Abstract
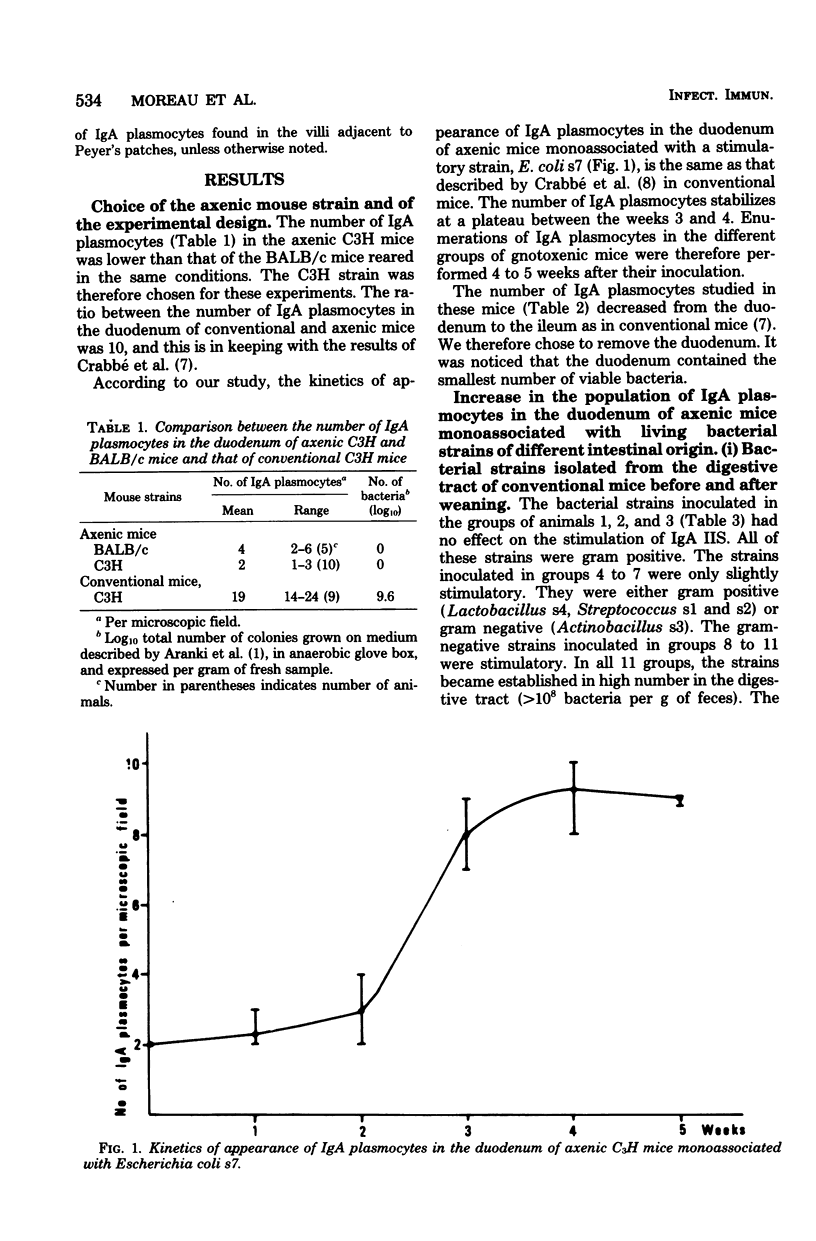
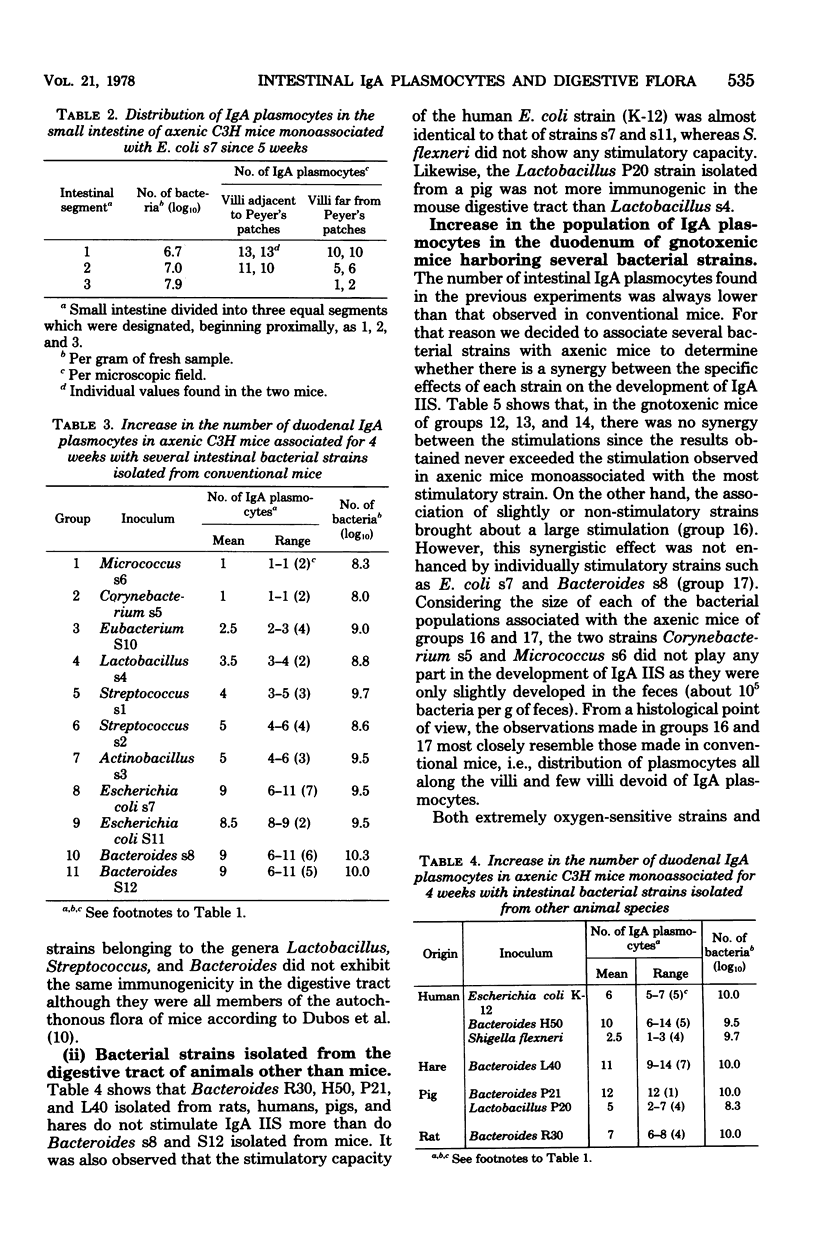
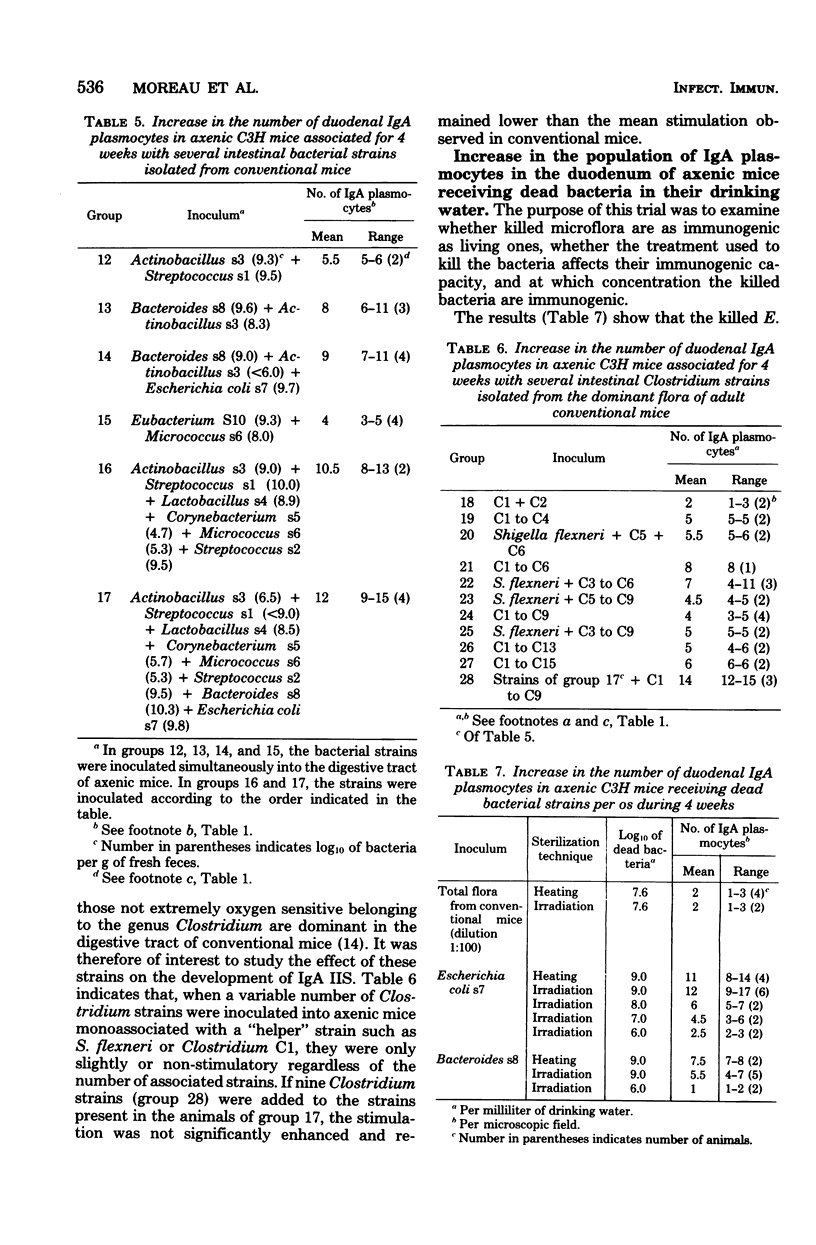
Various bacterial strains were tested for their ability to stimulate immunoglobulin A (IgA) plasmocytes to populate the duodenal lamina propria in axenic mice. The mice were associated with the strains for at least 4 weeks. The strains inhabiting the conventional mouse intestine and belonging to the genera Lactobacillus, Streptococcus, Eubacterium, Actinobacillus, Micrococcus, Corynebacterium, and Clostridium (including the extremely oxygen-sensitive ones) are only slightly or nonimmunogenic, whereas the strains belonging to the genera Bacteroides and Escherichia have an immunogenic effect. The same result was obtained with Bacteroides and Escherichia strains isolated from the digestive tract of other animal species. The kinetics of appearance of intestinal IgA plasmocytes are similar in axenic mice monoassociated with a stimulatory strain and in conventional mice. The association of two or more strains with axenic mice leads either to the same or a greater number of duodenal IgA plasmocytes as that obtained with the most stimulatory strain monoassociated with axenic mice. The maximum stimulation recorded in all of these trials represents about two-thirds of that observed in conventional mice and was obtained in the duodenum of gnotoxenic mice harboring four bacterial strains isolated from the conventional mouse microflora. The orally administered killed cells of two immunogenic strains, E. coli and Bacteroides sp., are as immunogenic as the living cells, provided that their concentration in the digestive tract is sufficient.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arank A., Syed S. A., Kenney E. B., Freter R. Isolation of anaerobic bacteria from human gingiva and mouse cecum by means of a simplified glove box procedure. