Abstract
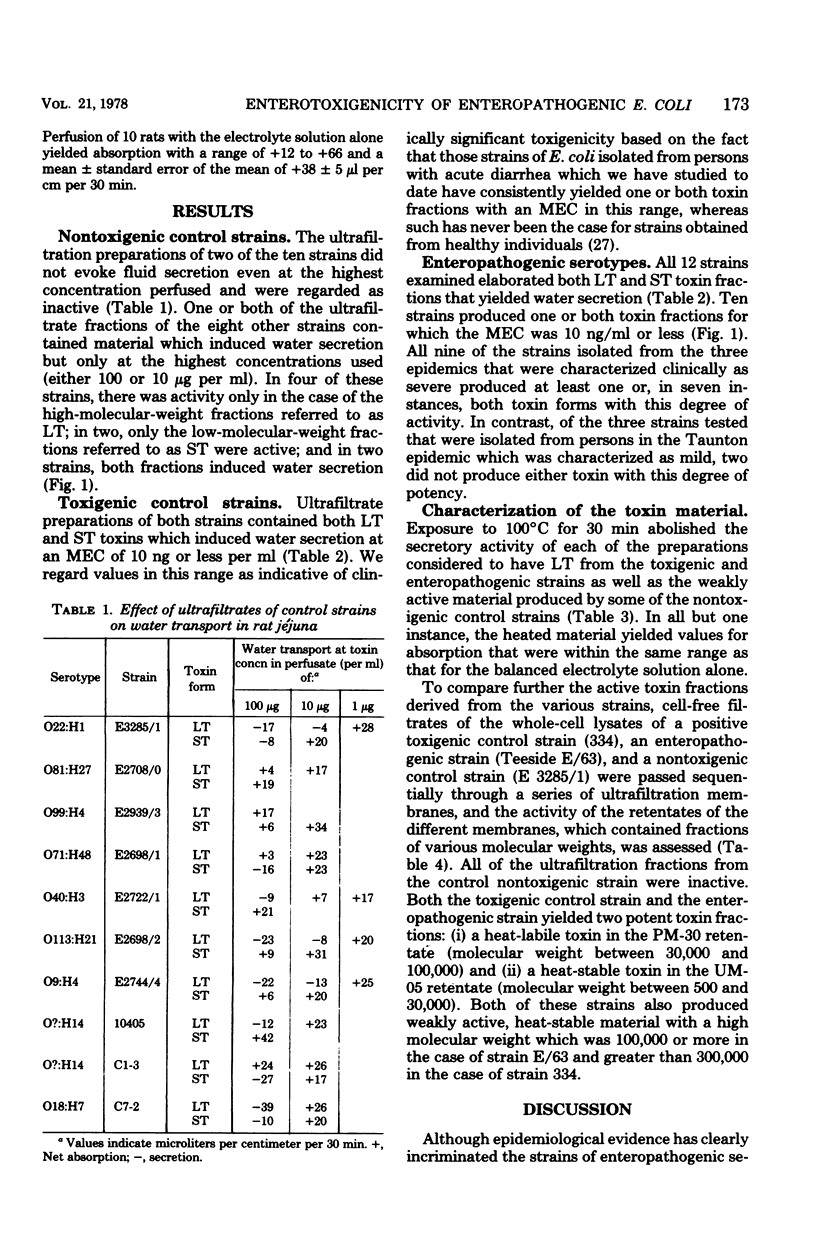
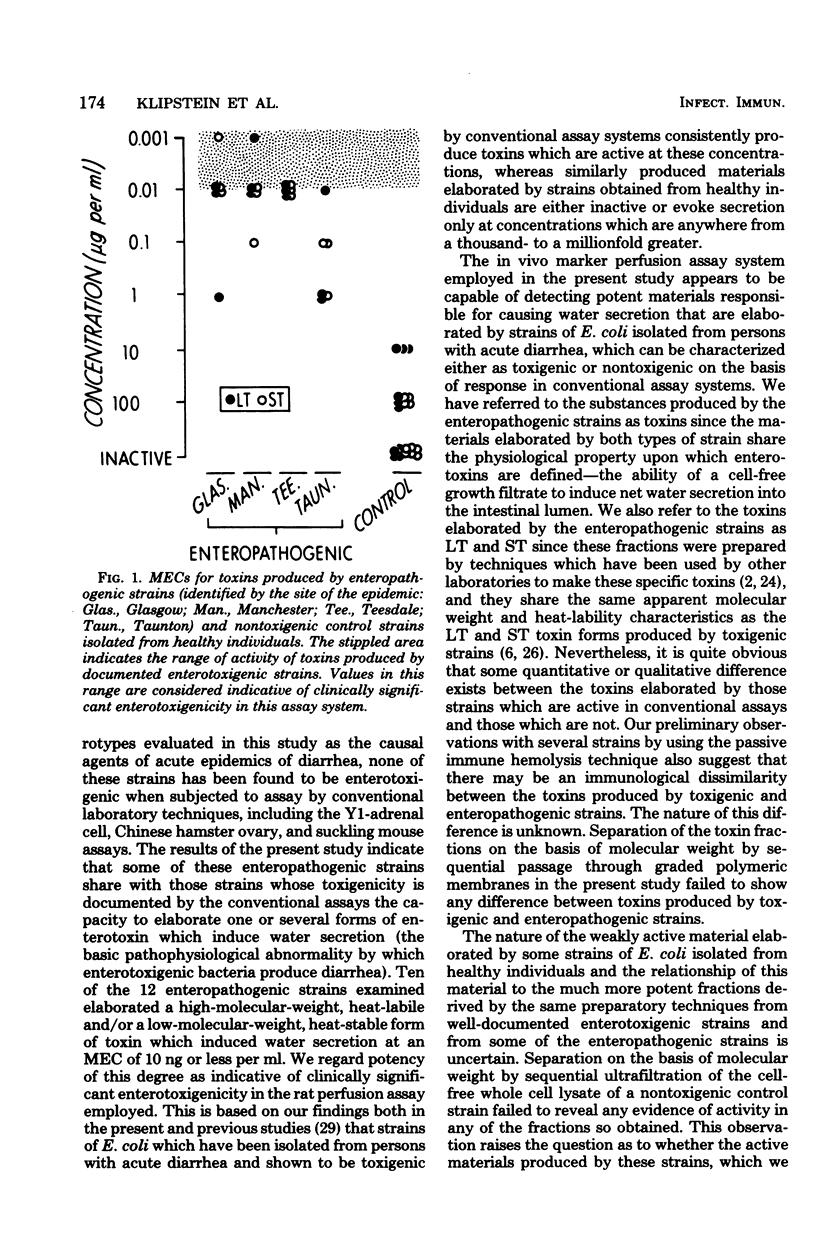
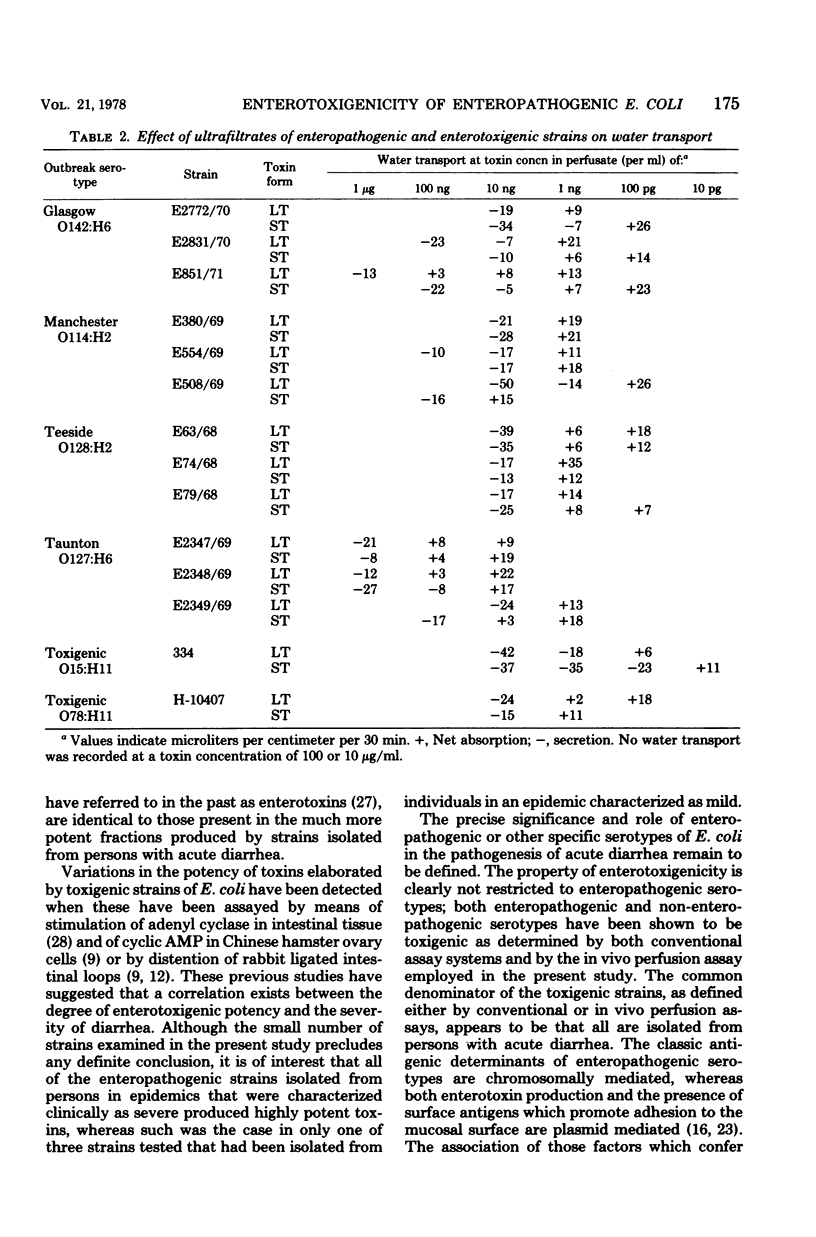
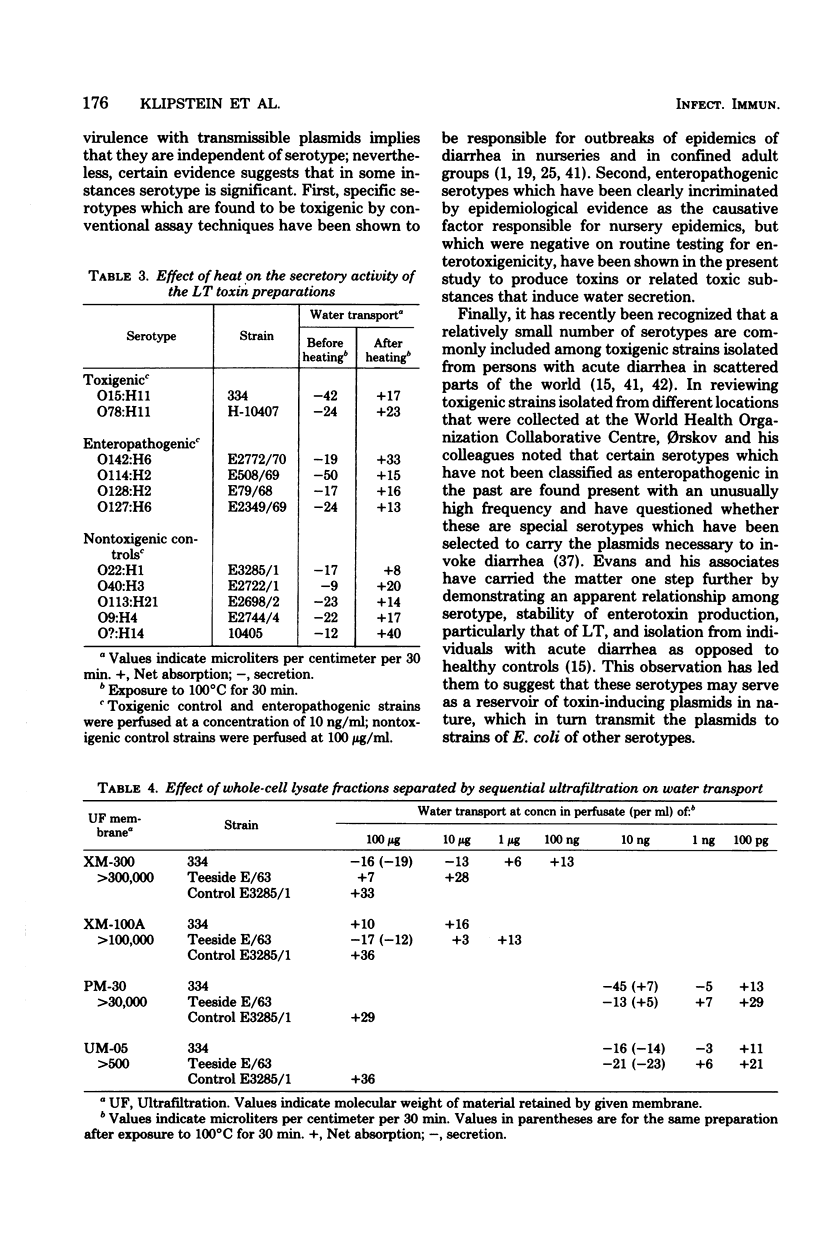
Enteropathogenic serotypes of Escherichia coli which have been incriminated by epidemiological evidence as responsible for epidemics of acute diarrhea in infants are often found to be nontoxigenic when tested by conventional systems such as Y1-adrenal, Chinese hamster ovary, and suckling mouse assays. Twelve such strains, representing four different enteropathogenic serotypes, were examined for their capacity to elaborate toxic materials which alter water transport. Ultrafiltration fractions prepared to contain either a high-molecular-weight, heatlabile or a low-molecular-weight, heat-stable form of toxin from each strain were perfused through rat jejuna in graded concentrations ranging from 100 μg to 0.1 ng/ml. Ten of the twelve enteropathogenic strains produced one or both toxin forms that induced water secretion at concentrations of 1 to 10 ng/ml. Values in this range are considered indicative of clinically significant enterotoxigenicity in this assay system, and toxins from well-documented toxigenic strains examined in this study were active at these same concentrations. Similar preparations from ten control strains from healthy persons were either inactive or evoked water secretion only at concentrations of 10 to 100 μg/ml. These observations suggest that enteropathogenic serotypes of E. coli isolated from epidemics of infantile diarrhea produce diarrhea by elaborating potent heat-labile and heat-stable toxin forms which alter water transport but which are inactive in conventional assay systems. The manner in which these toxins differ either quantitatively or qualitatively from those which stimulate the conventional test systems is unknown.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyer K. M., Petersen N. J., Farzaneh I., Pattison C. P., Hart M. C., Maynard J. E. An outbreak og gastroenteritis due to E. coli 0142 in a neonatal nursery. J Pediatr. 1975 Jun;86(6):919–927. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80230-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bywater R. J. Dialysis and ultrafiltration of heat-stable enterotoxin from Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 1972 Aug;5(3):337–343. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-3-337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R., Blake R. K. Diarrhea due to Escherichia coli in the rabbit: a novel mechanism. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):454–462. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Wallace R. B., Whipp S. C., Olarte J. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and diarrheal disease in Mexican children. