Abstract
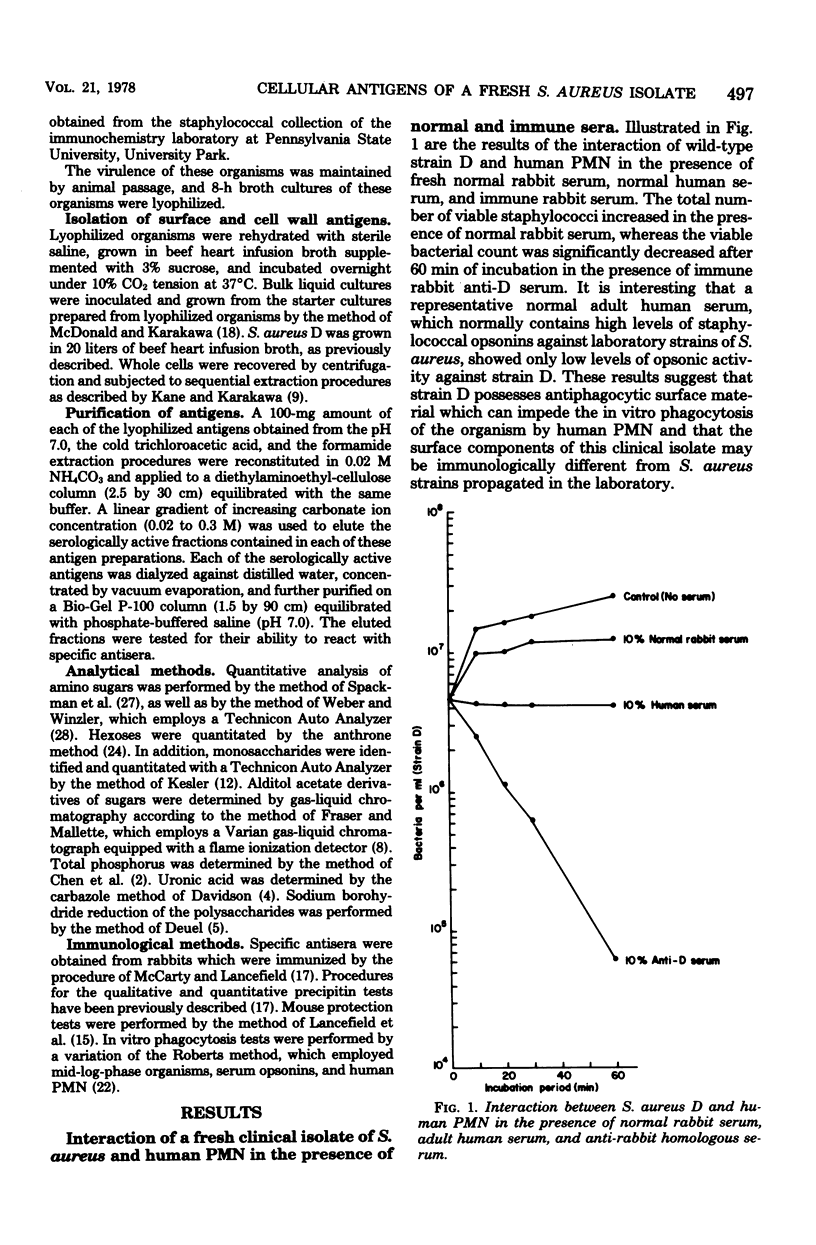
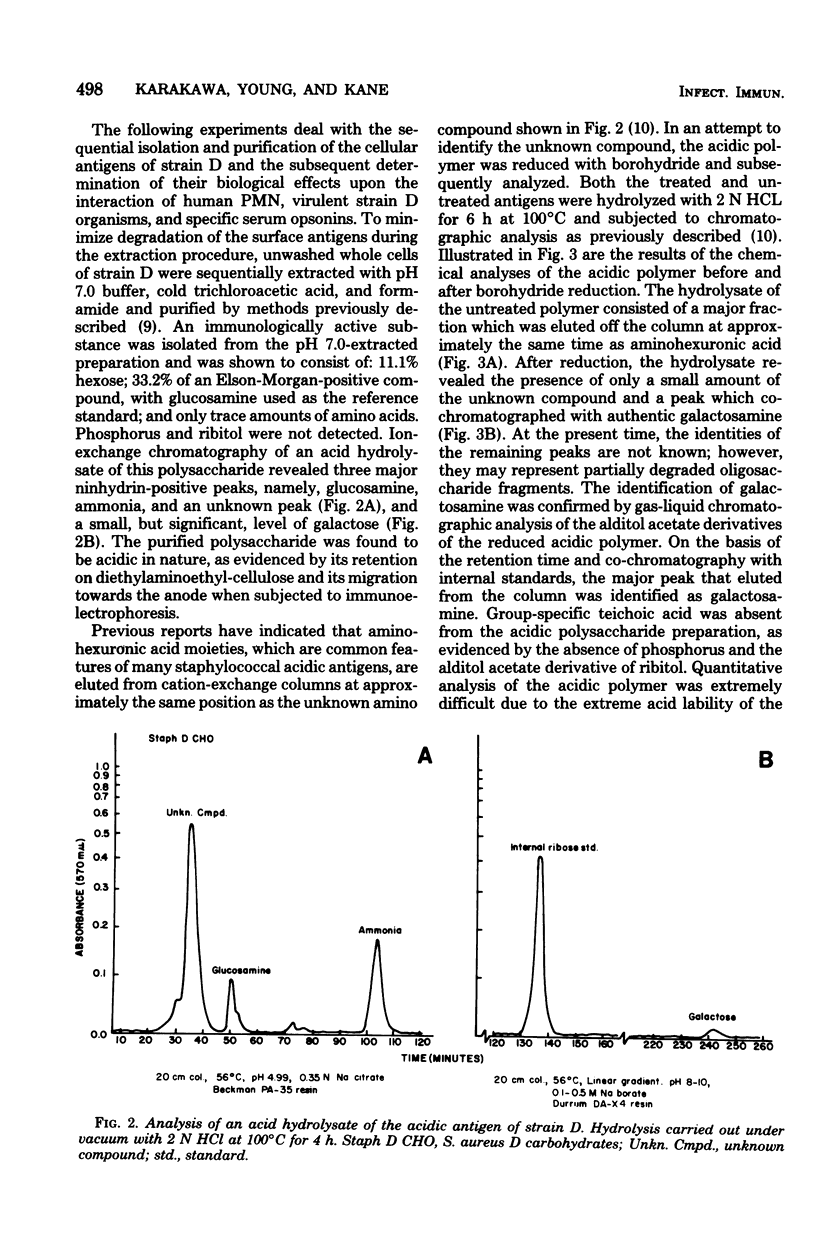
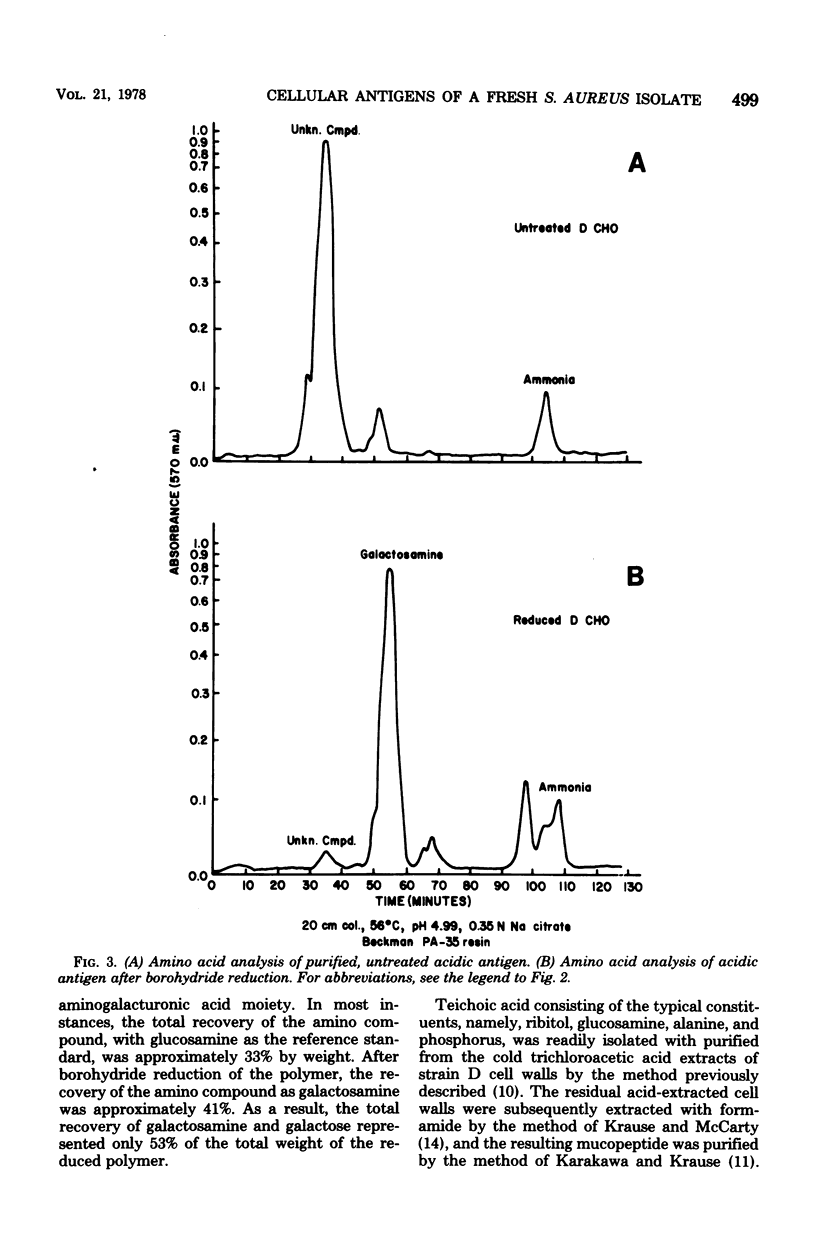
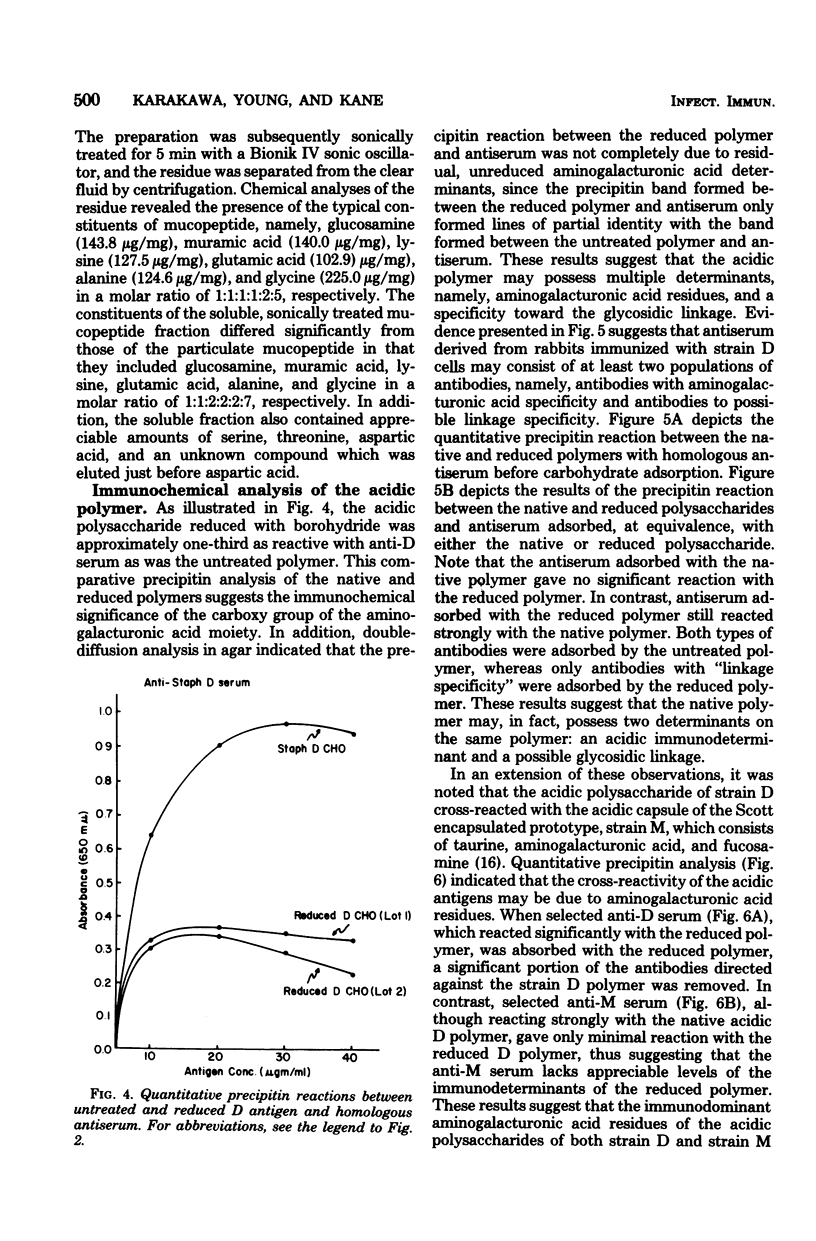
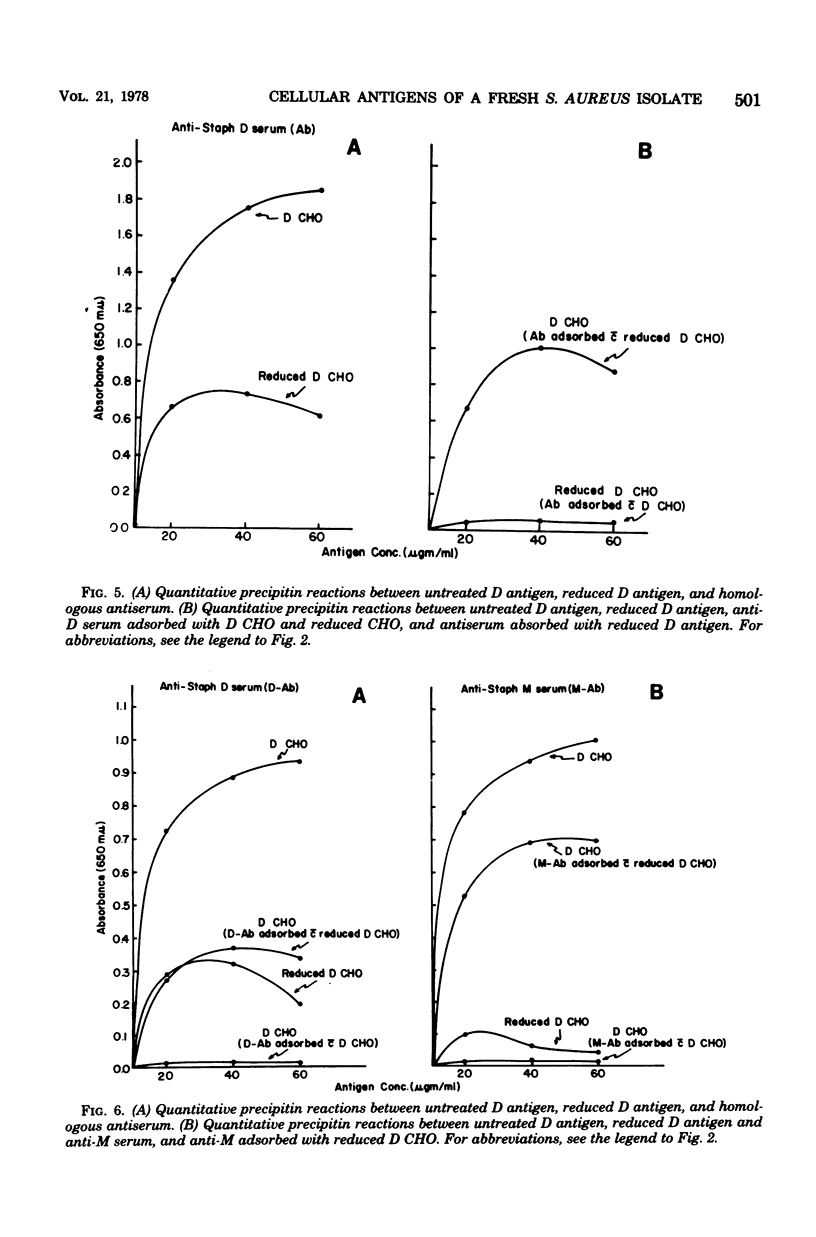
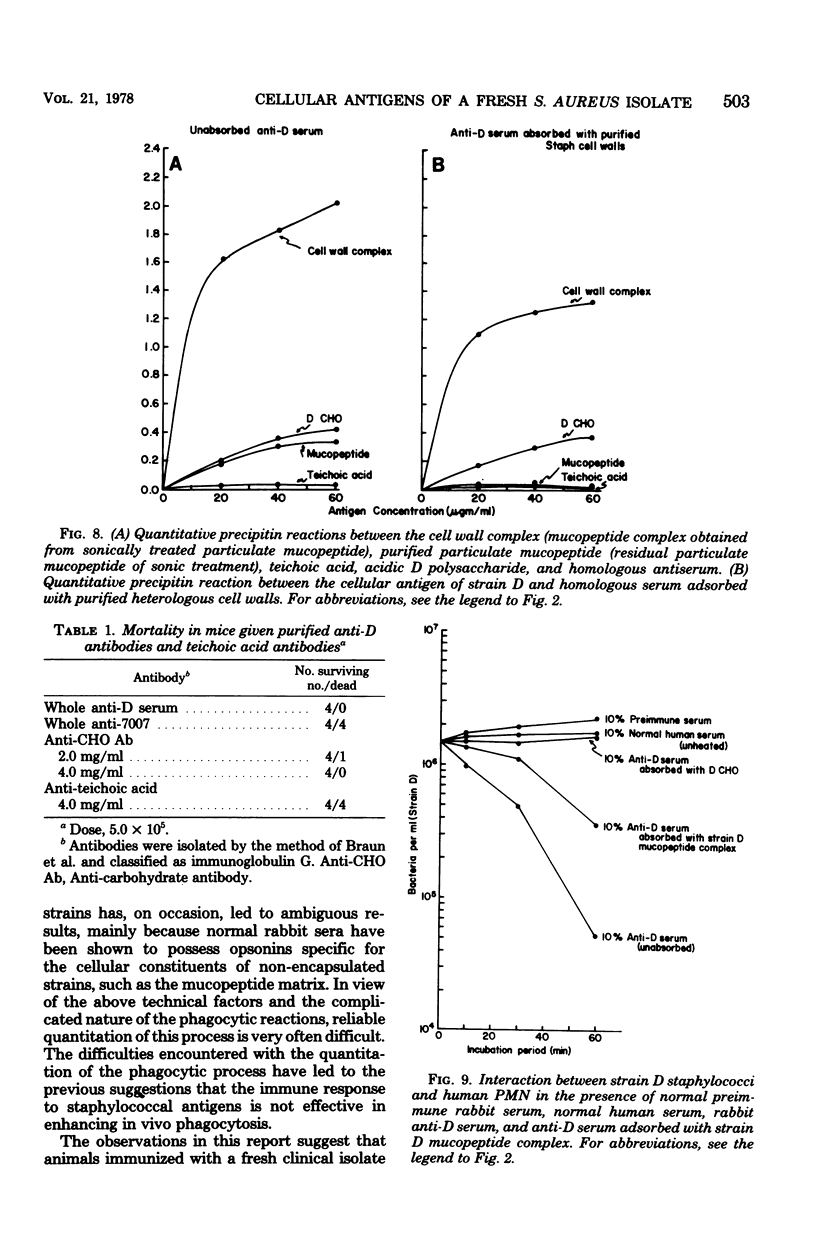
The in vitro interaction of a fresh clinical isolate of Staphylococcus aureus and polymorphonuclear leukocytes was investigated. The importance of the various cellular constituents as host immunological factors was analyzed, and the results suggested that two components, namely, an acidic polysaccharide consisting of a predominance of aminogalacturonic acid and a strain-specific mucopeptide complex, may be involved in impeding in vitro opsonization of the organism by leukocytes. Immunochemical analysis indicated that the acidic polysaccharide possessed the same immunodominant aminogalacturonic acid residues as the antiphagocytic acidic antigen of the encapsulated prototype Scott strain. Antisera derived from rabbits immunized with strain D contained two types of opsonins, those with acidic polymer specificity and those with mucopeptide complex specificity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braun D. G., Krause R. M. The individual antigenic specificity of antibodies to streptococcal carbohydrates. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):969–989. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugharty H., Martin R. R., White A. Antibodies against staphylococcal teichoic acids and type-specific antigens in man. J Immunol. 1967 Jun;98(6):1123–1129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easmon C. S., Glynn A. A. Comparison of subcutaneous and intraperitoneal staphylococcal infections in normal and complement-deficient mice. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):399–406. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.399-406.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekstedt R. D. Immune response to surface antigens of Staphylococcus aureus and their role in resistance to staphylococcal disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):203–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser B. A., Mallette M. F. An improved isolation method and new composition data for Forssman hapten from sheep erythrocytes. Immunochemistry. 1973 Nov;10(11):745–753. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAUSE R. M., MCCARTY M. Studies on the chemical structure of the streptococcal cell wall. I. The identification of a mucopeptide in the cell walls of groups A and A-variant streptococci. J Exp Med. 1961 Jul 1;114:127–140. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. A., Karakawa W. W. Multiple polysaccharide antigens of group B streptococcus, type Ia: emphasis on a sialic acid type-specific polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2155–2160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Kane J. A. Immunochemical analysis of a Smith-like antigen isolated from two human strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol. 1975 Aug;115(2):564–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Krause R. M. Studies on the immunochemistry of streptococcal mucopeptide. J Exp Med. 1966 Aug 1;124(2):155–171. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.2.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M. G., Melly M. A. The importance of surface antigens in staphylococcal virulence. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 23;128(1):231–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancefield R. C., McCarty M., Everly W. N. Multiple mouse-protective antibodies directed against group B streptococci. Special reference to antibodies effective against protein antigens. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):165–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liau D. F., Hash J. H. Structural analysis of the surface polysaccharide of Staphylococcus aureus M. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):194–200. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.194-200.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCARTY M., LANCEFIELD R. C. Variation in the group-specific carbohydrate of group A streptococci. I. Immunochemical studies on the carbohydrates of variant strains. J Exp Med. 1955 Jul 1;102(1):11–28. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald H. C., Karakawa W. W. Immunochemical analysis of a uronic acid polymer of Staphylococcus epidermidis, strain 53. J Immunol. 1970 Aug;105(2):389–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melly M. A., Duke L. J., Liau D. F., Hash J. H. Biological properties of the encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus M. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):389–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.389-397.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson D. S., Kazmierowski J. A., Dossett J. H., Williams R. C., Jr, Quie P. G. Studies of immune and normal opsonins during experimental staphylococcal infection in rabbits. J Immunol. 1969 May;102(5):1235–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Verhoef J., Sabath L. D., Quie P. G. Extracellular and bacterial factors influencing staphylococcal phagocytosis and killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):496–501. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.496-501.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. B. The relationship between group A and group C meningococcal polysaccharides and serum opsonins in man. J Exp Med. 1970 Mar 1;131(3):499–513. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D. E., Melly M. A. Speculations on the immunology of staphylococcal infections. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 23;128(1):274–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11644.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shayegani M. Failure of Immune Sera to Enhance Significantly Phagocytosis of Staphylococus aureus: Nonspecific Adsorption of Phagocytosis-Promoting Factors. Infect Immun. 1970 Dec;2(6):742–749. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.6.742-749.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shayegani M., Hisatsune K., Mudd S. Cell Wall Component Which Affects the Ability of Serum to Promote Phagocytosis and Killing of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1970 Dec;2(6):750–756. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.6.750-756.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P., Winzler R. J. Determination of hexosaminitols by ion-exchange chromatography and its application to alkali-labile glycosidic linkages in glycoproteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Feb;129(2):534–538. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]