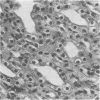
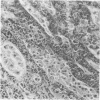
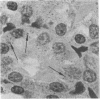
Abstract
Growth of Corynebacterium renale in vitro on low-iron medium (1.34 micron) was only slightly less than that on high-iron media (7.16 and 9.85 micron). However, studies on C. renale-induced pyelonephritis using the rat as an experimental model revealed that C. renale cultivated in high-iron media was capable of producing pyelonephritis, but when grown on low-iron medium, these bacteria were noninfective. This apparent avirulence of the bacteria cultivated on low levels of iron could be reversed by injecting the rats intramuscularly with ferric ammonium citrate.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bullen J. J., Cushnie G. H., Rogers H. J. The abolition of the protective effect of Clostridium welchii type A antiserum by ferric iron. Immunology. 1967 Mar;12(3):303–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARDS D. C., SEAMER P. A. The uptake of iron by Corynebacterium diphtheriae growing in submerged culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Jun;22:705–712. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-3-705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher J., Goldstein E. The effect of parenteral iron preparations on experimental pyelonephritis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1970 Jun;51(3):280–285. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Shimakura S., Yanagawa R. Minimum medium for Corynebacterium renale and filamentous growth due to deficiency or excess of inorganic ions. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1969 Jun;31(3):149–159. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.31.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Yanagawa R. Nutritional requriements of Corynebacterium renale. Jpn J Vet Res. 1967 Sep;15(3):121–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James A. N., Knox J. M., Williams R. P. Attachment of gonococci to sperm. Influence of physical and chemical factors. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Apr;52(2):128–135. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerusik R. J., Kadis S., Chapman W. L., Jr, Wooley R. E. Experimental Rat model for Corynebacterium renale-induced pyelonephritis. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):828–832. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.828-832.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerusik R. J., Kadis S., Chapman W. L., Jr, Wooley R. E. Influence of acetohydroxamic acid on experimental Corynebacterium renale pyelonephritis. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Oct;23(10):1448–1455. doi: 10.1139/m77-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LISTER A. J. The kinetics of urease activity in Corynebacterium renale. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Apr;14(2):478–484. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-2-478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclaren D. M. The influence of acetohydroxamic acid on experimental proteus pyelonephritis. Invest Urol. 1974 Sep;12(2):146–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nervig R. M., Kadis S. Effect of hydroxamic acids on growth and urease activity in Corynebacterium renale. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Apr;22(4):544–554. doi: 10.1139/m76-081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Iron-Binding Catechols and Virulence in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):445–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.445-456.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN HEYNINGEN W. E. The neurotoxin of Shigella shigae. 6. The relation between toxin and cytochrome production in the organism. Br J Exp Pathol. 1955 Aug;36(4):381–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERMEULEN C. W., GOETZ R. Experimental urolithiasis. VIII. Furadantin in treatment of experimental proteus infection with stone formation. J Urol. 1954 Aug;72(2):99–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and susceptibility to infectious disease. Science. 1974 May 31;184(4140):952–956. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4140.952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Nutritional immunity. Host's attempt to withold iron from microbial invaders. JAMA. 1975 Jan 6;231(1):39–41. doi: 10.1001/jama.231.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Role of iron in host-parasite interactions. J Infect Dis. 1971 Oct;124(4):401–410. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.4.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]