Abstract
Phytohemagglutinin is able to trigger interferon synthesis in spleen cell cultures from nude (nu/nu) mice as effectively as in splenic cell cultures from haired, control (nu/+), thymus-bearing mice. A minor theta-bearing cell population present in the spleen of nude mice appears essential to phytohemagglutinin interferon production, although cooperating cells are also required. The properties of nude mouse phytohemagglutinin interferon are indistinguishable from those displayed by the interferon induced in thymus-bearing mouse spleen cell cultures. Both interferons are unstable at pH 2 and cannot be neutralized by an antiviral interferon serum; hence, their characteristics correspond to those described for type T interferon. As in the case of viral interferon, pretreatment of L cells with nude phytohemagglutinin interferon induced specific enhanced phosphorylation of a 67,000-molecular-weight protein in vitro when cell extracts were incubated with double-stranded RNA and gamma-[32P]ATP.
Full text
PDF

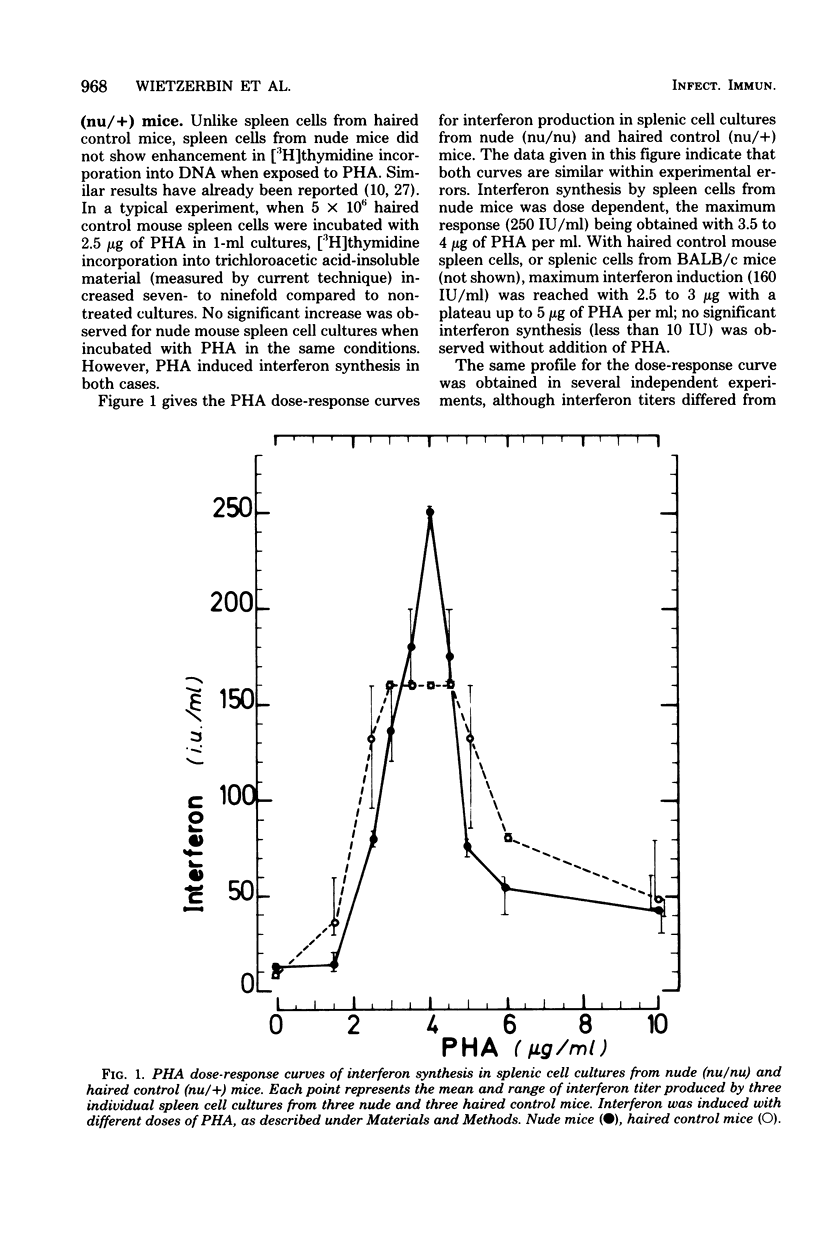

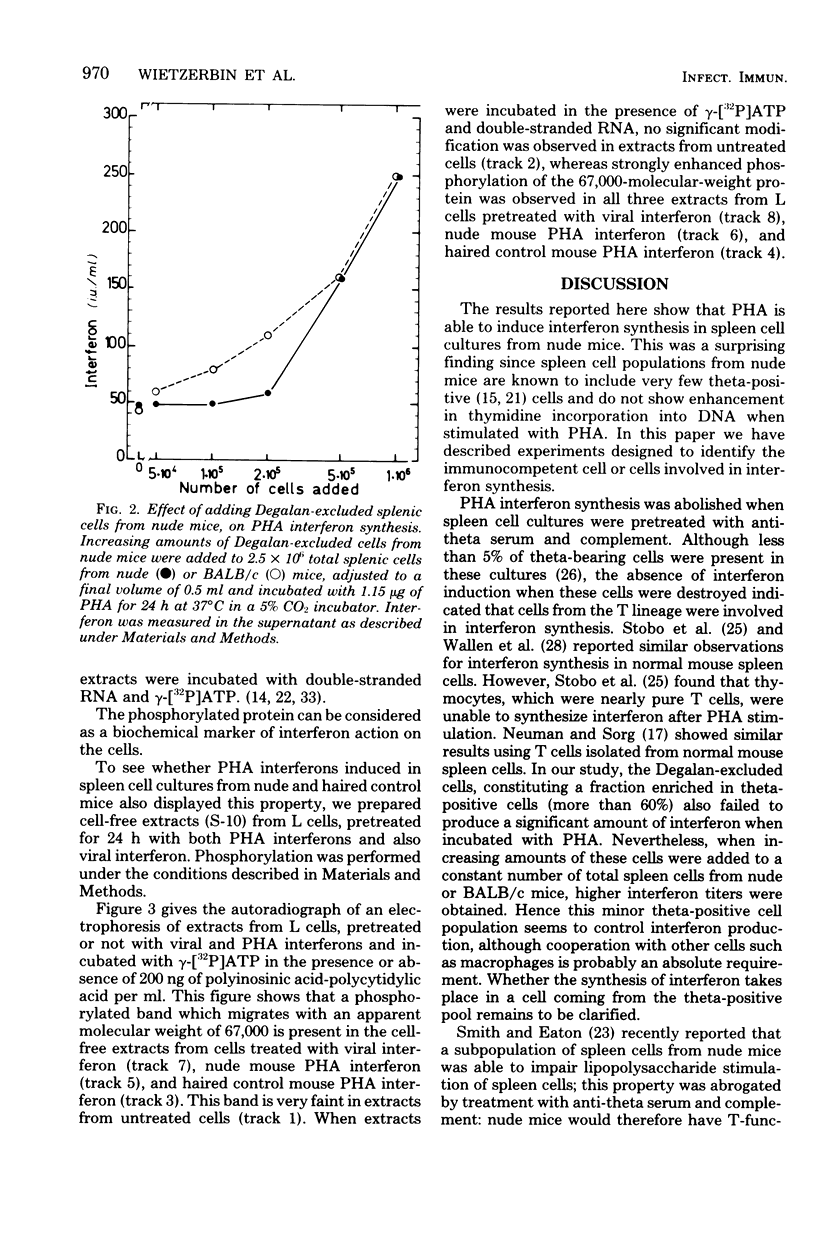
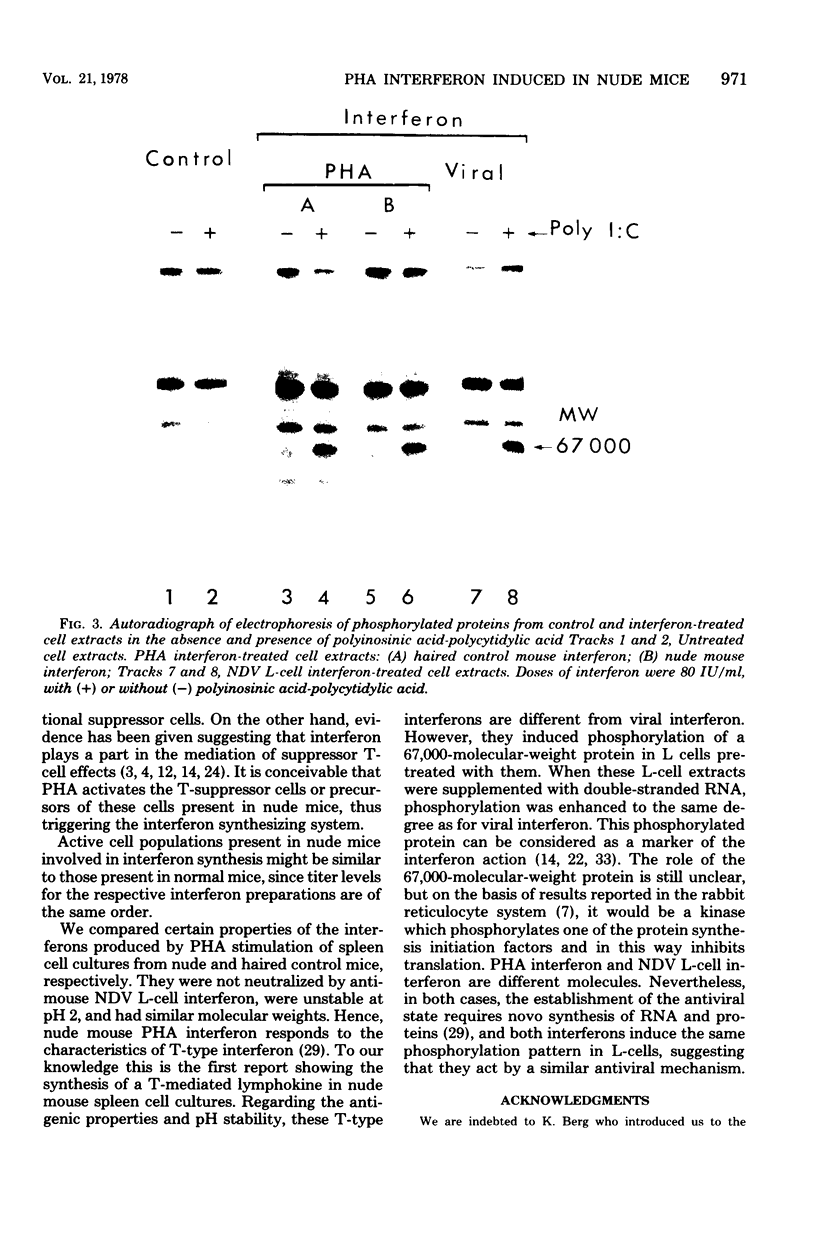

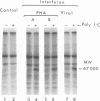
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barot-Ciorbaru R., Wietzerbin J., Petit J. F., Chedid L., Falcoff E., Lederer E. Induction of interferon synthesis in mice by fractions from Nocardia. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):353–356. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.353-356.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun D. G., Kindred B., Jacobson E. B. Streptococcal group A carbohydrate antibodies in mice: evidence for strain differences in magnitude and restriction of the response, and for thymus dependence. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Apr;2(2):138–143. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur B. R., Merigan T. C. Mechanism of the suppressive effect of interferon on antibody synthesis in vivo. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1323–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur B. R., Weinstein Y., Melmon K. L., Merigan T. C. Reciprocal changes in interferon production and immune responses of mouse spleen cells fractionated over columns of insolubilized conjugates of histamine. Cell Immunol. 1977 Mar 15;29(2):363–372. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcoff R., Fontaine-Brouty D., Falcoff E. Purification partielle et caractérisation de l'interféron provenant de cerveau de souris. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1968 Aug;115(2):279–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcoff R. Some properties of virus and immune-induced human lymphocyte interferons. J Gen Virol. 1972 Aug;16(2):251–253. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-16-2-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Balkow K., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Trachsel H. Phosphorylation of initiation factor elF-2 and the control of reticulocyte protein synthesis. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):187–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90330-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Vilcek J. Production of high-titered interferon in cultures of human diploid cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):476–484. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Greaves M. F. Lymphocyte activation. I. Response of T and B lymphocytes to phytomitogens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Oct;9(4):483–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Baron S. The nature of the suppressive effect of interferon and interferon inducers on the in vitro immune response. Cell Immunol. 1976 Jul;25(1):106–115. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebleu B., Sen G. C., Shaila S., Cabrer B., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3107–3111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loor F. The abnormal differentiation of the T-lymphoid system in the congenitally athymic (nude) mouse. