Abstract
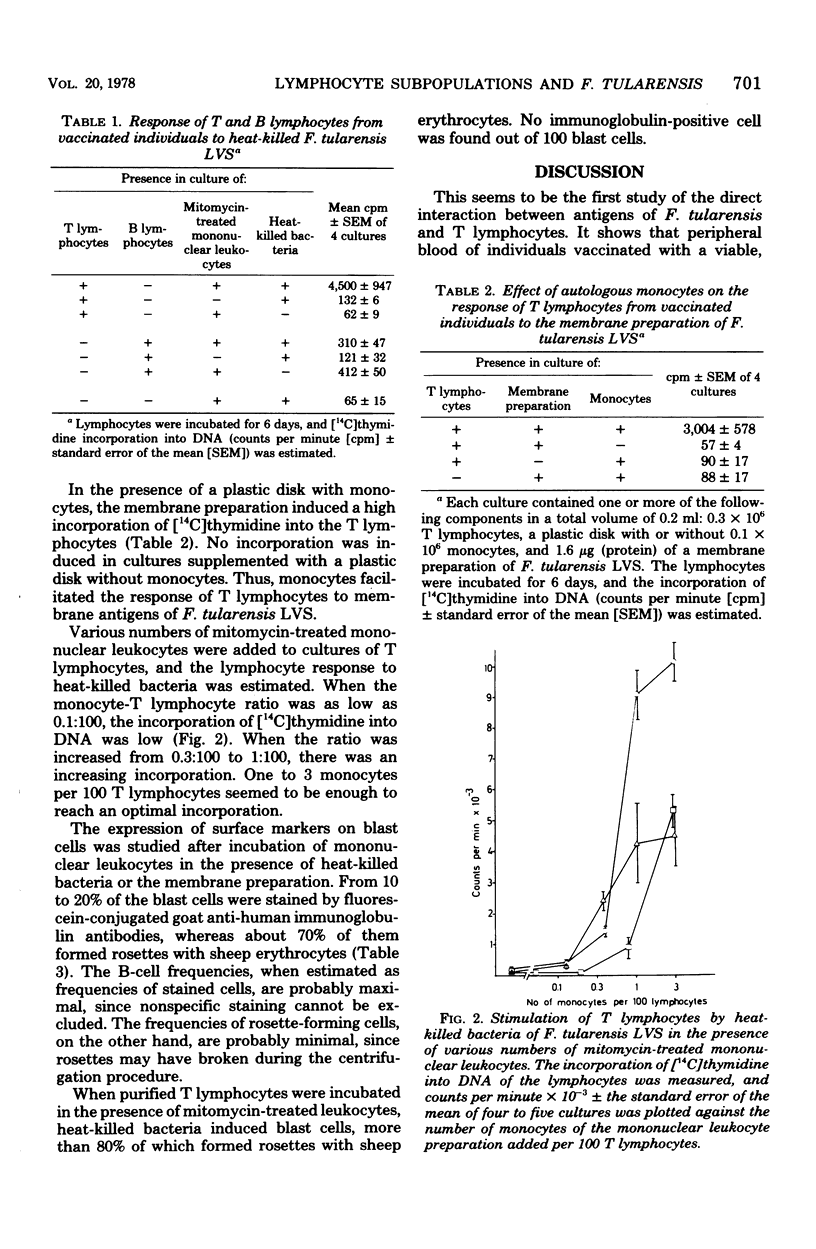
When purified T lymphocytes from individuals vaccinated with a viable, attenuated strain of Francisella tularensis were incubated in vitro in the presence of heat-killed bacteria or a membrane preparation of the vaccine strain, they were stimulated to form blast cells and to synthesize deoxyribonucleic acid. The blast cells had the characteristics of T cells, being devoid of surface immunoglobulin and able to form rosettes with sheep erythrocytes. The stimulation occurred only when monocytes were present. A lymphocyte preparation enriched in B lymphocytes did not respond to the heat-killed bacteria or to the membrane preparation. In a stimulated mononuclear leukocyte preparation, about 70% of the blast cells formed rosettes with sheep erythrocytes, and 10 to 20% of them had surface immunoglobulin. The results show that there is an enlarged population of specifically committed T lymphocytes after tularemia vaccination. It is suggested that the lymphocyte stimulation test measures mainly T-lymphocyte reactivity when membranes or whole bacteria of F. tularensis LVS are used as antigen, and that the stimulation of human T lymphocytes by whole bacteria or bacterial membranes is completely monocyte or macrophage dependent. The present experimental procedure may provide a model for study of antigen-induced stimulation of human lymphocytes under controlled conditions. The technique used gave a reproducible, extremely purified preparation of T lymphocytes and a preparation of monocytes especially suitable for microcultures.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN W. P. Immunity against tularemia: passive protection of mice by transfer of immune tissues. J Exp Med. 1962 Feb 1;115:411–420. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter B. J., Bach F. H. Lymphocyte reactivity in vitro. I. Cellular reconstitution of purified lymphocyte response. Cell Immunol. 1970 Jul;1(2):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach F. H., Voynow N. K. One-way stimulation in mixed leukocyte cultures. Science. 1966 Jul 29;153(3735):545–547. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3735.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chess L., MacDermott R. P., Schlossman S. F. Immunologic functions of isolated human lymphocyte subpopulations. II. Antigen triggering of T and B cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1122–1127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claflin J. L., Larson C. L. Infection-immunity in tularemia: specificity of cellular immunity. Infect Immun. 1972 Mar;5(3):311–318. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.3.311-318.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A. S., Chalmers D. G. Response of human blood lymphocytes to tuberculin PPD in tissue culture. Immunology. 1967 Apr;12(4):417–429. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIOGUARDI N., AGOSTONI A., FIORELLI G., LOMANTO B. Characterization of lactic dehydrogenase of normal human granulocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 May;61:713–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Schneeberger E., Rosen F. S., Merler E. Interaction of human thymus-derived and non-thymus-derived lymphocytes in vitro. Induction of proliferation and antibody synthesis in B lymphocytes by a soluble factor released from antigen-stimulated T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1230–1247. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Brown G. Purification of human T and B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):420–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzman R. J., Bach M. L., Bach F. H., Thurman G. B., Sell K. W. Precipitation of radioactively labeled samples: a semi-automatic multiple-sample processor. Cell Immunol. 1972 Jun;4(2):182–186. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh E. M., Harris J. E. Macrophage-lymphocyte interaction in the antigen-induced blastogenic response of human peripheral blood leukocytes. J Immunol. 1968 Jun;100(6):1184–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M. SRBC rosette formation as a human T lymphocyte marker. Scand J Immunol. 1976 Jun;Suppl 5:69–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb03857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. IV. Distribution of surface markers on resting and blast-transformed lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(6):739–747. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUPER S. W., BIGNALL J. R., LUCKCOCK E. D. A quantitative method for studying tumour cells in blood. Lancet. 