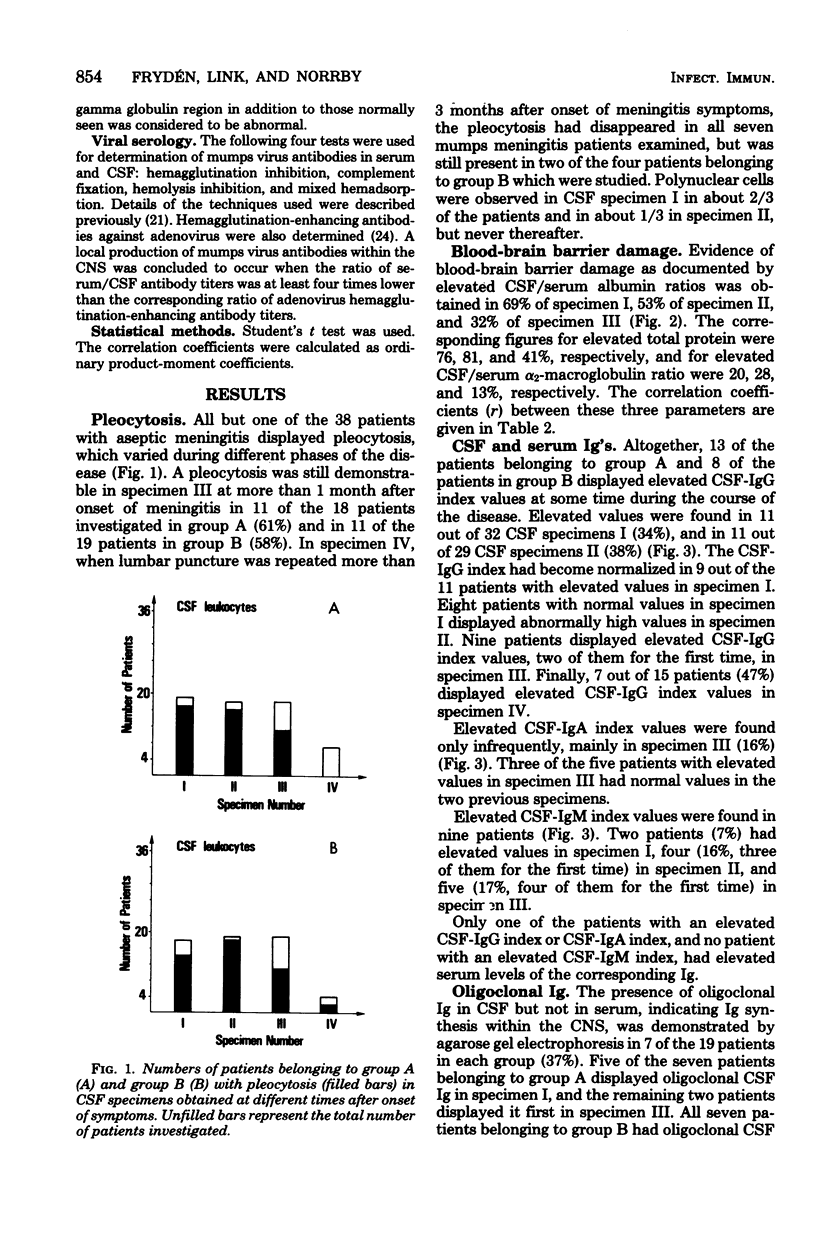
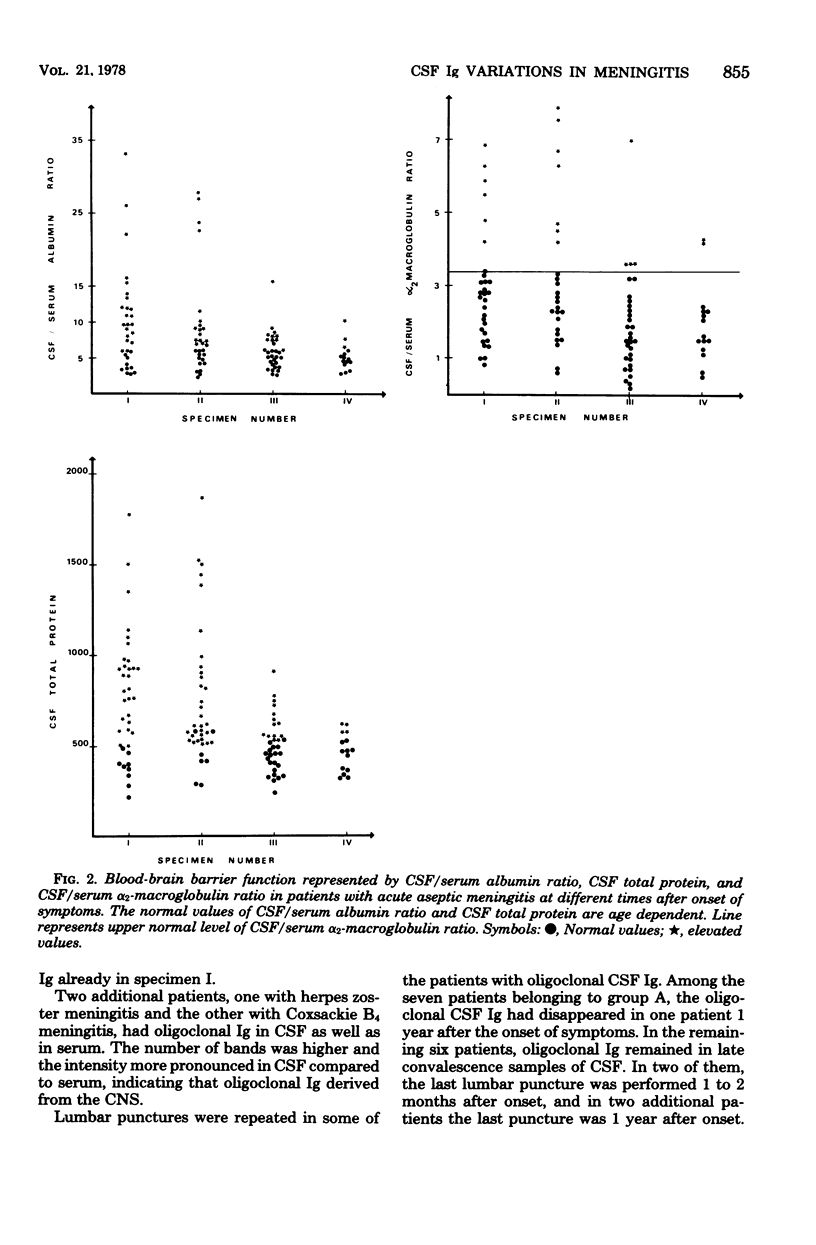
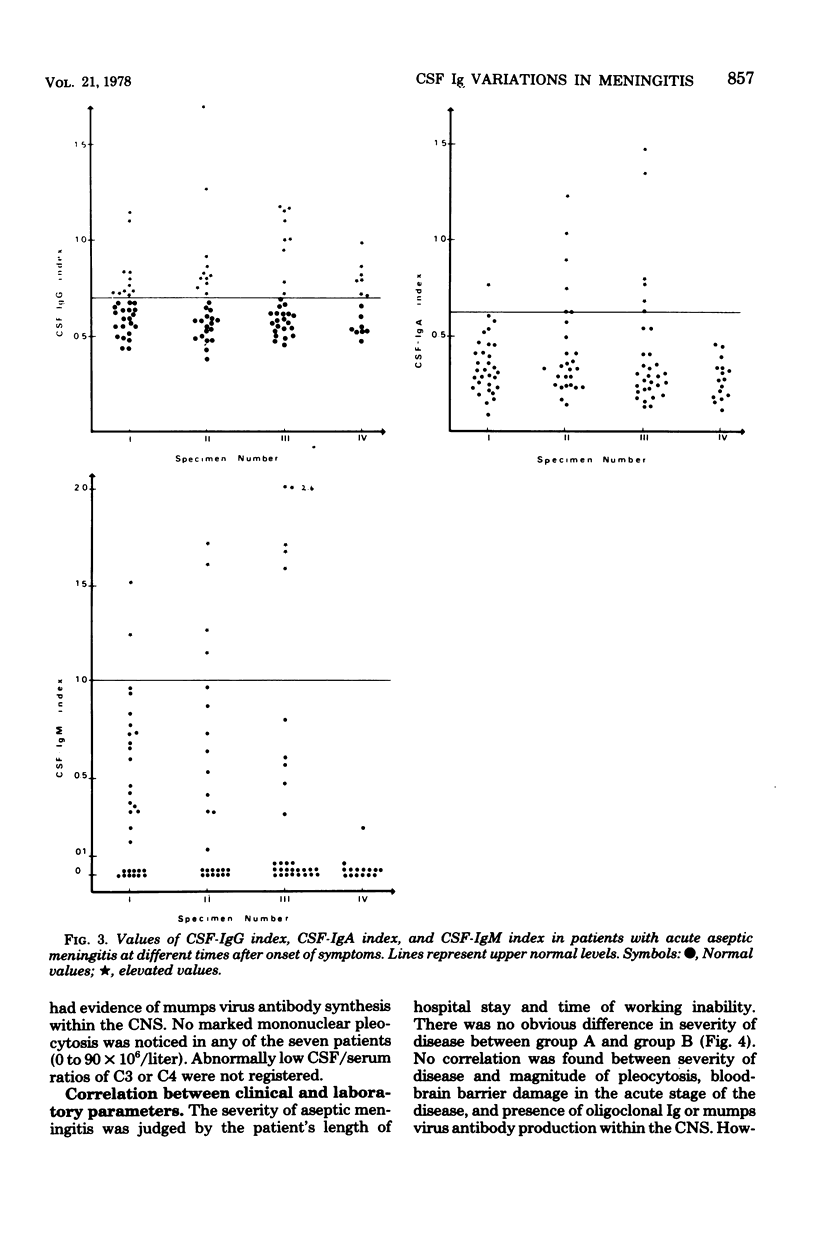
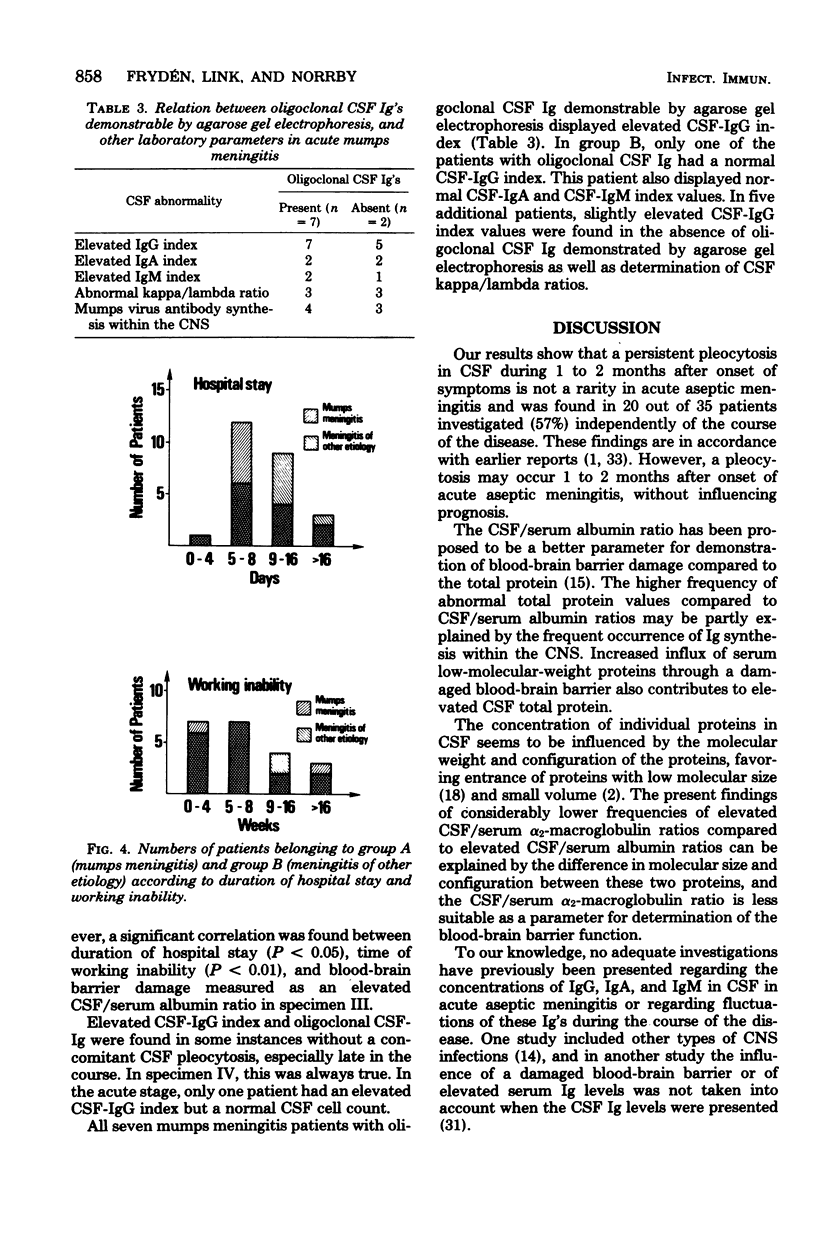
Abstract
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and serum from 19 patients with mumps meningitis and 19 patients with meningitis of other etiology were investigated on two or more occasions for at least 1 month after onset. Intrathecal synthesis of immunoglobulin (Ig) G was found in 55%, of IgA in 26%, and of IgM in 24% of the patients. Oligoclonal Ig was demonstrable by agarose gel electrophoresis in 37% of the patients, mostly already during the first week after onset, and could persist for years. Mumps virus antibody synthesis within the central nervous system occurred in 37% of the mumps meningitis patients. The inflammatory reaction within the central nervous system as reflected by mononuclear pleocytosis, Ig synthesis, and oligoclonal Ig was not correlated to the clinical course. The blood-brain barrier was evaluated by determination of the CSF total protein, CSF/serum albumin ratio, and CSF/serum alpha2-macroglobulin ratio. A significant correlation was found among these three parameters. Persistence of the elevated CSF/serum albumin ratio seems to influence prognosis, and this parameter is recommended for evaluation of the blood-brain barrier function.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azimi P. H., Shaban S., Hilty M. D., Haynes R. E. Mumps meningoencephalitis. Prolonged abnormality of cerebrospinal fluid. JAMA. 1975 Dec 15;234(11):1161–1162. doi: 10.1001/jama.234.11.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgenhauer K. Protein size and cerebrospinal fluid composition. Klin Wochenschr. 1974 Dec 15;52(24):1158–1164. doi: 10.1007/BF01466734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydén A. B and T lymphocytes in blood and cerebrospinal fluid in acute aseptic meningitis. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(12):1282–1288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydén A., Link H. Mitogen stimulation of cerebrospinal fluid lymphocytes in aseptic meningitis. Acta Neurol Scand. 1978 Jan;57(1):8–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1978.tb04494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydén A., Link H., Möller E. Demonstration of cerebrospinal fluid lymphocytes sensitized against virus antigens in mumps meningitis. Acta Neurol Scand. 1978 May;57(5):396–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1978.tb02843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hapel A. J. The protective role of thymus-derived lymphocytes in arbovirus-induced meningoencephalitis. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(3):267–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hapel A., Gardner I. Appearance of cytotoxic T cells in cerebrospinal fluid of mice with ectromelia virus-induced meningitis. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(3):311–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jersild C., Fog T., Hansen G. S., Thomsen M., Svejgaard A., Dupont B. Histocompatibility determinants in multiple sclerosis, with special reference to clinical course. Lancet. 1973 Dec 1;2(7840):1221–1225. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90970-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laterre E. C., Callewaert A., Heremans J. F., Sfaello Z. Electrophoretic morphology of gamma globulins in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis and other diseases of the nervous system. Neurology. 1970 Oct;20(10):982–990. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.10.982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. I., Lisak R. P., Zweiman B. Immunologic characterization of cerebrospinal fluid lymphocytes: preliminary report. Neurology. 