pierce N. F. Differences in the response of rabbit small intestine to heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):873–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.873-880.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., DuPont H. L., Orskov F., Orskov I. Patterns of loss of enterotoxigenicity by Escherichia coli isolated from adults with diarrhea: suggestive evidence for an interrelationship with serotype. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):105–111. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.105-111.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Kean B. H., Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Bessudo D. Travelers' diarrhea and toxigenic Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 1;292(18):933–936. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505012921801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Moore R. A., Kirschenfeld P. M., Sande M. A. Role of toxigenic and invasive bacteria in acute diarrhea of childhood. N Engl J Med. 1975 Sep 18;293(12):567–572. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197509182931201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T. M., Wu B. J. Biochemical properties of Escherichia coli low-molecular-weight, heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):342–347. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.342-347.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Partial purification and properties of Enterobacter cloacae heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1307–1314. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1307-1314.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Purification and properties of Klebsiella pneumoniae heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):373–381. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.373-381.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koupal L. R., Deibel R. H. Assay, characterization, and localization of an enterotoxin produced by Salmonella. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):14–22. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.14-22.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Caplan E. S., Waterman D., Cash R. A., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J. Diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli that produce only heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):78–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.78-82.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merson M. H., Morris G. K., Sack D. A., Wells J. G., Feeley J. C., Sack R. B., Creech W. B., Kapikian A. Z., Gangarosa E. J. Travelers' diarrhea in Mexico. A prospective study of physicians and family members attending a congress. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jun 10;294(24):1299–1305. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197606102942401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. D., Fung D. Y. Amino acid requirements for the production of enterotoxin B by Staphylococcus aureus S-6 in a chemically defined medium. Appl Microbiol. 1973 May;25(5):800–806. doi: 10.1128/am.25.5.800-806.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell I. de G., Tame M. J., Kenworthy R. Conditions for the production of Escherichia coli enterotoxin in a defined medium. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Aug;7(3):395–400. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalin D. R., Bhattacharjee A. K., Richardson S. H. Cholera-like toxic effect of culture filtrates of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):595–607. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder R. W., Sack D. A., Kapikian A. Z., McLaughlin J. C., Chakraborty J., Mizanur Rahman A. S., Merson M. H., Wells J. G. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Reovirus-like agent in rural Bangladesh. Lancet. 1976 Mar 27;1(7961):659–663. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92776-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Hirschhorn N., Brownlee I., Cash R. A., Woodward W. E., Sack D. A. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia-coli-associated diarrheal disease in Apache children. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 15;292(20):1041–1045. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505152922001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandefur P. D., Peterson J. W. Isolation of skin permeability factors from culture filtrates of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):671–679. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.671-679.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Halls S. Observations by the ligated intestinal segment and oral inoculation methods on Escherichia coli infections in pigs, calves, lambs and rabbits. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(2):499–529. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavric S., Jeffrey D. A modified bioassay for heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin1. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Mar;23(3):331–336. doi: 10.1139/m77-049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp S. C., Moon H. W., Lyon N. C. Heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin production in vivo. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):240–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.240-244.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