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1977 Apr-Jun;128C(3):719–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. D., Reed N. D., Shaffer C. F. Maintenance of skin xenografts of widely divergent phylogenetic origin of congenitally athymic (nude) mice. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):488–494. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann C., Sorg C. Immune interferon. I. Production by lymphokine-activated murine macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Oct;7(10):719–725. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830071014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogburn C. A., Berg K., Paucker K. Purification of mouse interferon by affinity chromatography on anti-interferon globulin-sepharose. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1206–1218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco D., Falcoff R., Catinot L., Floc'h F., Werner G. H., Falcoff E. Inhibitory effect of interferon on DNA and RNA synthesis in murine spleen cells stimulated by lectins. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1976 Mar-Apr;127(2):163–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantelouris E. M. Absence of thymus in a mouse mutant. Nature. 1968 Jan 27;217(5126):370–371. doi: 10.1038/217370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Siskind G. W. Hapten specificity of cellular immune responses as compared with the specificity of serum anti-hapten antibody. Immunology. 1970 Jun;18(6):921–930. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. K., Hovanessian A., Brown R. E., Clemens M. J., Kerr I. M. Interferon-mediated protein kinase and low-molecular-weight inhibitor of protein synthesis. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):477–480. doi: 10.1038/264477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Eaton G. J. Suppressor cells in spleens from "nude" mice: their effect on the mitogenic response of B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):319–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenfeld G., Mandel A. D., Merigan T. C. The immunosuppressive effect of type II mouse interferon preparations on antibody production. Cell Immunol. 1977 Dec;34(2):193–206. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90243-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobo J., Green I., Jackson L., Baron S. Identification of a subpopulation of mouse lymphoid cells required for interferon production after stimulation with mitogens. J Immunol. 1974 Apr;112(4):1589–1593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viac J., Schmitt D., Alario A., Thivolet J. La rate de souris "nude": étude immunologique et immunocytochimique. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1976 Sep-Oct;127(5):717–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vischer T. L. Mitogenic factors produced by lymphocyte activation: effect on T- and B-cells. J Immunol. 1972 Aug;109(2):401–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallen W. C., Dean J. H., Lucas D. O. Interferon and the cellular immune response: separation of interferon-producing cells from DNA-synthetic cells. Cell Immunol. 1973 Jan;6(1):110–122. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wietzerbin J., Falcoff R., Catinot L., Falcoff E. Affinity chromatographic analysis of murine interferons induced by viruses and by T and B cell stimulants. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1977 Apr-Jun;128C(3):699–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wortis H. H. Immunological studies of nude mice. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1974;3:243–263. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3045-5_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Salvin S. B. Production and properties of migration inhibitory factor and interferon in the circulation of mice with delayed hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1973 Dec;111(6):1914–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Federman P., Shulman L., Revel M. Specific phosphorylation in vitro of a protein associated with ribosomes of interferon-treated mouse L cells. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 15;68(1):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80418-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]