This study uses an RNAi screen in Drosophila to identify a UBX protein, Armless, as a novel positive regulator of the important Wingless/Wnt signaling pathway, acting to stabilize Armadillo/?-Catenin by antagonizing its turnover.
Abstract
The Wingless (Wg/Wnt) signaling pathway is essential for metazoan development, where it is central to tissue growth and cellular differentiation. Deregulated Wg pathway activation underlies severe developmental abnormalities, as well as carcinogenesis. Armadillo/β-Catenin plays a key role in the Wg transduction cascade; its cytoplasmic and nuclear levels directly determine the output activity of Wg signaling and are thus tightly controlled. In all current models, once Arm is targeted for degradation by the Arm/β-Catenin destruction complex, its fate is viewed as set. We identified a novel Wg/Wnt pathway component, Armless (Als), which is required for Wg target gene expression in a cell-autonomous manner. We found by genetic and biochemical analyses that Als functions downstream of the destruction complex, at the level of the SCF/Slimb/βTRCP E3 Ub ligase. In the absence of Als, Arm levels are severely reduced. We show by biochemical and in vivo studies that Als interacts directly with Ter94, an AAA ATPase known to associate with E3 ligases and to drive protein turnover. We suggest that Als antagonizes Ter94's positive effect on E3 ligase function and propose that Als promotes Wg signaling by rescuing Arm from proteolytic degradation, spotlighting an unexpected step where the Wg pathway signal is modulated.
Author Summary
The Wg/Wnt signaling pathway, found in most animals, is essential for regulating tissue growth and the formation of different cell types during development. Defects in the Wg/Wnt signaling relay can have serious consequences, ranging from aberrant organ patterning to malignant tumor formation. A pivotal step in the transmission of the Wg/Wnt signal is the stabilization of the protein Armadillo/β-Catenin, a key component of the pathway. However, the means by which the levels of this protein are regulated remain unclear. Here, we describe a novel control point of Armadillo/β-Catenin levels. Using RNA interference, we performed a screen in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster and identified Armless, a protein whose biological function was previously unknown, as a novel regulator of Wg/Wnt signaling, essential for the Wg/Wnt-dependent expression of downstream target genes. Our experiments suggest that Armless interferes with the tagging of Armadillo/β-Catenin with ubiquitin, thereby sparing it from proteasomal degradation. We also show that Armless directly interacts in vivo with Ter94, a ubiquitous ATPase involved in protein turnover. Our results suggest that Armless antagonizes Ter94's function in protein turnover, thereby acting as a positive regulator of Wg/Wnt signaling by promoting the stabilization of Armadillo/β-Catenin.
Introduction
The wingless (wg) gene was found nearly forty years ago with the characterization of a Drosophila mutant without wings [1]. The gene encodes a secreted glycoprotein, the founding member of the Wnt family of signaling proteins [2]. In the decades following its discovery, Wg/Wnt signaling has been shown to be essential during embryogenesis. Indeed, it is important throughout an organism's life, controlling also the homeostasis of different organs, for example, regeneration of epithelial cells in the intestine—the aberrant behavior of these cells in cancer is caused by constitutive Wg/Wnt signaling, which is consequently a key focus of medical and translational research [3],[4].
The relay of the Wg signal is controlled at different levels. However, the pivotal step is the regulation of the levels of Armadillo (Arm)/β-Catenin, the key transducer of the Wg/Wnt pathway. A multiprotein complex consisting of the scaffold proteins Axin and APC and the kinases Shaggy/GSK3β and Casein kinase I (CKI) recruits and phosphorylates Arm/β-Catenin. This marks Arm/β-Catenin for ubiquitination by the SCF/Slimb/βTRCP E3 ubiquitin ligase and subsequent degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS). When Wg/Wnt binds its receptors at the cell membrane, degradation of Arm/β-Catenin is prevented, presumably by protein interactions that lead to the dissociation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase from the Arm/β-Catenin destruction complex [5]. As a consequence, Arm/β-Catenin translocates into the nucleus, where it adopts its role as a transcriptional effector of Wg/Wnt signaling. Although this step is crucial, and is a potential point of regulation, little is known about the players involved in the processing of Arm/β-Catenin and its ultimate degradation.
In a genome-wide RNA interference (RNAi) screen we isolated Armless (Als) as a regulator of proximodistal growth of Drosophila limbs, and show in subsequent analyses that it exerts its function in the Wg pathway. Detailed genetic studies demonstrate that Als acts downstream of the destruction complex, at the level of the SCF/Slimb/βTRCP E3 Ub ligase. Cells depleted for Als exhibit strongly reduced Arm protein levels. Importantly, the activity of a constitutively active form of Arm, ArmS10, which cannot be phosphorylated and hence escapes ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation, is insensitive to depletion of Als. Using immunopurification and mass spectrometry analysis we found that Ter94 interacts with Als. Ter94 is an AAA ATPase associated with protein turnover and proteasomal degradation [6]. In sum, our data suggest that Als acts downstream of the Arm/β-Catenin destruction complex to positively regulate Arm protein levels, possibly by rescuing Arm from ubiquitination via Slimb. The human ortholog of Als, UBXN6, can substitute for Als in Drosophila, and Wnt target gene expression was impaired upon knock-down of UBXN6 in HEK-293 cells. We thus infer that Als and UBXN6 represent regulators of a conserved mechanism that ensures appropriate levels of Armadillo/β-Catenin by antagonizing its entry into the UPS.
Results
CG5469/armless Is Required for Wing Growth
Among its numerous developmental roles, Wg controls growth and patterning of the Drosophila wing. A hallmark phenotype of reduced wg function is nicked wings with reduced size. Positively acting components of the Wg pathway mostly display similar phenotypes when depleted via RNAi during larval stages. We established and used a tester system that allowed screening for genes involved in wing growth and margin formation. Our screen covered approximately 83% of all the predicted 14,306 genes of Drosophila. The details of the screen will be published elsewhere. CG5469 behaved as expected of a putative Wg signaling component: RNAi targeting its transcripts affected wing size in a non-allometric manner and caused a notched margin and loss of sensory bristles. This phenotype could be reproduced by the expression of nine independent UAS-CG5469RNAi lines with different Gal4 drivers (Figures 1B–1E and S1A–S1J). Expression of CG5469RNAi effectively reduced mRNA levels of CG5469 (Figure S1L, cf. Figure 1B–1E), and haplo-deficiency exacerbated the wing phenotypes (Figure S1M and S1N); these phenotypes were rescued upon overexpression of CG5469, as detailed in Text S1 and shown in Figure S2.
Figure 1. alsRNAi causes notched wing margins.

c765-Gal4 drives the expression of different UAS-alsRNAi transgenes in the entire wing primordium at 29°C, which results in nicked wing margins, accompanied by loss of sensory bristles. (A) Gal4 driver only, (B) VDRC line 39000, (C) VDRC line 105104, (D) oligo3, (E) oligo2.
Wing notches could be caused by increased apoptosis or reduced cell proliferation. To discriminate between these possibilities, we experimentally accelerated cell divisions by string/cdc25 overexpression [7], and inhibited apoptosis by Diap1 overexpression. Only string/cdc25 overexpression restored marginal wing tissue loss caused by depletion of CG5469 (Figure S3F). This finding is consistent with a role of CG5469 in Wg signaling, as impaired Wg pathway activity affects primarily proliferation (Figure S3A–S3C; [8],[9]). Because of its mutant phenotypes, which are caused by severely reduced levels of Arm (see below), we refer to CG5469 as armless (als; for the nomenclature see also Text S1).
als Interacts with the Wg Pathway and Is Required for Wg Target Gene Expression
To further test whether als interacts with Wg signaling, we analyzed the effects of alsRNAi in different, sensitized backgrounds. Interfering with the Wg pathway at various levels leads to typical wing margin notches and loss of distal wing tissue (Figure S3G–S3J). These phenotypes were enhanced upon als depletion (Figure S3G′–S3J′). To test whether als is also involved in the Wg pathway in other developmental contexts, we expressed alsRNAi in the primordia of the dorsal thorax and the legs. Again, consistent with a role of als in the Wg pathway (Figure S4D and S4H; [10],[11]), thorax and scutellum sizes were affected (Figure S4B, S4C, S4F, and S4G, cf. Figure S4A), and showed reduced or missing microchaete, a slight misorientation of remnant micro- and macrochaete, and mild thoracic clefts (Figure S4B and S4C). Depletion of als in the leg discs caused a reduction of tarsal segments along the proximodistal axis and a dorsolateral shift of the sex combs—phenotypes characteristic of reduced Wg signaling (Figure S4J–S4M; [12],[13]). Stronger alsRNAi expression caused a dorsalization of the leg as judged from the mirror-image patterning of leg trichomes (Figure S4K and S4M). To analyze the phenotype at earlier stages of development, we expressed alsRNAi or AlsHA (a dominant-negative-like version; see Text S1) in the embryo with da-Gal4. We found that cuticles were shorter than in control embryos, with ventral denticle belts partially fused, which is indicative of a segment polarity defect (Figure S4S–S4V, S4X, and S4Y). These phenotypes are reminiscent of milder Wg loss-of-function phenotypes caused by armRNAi or UAS-Lgs17E expression (Figure S4P–S4R and S4W) by da-Gal4.
To further test whether als is required for Wg signaling output, we monitored the expression of well-known Wg target genes. Wg is secreted from a stripe of cells at the dorsoventral (D/V) border and triggers a transcriptional response in cells along the D/V axis of imaginal wing discs (the future proximodistal axis of the adult wing). Wg activates the proneural gene senseless (sens) in sensory organ precursors, which develop into the bristles of the adult wing margin [8],[14]. alsRNAi expression in the P-compartment resulted in a loss of Sens therein (Figure 2A and 2A′). Expression of Distalless (Dll), frizzled3 (fz3), and wingful (wf), which are activated by Wg in a broader region centered on the D/V border [15],[16], was strongly reduced or lost in response to reduction of als function (Figure 2B–2E). Conversely, arrow (arr), which is normally repressed by Wg signaling in central pouch regions (Figure 2F; [17]), became ectopically activated towards the central wing pouch (Figure 2G). In sum, these observations strongly suggest that als encodes a component with a positive role in the Wg pathway.
Figure 2. als is required for Wg-dependent target expression.

L3 wing imaginal discs; anterior is to the left, posterior is to the right. alsRNAi expression in the P-compartment of wing imaginal discs (visualized by the co-expression of UAS-GFP, green fluorescence) (A–C′) or in the entire wing pouch (D–G) causes loss of expression of Wg-signaling-dependent target genes—Senseless (A and A′) (line 39000), Distalless (B and B′) (line oligo3), frizzled3 (C and C′) (line oligo3), or wingful (D and E; white arrows indicate the Wg-dependent expression domain of wf at the D/V border which is lost in E.) (line 39000)—and ectopic expression of arrow, which is a negative target (G c.f. F; white arrows indicate the extent of the domain that is free from arrow-lacZ expression) (line oligo3).
To try to gain insight into the pathways als might regulate, we further looked at als expression. In situ hybridization and lacZ reporter transgenes indicated that als is expressed at early third instar wing imaginal discs at the center of the pouch adjacent to the D/V border and, at faint levels, throughout the wing primordium (Figure S5A–S5C). Furthermore, the expression of UAS-alsRNAi in the P-compartment of wing imaginal discs caused a strong decrease in als expression (Figure S5B, inset). Interestingly, although normal when Wg signaling is inhibited, als expression could be upregulated when Wg signaling was activated by the overexpression of either Wg or ArmS10, and stimulation of Wg signaling by the inhibition of GSK3β caused elevated Als and als levels (Figures S5D and 8A). This is consistent with als functioning in the Wg pathway and having its activity fine-tuned by feedback mechanisms that ensure maximum pathway activity.
als Is Not Required for Notch or Hedgehog Signaling
Wing notching is a phenotype characteristic not only of impaired Wg signaling, but also of reduced Notch signaling. The activities of both pathways are required to establish the D/V border and subsequent proximodistal wing growth. To determine whether als also plays a role in the Notch pathway, we analyzed the expression of the following Notch targets: (1) the proneural gene e(spl)m8 (Figure S6A; [18]), (2) a Notch responsive element (NRE) reporter (Figure S6A inset; [19]), and (3) the vestigial (vg) “boundary enhancer” (Figure S6B; [20]). In contrast to what we observed for the Wg targets above, the expression patterns of these Notch reporters were unaltered upon als depletion (Figure S6A′–S6B″). Moreover, neither did reduction of als function suppress the phenotypes caused by elevated Notch signaling (Figure S6D and S6F, cf. Figure S6C and S6E), nor did it ever mimic a neurogenic thorax phenotype or fused tarsal segments (Figure S4), which are both typical for reduced Notch signaling. Finally, we monitored the expression of the wg gene itself, which is under control of Notch activity [21]–[23]. Neither wg transcription nor Wg protein expression were affected at the D/V boundary upon alsRNAi expression (Figure S7A–S7G).