1961 Apr 22;1(7182):852–853. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostiala A. A., McGregor D. D., Logie P. S. Tularaemia in the rat. I. The cellular basis on host resistance to infection. Immunology. 1975 May;28(5):855–869. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall W. H., Valentine F. T., Lawrence H. S. Cellular immunity in vitro. Clonal proliferation of antigen-stimulated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1969 Aug 1;130(2):327–343. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nutter J. E., Myrvik Q. N. In vitro interactions between rabbit alveolar macrophages and Pasteurella tularensis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):645–651. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.645-651.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OVERHOLT E. L., TIGERTT W. D., KADULL P. J., WARD M. K., CHARKES N. D., RENE R. M., SALZMAN T. E., STEPHENS M. An analysis of forty-two cases of laboratory-acquired tularemia. Treatment with broad spectrum antibiotics. Am J Med. 1961 May;30:785–806. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(61)90214-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet P. F., Vassalli P. Thymus-independent (B) cell proliferation in spleen cell cultures of mouse radiation chimeras stimulated by phytohemagglutinin or allogeneic cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Oct 1;136(4):962–967. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.4.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABINOWITZ Y. SEPARATION OF LYMPHOCYTES, POLYMORPHONUCLEAR LEUKOCYTES AND MONOCYTES ON GLASS COLUMNS, INCLUDING TISSUE CULTURE OBSERVATIONS. Blood. 1964 Jun;23:811–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstreich D. L., Farrar J. J., Dougherty S. Absolute macrophage dependency of T lymphocyte activation by mitogens. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):131–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger R. C., Oppenheim J. J. Synergistic interaction of macrophages and lymphocytes in antigen-induced transformation of lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1970 Jul 1;132(1):44–65. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORPE B. D., MARCUS S. PHAGOCYTOSIS AND INTRACELLULAR FATE OF PASTEURELLA TULARENSIS. 3. IN VIVO STUDIES WITH PASSIVELY TRANSFERRED CELLS AND SERA. J Immunol. 1965 Apr;94:578–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORPE B. D., MARCUS S. PHAGOCYTOSIS AND INTRACELLULAR FATE OF PASTEURELLA TULARENSIS. I. IN VITRO STUDIES WITH RABBIT PERITONEAL MONONUCLEAR PHAGOCYTES. J Immunol. 1964 Apr;92:657–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRESSELT H. B., WARD M. K. BLOOD-FREE MEDIUM FOR THE RAPID GROWTH OF PASTEURELLA TULARENSIS. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Nov;12:504–507. doi: 10.1128/am.12.6.504-507.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tärnvik A., Löfgren S. Stimulation of human lymphocytes by a vaccine strain of Francisella tularensis. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):951–957. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.951-957.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldron J. A., Jr, Horn R. G., Rosenthal A. S. Antigen-induced proliferation of guinea pig lymphocytes in vitro: obligatory role of macrophages in the recognition of antigen by immune T-lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Jul;111(1):58–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigzell H. Specific affinity fractionation of lymphocytes using glass or plastic bead columns. Scand J Immunol. 1976 Jun;Suppl 5:23–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb03853.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf-Watz H., Elmros T., Normark S., Bloom G. D. Cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: outer membrane and peptidoglycan composition of penicillin-sensitive and-resistant strains. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1332–1341. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1332-1341.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf-Watz H., Normark S., Bloom G. D. Rapid method for isolation of large quantities of outer membrane from Escherichia coli K-12 and its application to the study of envelope mutants. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):1191–1197. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.1191-1197.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


