Abstract
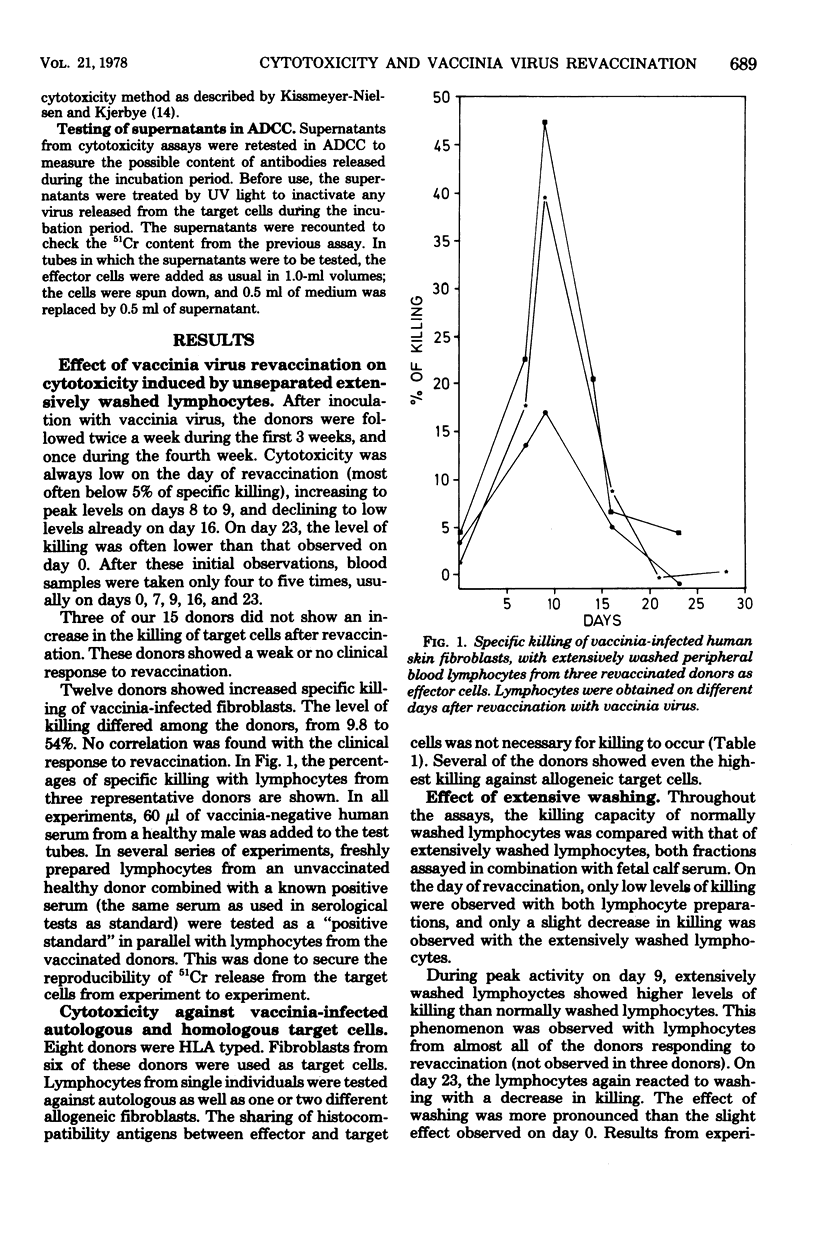
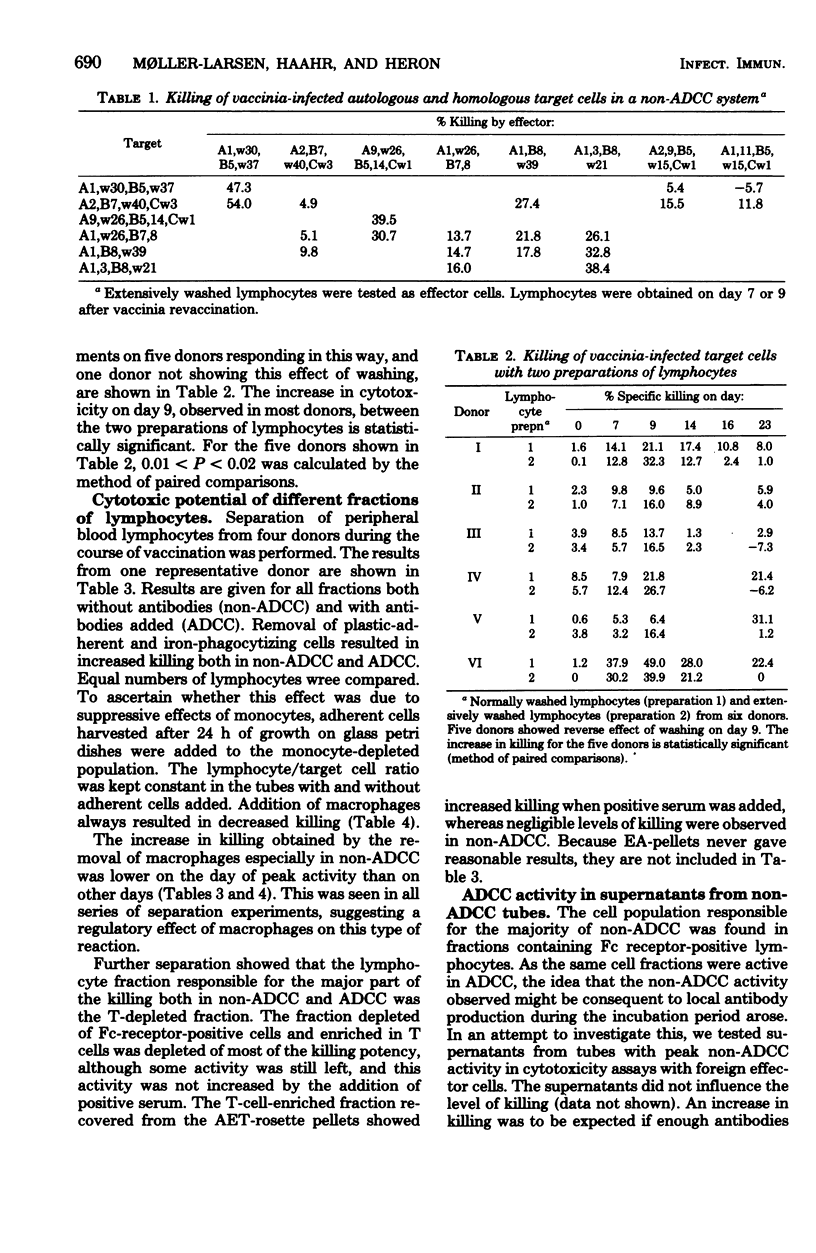
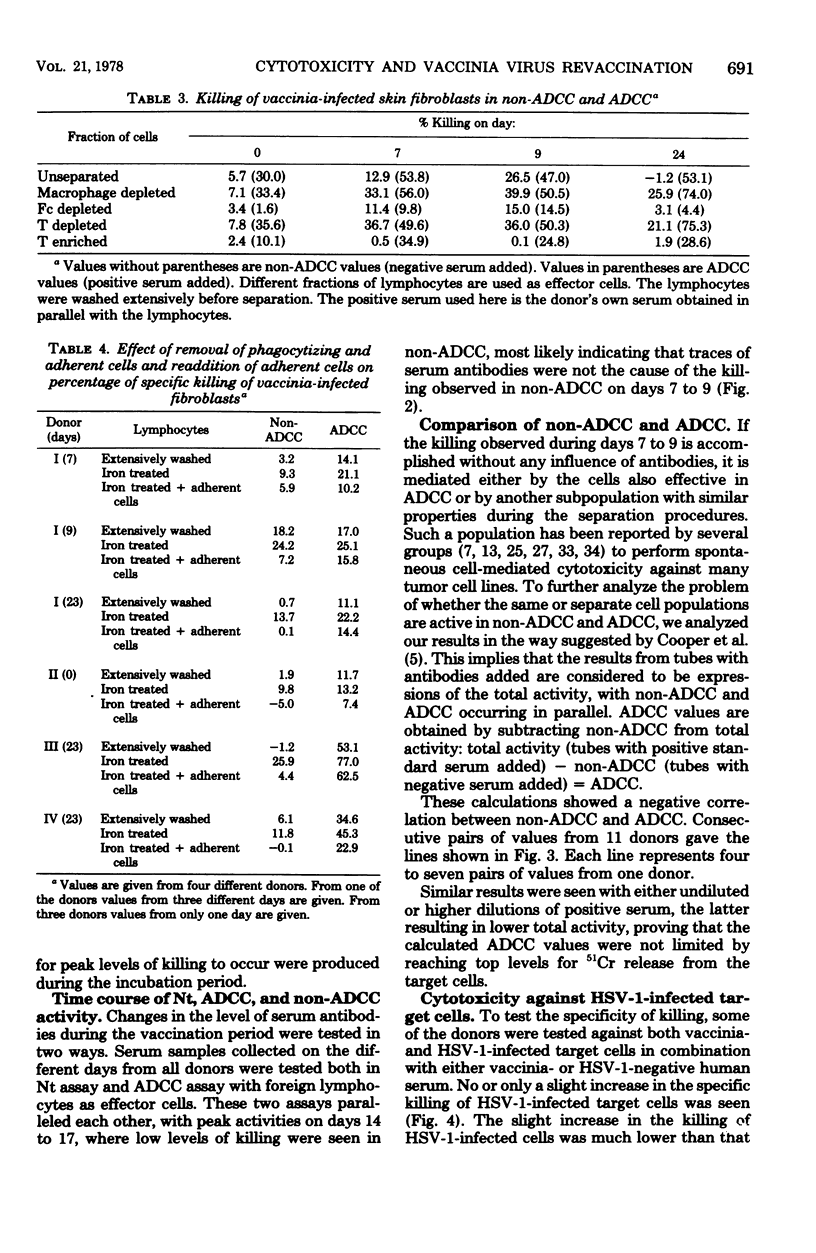
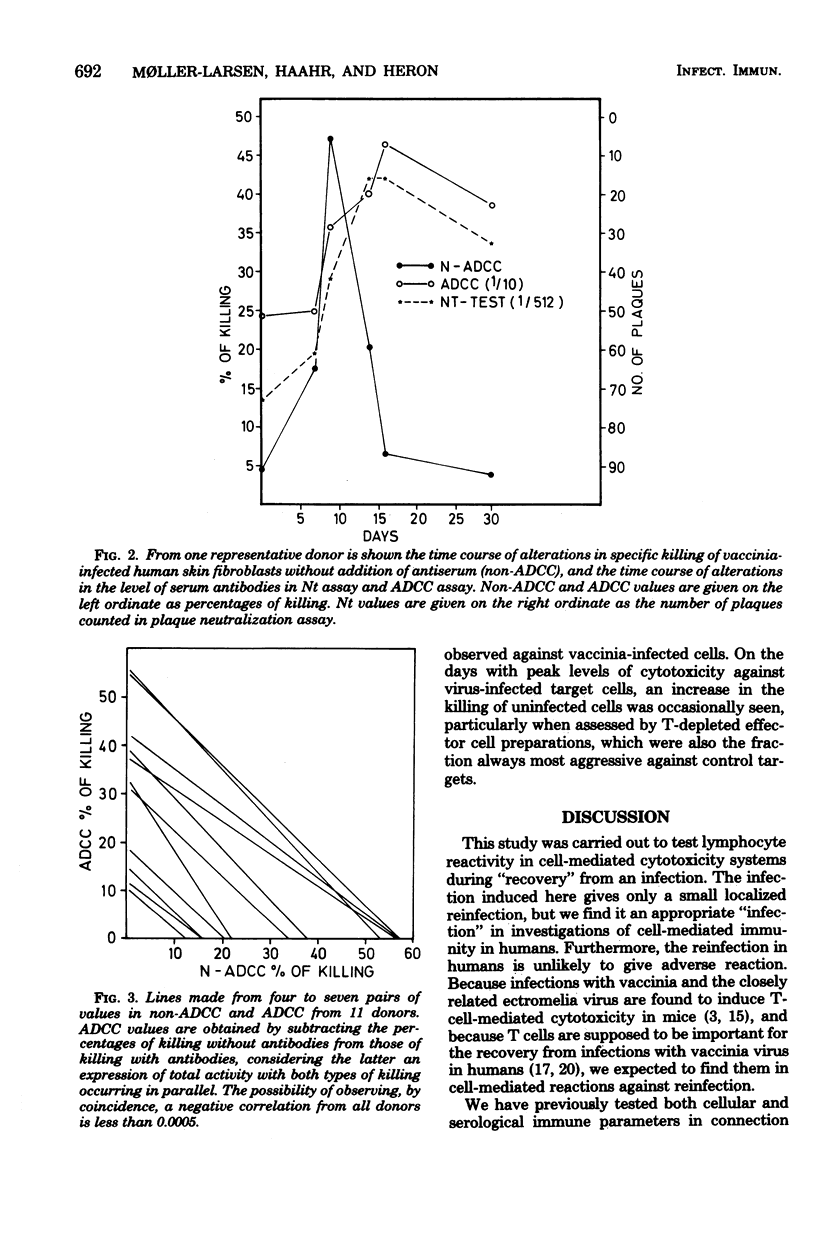
Fifteen healthy human volunteers were revaccinated with vaccinia virus. Blood samples (4 to 7) were obtained during the 3 weeks after revaccination. Peripheral blood lymphocytes were washed extensively and tested for cytotoxicity against vaccinia-infected autologous and/or homologous skin fibroblasts. Without addition of antibodies, peak levels of killing were observed on days 7 to 9. The killing did not depend on common HLA markers. On days with peak activity, extensively washed lymphocytes showed higher levels of killing than normally washed lymphocytes. By cell separation experiments, the cell most active in killing proved to be a nonadherent, non-phagocytizing lymphocyte with Fc receptors. Serum antibodies tested in two sensitive serological assays peaked on days 14 to 17. The question of whether the killing observed is dependent on or independent of antibodies is not clarified in the present study.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Yamaguchi T., Shimizu F., Kumagai K. Studies of surface immunoglobulins on human B lymphocytes. II. Characterization of a population of lymphocytes lacking surface immunoglobulins but carrying Fc receptor (SIg-Fc+ cell). J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1781–1787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakacs T., Gergely P., Klein E. Characterization of cytotoxic human lymphocyte subpopulations: the role of Fc-receptor-carrying cells. Cell Immunol. 1977 Aug;32(2):317–328. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Gardner I. D. The cell-mediated immune response to ectromelia virus infection. I. Kinetics and characteristics of the primary effector T cell response in vivo. Cell Immunol. 