Abstract
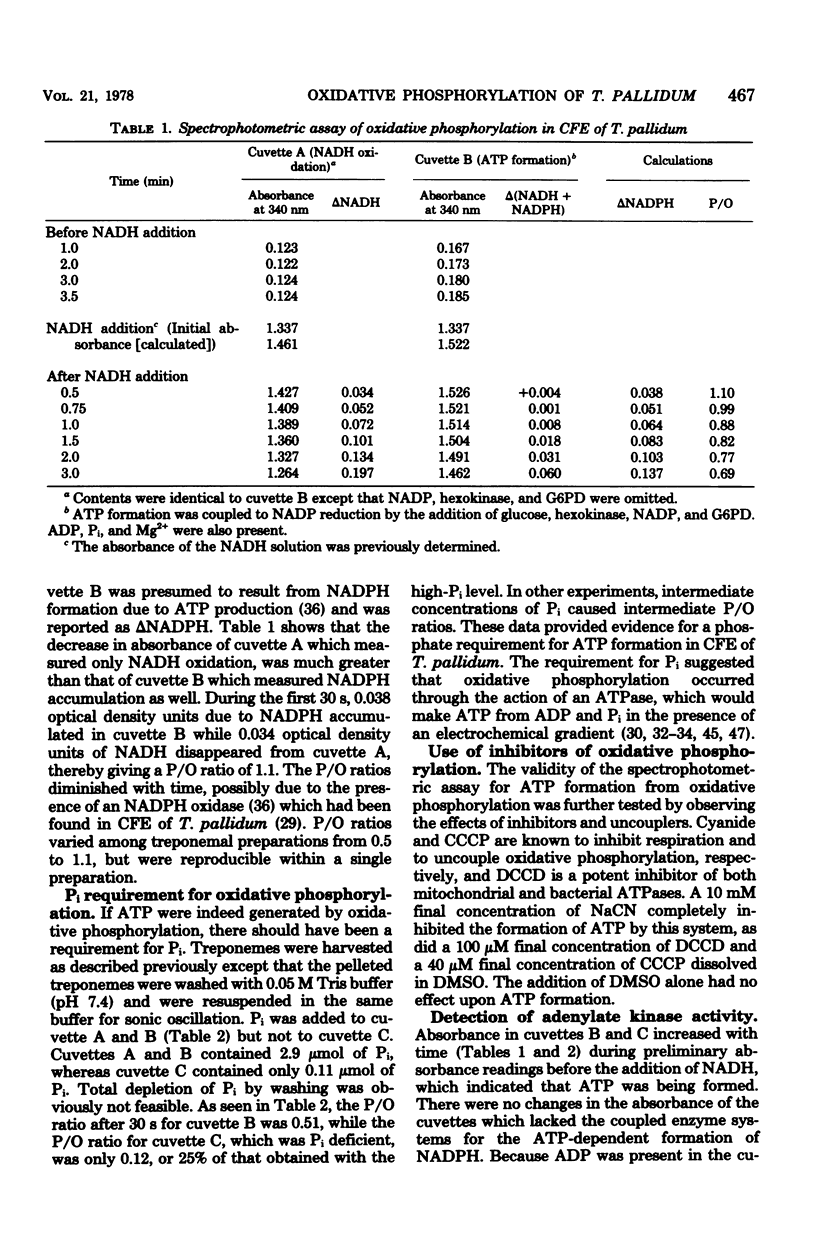
Exogenous and endogenously generated reduced pyridine nucleotides caused marked stimulation of O2 uptake when added to treponemal cell-free extracts, which indicated that terminal electron transport was coupled to the consumption of O2. Oxidation of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) was shown to correlate stoichiometrically with O2 reduction, suggesting that NADH was being oxidized through a mainstream respiratory chain dehydrogenase. Oxygen evolution in treponemal extracts was observed after the completion of O2 uptake which was stimulated by exogenous NADH and endogenously generated reduced NAD phosphate. Oxygen evolution was inhibited by both cyanide and pyruvate, which was consistent with O2 release from H2O2 by catalase. The addition of exogenous H2O2 to treponemal extracts caused rapid O2 evolution characteristic of a catalase reaction. A spectrophotometric assay was used to measure ATP formation in T. pallidum cell-free extracts that were stimulated with NADH. P/O ratios from 0.5 to 1.1 were calculated from the amounts of ATP formed versus NADH oxidized. Phosphorylating activity was dependent on Pi concentration and was sensitive to cyanide, N, N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, and carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazone. Adenine nucleotide pools of T. pallidum were measured by the firefly luciferin-luciferase assay. Shifts in adenine nucleotide levels upon the addition of NADH to cell-free extracts were impossible to evaluate due to the presence of NAD+ nucleosidase. However, when whole cells, previously incubated under an atmosphere of 95% N2-5% CO2, were sparged with air, ATP and ADP levels increased, while AMP levels decreased. The shift was attributed to both oxidative phosphorylation and to the presence of an adenylate kinase activity. T. pallidum was also found to possess an Mg2+ - and Ca2+ -stimulated ATPase activity which was sensitive to N, N′ -dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. These data indicated a capability for oxidative phosphorylation by T. pallidum.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMS A., McNAMARA P., JOHNSON F. B. Adenosine triphosphatase in isolated bacterial cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1960 Dec;235:3649–3662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson D. E., Walton G. M. Adenosine triphosphate conservation in metabolic regulation. Rat liver citrate cleavage enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 10;242(13):3239–3241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baak J. M., Postma P. W. Oxidative phosphorylation in intact Azotobacter vinelandii. FEBS Lett. 1971 Dec 15;19(3):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80511-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball W. J., Jr, Atkinson D. E. Adenylate energy charge in Saccharomyces cerevisiae during starvation. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):975–982. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.975-982.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Nichols J. C., Hayes N. C. Virulent Treponema pallidum: aerobe or anaerobe. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):704–711. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.704-711.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogin E., Higash T., Brodie A. F. Exogenous NADH oxidation and particulate fumarate reductase in Mycobacterium phlei. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jan;129(1):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90168-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan-Jones D. G., Whittenbury R. Haematin-dependent oxidative phosphorylation in Streptococcus faecalis. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Oct;58(2):247–260. doi: 10.1099/00221287-58-2-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattell K. J., Lindop C. R., Knight I. G., Beechey R. B. The identification of the site of action of NN'-dicyclohexylcarbodi-imide as a proteolipid in mitochondrial membranes. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):169–177. doi: 10.1042/bj1250169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman A. G., Fall L., Atkinson D. E. Adenylate energy charge in Escherichia coli during growth and starvation. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1072–1086. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1072-1086.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole H. A., Wimpenny J. W., Hughes D. E. The ATP pool in Escherichia coli. I. Measurement of the pool using modified luciferase assay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;143(3):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(67)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. D., Barber M. K. Oxygen uptake by Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):123–127. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.123-127.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhople A. M., Hanks J. H. Quantitative extraction of adenosine triphosphate from cultivable and host-grown microbes: calculation of adenosine triphosphate pools. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):399–403. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.399-403.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J. Membrane Mg-(Ca)-Activated Adenosine Triphosphatase of Escherichia coli: Characterization in the Membrane-Bound and Solubilized States. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1203–1212. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1203-1212.