We also tested other pathways involved in wing growth and patterning, such as Hedgehog (Hh) signaling. Increased Hh signaling causes wing overgrowth predominantly along the anteroposterior (A/P) axis, along with ectopic veins in the A-compartment (Figure S6G). als depletion impaired wing growth along the proximodistal axis, which is under control of Wg signaling, but not along the A/P axis, and it did not alter the vein patterning defects caused by increased Hh signaling (Figure S6H). Furthermore, expression of the Hh target gene patched (ptc) was not affected by als depletion (Figures S6I, S6J, and 8E). In addition, we tested Upd/Jak/Stat signaling and EGFR/Ras signaling and found that none of these pathways was affected by als depletion (Figure S6K–S6N). Our findings therefore suggest a specific role for als in Wg signaling in the tissues that we have tested.
Mapping Als Action by Cell Autonomy and Epistasis Analyses
To investigate whether Als functions in Wg producing or receiving cells, UAS-alsRNAi was expressed in clones of wing imaginal cells marked by GFP co-expression. Expression of the Wg target Sens was lost in early induced clones (Figure 3A–3A″). This effect is cell-autonomous, i.e., it also occurs when mutant cells are close to wild-type cells that produce Wg. Adult wing clones, marked by UAS-forkedRNAi co-expression, had wing notches and thickened veins (Figure 3B–3E), both of which were tightly associated with mutant cells. We observed similar phenotypes when Wg signaling was cell-autonomously impaired (Figure 3F–3I).
Figure 3. als acts in a cell-autonomous manner.
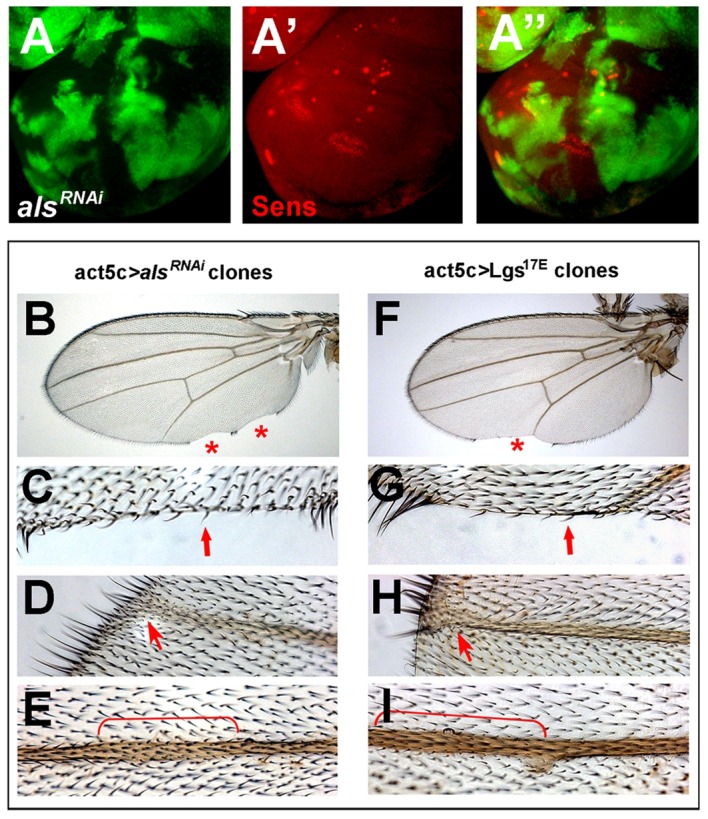
Wg target gene expression (Sens) is affected cell-autonomously upon impaired als function as judged from wing disc analysis at the late L3 stage (A–A″). GFP expression indicates cell clones expressing alsRNAi line oligo310UAS (A and A″). Adult wing phenotypes coincide with cell clones that experienced als depletion, as marked by forked wing hairs (B–E). This is reminiscent of adult wing phenotypes obtained when Wg signaling is impaired (Lgs17E expression) (F–I). Red asterisks (B and F) indicate notches at the wing margin; red arrows (C and G) indicate wing margin notches accompanied by loss of mechano- and sensory bristles; red arrows (D and H) and brackets (E and I) indicate broadened veins.
To map where Als acts in the Wg pathway, we used phenotypic assays based on the activation or inactivation of Wg signaling in the eye or the wing. Expression of Wg under control of the sevenless (sev) enhancer causes small, narrow eyes that lack interommatidial bristles (Figure 4B; [24],[25]). This phenotype is partially suppressed when Wg signal transduction is hindered, for example, by the expression of a dominant-negative form of Lgs (Lgs17E [26]; Figure 4G). Impaired als function also causes a suppression of the sev-wg phenotype (Figure 4C–4F). In contrast, depletion of als did not alter the small eye phenotype caused by the overexpression of Eiger (Figure 4H–4J), a trigger of the apoptotic pathway [27].
Figure 4. als acts downstream of Wg.
Control eye with ey-Gal4, GMR-Gal4/+ (A). The small eye phenotype based on sev-wg expression (B) can be suppressed by the expression of different UAS-alsRNAi transgenes (C–E), by expression of UAS-alsHA(DN) (F), and by overexpression of Lgs17E, which suppresses Wg signaling (G). The small eye phenotype based on enhanced apoptosis (H) is not altered upon als depletion (I and J).
We manipulated the Wg signaling cascade in the wing and the eye at successively more downstream positions and assessed the requirement of Als for the manifestation of the respective Wg gain-of-signaling phenotypes (see legend of Figure 5 for a detailed description of phenotypes). First, we found that Als depletion suppressed Wg pathway activation caused by RNAi of notum/wingful (encoding an extracellular inhibitor of Wg [28],[29]) or by overexpression of Arrow (co-receptor of Wg, [17]) or Dishevelled (Figure 5A–5B′, 5L, and 5L′). Next, we tested knock-downs of components of the destruction complex, both in the wing and the eye, and found that aberrant Wg output was suppressed by alsRNAi for Axin, APC, and Shaggy/GSK3β (Figure 5C, 5C′, 5D, 5D′, 5H–5K′, 5M, and 5M′). Only the phenotypes of RNAi against the SCF/Slimb/βTRCP E3 ubiquitin ligase [30] and expression of ArmS10, a constitutively active form of Arm/β-Catenin [31], could not be ameliorated by als depletion (Figure 5E–5F′ and 5O–5Q′). Interestingly, wild-type Arm could not overcome the alsRNAi phenotypes in the wing and the eye, and did not lead to the emergence of ectopic sensory bristles (Figure 5G, 5G′, 5R, and 5R′). We interpret these genetic findings to indicate that Als functions upstream of Arm, but downstream of the Arm/β-Catenin destruction complex, possibly at the level of the SCF/Slimb/βTRCP E3 Ub ligase.
Figure 5. als functions downstream of the Arm/β-Catenin destruction complex and upstream of activated Armadillo.
Overexpression of the positive components Arrow (A), Dishevelled (L), ArmS10 (F and Q), or Arm (G and R) and depletion of negative components such as wingful (B), shaggy (C, H, and I), apc (D and J), slimb (E, O, and P), and axin (K) cause phenotypes that reflect ectopic Wg signaling: ectopic sensory bristles (A–G), ectopic veins (A–C), and tissue overgrowth (A, H–K, O, and P), but also reduced organ size upon strong pathway activation (B–F, L, M, and Q) and caused ectopic head cuticle (H–J, L, and M). Co-expression of alsRNAi could suppress these phenotypes in the wing (A′–D′) and the eye (H′–M′). Phenotypes based on slimbRNAi and ArmS10 expression could not be suppressed upon als depletion (E′, O′, P′, F′, and Q′). Arm overexpession could not rescue alsRNAi phenotypes (G′ and R′). Heads were photographed from dorsal views (left pictures of H–K′) or lateral views, anterior to the left (right pictures of H–K′, L–R′). alsRNAi lines: oligo310UAS (A′–E′) and for the eye analysis; oligo2_5′utr (G′).
als Encodes a UBX Domain Protein That Localizes in the Cell Cortex and Depends on a Functional PUG-Domain
Three different protein domains can be distinguished within Als: (1) an N-terminal coiled-coil domain, (2) a PUG domain, and (3) a UBX domain (Figure S9). Coiled-coil domains function in protein oligomerization, whereas the PUG und UBX domains are found in ubiquitin regulatory proteins [32]. To find out more about its molecular role, we tested where Als localizes within cells and which of its protein domains are functionally required. N-terminally tagged HAAls localized close to the cell membrane in a punctate ring pattern (Figure S8A–S8B′), with strongest expression in the apical region of the cell (Figure S8C, S8D, S8E). This localization is reminiscent of that of E-Cadherin, Arm, and the Wg receptor Frizzled2 (Fz2, Figure S8C–S8E″). We then expressed Als protein variants that lacked particular domains and assessed whether these could rescue the alsRNAi phenotypes. For this we created tagged and untagged constructs that were either sensitive or insensitive to the RNAi used. Expression of AlsΔN and AlsΔPUG did not alter the alsRNAi phenotype (Figure S9A–S9I), irrespective of their tag or targetability. However, expression of AlsΔUBX as well as full-length Als protein substantially rescued the wing phenotypes caused by alsRNAi (Figure S9J–S9L). This suggests that the UBX domain is dispensable for Als function, whereas the N-terminal and the PUG domains are both important. The requirement of the PUG domain implicates Als in playing a role in a ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation process.
Als Interacts with Ter94, a Conserved ATPase Involved in Protein Turnover
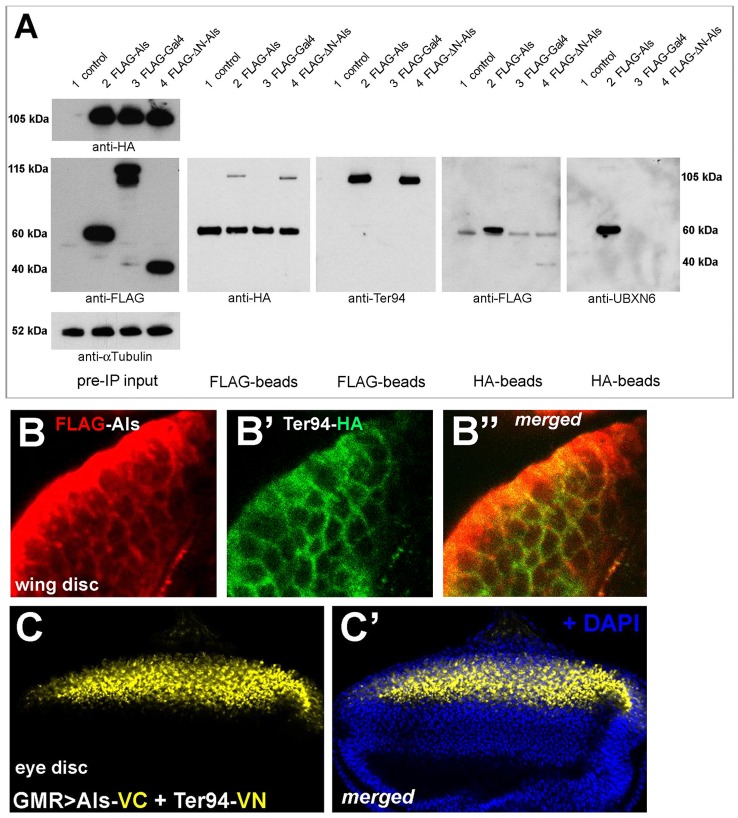
To further our understanding of Als function, we expressed HA-tagged variants of Als in Drosophila Kc-167 cells, and after affinity purification we subjected the samples to shotgun liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). In three independent experiments using AlsHA, HAAls, and HAAlsΔUBX, but not in the negative control sample, we identified Ter94 as the highest ranking protein interactor of Als (see Text S1), irrespective of the stimulation of the Wg pathway by Wg. Ter94 is the Drosophila ortholog of p97, an AAA ATPase found to be associated with ubiquitin-dependent protein degradation processes, and that can interact with different UBX domain proteins [33],[34]. To further validate the interaction between Als and Ter94 we co-expressed Ter94HA together with FLAGAls, FLAGAlsΔN, and FLAGGal4, which served as a negative control, in Kc-167 cells. Western blot analyses following reciprocal immunoprecipitations showed that (1) Ter94HA and endogenous Ter94 co-immunoprecipitated with FLAGAls and FLAGAlsΔN, and (2) FLAGAls, FLAGAlsΔN, and endogenous Als co-immunoprecipitated with Ter94HA (Figure 6A). When we expressed Ter94HA in wing imaginal discs, we found a strikingly similar sub-cellular distribution and co-localization with FLAGAls (Figure 6B–6B″). Importantly, we demonstrated a physical interaction between Als and Ter94 in vivo with bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) analysis (Figure 6C and 6C′; [35]; see also Materials and Methods), where the co-overexpression of Als-VC and Ter94-VN resulted in a Venus-YFP fluorescent signal. In sum, our biochemical and genetic results indicate that Als molecularly interacts with Ter94. The UBX domain is dispensable for Als to bind to Ter94, which is in agreement with our finding that Als lacking the UBX domain could still rescue the alsRNAi phenotype.