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Apr;17(4):568–576. doi: 10.1128/am.17.4.568-576.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazin H., André C., Heremans J. F. Revue générale. Réponses immunologiques induites par voie orale. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1973 May;124(2):253–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste J., Lespinats G., Adam C., Salomon J. C. Immunoglobulins in intact, immunized, and contaminated axenic mice: study of serum IgA. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1647–1655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste J., Lespinats G., Salomon J. Serum and secretory IgA in axenic and holoxenic mice. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1656–1662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. D., Savage D. C. Immunological responses and microorganisms indigenous to the gastrointestinal tract. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1364–1371. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabbé P. A., Bazin H., Eyssen H., Heremans J. F. The normal microbial flora as a major stimulus for proliferation of plasma cells synthesizing IgA in the gut. The germ-free intestinal tract. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;34(4):362–375. doi: 10.1159/000230130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabbé P. A., Nash D. R., Bazin H., Eyssen H., Heremans J. F. Immunohistochemical observations on lymphoid tissues from conventional and germ-free mice. Lab Invest. 1970 May;22(5):448–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig S. W., Cebra J. J. Peyer's patches: an enriched source of precursors for IgA-producing immunocytes in the rabbit. J Exp Med. 1971 Jul 1;134(1):188–200. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOS R., SCHAEDLER R. W., COSTELLO R., HOET P. INDIGENOUS, NORMAL, AND AUTOCHTHONOUS FLORA OF THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:67–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducluzeau R., Raibaud P. Influence de la vaccination sur l'implantation d'Escherichia coli et de Staphylococcus pyogenes dans le tractus digestif de la souris axénique. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1968 Jun;114(6):846–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddie D. S., Schulkind M. L., Robbins J. B. The isolation and biologic activities of purified secretory IgA and IgG anti-Salmonella typhimurium "O" antibodies from rabbit intestinal fluid and colostrum. J Immunol. 1971 Jan;106(1):181–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foo M. C., Lee A. Immunological response of mice to members of the autochthonous intestinal microflora. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):525–532. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.525-532.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. H., Dubos R. The anaerobic bacterial flora of the mouse cecum. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):251–260. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Grand D., Griscelli C., Vassalli P. The gut-associated lymphoid system: nature and properties of the large dividing cells. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Jun;4(6):435–443. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamelin J. P., Lisowska-Bernstein B., Matter A., Ryser J. E., Vassalli P. Mouse thymus-independent and thymus-derived lymphoid cells. I. Immunofluorescent and functional studies. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):984–1007. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita Y., Mitsuoka T. Antibody responses in germ-free chickens to bacteria isolated from various sources. Jpn J Microbiol. 1973 May;17(3):181–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1973.tb00724.