1976 Mar 15;22(2):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of leucocytes from human blood. Further observations. Methylcellulose, dextran, and ficoll as erythrocyteaggregating agents. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:31–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferluga J., Friou G. J., Allison A. C. Cytotoxic activity of human lymphocyte plasma membranes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Aug;25(2):347–351. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. C., Schedel I., Peter H. H., Deicher H. Inhibition of spontaneous and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity by sera and isolated antiglobulin preparations from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(3):173–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner I. D., Blanden R. V. The cell-mediated immune response to ectromelia virus infection. II. Secondary response in vitro and kinetics of memory T cell production in vivo. Cell Immunol. 1976 Mar 15;22(2):283–296. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegert D. G. Neuraminidase- and trypsin-induced exposure to membrane receptors for IgG and IgM molecules on human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Sep;29(3):457–463. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspel M. V., Pellegrino M. A., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Human histocompatibility determinants and virus antigens: effect of measles virus infection on HLA expression. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):146–156. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heron I., Moller-Larsen A., Berg K. Effector cell involved in cell-mediated cytotoxicity to cells infected with herpes simplex virus type 1. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):48–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.48-53.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokland P., Hokland M., Heron I. An improved technique for obtaining E rosettes with human lymphocytes and its use for B cell purification. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(2):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90156-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay H. D., Bonnard G. D., West W. H., Herberman R. B. A functional comparison of human Fc-receptor-bearing lymphocytes active in natural cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2058–2066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koszinowski U., Thomssen R. Target cell-dependent T cell-mediated lysis of vaccinia virus-infected cells. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Apr;5(4):245–251. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreth H. W., Wiegand G. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity against measles virus in SSPE. II. Analysis of cytotoxic effector cells. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):296–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merigan T. C. Host defenses against viral disease. N Engl J Med. 1974 Feb 7;290(6):323–329. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197402072900608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møller-Larsen A., Haahr S. Humoral and cell-mediated immune responses in humans before and after revaccination with vaccinia virus. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):34–39. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.34-39.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. C., Myers M. G., Tauraso N. M. Kinetics of the vaccinia virus plaque neutralization test. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):968–970. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.968-970.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkman R., Rosen F. S. Identification of a subpopulation of lymphocytes in human peripheral blood cytotoxic to autologous fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1520–1530. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin L. H., Tishon A., Oldstone M. B. Immunologic injury in measles virus infection. III. Presence and characterization of human cytotoxic lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):282–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin L. H., Zinkernagel R. M., Oldstone M. B. Immune response in humans after vaccination with vaccinia virus: generation of a virus-specific cytotoxic activity by human peripheral lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1977 Oct 1;146(4):949–969. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.4.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter H. H., Eife R. F., Kalden J. R. Spontaneous cytotoxicity (SCMC) of normal human lymphocytes against a human melanoma cell line: a phenomenon due to a lymphotoxin-like mediator. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):342–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter H. H., Pavie-Fischer J., Fridman W. H., Aubert C., Cesarini J. P., Roubin R., Kourilsky F. M. Cell-mediate cytotoxicity in vitro of human lymphocytes against a tissue culture melanoma cell line (igr3). J Immunol. 1975 Aug;115(2):539–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg E. B., McCoy J. L., Green S. S., Donnelly F. C., Siwarski D. F., Levine P. H., Herberman R. B. Destruction of human lymphoid tissue-culture cell lines by human peripheral lymphocytes in 51Cr-release cellular cytotoxicity assays. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Feb;52(2):345–352. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.2.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A. The direct antiviral cytotoxicity by bovine lymphocytes is not restricted by genetic incompatibility of lymphocytes and target cells. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):618–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela E., Imir T., Mäkelä O. Spontaneous, augmentable cell-mediated cytotoxicity with limited target cell specificity in human blood. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Mar;7(3):126–130. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh J., Elson C. J., Taylor R. B. Enrichment in B cells after separation of lymphocytes from peripheral blood. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Jul;5(2):111–119. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Saksela E. Human natural cell-mediated cytotoxicity against fetal fibroblasts. I. General characteristics of the cytotoxic activity. Cell Immunol. 1977 Oct;33(2):340–352. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Santoli D., Zmijewski C. M., Koprowski H. Functional correlation between antibody-dependent and spontaneous cytotoxic activity of human lymphocytes and possibility of an HLA-related control. Transplant Proc. 1977 Mar;9(1):881–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West W. H., Cannon G. B., Kay H. D., Bonnard G. D., Herberman R. B. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of human lymphocytes against a myeloid cell line: characterization of effector cells. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):355–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


