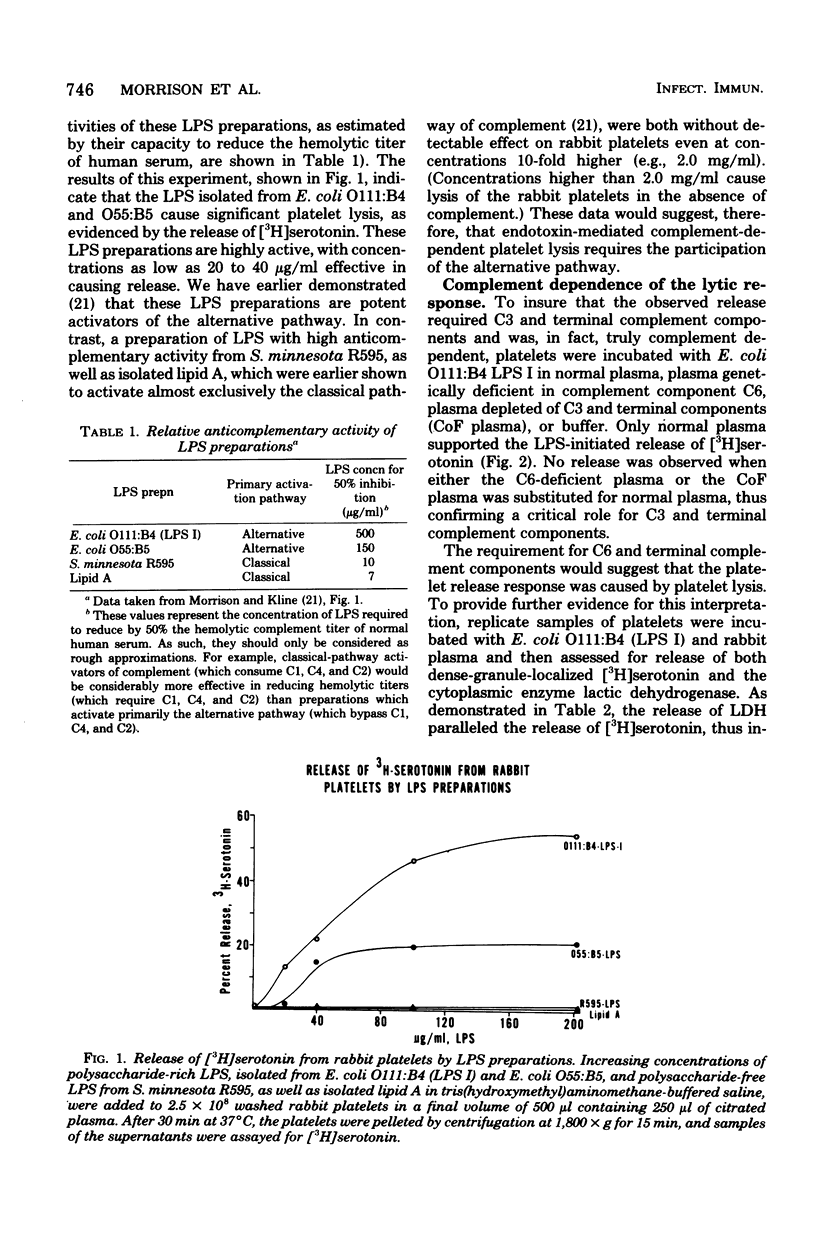
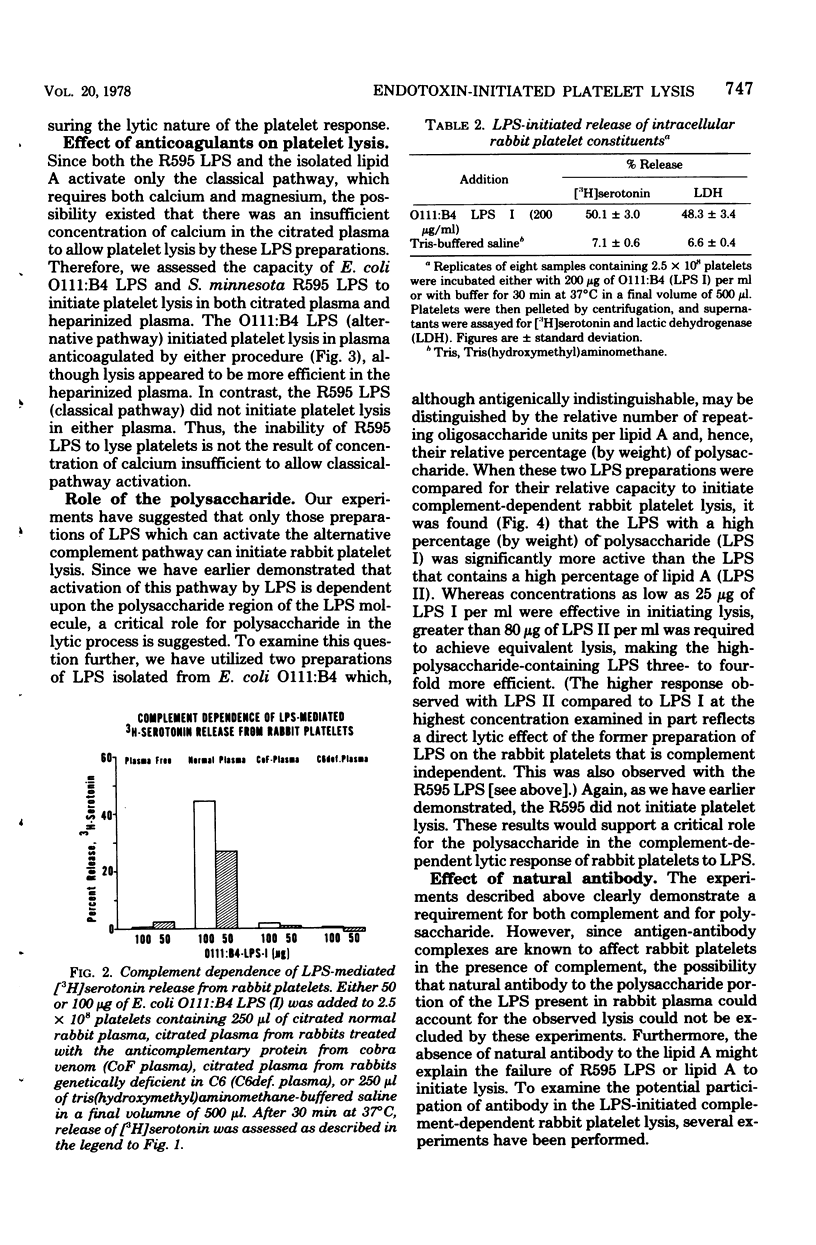
Abstract
Experiments were performed to examine the relationship of endotoxin-initiated complement activation and rabbit platelet lysis. The results of these experiments supported the concept that activation of the alternative pathway is required for endotoxin-initiated complement-dependent rabbit platelet lysis. Our data demonstrated that preparations of endotoxin or isolated lipid A, which activate selectively the classical pathway, are incapable of initiating platelet lysis. Essentially equivalent results were obtained in citrated or heparinized plasma, although the latter anticoagulated plasma appeared to be more efficient in supporting lysis. Additional data support the concept that natural antibody to either the polysaccharide or the lipid A region of the lipopolysaccharide, which might be present in rabbit plasma, probably did not play a prominent role in the complement-mediated lytic response.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown D. L., Lachmann P. J. The behaviour of complement and platelets in lethal endotoxin shock in rabbits. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1973;45(1):193–205. doi: 10.1159/000231028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS R. B., MEEKER W. R., Jr, BAILEY W. L. Serotonin release by bacterial endotoxin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Dec;108:774–776. doi: 10.3181/00379727-108-27063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DES PREZ R. M., HOROWITZ H. I., HOOK E. W. Effects of bacterial endotoxin on rabbit platelets. I. Platelet aggregation and release of platelet factors in vitro. J Exp Med. 1961 Dec 1;114:857–874. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.6.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. B. Electron microscopic changes in blood platelets induced by bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Exp Mol Pathol. 1966 Dec;5(6):559–574. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(66)90046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Prez R. M., Bryant R. E. Effects of bacterial endotoxin on rabbit platelets. IV. The divalent ion requirements of endotoxin-induced and immunologically induced platelet injury. J Exp Med. 1966 Nov 1;124(5):971–982. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.5.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Prez R. M. The effects of bacterial endotoxin on rabbit platelets. V. Heat labile plasma factor requirements of endotoxin-induced platelet injury. J Immunol. 