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):482–485. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner F., Jaksche H., Stöckl W. Escherichia coli enterotoxin: purification, partial characterization, and immunological observations. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133 (Suppl):142–156. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_1.s142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Formal S. B., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P., Sheahan D. G., LaBrec E. H., Kalas J. P. Pathogenesis of Escherichia coli diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 1;285(1):1–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107012850101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P. D., Chang C. P., Smith D. Enterotoxigenicity and invasive capacity of "enteropathogenic" serotypes of Escherichia coli. J Pediatr. 1976 Jul;89(1):8–10. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80917-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Blacklow N. R., Smith D. H. Role of heat-labile toxigenic Escherichia coli and Reovirus-like agent in diarrhoea in Boston children. Lancet. 1975 Dec 6;2(7945):1113–1116. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Louria C. J., Smith A. L., Smith D. Variation in enterotoxigenicity of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1977 Feb;135(2):195–200. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.2.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Editorial: E. coli enteritis. Lancet. 1975 Dec 6;2(7945):1131–1132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etkin S., Gorbach S. L. Studies on enterotoxin from Escherichia coli associated with acute diarrhea in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Jul;78(1):81–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Silver R. P., Evans D. J., Jr, Chase D. G., Gorbach S. L. Plasmid-controlled colonization factor associated with virulence in Esherichia coli enterotoxigenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):656–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.656-667.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G. Direct serological assay for the heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli, using passive immune hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):604–609. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.604-609.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., DuPont H. L., Orskov F., Orskov I. Patterns of loss of enterotoxigenicity by Escherichia coli isolated from adults with diarrhea: suggestive evidence for an interrelationship with serotype. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):105–111. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.105-111.