Abstract
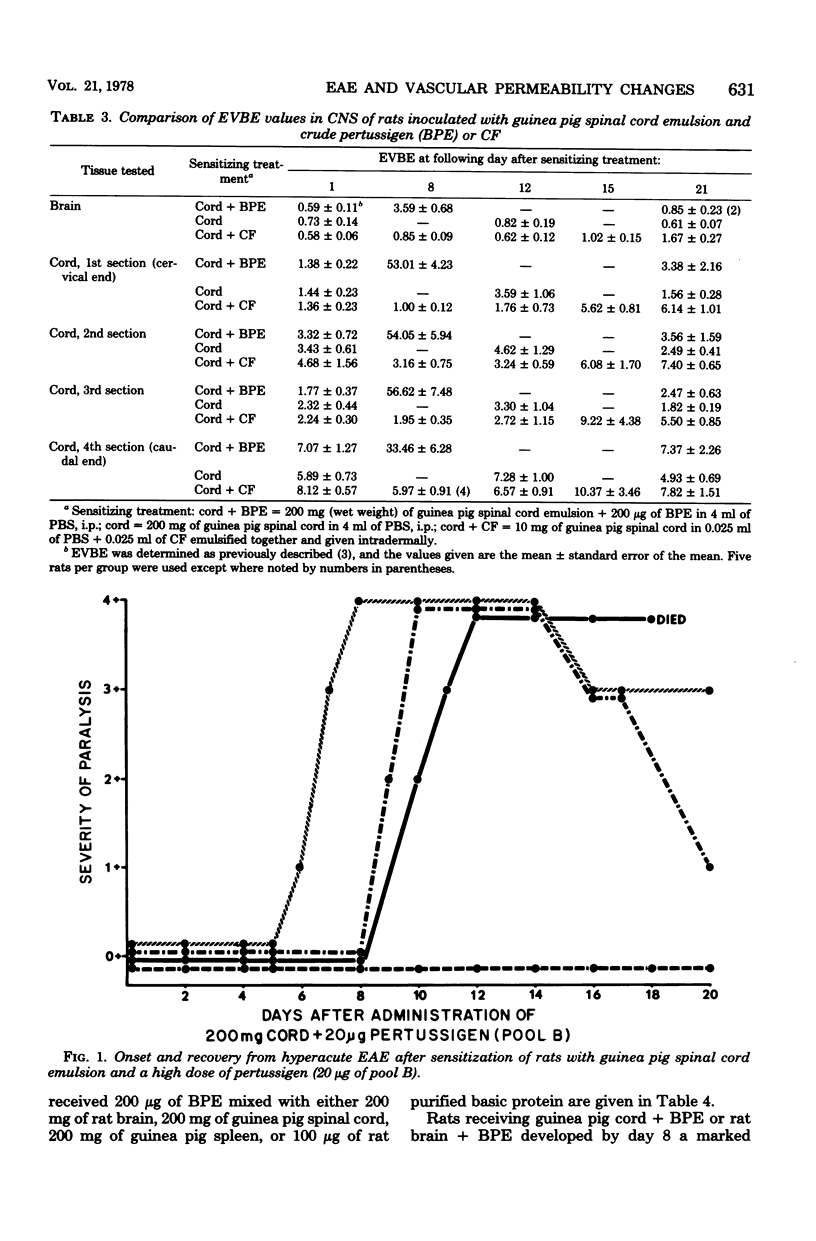
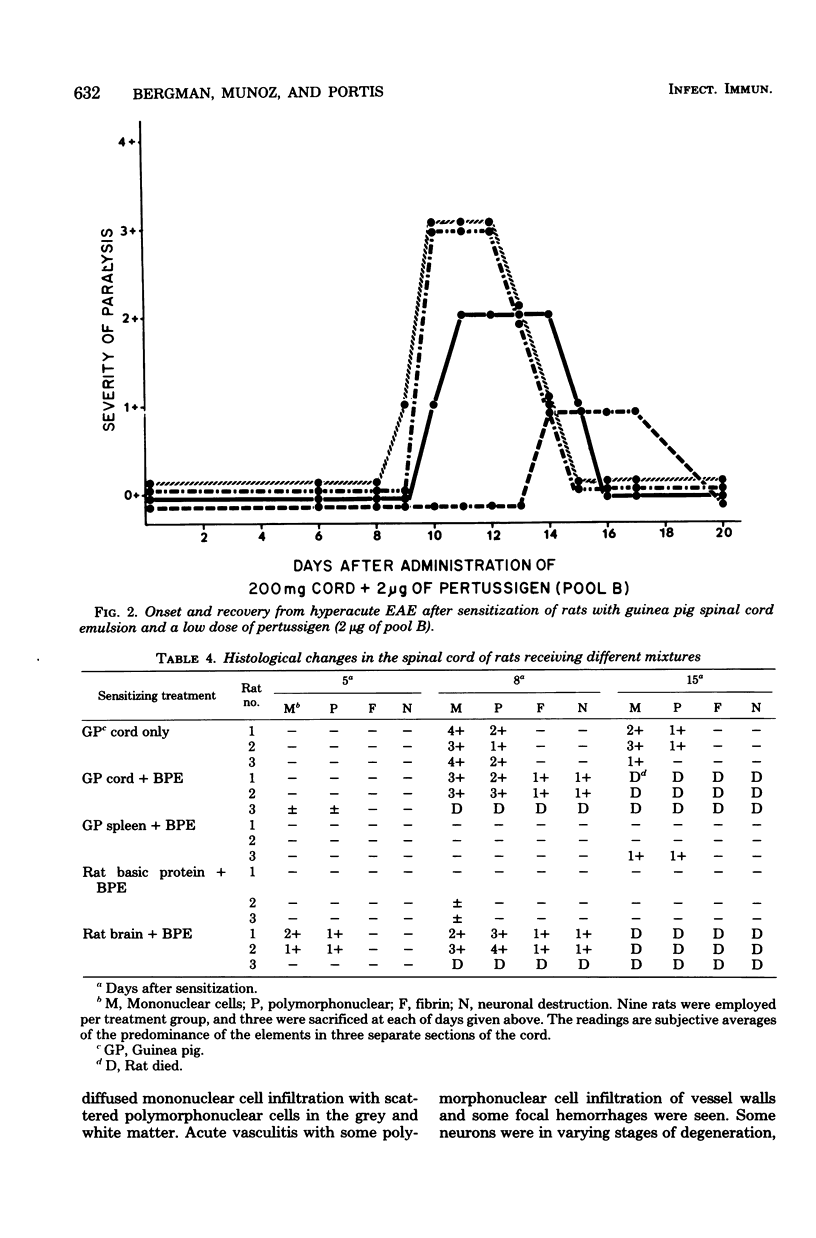
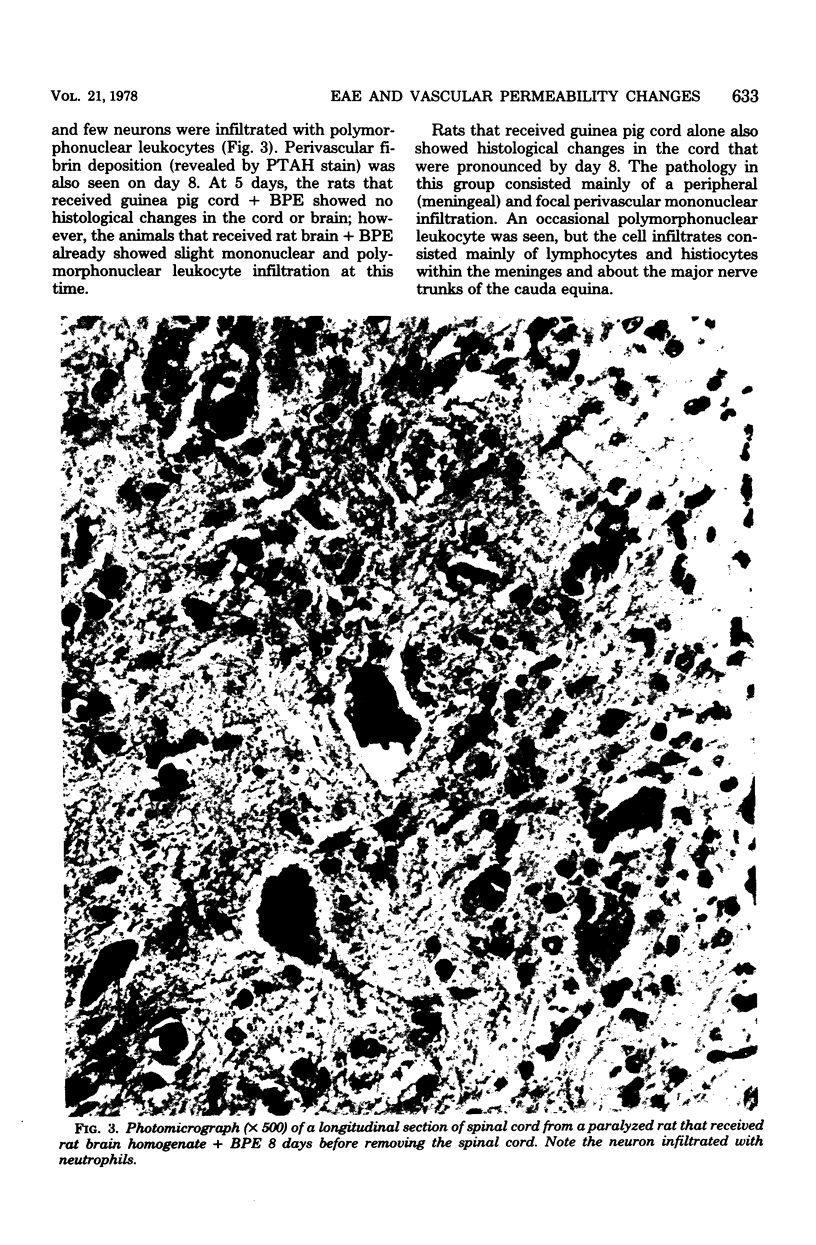
Development of hyperacute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats after intraperitoneal administration of a mixture of guinea pig spinal cord emulsion and pertussigen from Bordetella pertussis was accompanied by an increase in vascular permeability in the central nervous system. The increased permeability was most striking in the spinal cord and seemed to be associated with the ascending development of paralysis. Rats that had completely recovered from paralysis did not have any increased permeability in the central nervous system. Rats which developed paralysis after inoculation with either guinea pig spinal cord emulsion alone or with complete Freund adjuvant had only a small degree, if any, of increased permeability in the vascular system of the central nervous system.