1976 Jul;26(7):693–695. doi: 10.1212/wnl.26.7.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindbak H., Halvorsen S., Julsrud O. J., Skandsen S. Agarosegelektroforese av spinalvaeske. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 1974 Jan 30;94(3):152–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H. Comparison of electrophoresis on agar gel and agarose gel in the evaluation of gamma-globulin abnormalities in cerebrospinal fluid and serum in multiple sclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Jul 27;46(4):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90251-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H. Immunoglobulin G and low molecular weight proteins in human cerebrospinal fluid. Chemical and immunological characterisation with special reference to multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand. 1967;43(Suppl):1–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H., Tibbling G. Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. II. Relation of the concentration of the proteins in serum and cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(5):391–396. doi: 10.1080/00365517709091497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H., Tibbling G. Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. III. Evaluation of IgG synthesis within the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(5):397–401. doi: 10.1080/00365517709091498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H., Zettervall O., Blennow G. Individual cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) proteins in the evaluation of increased CSF total protein. Z Neurol. 1972;203(2):119–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00316040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H., Zettervall O. Multiple sclerosis: disturbed kappa: lambda chain ratio of immunoglobulin G in cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Mar;6(3):435–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Grandien M., Orvell C. New tests for characterization of mumps virus antibodies: hemolysis inhibition, single radial immunodiffusion with immobilized virions, and mixed hemadsorption. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Mar;5(3):346–352. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.3.346-352.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Link H., Olsson J. E. Measles virus antibodies in multiple sclerosis. Comparison of antibody titers in cerebrospinal fluid and serum. Arch Neurol. 1974 Apr;30(4):285–292. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490340013002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Link H., Olsson J. E., Panelius M., Salmi A., Vandvik B. Comparison of antibodies against different viruses in cerebrospinal fluid and serum samples from patients with multiple sclerosis. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):688–694. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.688-694.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., van der Veen J., Espmark A. A new serological technique for identification of adenovirus infections. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jul;134(3):889–895. doi: 10.3181/00379727-134-34905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehmichen M., Grüninger H. Cytokinetic studies on the orgin of cells of the cerebrospinal fluid. With a contribution to the cytogenesis of the leptomeningeal mesenchyme. J Neurol Sci. 1974 Jun;22(2):165–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(74)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson J. E., Link H. Immunoglobulin abnormalities in multiple sclerosis. Relation to clinical parameters: exacerbations and remissions. Arch Neurol. 1973 Jun;28(6):392–399. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490240052009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petz L. D., Sharp G. C., Cooper N. R., Irvin W. S. Serum and cerebral spinal fluid complement and serum autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Medicine (Baltimore) 1971 Jul;50(4):259–275. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197107000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmi A. A., Norrby E., Panelius M. Identification of different measles virus-specific antibodies in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid from patients with subacute sclerosing pancencephalitis and multiple sclerosis. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):248–254. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.248-254.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmi A., Panelius M., Vainionpä R. Antibodies against different viral antigens in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases. Acta Neurol Scand. 1974;50(2):183–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1974.tb02771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg-Wollheim M. Immunoglobulin synthesis in vitro by cerebrospinal fluid cells in patients with meningoencephalitis of presumed viral origin. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(7):617–622. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H., Bannister B. Cerebrospinal-fluid immunoglobulins in meningitis. Lancet. 1973 Sep 15;2(7829):591–593. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92417-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbling G., Link H., Ohman S. Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. I. Establishment of reference values. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(5):385–390. doi: 10.1080/00365517709091496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