1967 Nov;99(5):966–973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Rietschel E. T., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Interaction of lipopolysaccharides and lipid A with complement. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Mar 1;19(1):143–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOROWITZ H. I., DES PREZ R. M., HOOK E. W. Effects of bacterial endotoxin on rabbit platelets. II. Enhancement of platelet factor 3 activity in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Med. 1962 Nov 1;116:619–633. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.5.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. Activation and desensitization of platelets by platelet-activating factor (PAF) derived from IgE-sensitized basophils. I. Characteristics of the secretory response. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):937–952. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. Release of vasoactive amines from rabbit platelets induced by antiplatelet antibody in the presence and absence of complement. J Immunol. 1970 Apr;104(4):924–934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns M. A., Bruins S. C., McCabe W. R. Immunization with R mutants of Salmonella minnesota. II. Serological response to lipid A and the lipopolysaccharide of Re mutants. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):9–15. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.9-15.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Thompson R. A. Reactive lysis: the complement-mediated lysis of unsensitized cells. II. The characterization of activated reactor as C56 and the participation of C8 and C9. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):643–657. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M., Bitter-Suermann D., Dierich M. Interaction of the first (C1), the second (C2) and the fourth (C4) component of complement with different preparations of bacterial lipopolysaccharides and with lipid A. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):935–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marney S. R., Jr, Colley D. G., Des Prez R. M. Alternate complement pathway induction of aggregation and release of 5-hydroxytryptamine and adenosine diphosphate by rabbit platelets. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):696–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Jacobs D. M. Binding of polymyxin B to the lipid A portion of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Immunochemistry. 1976 Oct;13(10):813–818. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Kline L. F. Activation of the classical and properdin pathways of complement by bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS). J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):362–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Leive L. Fractions of lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli O111:B4 prepared by two extraction procedures. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2911–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Verroust P., Weigle W. O. Anticomplementary activity of lipid A isolated from lipopolysaccharides. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Sep;143(4):1025–1030. doi: 10.3181/00379727-143-37462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E., WESTPHAL O., LUDERITZ O., GORZYNSKI E. A., EICHENBERGER E. Studies of enterobacterial lipopolysaccharides; effects of heat and chemicals on erythrocyte-modifying, antigenic, toxic and pyrogenic properties. J Immunol. 1956 May;76(5):377–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagayama M., Zucker M. B., Beller F. K. Effects of a variety of endotoxins on human and rabbit platelet function. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1971 Dec 31;26(3):467–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STETSON C. A., Jr Studies on the mechanism of the Shwartzman phenomenon; certain factors involved in the production of the local hemorrhagic necrosis. J Exp Med. 1951 May;93(5):489–504. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.5.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siraganian R. P. Platelet requirement in the interaction of the complement and clotting systems. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 18;239(94):208–210. doi: 10.1038/newbio239208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siraganian R. P., Sandberg A. L., Alexander A., Osler A. G. Platelet injury due to activation of the alternate complement pathway. J Immunol. 1973 Feb;110(2):490–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielvogel A. R. An ultrastructural study of the mechanisms of platelet-endotoxin interaction. J Exp Med. 1967 Aug 1;126(2):235–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J., Cochrane C. G. Complement-dependent hemodynamic and hematologic changes in the rabbit. Inflammation. 1977 Sep;2(3):199–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00917596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J., Cochrane C. G., Henson P. M., Morrison D. C., Doe W. F. Mediation systems in bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced hypotension and disseminated intravascular coagulation. I. The role of complement. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1570–1590. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