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G. Inhibition of immune hemolysis: serological assay for the heat-labile enterotoxin of Excherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):100–105. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.100-105.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt M. C., DuPont H. L. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli: lack of correlation of serotype with pathogenicity. J Infect Dis. 1976 Feb;133(2):153–156. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.2.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Khurana C. M. Toxigenic Escherichia coli: a cause of infantile diarrhea in Chicago. N Engl J Med. 1972 Oct 19;287(16):791–795. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197210192871603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. J., Rowe B., Henderson A., Byatt M. E., Maclaurin J. C. A NEW Escherichia coli O-group, O159, associated with outbreaks of enteritis in infants. Scand J Infect Dis. 1976;8(3):195–198. doi: 10.3109/inf.1976.8.issue-3.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. J., Scotland S. M., Rowe B. Enterotoxin testing of Escherichia coli causing epidemic infantile enteritis in the U.K. Lancet. 1976 Mar 20;1(7960):629–631. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Ganguly U., Casper A. G., Moore E. J., Pierce N. F., Carpenter C. C. Effect of Escherichia coli on fluid transport across canine small bowel. Mechanism and time-course with enterotoxin and whole bacterial cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1707–1714. doi: 10.1172/JCI107352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L., Barnum D. A. A heat-labile enterotoxin from strains of Eschericha coli enteropathogenic for pigs. J Infect Dis. 1969 Oct;120(4):419–426. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C., So M., Falkow S. The enterotoxin plasmids of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jul;130(1):40–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs B. C., Rowe B., Kendall M., Turnbull P. C., Ghosh A. C. Escherichia coli O 27 in adult diarrhoea. J Hyg (Lond) 1976 Dec;77(3):393–400. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400055777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T. M., Wu B. J. Biochemical properties of Escherichia coli low-molecular-weight, heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):342–347. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.342-347.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S. I., Holzel A., Wolman B., Keen J. H., Miller V., Taylor J., Gross R. J. Outbreak of infantile gastro-enteritis caused by Escherichia coli O114. Arch Dis Child. 