Figure 6. Als co-localizes and interacts with Ter94.
(A) Western blot analysis after immunoprecipitation (IP) of FLAGAls or Ter94HA. Condition 1: negative control (empty pUAST-attB vector), condition 2: FLAGAls (60 kDa), condition 3: negative control (FLAGGal4, 115 kDa), condition 4: FLAGΔN-Als (40 kDa); Ter94HA (105 kDa) was co-expressed in conditions 2–4. Ter94 binds to full-length Als (condition 2) and ΔN-Als (condition 4), and vice versa. The anti-human-UBXN6 peptide antibody recognizes only the full-length Als, but not ΔN-Als. (B–B″) Transgene expression by nubbin-Gal4 in wing imaginal disc cells shows that FLAGAls co-localizes with Ter94HA. (C and C′) Co-expression of Als-VC and Ter94-VN with GMR-Gal4 in eye imaginal discs results in a Venus YFP fluorescence signal, which demonstrates a physical interaction between Als and Ter94.
Armadillo Levels Depend on als Activity
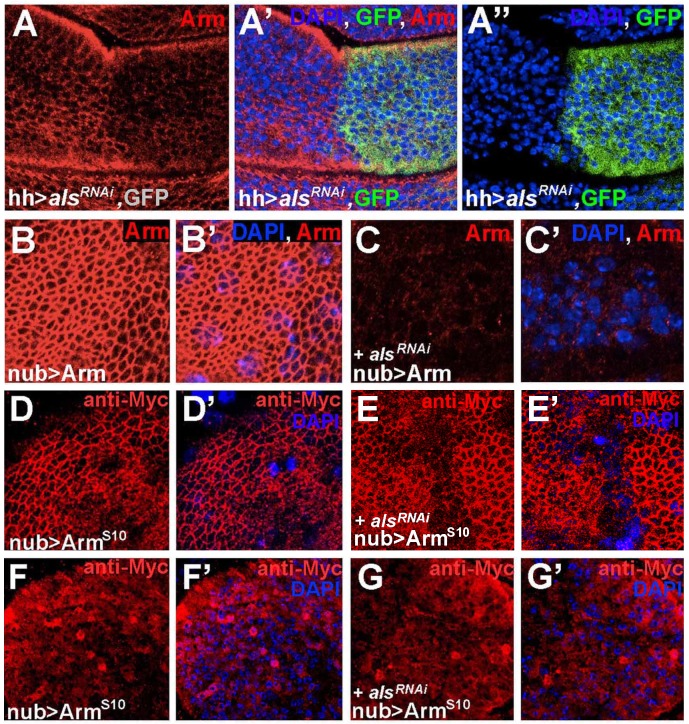
Our biochemical and genetic studies suggest that Als is functionally linked to the proteasomal degradation pathway. Since Als is positively required for Wg signaling, it could exert its function in the pathway either by suppressing the degradation of a positive component, or by enhancing the degradation of a negative component. We first analyzed the protein levels of key negative pathway components in wing imaginal discs. We expressed different alsRNAi lines in the wing primordium with nub-Gal4; however, neither Axin nor Shaggy nor Apc2 levels were affected upon als depletion (Figure S10A–S10L); [36]). In contrast, we found that the protein levels of Arm, the key positive signaling component, were dependent on als: when alsRNAi was expressed in the P-compartment under the control of hh-Gal4, Arm levels were strongly reduced in P but not A cells (Figure 7A–7A″). Even when we overexpressed Arm under the control of nub-Gal4, co-expression of alsRNAi led to strongly reduced Arm levels (Figure 7C and 7C′, cf. Figure 7B and 7B′). DAPI staining shows that all cells have normally shaped nuclei and are thus not apoptotic (Figure 7A′, 7A″, 7C, and 7C′). Constitutively active, non-degradable ArmS10 localizes like Arm to the apical membrane upon overexpression (Figure 7D and 7D′), and was also observed at higher levels in the cytoplasm (Figure 7F and 7F′). Importantly, we found that ArmS10 levels were not altered in als-depleted wing imaginal disc cells (Figure 7E, 7E′, 7G, and 7G′). This is consistent with our finding that ArmS10 overexpression could completely overcome the phenotypes caused by als depletion (Figure 5F, 5F′, 5Q, and 5Q′). Other positively acting components of the Wg pathway, Arrow and Fz2, did not exhibit alterations in protein levels upon alsRNAi expression (Figure S10M–S10P). The observation that Arm is subject to degradation in the absence of als function is in agreement with our observation that overexpressed Arm—in contrast to ArmS10—is not able to rescue alsRNAi phenotypes in wing and eye primordia (Figure 5G′ and 5R′).
Figure 7. Reduction of Armadillo levels upon als depletion.
(A–A″) als depletion (line oligo310UAS) in the P-compartment of wing imaginal discs caused reduced Arm protein levels compared to the A-compartment (A′ and A″). CD8-GFP expression marks the cell membranes of the P-compartment, and DAPI staining marks all cellular nuclei. (B and B′) The expression of Arm driven from a transgene by nub-Gal4 is similar to endogenous Arm (cf. Figure S8D′). (C and C′) Upon als depletion (line 39000), Arm levels were strongly reduced. (D–G′) DAPI staining (D′–G′) visualizes the large nuclei of the peripodial membrane (blue, out of the focal plane), which overlies the apical part of wing disc cells including Arm (in the focal plane of D–E′). The expression of ArmS10-Myc (F–G′) was not altered upon depletion of als (line oligo310UAS). (D–E′): apical confocal sections; (F–G′): deeper confocal Z-sections, which show enhanced cytoplasmic ArmS10 levels.
The rescue experiments with Arm and ArmS10 suggested that Als acts upstream of Arm's proteasomal degradation. To further corroborate this idea, we reduced the levels of ubiquitin in addition to als depletion. This led to a suppression of the alsRNAi phenotypes in the wing and the eye (Figure S11I, S11L, and S11O, cf. Figure S11G, S11J, and S11M). Reduction of ubiquitin also suppressed Wg loss-of-function phenotypes that were based on elevated activity of the destruction complex by Axin overexpression (Figure S11A and S11C). In contrast, depletion of ubiquitin did not suppress the Lgs17E overexpression phenotype, which intersects the Wg pathway downstream of the proteasome (Figure S11D and S11F). These findings support the idea that Als acts upstream of Arm's proteasomal degradation.
To check whether Als directly interacts with Arm, we carried out selected reaction monitoring, a highly sensitive mass spectrometry approach that allows the detection of low amounts of peptides in a complex sample [37]. Als and Ter94 were used as bait. In none of the studies was an interaction between Arm and Als detected. Additionally, in shotgun affinity purification mass spectrometry using Arm or ArmS10 as a bait we did not find Als, whereas, as expected, components of the degradation complex such as Apc2, Axin, Sgg, and CKI were detected in the cytoplasm (Text S1).
We further analyzed the consequences of als depletion for Wg signaling in Kc-167 cells (Figure 8). Stimulation of the Wg pathway by the inhibition of GSK3β led to strong transcriptional upregulation of the Wg targets naked (nkd) and wingful (wf) (Figure 8B and 8C, bar 2), and an increase in Arm levels (Figure 8D, lanes 3 and 11). Consistent with the in vivo data, double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)–mediated knockdown of als (Figure 8A) caused a reduction in nkd and wf expression in stimulated cells (Figure 8B and 8C, bar 6, cf. bar 2). Importantly, the increase in Arm levels based on GSK3β inhibition was significantly reduced when als was knocked down (Figure 8D, lane 4, cf. lane 3, and lane 13 and 14, cf. lane 11). When the pathway was stimulated by inhibiting E1 Ub ligase activity, which caused a milder upregulation of nkd and wf than the GSK3β inhibition (Figure 8B and 8C, bar 3; see also Materials and Methods), transcriptional upregulation was still decreased upon als depletion (Figure 8B and 8C, bar 7), but to a far lesser extent; at the same time, Arm was reduced upon als depletion (Figure 8D, lane 6, cf. lane 5). Inhibition of the 26S proteasome increased Arm levels in both control and als-dsRNA conditions (Figure 8D, lanes 9 and 10).
Figure 8. Als acts downstream of GSK3β and upstream of SCF/Slimb/βTRCP E3 Ub ligase.
(A) als mRNA levels are downregulated upon als-dsRNA treatment. Stimulation of Wg signaling by inhibition of GSK3β (CHIR) or E1 ligase (PYR-41) causes an upregulation of als expression. (B and C) The positive Wg targets nkd and wf were induced upon GSK3β inhibition (bar 2 in [B and C]) and E1 ligase inhibition (bar 3 in [B and C]) in control cells. In als-dsRNA-treated cells, nkd and wf were strongly reduced in GSK3β-inhibited cells (bar 6 in [B and C]) and only mildly reduced in PYR-41-treated cells (bar 7 in [B and C]). Inhibition of the proteasome (MG-132) did not cause upregulated Wg target expression (bars 4 and 8). (D) Inhibition of GSK3β (CHIR) or E1 ligase (PYR) caused an increase of Arm protein levels in control cells (lanes 3 and 5); this increase was reduced upon als-dsRNA treatment (lanes 4 and 6); proteasome inhibition (MG132) caused elevated Arm levels in both control and als-dsRNA conditions (lanes 9 and 10). Combined depletion of ter94 and als could ameliorate Arm levels (lane 12, cf. lanes 13 and 14, which represent als depletion based on different als siRNA target regions). (E) Control expression levels are depicted as white bars. In wing imaginal discs (left bar diagram), als depletion caused a strong reduction of wf expression, a positive Wg target gene (lane 1), and an elevation of arr expression, a negative Wg target gene (lane 4). Combined als and ter94 depletion caused an elevation of wf (lane 2) or a decrease of arr (lane 5). No alteration was observed for the Hh target gene ptc (lanes 7–9). In Kc-167 cells (middle bar diagram), a co-depletion of als and ter94 caused an upregulation of the positive Wg targets nkd and wf (lanes 3 and 6), which were reduced upon als depletion (lanes 1 and 4). No alteration was observed for the Hh target gene ptc (lanes 7–9). Reduced nkd expression of als-depleted, GSK3β-stimulated Kc-167 cells (right bar diagram) could be ameliorated upon co-depletion of ter94. (F–I) The wing and eye phenotypes caused by the expression of the dominant-negative-like AlsHA were suppressed by the overexpression of Ter94HA. co-i, control siRNA.
When we depleted ter94 in wing imaginal discs and in Kc-167 cells, we found an upregulation of the positive Wg target genes nkd and wf, and a downregulation of the negative Wg target arr (Figure 8E). Moreover, in als-depleted cells, ter94 reduction led to an amelioration of the changes in Wg target expression (Figure 8E), and to a partial restoration of Arm levels (Figure 8D, lane 12). In contrast, the Hh target gene ptc was not altered (Figure 8E). Overexpression of ter94RNAi in wing imaginal discs, however, caused pupal lethality. Because of this, it was difficult to analyze the adult wing phenotype caused by the combined depletion of ter94 and als; because of ter94's pleiotropic role, the analysis of the consequences of ter94 depletion is challenging [38].
