Abstract
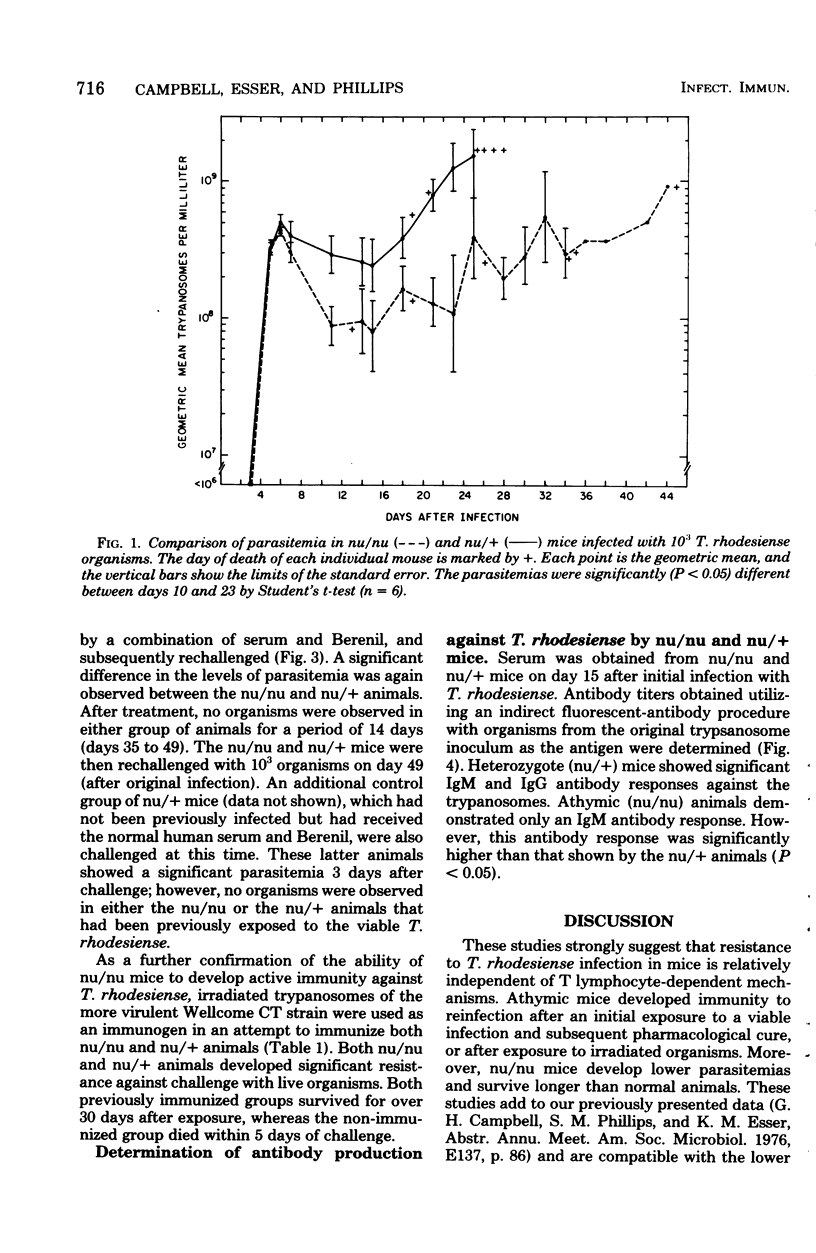
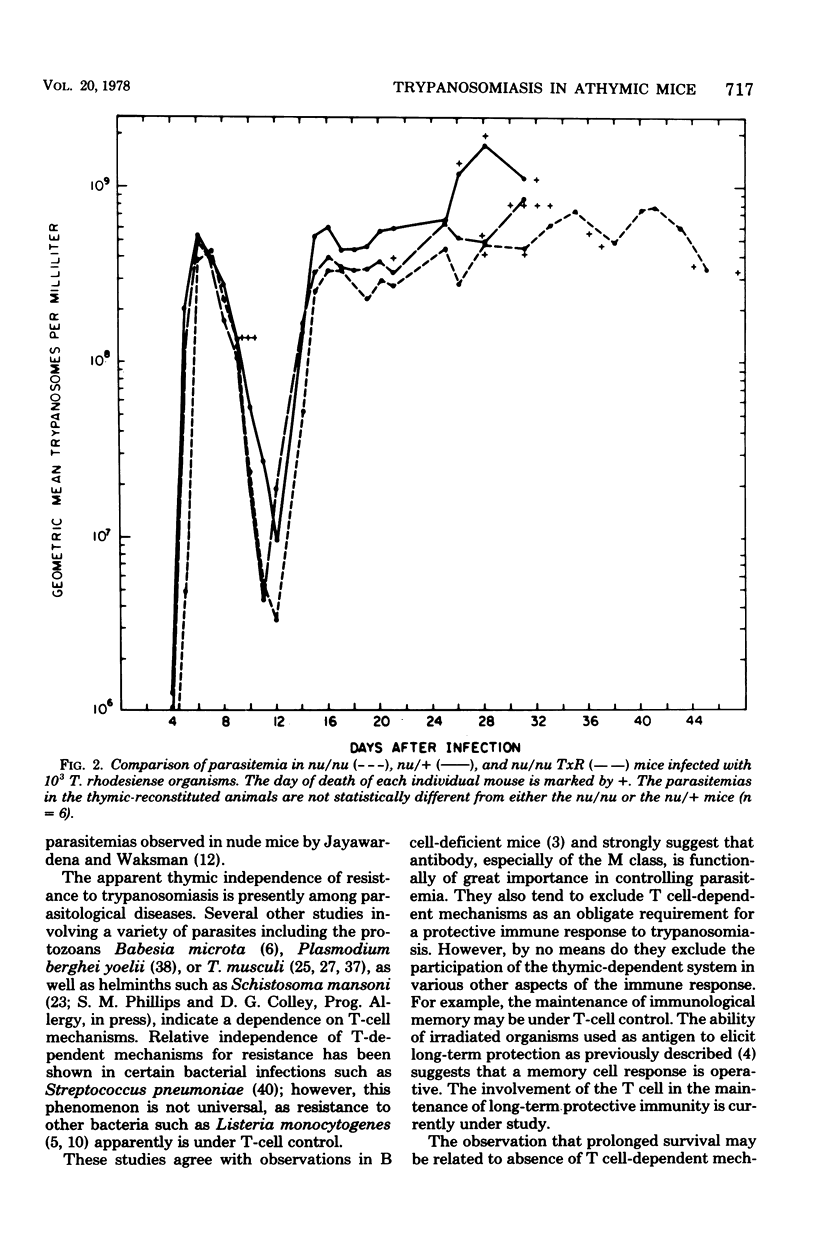
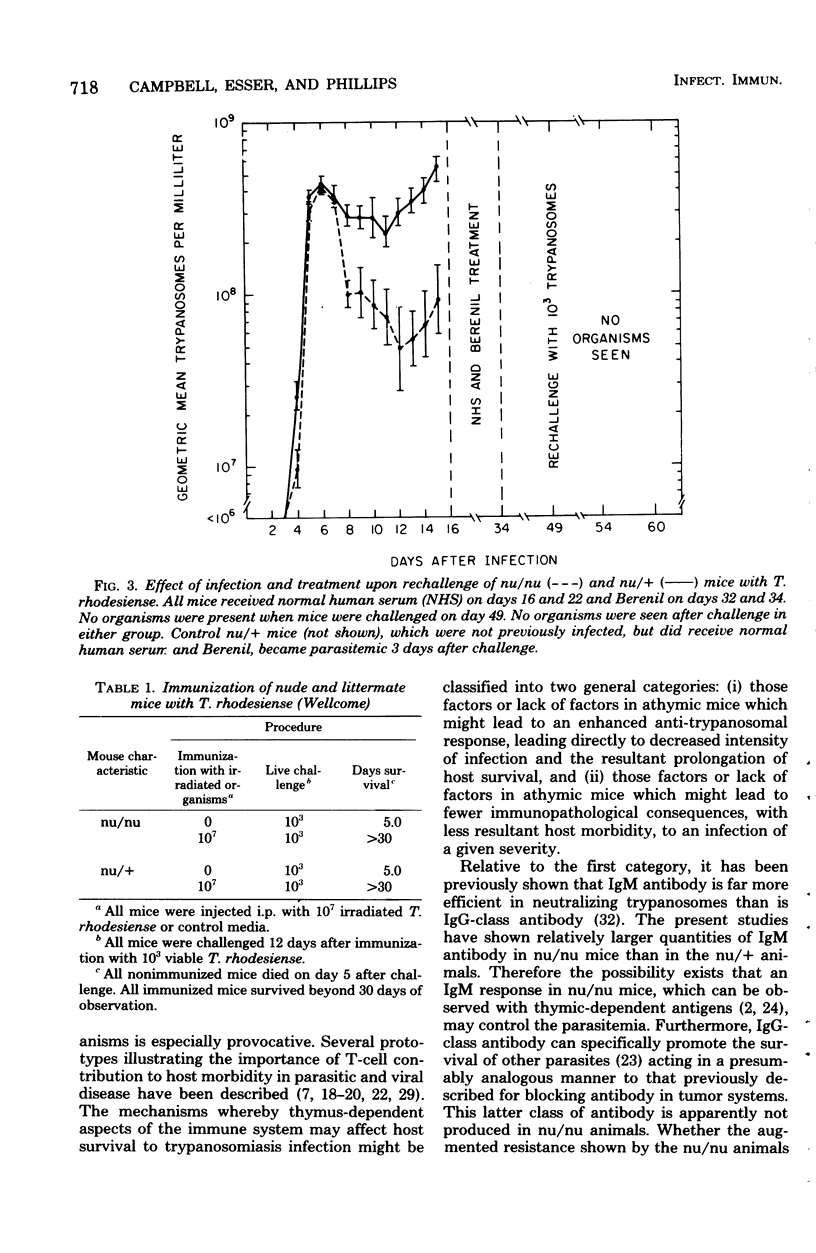
Athymic nude mice (nu/nu), heterozygous litter mates (nu/+), and thymic reconstituted homozygous animals (nu/nu TxR) were infected with Trypanosoma rhodesiense. A reduced parasitemia and prolonged survival were observed in the nu/nu animals after infection and cure or after immunization with irradiated organisms. These studies indicate that resistance of mice to T. rhodesiense infection is relatively independent of thymic lymphocyte function.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. J., Stashak P. W., Amsbaugh D. F., Prescott B., Barth R. F. Evidence for the existence of two functionally distinct types of cells which regulate the antibody response to type 3 pneumococcal polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1581–1583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns W., Billups L. C., Notkins A. L. Thymus dependence of viral antigens. Nature. 1975 Aug 21;256(5519):654–656. doi: 10.1038/256654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell G. H., Esser K. M., Weinbaum F. I. Trypanosoma rhodesiense infection in B-cell-deficient mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):434–438. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.434-438.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell G. H., Phillips S. M. Adoptive transfer of variant-specific resistance to Trypanosoma rhodesiense with B lymphocytes and serum. Infect Immun. 1976 Nov;14(5):1144–1150. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.5.1144-1150.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., Waller R. Activated macrophages in congenitally athymic "nude mice" and in lethally irradiate mice. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):844–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Allison A. C. Babesia microti and Plasmodium berghei yoelii infections in nude mice. Nature. 1974 Nov 22;252(5481):328–329. doi: 10.1038/252328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Despommier D., Weisbroth S., Fass C. Circulating eosinophils and trichinosis in the rat: the parasitic stage responsible for induction during infection. J Parasitol. 1974 Apr;60(2):280–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eardley D. D., Jayawardena A. N. Suppressor cells in mice infected with Trypanosoma brucei. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1029–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerling P., Finger H., Bockemühl J. Listeria monocytogenes infection in nude mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):437–439. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.437-439.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayawardena A. N., Waksman B. H. Suppressor cells in experimentally trypanosomiasis. Nature. 1977 Feb 10;265(5594):539–541. doi: 10.1038/265539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanham S. M., Godfrey D. G. Isolation of salivarian trypanosomes from man and other mammals using DEAE-cellulose. Exp Parasitol. 1970 Dec;28(3):521–534. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(70)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller G., Coutinho A. Factors influencing activation of B-cells in immunity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Feb 28;249:68–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle R. B., Ward P. A., Lindsley H. B., Sadun E. H., Johnson A. J., Berkaw R. E., Hildebrandt P. K. Experimental infections with African Trypanosomes. VI. Glomerulonephritis involving the alternate pathway of complement activation. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1974 Jan;23(1):15–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen K., Fogh L., Andersen S. Eosinophil response to migrating Ascaris suum larvae in normal and congenitally thymus-less mice. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Dec;82(6):919–920. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Pathogenesis of chronic disease associated with persistent lymphocytic choriomeningitis viral infection. I. Relationship of antibody production to disease in neonatally infected mice. J Exp Med. 1969 Mar 1;129(3):483–505. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.3.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Pathogenesis of chronic disease associated with persistent lymphocytic choriomeningitis viral infection. II. Relationship of the anti-lymphocytic choriomeningitis immune response to tissue injury in chronic lymphocytic choriomeningitis disease. J Exp Med. 1970 Jan 1;131(1):1–19. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantelouris E. M. Absence of thymus in a mouse mutant. Nature. 