1970 Oct;45(243):656–663. doi: 10.1136/adc.45.243.656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor H. S., Tao P., Gorbach S. L. Stimulation of intestinal adenyl cyclase by Escherichia coli enterotoxin: comparison of strains from an infant and an adult with diarrhea. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jan;129(1):1–9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Short H. B. Relative enterotoxigenicity of coliform bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136(2):205–215. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.2.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Horowitz I. R., Engert R. F., Schnenk E. A. Effect of Klebsiella pneumoniae enterotoxin on intestinal transport in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):799–807. doi: 10.1172/JCI108158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Lee C. S., Engert R. F. Assay of Escherichia coli enterotoxins by in vivo perfusion in the rat jejunum. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1004–1010. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1004-1010.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Caplan E. S., Waterman D., Cash R. A., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J. Diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli that produce only heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):78–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.78-82.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love W. C., Gordon A. M., Gross R. J., Rowe B. Infantile gastroenteritis due to Escherichia coli 0142. Lancet. 1972 Aug 19;2(7773):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91738-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Merson M. H., Sack D. A., Wells J. G., Martin W. T., Dewitt W. E., Feeley J. C., Sack R. B., Bessudo D. M. Laboratory investigation of diarrhea in travelers to Mexico: evaluation of methods for detecting enterotoxigenic Echerichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 May;3(5):486–495. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.5.486-495.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neter E. Editorial: Escherichia coli as a pathogen. J Pediatr. 1976 Jul;89(1):166–168. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80975-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I., Evans D. J., Jr, Sack R. B., Sack D. A., Wadström T. Special Escherichia coli serotypes among enterotoxigenic strains from diarrhoea in adults and children. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1976 Jun 1;162(2):73–80. doi: 10.1007/BF02121318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Wallace C. K. Stimulation of jejunal secretion by a crude Escherichia coli enterotixin. Gastroenterology. 