In addition, we found that overexpression of Ter94HA suppressed the strong dominant-negative-like effect of AlsHA overexpression in the wing and the eye primordium (Figure 8F–8I), while overexpression of Ter94HA could not suppress phenotypes caused by alsRNAi (Figure S2M). This is consistent with the finding that overexpression of Ter94HA alone did not cause any phenotype (Figure S2N); however, it suggests that an excess of Ter94HA can neutralize the excess of the dominant-negative AlsHA.
Together, these results suggest that Als functions downstream of GSK3β and downstream or at the level of E1 Ub ligase and that Als is required to antagonize Ter94 to allow normal Wg signaling. This is in agreement with our genetic epistasis experiments (Figure 5) and is corroborated by the further finding that overexpression of CSN6, an essential de-ubiquitinating enzyme and negative regulator of SCF/Slimb/βTRCP E3 Ub ligase [39], reverted the alsRNAi phenotypes in the wing and the eye (Figure S11H–S11N). Of note, CSN6 overexpression suppressed the Wg signaling defects caused by Axin overexpression (Figure S11A and S11B), but did not suppress Wg signaling defects caused by Lgs17E overexpression (Figure S11D and S11E).
Human UBXN6 Is the Functional Ortholog of Als
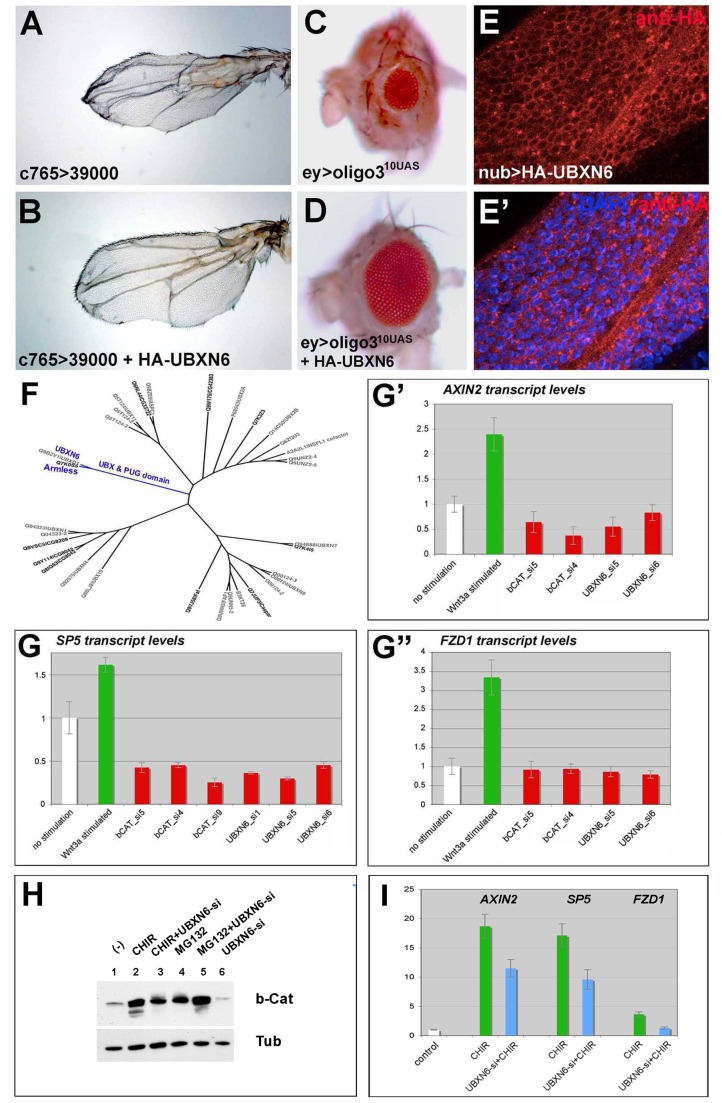
To address the evolutionary conservation of Als's function, we tested whether the human ortholog of Als, UBXN6, can substitute for Als in wing and eye development. Overexpression of HAUBXN6 in imaginal discs could largely rescue the wing phenotypes and fully rescue the eye phenotypes caused by alsRNAi (Figure 9A–9D). Further, we found that HAUBXN6 localizes in cells of imaginal discs in a manner similar to HAAls (Figure 9E and 9E′, cf. Figure S8A–S8E). The UBXN6 and Als proteins share 33% identity and belong to the same subfamily of UBX domain proteins, which is specified by the presence of an UBX and a PUG domain (Figure 9F). We next asked whether UBXN6 is required for Wnt signaling in human cells. We stimulated the Wnt pathway in HEK-293 cells with mouse Wnt3a (mWnt3a) while targeting UBXN6 by small interfering RNA (siRNA). siRNA against CTNNB1/β-Catenin served as a control. To monitor the output of the Wnt pathway, we analyzed three established Wnt-responsive genes, SP5, AXIN2, and FZD1, by real-time PCR. All three targets were upregulated upon pathway stimulation (Figure 9G–9G″, green bars), and this response was abolished upon siRNA treatment of UBXN6 (Figure 9G–9G″, red bars). The depletion of β-Catenin caused a similar downregulation of Wnt target gene expression. Further, we found β-Catenin levels reduced upon UBXN6 depletion in HEK-293 cells (Figure 9H, lane 6, cf. lane 1). Similar to mWnt3a, the stimulation of the pathway by GSK3β inhibition caused an increase of Wnt target genes. Depletion of UBXN6 reduced this effect (Figure 9I). These findings suggest that UBXN6 is a functional ortholog of Als and that UBXN6 might play a similar role for Wnt signaling in human cells.
Figure 9. Human UBXN6 is the functional ortholog of Als.
(A–D) Human UBXN6 expression could largely or completely rescue alsRNAi wing and eye phenotypes. (E and E′) When expressed in wing imaginal discs HAUBXN6 localization resembles that of HAAls (cf. Figure S8A–S8E). (F) UBXN6 and Armless belong to the same protein subfamily of UBX domain proteins (blue). (G–G″) Expression of the WNT target genes SP5, AXIN2, and FZD1 was upregulated upon stimulation of the pathway with mWnt3a (green bar), and was reduced upon siRNA against human UBXN6 in HEK-293 cells. Depletion of β-Catenin served as a control. (H) β-Catenin levels were reduced upon siRNA against human UBXN6 in HEK-293 cells (lane 6, cf. lane 1; and lane 3, cf. 2), whereas depletion of UBXN6 had no effect on β-Catenin levels upon inhibition of the proteasome (MG132; lane 5, cf. lane 4). (I) WNT target genes were upregulated upon GSK3β inhibition (CHIR; green bars), and were reduced upon depletion of UBXN6 (blue bars).
Discussion
A prevalent mechanism for controlling information flow in signaling pathways is the alteration of the protein levels of key components. In the Wg/Wnt pathway, the Arm/β-Catenin destruction complex targets Arm/β-Catenin for ubiquitination by the SCF/Slimb/βTRCP E3 Ub ligase, resulting in proteasomal degradation and low cytoplasmic levels of Arm/β-Catenin in the Wnt pathway off state. If the pathway is turned on, Slimb-mediated ubiquitination is prevented, thus rescuing Arm from its proteasomal fate and causing a concomitant increase in Arm protein levels [5]. Here we describe Als as a new component of this control system; we found that Als is required to prevent the degradation of Arm/β-Catenin.
Als/UBXN6 Is a Novel Regulator of the Wnt/Wg Pathway
We identified als in a genome-wide in vivo RNAi screen in Drosophila. Because we did not succeed in isolating an EMS- or P-element-induced null allele and because another gene overlaps with als, we demanded, and obtained, particularly thorough evidence validating als gene function. (1) The alsRNAi phenotypes could be reproduced by nine different UAS-RNAi transgenes encoding independent RNA target sites. Together with an extended off target analysis, we could rule out unintentional RNAi as a cause for the als phenotypes. (2) RNAi-mediated inhibition of als expression was ascertained by monitoring als mRNA expression via real-time PCR and antisense mRNA in situ hybridization. (3) Expression of HAAls with different RNAi-insensitive rescue transgenes, as well as with its human ortholog UBXN6, rescued alsRNAi phenotypes.
Our analyses show that als encodes an essential positive Wg signaling component. This conclusion is based on the following evidence. als depletion caused wings with notched wing margins and loss of sensory bristles, which is characteristic of impaired Wg signaling. The distal wing region is most sensitive to als levels, as is the case for other positive components of Wg signaling. In agreement with this, we found increased als expression in the central wing pouch, at least in earlier L3 larval stages. Stimulation of the Wg pathway in wing imaginal discs or Kc-167 cells caused higher als expression, suggesting that als can be positively controlled by Wg signaling. However, Als levels must be precisely controlled since already mild overexpression of UAS-als elicits a dominant-negative effect on Wg signaling. The function of als for Wg signaling is not restricted to the wing: also in other tissues, such as the thorax, eyes, legs, and the embryo, alsRNAi phenotypes are identical to those seen when Wg signaling is disturbed. Also in human HEK-293 cells we found UBXN6/UBXD1, the ortholog of Als, to be required for Wnt signaling, and human HAUBXN6 largely rescued the alsRNAi phenotypes in Drosophila, which suggests their functional conservation. Depletion of als also enhanced Wg-sensitized phenotypes, further supporting the notion that its product is a Wg pathway component. Moreover, the expression of positively regulated Wg target genes is reduced or abolished upon loss of als function, while Wg-repressed target gene expression is ectopically activated. Importantly, while interfering with als function suppressed Wg signaling, it did not affect other pathways, such as Notch and Hh, Jak/Stat, or EGFR signaling. However, we cannot rule out that als is not required in another pathway in a different biological context. In humans, UBXN6 is reported to play a role in diverse scenarios: for example, it was shown to play a role in Caveolin turnover in human osteosarcoma U2OS cells [40]. This might indicate a broader role of UBXN6 in mammalians.
Als: A Protector of Armadillo
Our data show that Als regulates Armadillo protein levels. Based on our epistasis experiments, Als acts downstream of Shaggy/GSK3β and upstream of the SCF/Slimb/βTRCP E3 Ub ligase, which is known to ubiquitinate Arm, a prerequisite for proteasomal degradation. Consistent with this, the degradation-resistant form of Arm, ArmS10, could completely bypass the requirement for als, in contrast to the wild-type form of Arm. This suggests that proteasomal degradation acts downstream of als; however, we would like to point out that this cannot be taken as an unambiguous proof. Importantly, depletion of ubiquitin and overexpression of CSN6, a negative regulator of SCF/Slimb/βTRCP E3 Ub ligase, could ameliorate the als phenotype (as well as phenotypes based on the overexpression of Axin or Shaggy, which overactivate the destruction complex, thus resulting in enhanced Arm degradation). In contrast, altering these factors did not ameliorate the Lgs17E phenotype, which is caused by interfering more downstream in the Wg pathway. These findings suggest that als works upstream of proteasomal degradation. A further informative experiment was monitoring Wg pathway components with respect to protein levels: Arr, Fz, Axin, APC, Sgg, and Arm. The only change in the absence of Als function was Arm: its levels were strongly reduced upon als depletion. The effects on Arm levels could be due either to a direct effect on Arm or to an indirect effect on a negative component. Importantly, the rate-limiting factor Axin as well as other key negative components of the Arm/β-Catenin destruction complex were unaltered upon als depletion.
Als Interacts with Ter94 ATPase
Some further mechanistic insight was obtained with our finding that Ter94 interacts in vitro and in vivo with Als. Interestingly, we found that Als-Ter94 localizes at the cell cortex, as was similarly observed for the Arm/β-Catenin destruction complex [41]. Our studies are consistent with earlier work that showed that the human ortholog of Ter94, p97, interacts with UBXN6 [42]. Ter94/p97/Cdc48 is a conserved and highly abundant AAA ATPase that was found to associate with SCF/Slimb/βTRCP E3 Ub ligases or proteasomal shuttle factors to mediate UPS-mediated protein degradation ([33],[42]–[45]; reviewed in [6],[34]). Specifications of the diverse activities of Ter94/p97 and the fate of its substrates are mainly exerted by UBX domain protein co-factors, which eventually either promote or hinder p97's function in protein turnover; an example of the latter involves the dissociation of the SCF/Slimb/βTRCP E3 Ub ligase complex, eventually leading to its inactivation [45]. Interestingly, it was recently reported that inactivation of the E3 ligase complex upon Wnt signaling is achieved by its dissociation from the destruction complex [5]. Based on our experiments and what is known about Ter94/p97, we suggest as a possible mechanism that Als antagonizes Ter94's positive effect on E3 ligase function, thereby rescuing Arm levels. We, however, did not observe increased protein levels of Slimb, Axin, Shaggy, or APC in our analyses; thus, our results favor a model in which Als antagonizes Ter94 to hinder the transfer of Arm to the proteasome by interfering with the SCF/Slimb/βTRCP E3 Ub ligase function or its assembly. Importantly, we did not find an interaction between Arm and Als. This is consistent with the finding that UBX domain family members lacking an UBA domain, such as UBXN6/Als, do not directly interact with substrate proteins [44], but are necessary for the activity or fate of the Ter94/p97.
