Abstract
Stools from a patient with antibiotic-associated colitis and cecal contents from a hamster with clindamycin-induced enterocolitis were compared in a cytotoxicity assay to determine common properties. Both specimens produced actinomorphic changes in human amnion cells at 10(-7) dilutions. The toxin was acid labile, heat labile, nonether extractable, non-dialyzable, and produced maximum activity at 60% with ammonium sulfate precipitation. Cytotoxicity was neutralized with clostridial antitoxin but not with equine serum. Clostridium difficile was recovered in high concentrations in specimens from both the hamster and patients. The supernatants of these C. difficile strains produced cytoxic effects which were also neutralized by clostridial antitoxins. These results indicate that clindamycin-induced enterocolitis in hamsters is a model of human disease and implicate toxin-producing clostridia as responsible agents.
Full text
PDF

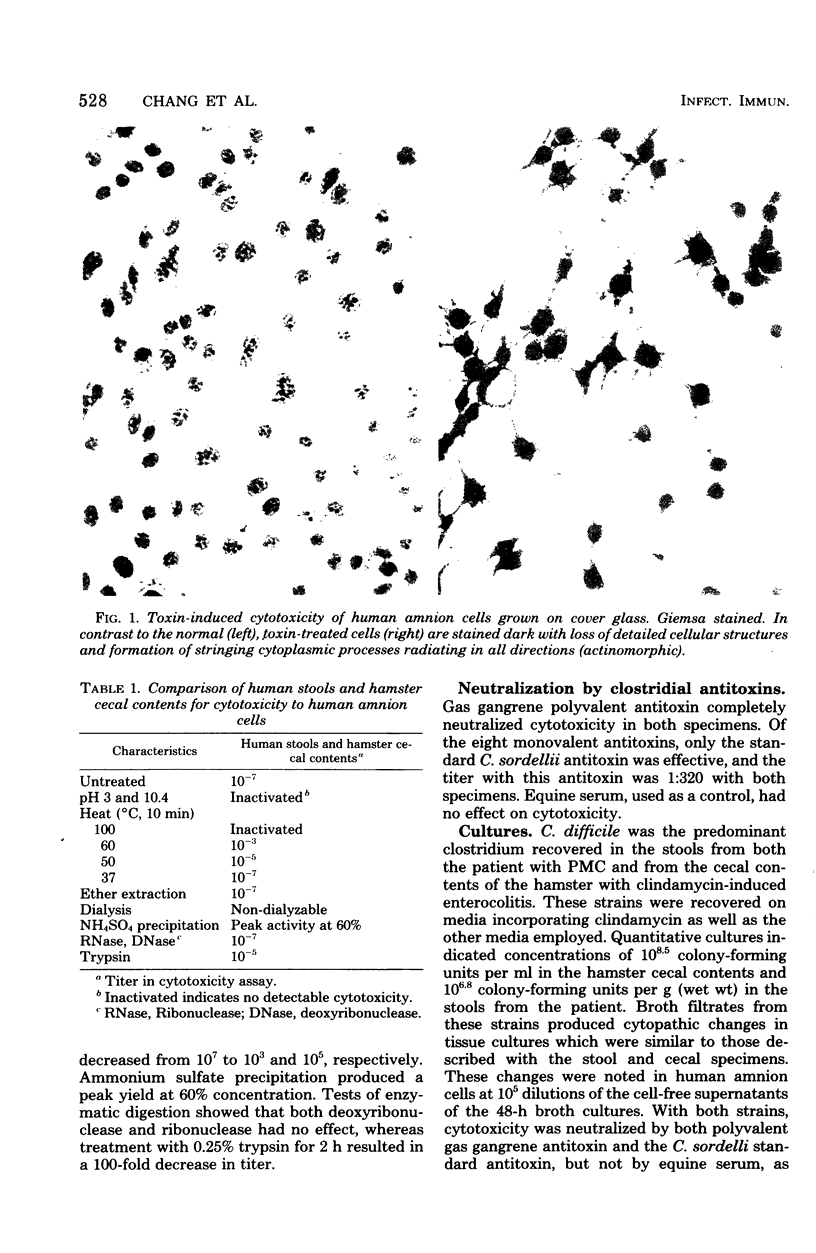

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L. Pseudomembranous enterocolitis (antibiotic-related colitis). Adv Intern Med. 1977;22:455–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Gorbach S. L. Production of vascular permeability factor by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from man. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):725–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.725-730.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson H. E., Parry J. V., Price A. B., Davies D. R., Dolby J., Tyrrell D. A. Undescribed toxin in pseudomembranous colitis. Br Med J. 1977 May 14;1(6071):1246–1248. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6071.1246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. D. Fatal enterocolitis in hamsters given lincomycin hydrochloride. Lab Anim Care. 1968 Aug;18(4):411–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