1968 Jan 27;217(5126):370–371. doi: 10.1038/217370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M., Reid W. A., Bruce J. I., Hedlund K., Colvin R. C., Campbell R., Diggs C. L., Sadun E. H. The cellular and humoral immune response to Schistosoma mansoni infections in inbred rats. I. Mechanisms during initial exposure. Cell Immunol. 1975 Sep;19(1):99–116. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90295-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. M., DiConza J. J., Gold J. A., Reid W. A. Schistosomiasis in the congenitally athymic (nude) mouse. I. Thymic dependency of eosinophilia, granuloma formation, and host morbidity. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):594–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Playfair J. H., Purves E. C. Antibody formation by bone marrow cells in irradiated mice. I. Thymus-dependent and thymus-independent responses to sheep erythrocytes. Immunology. 1971 Jul;21(1):113–121. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouliot P., Viens P., Targett G. A. T lymphocytes and the transfer of immunity to Trypanosoma musculi in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Mar;27(3):507–511. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rane L., Rane D. S., Kinnamon K. E. Screening large numbers of compounds in a model based on mortality of Trypanosoma rhodesiense infected mice. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1976 May;25(3):395–400. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1976.25.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rank R. G., Roberts D. W., Weidanz W. P. Chronic infection with Trypanosoma musculi in congenitally athymic nude mice. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):715–716. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.715-716.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V., Trainin N. Thymus cell population exerting a regulatory function in the immune response of mice to polyvinyl pyrrolidone. Cell Immunol. 1974 Jul;13(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90228-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruitenberg E. J., Steerenberg P. A. Intestinal phase of Trichinella spiralis in congenitally athymic (nude) mice. J Parasitol. 1974 Dec;60(6):1056–1057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadun E. H., Johnson A. J., Nagle R. B., Duxbury R. E. Experimental infections with African trypanosomes. V. Preliminary parasitological, clinical, hematological, serological, and pathological observations in rhesus monkeys infected with Trypanosoma rhodesiense. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1973 May;22(3):323–330. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1973.22.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayanagi T., Enriquez G. L. Effects of the IgG and IgM immunoglobulins in Trypanosoma gambiense infections in mice. J Parasitol. 1973 Aug;59(4):644–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayanagi T., Nakatake Y. Trypanosoma gambiense: enhancement of agglutinin and protection in subpopulations by immune spleen cells. Exp Parasitol. 1975 Oct;38(2):233–239. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(75)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayanagi T., Nakatake Y. Trypanosoma gambiense: immunity with thymic cell transfer in mice. Exp Parasitol. 1976 Apr;39(2):234–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(76)90123-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tizard I. R., Soltys M. A. Cell-mediated hypersensitivity in rabbits infected with Trypanosoma brucei and Trypanosoma rhodesiense. Infect Immun. 1971 Dec;4(6):674–677. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.6.674-677.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viens P., Targett G. A., Leuchars E., Davies A. J. The immunological response of CBA mice to Trypanosoma musculi. I. Initial control of the infection and the effect of T-cell deprivation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Feb;16(2):279–294. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS J. S., DUXBURY R. E., ANDERSON R. I., SADUN E. H. Fluorescent antibody reactions in Trypanosoma rhodesiense and T. gambiense in experimental animals. J Parasitol. 1963 Jun;49:380–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinbaum F. I., Evans C. B., Tigelaar R. E. Immunity to Plasmodium Berghei yoelii in mice. I. The course of infection in T cell and B cell deficient mice. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1999–2005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelstein J. A., Swift A. J. Host defense against the pneumococcus in T-lymphocyte-deficient, nude mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1222–1223. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1222-1223.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