Interestingly, Zhang et al. [38] found that ter94 depletion affected the partial proteolysis of Ci. However, they observed neither any typical consequence of disturbed Hh signaling per se (i.e., no alteration of Hh target gene expression in genes such as ptc) nor any phenotypical consequence upon overexpression of a dominant negative form of Ter94 (i.e., aberrant wing patterning and growth typical for Hh signaling). This is consistent with our data that neither Ci target expression nor Hh signaling was affected upon als or ter94 depletion (Figures S6G–S6J and 8E).
p97/Ter94 is known as a highly pleiotropic AAA ATPase associated with many cellular functions. Further, p97/Ter94 acts in multifaceted and large protein–protein complexes, and it is its regulatory co-factors, including UBX domain proteins, that render p97/Ter94 specific for a certain task in a particular cellular context. For example, p47/Shp1 is a co-factor of p97/Ter94 that blocks other co-factors from Ter94 binding [46],[47]. Interestingly, in our Kc-167 cell mass spectroscopy experiments, we found p47 in Ter94/Als protein complexes, but only in the absence of Wg stimulation (Text S1). On the other hand, we found als transcript and Als protein levels elevated upon Wg signaling (Figures 8A and S5D). These findings suggest a dynamic regulation of the Ter94 complex upon signaling inputs. The identification and functional analysis of all key components of the Als-Ter94 complex will be needed to obtain a refined insight into Als-Ter94's molecular mechanism.
Concluding Remarks
Critically, our work spotlights an underappreciated facet in the control of the output of the entire canonical Wg/Wnt pathway—how Arm/β-Catenin is handed over to the proteasome— and the potential for regulating this step; our works also indicates that this step, in contrast to the conventional wisdom, is tunable. Our identification and characterization of the UBX protein Als as a positive regulator of Wg/Wnt signaling contributes to this layer of pathway control.
Materials and Methods
Drosophila Strains
UAS-alsRNAi lines
als was identified in a genome-wide RNAi screen based on the Vienna Drosophila Resource Center (VDRC) RNAi library [48] with the VDRC line 28998 (II/CyO).
To further validate this phenotype we used the UAS-RNAi lines GD-39000 (Chromosome 3) and KK-105104 (Chromosome 2), both obtained from the VDRC. Seven further lines were generated by us, representing six different target regions that target either the coding sequence or the UTRs of als (Figure S1A). The algorithm used to design the RNAi target site of the 21-mer oligos [49] is indicated as superscript. All lines are based on Chromosome 3 site-specific insertion using the attP-86Fb line (FlyORF, [50]): pNE3::oligo2Dharmacon (ORF) (target site: 5′-CCGCCAAAAGTATGAGGCCTA-3′), pNE3::oligo3Dharmacon (ORF) (target site: 5′-CGGACGAAAGCCTGGATTTTA-3′), pWAL20::oligo3Dharmacon (ORF) (target site: 5′-CGGACGAAAGCCTGGATTTTA-3′), pWAL20::oligo1DSIR (ORF) (target site: 5′-GCAAGATACGGATGTCCAACA-3′), pWAL20::oligo2Dharmacon (3′utr) (target site: 5′-CAGCGGTATTTGTCCCTTATA-3′), pWAL20::oligo2Dharmacon (5′utr) (target site: 5′-CAAGGAAATCGAGGAGCTTAA-3′), pWAL20::oligo3Dharmacon (5′utr) (target site: 5′-CGGCTATTCGTGGTCCATTTA-3′).
pNE3-based RNAi lines contain five copies of UAS; pWAL20-based RNAi lines contain ten copies of UAS. The pNE3 vector was obtained from B. Haley and is a derivative of the pUAST-attB vector [49],[50]; the pWAL20 (pWALIUM20) vector was obtained from J. Ni (Transgenic RNAi Resource Project [TRiP], Drosophila RNAi Screening Center).
RNAi off target analysis
We analyzed the mRNA levels of computer-predicted, putative off targets of the VDRC lines upon expression of UAS-VDRC-RNAi transgenes in wing imaginal discs by real-time PCR. We did not find specific alterations of the putative off targets. For the generation of our UAS-oligo-RNAi transgenes, we employed the DRSC off-target-finder algorithm (16-mer allowed) to exclude off-target-prone RNAi target sites.
Genetic interaction
We used the als Exelixis deficiency line BL7894, Df(2R)Exel7157/CyO (homozygous lethal), to test the genetic ineraction with alsRNAi.
Lines for overexpression: UAS-als lines
Transgenic lines are based on the ΦC31 transgenesis system, using the line ZH-86Fb attB as the landing site on Chromosome 3.
cDNA for the 1.327-kb long coding region of als was obtained by PCR on cDNA from L3 wing imaginal disc after total RNA extraction. A Drosophila Kozak consensus region was attached in front of the ATG. N- and C-terminally epitope-tagged versions are as follows: UAS-alsHA (C-terminal triple HA-tag), UAS-HAals (N-terminal triple HA-tag), UAS-FLAGals (N-terminal double FLAG-tag), UAS-HAalsoligo3-mut (N-terminal triple HA-tag); within the oligo3 target site we introduced seven conservative basepair mutations by alternative codon usage (5′-CTGATGAGAGTCTAGACTTCA-3′).
Als protein domain deletion variants
Deletions of the PUG, UBX, and N-terminal domains were generated by overlap extension or conventional PCR.
UAS-HAUBXN6 line
The coding region of human UBXN6 was isolated by PCR on cDNA derived from HEK-293 cells after total RNA extraction.
Further transgenic lines for wing and eye analysis
The following lines were used: UAS-Lgs17E (K. Basler laboratory [K. B.]), UAS-HLHmbeta (FlyORF), UAS-e(spl)m8 (FlyORF), UAS-ras85DRNAi (VDRC), sal>smoI (K. B.), UAS-panRNAi (VDRC), UAS-wingful/notumRNAi (VDRC 45905), UAS-shaggy/gsk3βRNAi (VDRC 101538, TRiP BL 38293, 35364), UAS-slimbRNAi (TRiP BL 33898), UAS-apc2RNAi (NIG-FLY 3060R-3), UAS-apcRNAi (TRiP BL 51468), UAS-axinRNAi (TRiP BL 31705), UAS-dsh (FlyORF), UAS-axin, UAS-shaggy, UAS-axin-GFP [36], UAS-shaggyHA (FlyORF), UAS-apc2HA (FlyORF), UAS-fz2HA (FlyORF), UAS-arrowHA [17], UAS-CG42306 (K. B.), UAS-GFP (K. B.), UAS-arm (K. B.); UAS-armS10-Myc [31], sev-wg eye tester: yw, ey-flp (X chromosome; K. B.), ey-Gal4,GMR-Gal4/CyO (Chromosome 2; K. B.), sev>y+>wg/TM6b (Chromosome 3; K. B.), UAS-diap1 (K. B.), UAS-string, GMR>eiger/CyO (K. B.), UAS-Ter94HA (FlyORF), UAS-CSN6 (FlyORF), UAS-ubip5ERNAi (TRiP BL 38967), UAS-ter94RNAi (VDRC 24354, TRiP BL 32869).
Gal4 driver lines
The following lines were used: nubbin (nub)-Gal4, c765-Gal4, MS1096-Gal4, apterous-Gal4, hedgehog (hh)-Gal4 (combined with UAS-CD8-GFP), engrailed (en)-Gal4 (combined with UAS-GFP), spalt (salE)-Gal4, vestigial (vg)181-Gal4, distalless (dll)-Gal4, pannier (pnr)-Gal4, eyeless (ey)-Gal4, GMR-Gal4, da-Gal4).
Cell clone analysis
For cell clone analysis in wing imaginal discs (Figure 4) and adult wings, somatic clones were generated in animals of the following genotype: yw, hsflp/+; +/+; actin5c>CD2>Gal4, UAS-GFP, UAS-forkedRNAi/UAS-alsRNAi (VDRC line 39000 or line oligo310UAS) or UAS-alsHA. Heat shock flippase (hsflp) was induced 2 and 3.5 d after egg deposition (30 min, 37°C). Third instar larvae were fixed and stained for Wg target expression by standard immunohistochemical techniques. UAS-forkedRNAi was used to mark adult cell clones (trichomes of the wing epithelium are shorter and adopt a forked-like shape).
Transcriptional reporter lines
The following lines were used: wingless-lacZ, arrow-lacZ l(2)k08131, frizzled3-lacZ, distalless-lacZ, wingful-lacZ, e(spl)m8HLH.1.25-lacZ, NRE-eGFP (TRiP BL 30728).
als-lacZ transgenic lines
4,978 kbp (HindIII-XbaI) and 2,927 kbp (StuI-XbaI) of als's upstream genomic DNA (down to the start codon) were cloned into a pattB-lacZ vector. Wing imaginal disc expression of the lines was analyzed by X-Gal staining (brightfield microscopy) and by anti-βGal antibody staining, visualized by Alexa Fluor 594 secondary antibody (UV confocal microscopy).
In Vivo Interaction of Als with Ter94 (BiFC Analysis)
Ter94-VNm9 (Ter94 fused to the N-terminal part of Venus-YFP) and Als-VC155 (Als fused to the C-terminal part of Venus-YFP) were co-expressed and analyzed for interaction by BiFC [34]. Direct interaction of two proteins causes a reconstitution of the two non-fluorescent YFP subfragments into a functional YFP, resulting in a yellow fluorescent signal.
Immunohistochemistry of Imaginal Discs
Primary antibodies
mouse anti-β-Galactosidase (1∶2,000, Promega), rabbit anti-Arrow (1∶15,000, generous gift from S. DiNardo), guinea pig anti-Senseless (1∶800, gift from H. Bellen), rat anti-Distalless (1∶500, gift from S. Cohen), mouse anti-Wingless (1∶1,000, 4D4, Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank [DSHB]), rabbit anti-E-Cadherin (1∶100, DSHB), mouse anti-Frizzled2 (1∶20, DSHB), mouse anti-Armadillo (1∶100, N2 7A1, DSHB); mouse anti-HA (1∶500, 6E2, Covance), rabbit anti-HA (1∶200, SC805, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), mouse anti-c-Myc (1∶200, 9E10, DSHB).
Secondary antibodies
Alexa Fluor 594 and 488 (1∶400, Molecular Probes) were used as secondary antibodies. Larval head pieces were fixed in 4% formaldehyde for 30 min at room temperature. Imaginal discs were mounted in Vectashield (Vector Laboratories).
Imaging
Images of immunostainings were generated with a Zeiss Lsm710 confocal microscope using 40× and 60× oil objectives. Images were analyzed with ImageJ software. Adult fly wings were mounted in Euparal, and images were generated with a Zeiss Axioplan microscope.
In Situ mRNA Hybridization
RNA probes were generated by run-off transcription of antisense mRNA with T7 RNA polymerase (Promega) from linearized plasmid templates with the PCR-amplified als coding region (full-length template as well as an EcoRV-truncated template, generating the first half of the coding sequence). Antisense mRNA was generated with a 3′ primer containing the T7 RNA polymerase binding sequence (5′-GAATTTAATACGACTCACTATAGG-3′).
Real-time PCR
UAS-alsRNAi was expressed under the control of c765-Gal4 (Figure S1L) in wing imaginal discs, which were collected at the late third instar larval stage for total RNA isolation (RNeasy Kit, Qiagen, or TRI-Reagent, Sigma-Aldrich). 1 µg of total RNA was used as a template for reverse cDNA transcription (Superscript-RT-II, Roche). Quantitative PCR reactions were carried out with ¼ of the real-time PCR reaction and als-specific primers, 25 cycles, in the presence of SYBR Green (Roche), which enabled quantitative detection of the amplicons. Primers were designed by Roche Universal ProbeLibrary and are intron-spanning (als primer pair a: forward: ggaaaagacactatatgactgcaaact; reverse: aaggagcgggtgtatcattg; als primer pair b: forward: gaaaccatgtccaagattaagaagt; reverse: atgccgctgccagttaaa). Real-time PCR was carried out on an Eppendorf Realplex Mastercycler. mRNA levels were calculated with the comparative CT (threshold concentration) method and were normalized for three external standards (actin5C, TBP, and gpdh). For each RNAi condition, data were obtained from three biological replicates (i.e., three independent but identical Gal4×UAS-RNAi fly crosses), and real-time PCR was carried out in technical triplicates per experiment.
