Abstract
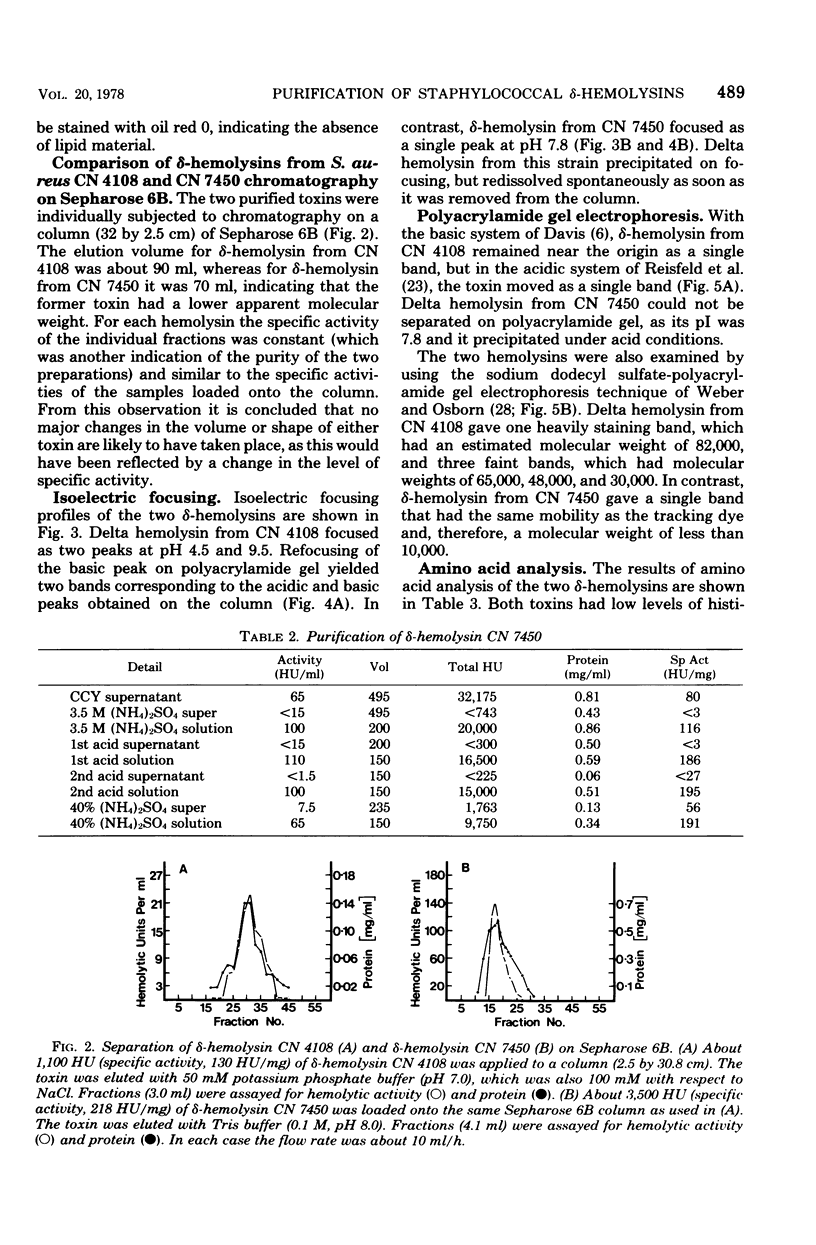
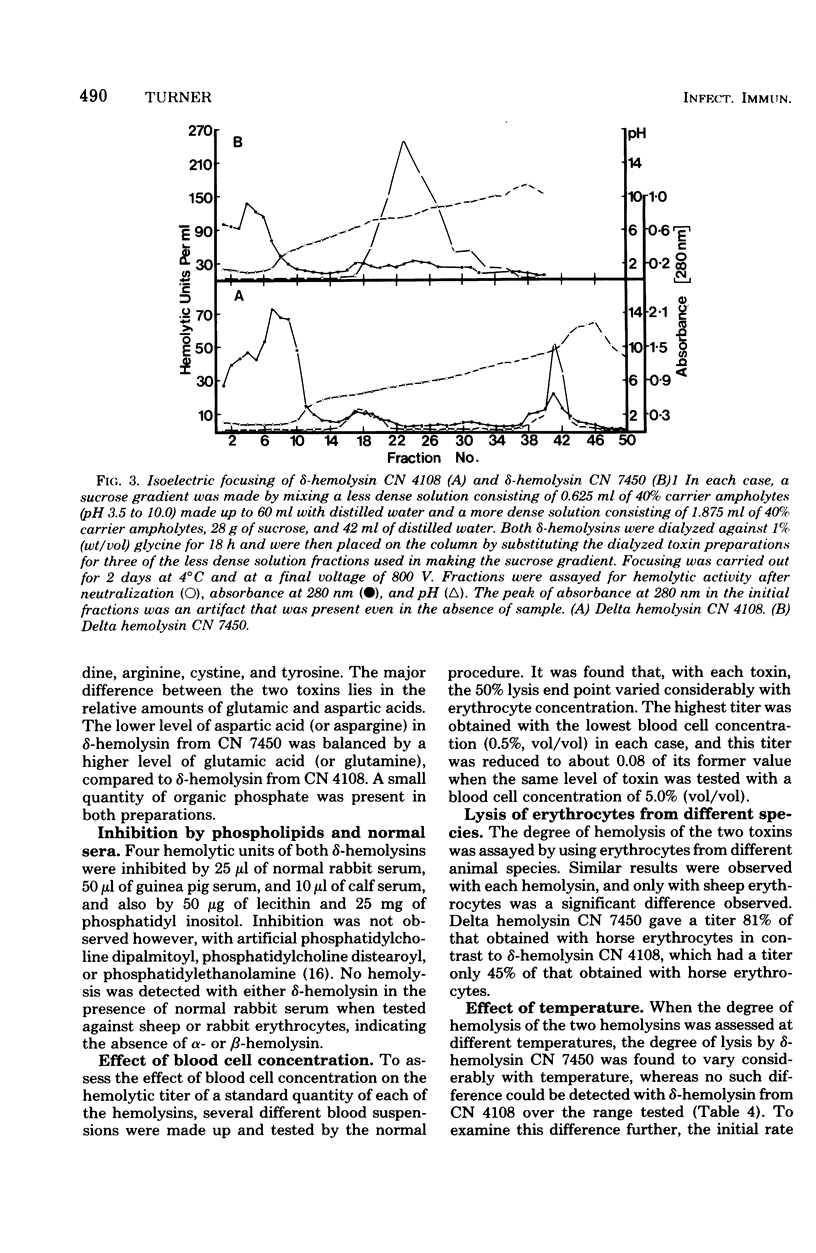
Culture supernatants of 26 strains of Staphylococcus aureus possessing delta-hemolytic activity have been tested by immunodiffusion against a serum raised against purified delta-hemolysin from S. aureus CN 4108 (Newman D2). Supernatants from 14 strains of canine origin gave a reaction of partial identity with delta-hemolysin from CN 4108, whereas supernatants from all other strains had full identity. Delta hemolysin from one of these canine strains, CN 7450, was purified by ammonium sulfate fractionation and precipitation at pH 4.5. The physical, chemical, and biological properties of this toxin were compared with those of delta-hemolysin from CN 4108. Differences in molecular weight (as judged by Sepharose 6B chromatography), isoelectric point, and amino acid composition were found. Both toxins caused dermonecrosis in rabbits, lysed erythrocytes from several different species, and were inhibited by normal sera and phospholipids. Unlike delta-hemolysin from CN 4108, the hemolytic activity of delta-hemolysin from CN 7450 was found to be dependent on the incubation temperature over the range of 25 to 37 degrees C. Immunodiffusion results obtained with antisera raised against purified delta-hemolysin from CN 7450 indicated that delta-hemolysins from the canine strains were probably identical and confirmed that these differ immunologically from delta-hemolysin from CN 4108.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COLBECK J. C. Studies in hospital infections. I. Can Serv Med J. 1956 Jul-Aug;12(7):563–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caird J. D., Wiseman G. M. Purification of the delta toxin os Staphylococcus aureus. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Aug;16(8):703–708. doi: 10.1139/m70-120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fackrell H. B., Wiseman G. M. Immunogenicity of the delta-haemolysin of Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Nov;7(4):411–414. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-4-411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLADSTONE G. P., VAN HEYNINGEN W. E. Staphylococcal leucocidins. Br J Exp Pathol. 1957 Apr;38(2):123–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gow J. A., Robinson J. Properties of purified staphylococcal beta-hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1026–1032. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1026-1032.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heatley N. G. Production of antibody to staphylococcal delta-haemolysin in the rabbit. Br J Exp Pathol. 1977 Aug;58(4):400–411. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay J. M. Production of lysozyme by staphylococci and its correlation with three other extracellular substances. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1804–1810. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1804-1810.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor H. S., Temples B., Shaw W. V. Staphylococcal delta hemolysin: purification and characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jul;151(1):142–156. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90483-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A. Effect of fatty acids on Staphylococcus aureus delta-toxin hemolytic activity. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):114–119. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.114-119.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A. Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus delta hemolysin by phospholipids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Nov;141(2):519–521. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S., Kim K. S., Zaboretzky F., Bernheimer A. W. Purification and properties of staphylococcal delta hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1971 Mar;3(3):449–465. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.3.449-465.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKS J., VAUGHAN A. C. T. Staphylococcal delta-haemolysin. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1950 Oct;62(4):597–615. doi: 10.1002/path.1700620411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny P., Turner W. H. Immunological heterogeneity of pili of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jul;89(1):87–92. doi: 10.1099/00221287-89-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omenn G. S., Friedman J. Isolation of mutants of Staphylococcus aureus lacking extracellular nuclease activity. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):921–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.921-924.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISFELD R. A., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Disk electrophoresis of basic proteins and peptides on polyacrylamide gels. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:281–283. doi: 10.1038/195281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Righetti P. G., Drysdale J. W. Isoelectric focusing in gels. J Chromatogr. 1974 Sep 25;98(2):271–321. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)92076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIERRA G. A simple method for the detection of lipolytic activity of micro-organisms and some observations on the influence of the contact between cells and fatty substrates. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1957;23(1):15–22. doi: 10.1007/BF02545855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler K. C., de Waart J., Grootsen C. Lysogenic conversion of staphylococci to loss of beta-toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Jun;39(3):321–333. doi: 10.1099/00221287-39-3-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]