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Gowans J. L. Cellular kinetics of the intestinal immune response to cholera toxoid in rats. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1550–1563. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard M., Sharon N. Responses of the Peyer's Patches in Germ-Free Mice to Antigenic Stimulation. Infect Immun. 1970 Jul;2(1):96–100. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.1.96-100.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud P., Dickinson A. B., Sacquet E., Charlier H., Mocquot G. La microflore du tube digestif du rat. I. Techniques d'étude et milieux de culture proposés. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Apr;110(4):568–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud P., Galpin J. V., Ducluzeau R., Mocquot G., Oliver G. Le genre Lactobacillus dans le tube digestif du rat. I. Caractéres des souches homofermentaires isolées de rats holo- et gnotoxéniques. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1973 Jan;124(1):83–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacquet E., Raibaud P., Garnier J. Etude comparée de la microflore de l'estomac, de l'intestin grêle et du caecum du rat "holoxénique" (conventionnel), et de ses modifications à la suite de diverses interventions chirurgicales: anse aveugle jéjunale, déviations biliaires. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1971 Apr;120(4):501–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearman D. J., Parkin D. M., McClelland D. B. The demonstration and function of antibodies in the gastrointestinal tract. Gut. 1972 Jun;13(6):483–499. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.6.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman R. H., Ganguly R. Immunity to infections on secretory surfaces. J Infect Dis. 1974 Oct;130(4):419–440. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