Drosophila Cell Culture and Immunoprecipitation of Epitope-Tagged Proteins
Kc-167 cells were cultured in Schneider's Drosophila medium (Invitrogen) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin at 25°C. For each experimental condition, 2× T75 (8 ml) culture flasks of 90% confluent Kc-167 cells were seeded at 60% confluency. 1 d after seeding, cells were transfected with the UAS transgenes (UAS-alsHA, UAS-ter94HA, UAS- FLAGals, UAS- FLAGΔN-als). UAS-GFP served as a control for transfection efficiency; empty pUAST-attB vector and UAS-FLAGGal4 vector served as negative controls; UAS transgenes were expressed under the control of tubulin-Gal4. DNA input per T75 flask was 0.5 µg of tubulin-Gal4, 0.75 µg of UAS-GFP, 0.5 µg of control vector, and 1.5 µg of the respective UAS transgene. Effectene (Qiagen) was used for transfection, according to the manufacturer's protocol. For stimulation of the Wg pathway, the supernatant of cells containing secreted Wg was added to the cell culture 24 h after transfection.
Immunoprecipitation
Cells were harvested 48 h post-transfection. Per each experimental condition, cells of two T75 flasks were pooled and lysed in lysis buffer (8× of pellet volume) containing 20 mM Na2H2PO4 (pH 7.4), 200 mM NaCl, 0.5% Nonidet P-40, 2 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, 1.5 mM Na3VO4, and protease inhibitor (Complete Mini; Roche). Cell suspension was dounced 20×, incubated 10 min at room temperature, and centrifuged with 13,000 rpm at 4°C. The supernatant (total cell lysates) was incubated either with rabbit anti-HA antibody (Abcam) or mouse anti-FLAG antibody (Sigma), conjugated to Protein-A Sepharose beads (Sigma), and allowed to rotate 3 h at 4°C. The beads were then collected (3,600 rpm, 10 min at 4°C), washed 3× with the lysis buffer, and transferred to a column to allow gravity flow. Protein complexes were eluted with 3×50 µl of glycine (0.2 M, pH 2.5) and neutralized with 50 µl of 8 M urea (containing 100 mM NH4CO3). The pH of the eluted protein complex was adjusted with NH4HCO3 to a final pH of 8.8 and stored at −20°C prior to sample preparation for mass spectroscopy (see below).
For Western blot analysis, protein complexes were denaturated and resolved on 4%–12% NuPAGE Bis-Tris Mini Gels (Invitrogen) and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. After blocking, the membrane was incubated with either anti-HA antibody (mouse, 1∶1,000, HA.11, Covance) or anti-FLAG M2 antibody (mouse, 1∶1,000, Sigma), followed by the respective secondary goat anti-mouse antibodies conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (1∶10,000). Signals were detected with ECL reagents (Amersham), followed by autoradiography. Membranes were stripped (Re-Blot Plus Strong Solution, Millipore), blocked, and reused for incubation with further primary antibodies (mouse anti-αTubulin, 1∶2,000, Sigma; rabbit anti-UBXD1, 1∶1,000; rabbit anti-Ter94 1∶1,000).
For dsRNA experiments, 45 µg of dsRNA (control gfp-dsRNA or als-dsRNA) was incubated with 7.5×106 cells per condition for 1 h before transfer into T75 flasks. Cells were harvested 3.5 d after seeding. The GSK3β inhibitor CHIR 99021 was added to the cells 20 h before cell harvest (12 µM), the E1 ligase inhibitor PYR-41 (Calbiochem) was added 2 h before cell harvest (50 µM), and the proteasome inhibitor MG-132 was added 6 h before cell harvest (25 µM). Primary antibodies for Western blots after immunprecipitation were rabbit anti-Phospho-β-Catenin (Ser33/37) (1∶750, Cell Signalling), mouse anti-Armadillo (1∶50, N27A1, DSHB).
Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Epitope-Tagged Als and Ter94
Sample preparation for mass spectrometry
Proteins isolated via immunoprecipitation against the hemagglutinin-tag were reduced with 5 mM TCEP and treated with 10 mM iodoacetamide to modify cysteine residues. Tryptic digestion was performed overnight using 2–5 µg of trypsin per sample. Digested peptides were purified by reverse phase C-18 chromatography (Sep-PaK, Waters). For mass spectrometry analysis, samples were resuspended in buffer containing 5% acetonitrile and 0.2% formic acid.
Mass spectrometry parameters and data analysis
For each sample, 4 µl was loaded on a LTQ-Orbitrap XL ETD mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The instrument was coupled to an Eksigent NanoLC system. Samples were automatically injected into a 10-µl sample loop and loaded onto an analytical column that was packed in-house with Magic C18 AQ beads (3 µm, 200 Å, Bischoff Chromatography) and was 8 cm in length, with an internal diameter of 75 µm. Peptide mixtures were delivered to the analytical column at a flow rate of 500 nl/min (3% acetonitrile, 0.2% formic acid) for 16 min and then eluted using a gradient of acetonitrile (3%–35%; 0.53%/min) with 0.2% formic acid at a flow rate of 250 nl/min. The samples were measured in a survey scan from 300 to 2,000 amu, followed by six data-dependent LC-MS/MS scans with dynamic exclusion (isolation width 2 amu, three repeat counts, exclusion list size 500, dynamic exclusion duration 60 s). LC-MS/MS spectra were assigned to peptide sequences using Mascot software, version 2.4 (Matrix Science). All peptide assignments where the Mascot ion score was greater than the homology score and where the Mascot expect score was smaller than 0.05 were accepted.
Human Cell Culture
HEK-293 cells were seeded into a 96-well plate (40,000 cells/well). 1 d after seeding cells were transfected (Lipofectamine 2000, Invitrogen) with siRNAs targeting human β-Catenin, human UBXN6, or a negative control siRNA (Qiagen FlexiTube siRNA). The siRNA concentration per well was 0.05 µM. Co-transfected histone2B-RFP served as the control of the transfection efficiency. The Wnt pathway was stimulated by mWnt3a from co-transfected pcDNA3::mWnt3a. Each experimental condition was made in triplicate. 48 h after transfection, cells were harvested, and an aliquot was used for real-time PCR (1) to analyze the siRNA-mediated knockdown of β-Catenin or UBXN6 and (2) to analyze the transcriptional level of the Wnt targets SP5, AXIN2, and FRIZZLED-1. To analyze β-Catenin levels, siRNA (Qiagen FlexiTube siRNA, Thermo Scientific SMART pool) was applied two times (the second siRNA application was done 1.5 d after the first siRNA application), and cells were harvested 86 h after the first transfection.
Supporting Information
Validation of the alsRNAi phenotype by different RNAi target sites. (A) Location of 16 different siRNA target sites encoded by 16 RNAi lines with respect to the als cDNA region. The 16 different target sites are based on three different algorithms (VDRC, three different sites; Dharmacon, nine different sites; DSIR, four different sites). Nine of 16 target sites caused similar wing notching phenotypes (red bars in [A], similar phenotypes in [B–J]). Impairing Wg signaling via the overexpression of a dominant-negative pathway component, Lgs17E, causes a phenotype reminiscent of als depletion (K). Six target sites did not result in any phenotype (blue bars in [A]), and one target site caused a phenotype completely different from the nine other positive target sites, which we attribute to an off-target effect (OTE; purple bar in [A]). (L) Real-time PCR shows that ubiquitous expression of UAS-alsRNAi by c765-Gal4 effectively reduced als transcript levels in wing imaginal discs as monitored by two different real-time PCR primer pairs for als (a and b in the bar diagram). The degree of the mRNA knockdown correlates with the strength of the phenotype (cf. Figure 1B–1E). (M) Expression of alsRNAi-39000 with c765-Gal4 does not cause a phenotype. (N) Haplo-deficiency for als causes wing notches in combination with c765>alsRNAi-39000 expression.
(TIF)
Als can rescue alsRNAi phenotypes. (A) Overexpression of Als in wing imaginal discs often caused no phenotype, or mild notches at elevated expression (inset). (B) Overexpression of C-terminally epitope-tagged Als (AlsHA) caused wings with strong notches. (C) Targeting the 5′ UTR of endogenous als by alsoligo3_5′utr caused wings with notches. (D) Overexpression of N-terminally tagged Als (HAAls), which lacks UTRs, could rescue the alsRNAi-utr phentoype. (E) Expression of alsRNAi, which targets the ORF of endogenous als (alsoligo3_10UAS_ORF), caused wings with marginal notches or a small eye phenotype (G). These phenotypes could largely or completely be rescued by the overexpression of an RNAi-insensitive version of HAAls, which contains a mutated oligo3_ORF target site (F and H). Expression of UAS-GFP or UAS-CG42306 did not rescue the alsRNAi phenotype (I and J). Expression of UAS-CG42306 did not cause a phenotype in the wing (K) and caused legs devoid of the entire tarsal region (L). (M) Ter94HA overexpression did not rescue the alsRNAi phenotype, and did not show any phenoype in the wing (N).
(TIF)
Genetic interaction of als with the cell cycle and Wg signaling. (A–F) Underproliferation, not apoptosis, underlies the alsRNAi wing phenotype. Overexpression of a negative Wg pathway component, Lgs17E (A), and of alsRNAi (D) causes wing margin notches. Inhibition of apoptosis by overexpression of Diap1 could not rescue the wing phenotypes (B and E), whereas acceleration of the cell cycle by overexpression of String could rescue the wing phenotypes (C and F). (G–J″) als interacts with the Wg pathway. Reduction of Wg signaling (G–J) was provoked by (G) overexpression of a dominant-negative mutant form of Legless, Lgs17E, (H) depletion of pangolin (pan), (I) overexpression of Shaggy (Sgg), or (J) overexpression of Axin. Simultaneously depleting als (G″–J″) leads to an enhancement of the notched wing margin phenotype observed with depleting als alone (G′–J′).
(TIF)
als depletion in the thorax and legs. (A–H) alsRNAi expression in the notum, the primordium of the thorax, by pannier-Gal4, which is active in the mesothorax (E). als depletion causes mild thoracic clefts (B and C), a slight polarity defect of thoracic bristles, reduced or lost dorsocentral microchaete, and an overall shortening of the thorax and scutellum (B, C, F, and G). These phenotypes are reminiscent of impaired Wg signaling, for example, based on panRNAi expression (D) or based on Lgs17E overexpression (H). (I–K) alsRNAi expression in the leg primordium by distalless-Gal4 caused, similarly to impaired Wg signaling, a shortening of tarsal segments and a dorsolateral shift of the sex combs (J, K, L, and M), along with a significant dorsalization (K and M). (N) Impaired Notch signaling caused a loss of segmental junctions along the tarsus, resulting in a complete fusion of the tarsal segments. (O–Y) Analysis of impaired als function in the embryo. Expression of alsRNAi or the dominant-negative-like AlsHA by da-Gal4 ([S] alsRNAi lines: oligo2_3′utr; [T] oligo310UAS) caused shorter cuticles than in control embryos, with ventral denticle belts partially fused (S–V, X, and Y). Expression of armRNAi (P and Q) or UAS-Lgs17E by da-Gal4 (R and W) caused similar phenotypes.
(TIF)
als is expressed in the center of the wing pouch. (A and B) als in situ hybridization reveals a pronounced expression of als in the center of the wing pouch and a low level of expression in the remaining part of the wing disc. (B) (inset) Expression of UAS-alsRNAi by hh-Gal4 in the P-compartment (arrows) of wing imaginal discs caused a strong decrease in als expression. (C) Reporter expression from a genomic als-lacZ transgene is similar to als expression visualized by in situ hybridization. (D) Activation of Wg signaling by the overexpression of either UAS-wg or UAS-armS10 with nubbin-Gal4 at 29°C in wing imaginal discs was monitored by the upregulation of the Wg targets wingful (wf), naked (nkd), and senseless (sens) (bars 2–7). Similarly, activation of Wg signaling caused an upregulation of als expression (bars 8 and 9). Als was upregulated upon stimulation of the Wg pathway by inhibiting GSK3β in Kc-167 cells (detected by anti-UBXN6 antibody).