1972 Sep;63(6):439–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe B., Gross R. J., Scotland S. M. Letter: Rheovirus and E. coli in infantile enteritis. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Aug;29(8):761–762. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.8.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe B., Gross R. J., Scotland S. M. Letter: Serotyping of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Lancet. 1975 Nov 8;2(7941):925–926. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92160-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder R. W., Wachsmuth I. K., Buxton A. E., Evans D. G., DuPont H. L., Mason E., Barrett F. F. Infantile diarrhea produced by heat-stable enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 14;295(16):849–853. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610142951601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Kaminsky D. C., Sack R. B., Wamola I. A., Orskov F., Orskov I., Slack R. C., Arthur R. R., Kapikian A. Z. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhea of travelers: a prospective study of American Peace Corps volunteers. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1977 Aug;141(2):63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., McLaughlin J. C., Sack R. B., Orskov F., Orskov I. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from patients at a hospital in Dacca. J Infect Dis. 1977 Feb;135(2):275–280. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.2.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Editorial: Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli--an emerging pathogen. N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 14;295(16):893–895. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610142951611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Hirschhorn N., Brownlee I., Cash R. A., Woodward W. E., Sack D. A. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia-coli-associated diarrheal disease in Apache children. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 15;292(20):1041–1045. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505152922001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Letter: Serotyping of E. coli. Lancet. 1976 May 22;1(7969):1132–1132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore E. G., Dean A. G., Holik K. J., Davis B. R. Enterotoxin-producing Escherichia coli and diarrheal disease in adult travelers: a prospective study. J Infect Dis. 1974 May;129(5):577–582. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.5.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. Infectious infantile enteritis, yesterday and today. Proc R Soc Med. 1970 Dec;63(12):1297–1301. doi: 10.1177/003591577006301233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