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddock B. A., Jones C. W. Bacterial respiration. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):47–99. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.47-99.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Baarda J. R., Baron C., Abrams A. Inhibition of membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase and of cation transport in Streptococcus faecalis by N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2261–2268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempfling W. P. Studies of the efficiency of oxidative phosphorylation in intact Escherichia coli B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;205(2):169–182. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90247-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemme J. H., Gest H. Regulatory properties of an inorganic pyrophosphatase from the photosynthic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):721–725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lysko P. G., Cox C. D. Terminal electron transport in Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):885–890. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.885-890.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P. Coupling of phosphorylation to electron and hydrogen transfer by a chemi-osmotic type of mechanism. Nature. 1961 Jul 8;191:144–148. doi: 10.1038/191144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C., Kashket E. R., Wilson T. H. A protonmotive force drives ATP synthesis in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3896–3900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. J., Jones C. W. Oxidative phosphorylation in bacteria which contain different cytochrome oxidases. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):144–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. A chemiosmotic molecular mechanism for proton-translocating adenosine triphosphatases. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jul 15;43(2):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80997-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Chemiosmotic coupling in oxidative and photosynthetic phosphorylation. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1966 Aug;41(3):445–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1966.tb01501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. C., Baseman J. B. Carbon sources utilized by virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1044–1050. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1044-1050.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINCHOT G. B. A rapid method for measuring phosphorylation coupled to the oxidation of reduced diphosphopyridine nucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1957 Nov;229(1):11–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchey T. W., Seeley H. W. Cytochromes in Streptococcus faecalis var. zymogenes grown in a haematin-containing medium. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Dec;85(2):220–228. doi: 10.1099/00221287-85-2-220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberton A. M., Wolfe R. S. Adenosine triphosphate pools in Methanobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):43–51. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.43-51.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J., Cooper J. M. Method of determining oxygen concentrations in biological media, suitable for calibration of the oxygen electrode. Anal Biochem. 1970 Feb;33(2):390–399. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorth M., Jensen P. K. Determination of catalase activity by means of the Clark oxygen electrode. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 16;139(1):171–173. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller N. L., Cox C. D. Catabolism of glucose and fatty acids by virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):60–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.60-68.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Verseveld H. W., Stouthamer A. H. Oxidative phosphorylation in Micrococcus denitrificans: calculation of the P/O ratio in growing cells. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Apr 1;107(3):241–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00425334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C., SMITH L. LOCALIZATION OF THE ENZYMES THAT CATALYZE HYDROGEN AND ELECTRON TRANSPORT IN HEMOPHILUS PARAINFLUENZAE AND THE NATURE OF THE RESPIRATORY CHAIN SYSTEM. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3956–3963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I. C., Mitchell P. The proton-translocating ATPase of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 15;40(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80880-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. M., Alderette J. F., Maloney P. C., Wilson T. H. Protonmotive force as the source of energy for adenosine 5'-triphosphate synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):327–337. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.327-337.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Thienen G., Postma P. W. Coupling between energy conservation and active transport of serine in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 25;323(3):429–440. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Beek E. G., Stouthamer A. H. Oxidative phosphorylation in intact bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973;89(4):327–339. doi: 10.1007/BF00408900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