(TIF)
als does not interfere with Notch or Hedghog signaling. m8-lacZ expression at the D/V boundary of wing imaginal discs (A) is not altered upon als depletion (A′ and A″). NRE-GFP expression is not altered upon als depletion (inset of A and A″). vg-BE-lacZ expression (B) is not altered upon als depletion (B′ and B″). (C) Overexpression of E(spl), the nuclear mediator of Notch signaling, causes reduction and loss of wing veins. (D) E(spl) co-expressed with alsRNAi resulted in wings with lost veins combined with wing notches. (E) Overexpression of HLHmbeta, a positive target of Notch signaling, abolishes wing veins. (F) HLHmbeta co-expressed with alsRNAi resulted in veinless wings with marginal notches. (G) Overexpression of SmoI constitutively activates Hh signaling, which results in overgrown wings and ectopic veins. (H) Ectopic Hh signaling combined with alsRNAi resulted in a wing size reduction predominantly of distal tissue, without altering the phenotypes symptomatic for elevated Hh signaling, like overgrowth along the A/P axis or ectopic veins. (I and J) ptc-lacZ expression is not altered upon depletion of als. (K) Ectopic expression of Upd, the ligand of the Jak/Stat pathway, caused overgrown eyes, which was not altered upon co-expression of alsRNAi (L). (M) Impaired Ras/EGFR signaling caused slightly smaller wings lacking wing veins; co-expression of alsRNAi resulted in veinless wings with marginal notches (N).
(TIF)
als depletion does not affect Wg expression. (A–F′) wg-lacZ and Wg protein expression is not altered upon expression of alsRNAi. Adult phenotypes corresponding to the respective genetic manipulations during wing disc development are shown for line 39000 (A–C), line oligo310UAS (D–E), and line oligo310UAS (F–G). (F–G) Upon strong RNAi expression by hh-Gal4 in the P-compartment (green, GFP expression), the P-compartment strongly undergrows, yet shows normal Wg expression.
(TIF)
Als localizes adjacent to the apicolateral cell membrane. HAAls expressed with nubbin-Gal4 in the wing pouch localizes in the cytoplasm adjacent to the cell membrane (A–E″). HAAls localization overlaps to a large extent with that of E-Cadherin (C′ and C″), Arm (D′ and D″), and Fz2 (E′ and E″). Cell nuclei are blue (DAPI in the color-merged pictures [B′, C″, D″, and E″]).
(TIF)
The PUG and the coiled-coil domains are essential for Als function. Expression of alsRNAi in the wing primordium with nubbin-Gal4 (A) or with 181-Gal4 (B and C) causes nicked wing margins. Co-expression of AlsΔPUG (D–F) or AlsΔN (G–I) did not alter the alsRNAi phenotype, whereas AlsΔUBX rescued the alsRNAi phenotype (J–L) comparably to full-length Als (insets of J–L). cc (coiled coil domain, within the N-terminal region of Als).
(TIF)
Negative pathway components are not altered upon als depletion. (A–D′) Axin-GFP expression levels are not changed upon depletion of als (line 39000 [C–D′, cf. A–B′]). Expression of Apc2HA (E–H) and ShaggyHA (I–L) is not altered upon als depletion (line 39000). (M–P) Expression levels of endogenous Fz2 (anti-Fz2-antibody staining) and ArrowHA were not altered upon depletion of als (line oligo310UAS, 29°C). Confocal pictures were taken at 40× magnification/2.5× zoom, except (A, A′, C, and C′): 40× magnification, 1× zoom; (E–L, O, and P): anti-HA antibody staining.
(TIF)
Als acts upstream of Arm's proteasomal degradation. The overexpression of CSN6 suppressed als RNAi phenotypes (H, K, and N, cf. G, J, and M) as well as a Wg loss-of-function phenotype caused by Axin overexpression (B, cf. A), but not as well as a Wg loss-of-function phenotype caused by the overexpression of Lgs17E (E, cf. D). Similarly, depletion of ubiquitin could suppress phenotypes based on als RNAi (I, L, and O, cf. G, J, and M) and Axin overexpression (C, cf. A), but could not ameliorate the Lgs17E overexpression phenotype (F, cf. D).
(TIF)
Supporting information.
(DOCX)
Acknowledgments
We thank the VDRC and TRiP at Harvard Medical School for providing transgenic RNAi fly stocks and the TRiP pWALIUM20 plasmid vector used in this study, FlyORF (Zurich ORFeome Project) for UAS-ORF lines, M. Bienz for the UAS-axin-GFP transgene, C. Lehner for the UAS-string transgene, E. Furger and J. Bischof for the BiFC analysis, E. Brunner for discussion and mass spectrometry measurement, I. Meyer for her assistance with mass spectrometry sample preparation, E. Escher for DNA sequencing, M. Moser for his assistance with real-time PCR, S. Luschnig for providing a darkfield microscope, P. Young and H. Meyer for their generous gift of the anti-Ter94 and the anti-UBXD1 antibodies, S. Wanka for generating the phylogenetic tree of UBX proteins, T. Valenta for discussions, and G. Hausmann for discussions and comments on the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- A/P
anteroposterior
- BiFC
bimolecular fluorescence complementation
- D/V
dorsoventral
- DSHB
Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank
- dsRNA
double-stranded RNA
- LC-MS/MS
liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry
- mWnt3a
mouse Wnt3a
- NRE
Notch responsive element
- RNAi
RNA interference
- siRNA
small interfering RNA
- TRiP
Transgenic RNAi Resource Project
- UPS
ubiquitin-proteasome system
- VDRC
Vienna Drosophila Resource Center
Funding Statement
This work was supported by a grant from the EMBO to GR, by a grant from the 7th Framework Programme of the European Union (Contract no. 262067-PRIME-XS) and an SNSF (Swiss National Science Foundation) grant (Marie-Heim Voegtlin, PMPDP3_122836) to SG, by an ERC grant to KB, as well as by support from the Swiss National Science Foundation and the Kanton of Zurich. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1. Sharma RP, Chopra VL (1976) Effect of the Wingless (wg1) mutation on wing and haltere development in Drosophila melanogaster . Dev Biol 48: 461–465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Rijsewijk F, Schuermann M, Wagenaar E, Parren P, Weigel D, Nusse R (1987) The Drosophila homolog of the mouse mammary oncogene int-1 is identical to the segment polarity gene wingless . Cell 50: 649–657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Klaus A, Birchmeier W (2008) Wnt signalling and its impact on development and cancer. Nat Rev 8: 387–398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Clevers H, Nusse R (2012) Wnt/β-Catenin signalling and disease. Cell 149: 1192–1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Li VSW, Ng SS, Boersema PJ, Low TY, Karthaus WR, et al. (2012) Wnt signalling through inhibition of b-catenin degradation in an intact Axin1 complex. Cell 149: 1245–1256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Schuberth C, Buchberger A (2008) UBX domain proteins: major regulators of the AAA ATPase Cdc48/p97. Cell Mol Life Sci 65: 2360–2371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Neufeld TP, de la Cruz AFA, Johnston LA, Edgar BA (1998) Coordination of growth and cell division in the Drosophila wing. Cell 93: 1183–1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Couso JP, Bishop SA, Martinez Arias A (1994) The Wingless signalling pathway and the patterning of the wing margin in Drosophila . Development 120: 621–636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Giraldez AJ, Cohen SM (2003) Wingless and Notch signalling provide cell survival cues and control cell proliferation during wing development. Development 130: 6533–6543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Phillips RG, Whittle JRS (1993) Wingless expression mediates determination of peripheral nervous system elements in late stages of Drosophila wing disc development. Development 118: 427–438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Neumann CJ, Cohen SM (1996) Sternopleural is a regulatory mutation of wingless with both dominant and recessive effects on larval development of Drosophila melanogaster . Genetics 142: 1147–1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Couso JP, Bate M, Martinez Arias A (1993) A wingless dependent polar coordinate system in Drosophila imaginal discs. Science 259: 484–489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Brunner E, Peter O, Schweizer L, Basler K (1997) pangolin encodes a Lef-1 homologue that acts downstream of Armadillo to transduce the Wingless signal in Drosophila . Nature 385: 829–833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Blair SS (1996) Notch and Wingless signals collide. Science 271: 1822–1823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Sato A, Kojima T, Ui-Tei K, Miyata Y, Saigo K (1999) Dfrizzled-3, a new Drosophila Wnt receptor, acting as an attenuator of Wingless signalling in wingless hypomorphic mutants. Development 126: 4421–4430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Sivasankaran R, Calleja M, Morata G, Basler K (2000) The Wingless target gene Dfz3 encodes a new member of the Drosophila Frizzled family. Mech Dev 91: 427–431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Wehrli M, Dougan ST, Caldwell K, O'Keefe L, Schwartz S, et al. (2000) arrow encodes an LDL-receptor-related protein essential for Wingless signalling. Nature 407: 527–530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Kramatschek B, Campos-Ortega JA (1994) Neuroectodermal transcription of the Drosophila neurogenic genes E(spl) and HLH-m5 is regulated by proneural genes. Development 120: 815–826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Furriols M, Bray S (2001) A model Notch response element detects suppressor of Hairless-dependent molecular switch. Curr Biol 11: 60–64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Kim J, Sebring A, Esch JJ, Kraus ME, Vorkwerk K, et al. (1996) Integration of positional signals and regulation of wing formation and identity by Drosophila vestigial gene. Nature 382: 133–138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Diaz-Benjumea FJ, Cohen SM (1995) Serrate signals through Notch to establish a Wingless-dependent organizer at the dorsal/ventral compartment boundary of the Drosophila wing. Development 121: 4215–4225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Rulifson EJ, Blair SS (1995) Notch regulates wingless expression and is not required for reception of the paracrine wingless signal during wing margin neurogenesis in Drosophila . Development 121: 2813–2824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. de Celis JF, Garcia-Bellido A, Bray SJ (1996) Activation and function of Notch at the dorsal-ventral boundary of the wing imaginal disc. Development 122: 359–369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Brunner E, Brunner D, Weimin F, Hafen E, Basler K (1999) The dominant mutation Glazed is a gain-of-function allele of wingless that, similar to loss of APC, interferes with normal eye development. Dev Biol 206: 178–188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Bänziger C, Soldini D, Schütt C, Zipperlen P, Hausmann G, et al. (1996) Wntless, a conserved membrane protein dedicated to the secretion of Wnt proteins from signalling cells. Cell 125: 509–522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Kramps T, Peter O, Brunner E, Nellen D, Froesch B, et al. (2002) Wnt/Wingless signalling requires BCL9/Legless-mediated recruitment of Pygopus to the nuclear beta-Catenin-TCF complex. Cell 109: 47–60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Geuking P, Narasimamurthy R, Basler K (2005) A genetic screen targeting the tumor necrosis factor/Eiger signalling pathway: identification of Drosophila TAB2 as a functionally conserved component. Genetics 171: 1683–1694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Giraldez AJ, Copley RR, Cohen SM (2002) HSPG modification by the secreted enzyme Notum shapes the Wingless morphogen gradient. Dev Cell 2: 667–676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Gerlitz O, Basler K (2002) Wingful, an extracellular feedback inhibitor of Wingless. Genes Dev 16: 1055–1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Jiang J, Struhl G (1998) Regulation of the Hedgehog and Wingless signaling pathways by the F-box/WD40-repeat protein Slimb. Nature 391: 493–496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Pai LM, Orsulic S, Bejsovec A, Peifer M (1997) Negative regulation of Armadillo, a Wingless effector in Drosophila . Development 124: 2255–2266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Doerks T, Copley RR, Schultz J, Ponting CP, Bork P (2002) Systematic identification of novel protein domain families associated with nuclear functions. Genome Res 12: 47–56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Pinter M, Jekely G, Szepesi RJ, Farkas A, Theopold U, et al. (1998) Ter94, a Drosophila homolog of the membrane fusion protein CDC48/p97, is accumulated in nonproliferating cells: in the reproductive organs and in the brain of the imago. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 28: 91–98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Meyer H, Bug M, Bremer S (2012) Emerging functions of the VCP/p97 AAA-ATPase in the ubiquitin system. Nat Cell Biol 14: 117–123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Bischof J, Bjoerklund M, Furger E, Schertel C, Taipale J, et al. (2013) A versatile platform for creating a comprehensive UAS-ORFeome library in Drosophila . Development 140: 2434–2442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Fiedler M, Mendoza-Topas C, Rutherford T, Miesczczanek J, Bienz M (2011) Dishevelled interacts with the DIX domain polymerization interface of Axin to interfere with its function in down-regulating β-Catenin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108: 1937–1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Lange V, Picotti P, Domon B, Aebersold R (2008) Selected reaction monitoring for quantitative proteomics: a tutorial. Mol Syst Biol 4: 222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Zhang Z, Lv X, Yin WC, Zhang X, Feng J, et al. (2013) Ter94 ATPase complex targets k11-linked ubiquitinated Ci to proteasomes for partial degradation. Dev Cell 25: 636–644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Ullah Z, Buckley MS, Arnosti DN, Henry RW (2007) Retinoblastoma protein regulation by the COP9 signalosome. Mol Biol Cell 18: 1179–1186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Ritz D, Vuk M, Kirchner P, Bug M, Schütz S, et al. (2011) Endolysosomal sorting of uqiquitinated caveolin-1 is regulated by VCP/p97 and UBXD1 and impaired by VCP disease mutations. Nat Cell Biol 13: 1116–1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Stamos JL, Weis WI (2013) The β-Catenin destruction complex. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5: a007898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Madsen L, Andersen KM, Prag S, Moos T, Semple CA, et al. (2008) Ubxd1 is a novel co-factor of the human p97 ATPase. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40: 2927–2942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Ghislain M, Dohmen RJ, Lévy F, Varshavsky A (1996) Cdc48p interacts with Ufd3p, a WD repeat protein required for ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae . EMBO J 15: 4884–4899. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Beskow A, Grimberg KB, Bott LC, Salomons FA, Dantuma NP, et al. (2009) A conserved unfoldase activity for the p97 AAA-ATPase in proteasomal degradation. J Mol Biol 394: 732–746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Yen JL, Flick K, Papagiannis CV, Mathur R, Tyrrell A, et al. (2012) Signal-induced disassembly of the SCF ubiquitin ligase complex by CDC48/p97. Mol Cell 48: 288–297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Kondo H, Rabouille C, Newman R, Levine TP, Pappin D, et al. (1997) p47 is a cofactor for p97-mediated membrane fusion. Nature 388: 75–87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Bruderer RM, Brasseur C, Meyer HH (2004) The AAA ATPase p97/VCP interacts with its alternative co-factors, Ufd1-Npl4 and p47, through a common bipartite binding mechanism. J Biol Chem 279: 49609–49615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Dietzl G, Chen D, Schnorrer F, Su KC, Barinova Y, et al. (2007) A genome-wide transgenic RNAi library for conditional gene inactivation in Drosophila . Nature 448: 151–156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Haley B, Hendrix D, Trang V, Levine M (2008) A simplified miRNA-based gene silencing method for Drosophila melanogaster . Dev Biol 321: 482–490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Bischof J, Maeda RK, Hediger M, Karch F, Basler K (2007) An optimized transgenesis system for Drosophila using germ-line-specific φC31 integrases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: 3312–3317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Validation of the alsRNAi phenotype by different RNAi target sites. (A) Location of 16 different siRNA target sites encoded by 16 RNAi lines with respect to the als cDNA region. The 16 different target sites are based on three different algorithms (VDRC, three different sites; Dharmacon, nine different sites; DSIR, four different sites). Nine of 16 target sites caused similar wing notching phenotypes (red bars in [A], similar phenotypes in [B–J]). Impairing Wg signaling via the overexpression of a dominant-negative pathway component, Lgs17E, causes a phenotype reminiscent of als depletion (K). Six target sites did not result in any phenotype (blue bars in [A]), and one target site caused a phenotype completely different from the nine other positive target sites, which we attribute to an off-target effect (OTE; purple bar in [A]). (L) Real-time PCR shows that ubiquitous expression of UAS-alsRNAi by c765-Gal4 effectively reduced als transcript levels in wing imaginal discs as monitored by two different real-time PCR primer pairs for als (a and b in the bar diagram). The degree of the mRNA knockdown correlates with the strength of the phenotype (cf. Figure 1B–1E). (M) Expression of alsRNAi-39000 with c765-Gal4 does not cause a phenotype. (N) Haplo-deficiency for als causes wing notches in combination with c765>alsRNAi-39000 expression.
(TIF)
Als can rescue alsRNAi phenotypes. (A) Overexpression of Als in wing imaginal discs often caused no phenotype, or mild notches at elevated expression (inset). (B) Overexpression of C-terminally epitope-tagged Als (AlsHA) caused wings with strong notches. (C) Targeting the 5′ UTR of endogenous als by alsoligo3_5′utr caused wings with notches. (D) Overexpression of N-terminally tagged Als (HAAls), which lacks UTRs, could rescue the alsRNAi-utr phentoype. (E) Expression of alsRNAi, which targets the ORF of endogenous als (alsoligo3_10UAS_ORF), caused wings with marginal notches or a small eye phenotype (G). These phenotypes could largely or completely be rescued by the overexpression of an RNAi-insensitive version of HAAls, which contains a mutated oligo3_ORF target site (F and H). Expression of UAS-GFP or UAS-CG42306 did not rescue the alsRNAi phenotype (I and J). Expression of UAS-CG42306 did not cause a phenotype in the wing (K) and caused legs devoid of the entire tarsal region (L). (M) Ter94HA overexpression did not rescue the alsRNAi phenotype, and did not show any phenoype in the wing (N).
(TIF)
Genetic interaction of als with the cell cycle and Wg signaling. (A–F) Underproliferation, not apoptosis, underlies the alsRNAi wing phenotype. Overexpression of a negative Wg pathway component, Lgs17E (A), and of alsRNAi (D) causes wing margin notches. Inhibition of apoptosis by overexpression of Diap1 could not rescue the wing phenotypes (B and E), whereas acceleration of the cell cycle by overexpression of String could rescue the wing phenotypes (C and F). (G–J″) als interacts with the Wg pathway. Reduction of Wg signaling (G–J) was provoked by (G) overexpression of a dominant-negative mutant form of Legless, Lgs17E, (H) depletion of pangolin (pan), (I) overexpression of Shaggy (Sgg), or (J) overexpression of Axin. Simultaneously depleting als (G″–J″) leads to an enhancement of the notched wing margin phenotype observed with depleting als alone (G′–J′).
(TIF)
als depletion in the thorax and legs. (A–H) alsRNAi expression in the notum, the primordium of the thorax, by pannier-Gal4, which is active in the mesothorax (E). als depletion causes mild thoracic clefts (B and C), a slight polarity defect of thoracic bristles, reduced or lost dorsocentral microchaete, and an overall shortening of the thorax and scutellum (B, C, F, and G). These phenotypes are reminiscent of impaired Wg signaling, for example, based on panRNAi expression (D) or based on Lgs17E overexpression (H). (I–K) alsRNAi expression in the leg primordium by distalless-Gal4 caused, similarly to impaired Wg signaling, a shortening of tarsal segments and a dorsolateral shift of the sex combs (J, K, L, and M), along with a significant dorsalization (K and M). (N) Impaired Notch signaling caused a loss of segmental junctions along the tarsus, resulting in a complete fusion of the tarsal segments. (O–Y) Analysis of impaired als function in the embryo. Expression of alsRNAi or the dominant-negative-like AlsHA by da-Gal4 ([S] alsRNAi lines: oligo2_3′utr; [T] oligo310UAS) caused shorter cuticles than in control embryos, with ventral denticle belts partially fused (S–V, X, and Y). Expression of armRNAi (P and Q) or UAS-Lgs17E by da-Gal4 (R and W) caused similar phenotypes.
(TIF)
als is expressed in the center of the wing pouch. (A and B) als in situ hybridization reveals a pronounced expression of als in the center of the wing pouch and a low level of expression in the remaining part of the wing disc. (B) (inset) Expression of UAS-alsRNAi by hh-Gal4 in the P-compartment (arrows) of wing imaginal discs caused a strong decrease in als expression. (C) Reporter expression from a genomic als-lacZ transgene is similar to als expression visualized by in situ hybridization. (D) Activation of Wg signaling by the overexpression of either UAS-wg or UAS-armS10 with nubbin-Gal4 at 29°C in wing imaginal discs was monitored by the upregulation of the Wg targets wingful (wf), naked (nkd), and senseless (sens) (bars 2–7). Similarly, activation of Wg signaling caused an upregulation of als expression (bars 8 and 9). Als was upregulated upon stimulation of the Wg pathway by inhibiting GSK3β in Kc-167 cells (detected by anti-UBXN6 antibody).
(TIF)
als does not interfere with Notch or Hedghog signaling. m8-lacZ expression at the D/V boundary of wing imaginal discs (A) is not altered upon als depletion (A′ and A″). NRE-GFP expression is not altered upon als depletion (inset of A and A″). vg-BE-lacZ expression (B) is not altered upon als depletion (B′ and B″). (C) Overexpression of E(spl), the nuclear mediator of Notch signaling, causes reduction and loss of wing veins. (D) E(spl) co-expressed with alsRNAi resulted in wings with lost veins combined with wing notches. (E) Overexpression of HLHmbeta, a positive target of Notch signaling, abolishes wing veins. (F) HLHmbeta co-expressed with alsRNAi resulted in veinless wings with marginal notches. (G) Overexpression of SmoI constitutively activates Hh signaling, which results in overgrown wings and ectopic veins. (H) Ectopic Hh signaling combined with alsRNAi resulted in a wing size reduction predominantly of distal tissue, without altering the phenotypes symptomatic for elevated Hh signaling, like overgrowth along the A/P axis or ectopic veins. (I and J) ptc-lacZ expression is not altered upon depletion of als. (K) Ectopic expression of Upd, the ligand of the Jak/Stat pathway, caused overgrown eyes, which was not altered upon co-expression of alsRNAi (L). (M) Impaired Ras/EGFR signaling caused slightly smaller wings lacking wing veins; co-expression of alsRNAi resulted in veinless wings with marginal notches (N).
(TIF)
als depletion does not affect Wg expression. (A–F′) wg-lacZ and Wg protein expression is not altered upon expression of alsRNAi. Adult phenotypes corresponding to the respective genetic manipulations during wing disc development are shown for line 39000 (A–C), line oligo310UAS (D–E), and line oligo310UAS (F–G). (F–G) Upon strong RNAi expression by hh-Gal4 in the P-compartment (green, GFP expression), the P-compartment strongly undergrows, yet shows normal Wg expression.
(TIF)
Als localizes adjacent to the apicolateral cell membrane. HAAls expressed with nubbin-Gal4 in the wing pouch localizes in the cytoplasm adjacent to the cell membrane (A–E″). HAAls localization overlaps to a large extent with that of E-Cadherin (C′ and C″), Arm (D′ and D″), and Fz2 (E′ and E″). Cell nuclei are blue (DAPI in the color-merged pictures [B′, C″, D″, and E″]).
(TIF)
The PUG and the coiled-coil domains are essential for Als function. Expression of alsRNAi in the wing primordium with nubbin-Gal4 (A) or with 181-Gal4 (B and C) causes nicked wing margins. Co-expression of AlsΔPUG (D–F) or AlsΔN (G–I) did not alter the alsRNAi phenotype, whereas AlsΔUBX rescued the alsRNAi phenotype (J–L) comparably to full-length Als (insets of J–L). cc (coiled coil domain, within the N-terminal region of Als).
(TIF)
Negative pathway components are not altered upon als depletion. (A–D′) Axin-GFP expression levels are not changed upon depletion of als (line 39000 [C–D′, cf. A–B′]). Expression of Apc2HA (E–H) and ShaggyHA (I–L) is not altered upon als depletion (line 39000). (M–P) Expression levels of endogenous Fz2 (anti-Fz2-antibody staining) and ArrowHA were not altered upon depletion of als (line oligo310UAS, 29°C). Confocal pictures were taken at 40× magnification/2.5× zoom, except (A, A′, C, and C′): 40× magnification, 1× zoom; (E–L, O, and P): anti-HA antibody staining.
(TIF)
Als acts upstream of Arm's proteasomal degradation. The overexpression of CSN6 suppressed als RNAi phenotypes (H, K, and N, cf. G, J, and M) as well as a Wg loss-of-function phenotype caused by Axin overexpression (B, cf. A), but not as well as a Wg loss-of-function phenotype caused by the overexpression of Lgs17E (E, cf. D). Similarly, depletion of ubiquitin could suppress phenotypes based on als RNAi (I, L, and O, cf. G, J, and M) and Axin overexpression (C, cf. A), but could not ameliorate the Lgs17E overexpression phenotype (F, cf. D).
(TIF)
Supporting information.
(DOCX)