Full text
PDF







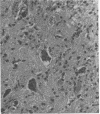
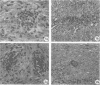
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALVORD E. C., Jr, SHAW C. M., HRUBY S., KIES M. W. ENCEPHALITOGEN-INDUCED INHIBITION OF EXPERIMENTAL ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS: PREVENTION, SUPPRESSION AND THERAPY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:333–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste J., Henson P. M., Cochrane C. G. Leukocyte-dependent histamine release from rabbit platelets. The role of IgE, basophils, and a platelet-activating factor. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1356–1377. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman R. K., Munoz J. J. Effect of Bordetella pertussis extract and vasoactive amines on vascular permeability. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975 Jun;55(6):378–385. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(75)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen C. R., Munoz J., Bergman R. K. Reaginic-type of antibody in mice stimulated by extracts of Bordetella pertussis. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):768–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE J. M., OLITSKY P. K. Simple method for enhancing development of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis in mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Jun;89(2):263–266. doi: 10.3181/00379727-89-21778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE S., WENK E. J. A HYPERACUTE FORM OF ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS. Am J Pathol. 1965 Jul;47:61–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE S., WENK E. J., MULDOON T. N., COHEN S. G. Enhancement of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by adrenalectomy. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Nov;111:383–385. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer S. B., Tan E. M., Vaughan J. H. Extraction and partial purification of the histamine-sensitizing factor of Bordetella pertussis. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):18–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer S. B., Vaughn J. H., Tan E. M. Enhancement of reaginic and hemagglutinating antibody production by an extract of Bordetella pertussis containing histamine sensitizing factor. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):178–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz S., Kennedy L. Cerebral vascular permeability and cellular infiltration in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Immunology. 1972 May;22(5):859–869. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S. Relationship of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis to human disease. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1971;49:33–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S., Simon J., Wenk E. J. Edema of the spinal cord in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Nov;123(2):539–541. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S., Sowinski R. Hyperacute allergic encephalomyelitis. A localized form produced by passive transfer and pertussis vaccine. Am J Pathol. 1973 Oct;73(1):247–260. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S., Wenk E. J., Devlin H. B., Pieroni R. E., Levine L. Hyperacute allergic encephalomyelitis: adjuvant effect of pertussis vaccines and extracts. J Immunol. 1966 Sep;97(3):363–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. I., Morse J. H. Isolation and properties of the leukocytosis- and lymphocytosis-promoting factor of Bordetella pertussis. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1483–1502. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J., Bergman R. K. Histamine-sensitizing factors from microbial agents, with special reference to Bordetella pertussis. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Jun;32(2):103–126. doi: 10.1128/br.32.2.103-126.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATERSON P. Y., HARWIN S. M. Suppression of allergic encephalomyelitis in rats by means of antibrain serum. J Exp Med. 1963 May 1;117:755–774. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.5.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson P. Y. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and autoimmune disease. Adv Immunol. 1966;5:131–208. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60273-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson P. Y. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: role of fibrin deposition in immunopathogenesis of inflammation in rats. Fed Proc. 1976 Nov;35(13):2428–2434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLEY D. A., CHUTKOW J., ATTIG C. Severe active cutaneous hypersensitivity in the rat produced by Hemophilus pertussis vaccine. J Exp Med. 1959 Nov 1;110:751–769. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.5.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Arai H. Leucocytosis-promoting factor of Bordetella pertussis. I. Purification and characterization. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):899–904. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.899-904.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanborg R. H. Maintenance of immunologic self-tolerance by nonimmunogenic forms of antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Dec;26(3):597–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swierkosz J. E., Swanborg R. H. Suppressor cell control of unresponsiveness to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):631–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada T., Okumura K., Ochiai T., Iwasa S. Effect of lymphocytosis-promoting factor of Bordetella pertussis on the immune response. II. Adjuvant effect for the production of reaginic antibody in the rat. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1972;43(2):207–216. doi: 10.1159/000230838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]