Abstract
Inactivated Brucella abortus organisms of the smooth (S) or rough (R) strain were tested comparatively on two T-dependent immune responses: mixed-lymphocyte reaction and delayed-type hypersensitivity. The intravenous injection of S organisms depressed the two tests, whereas R organisms increased mixed-lymphocyte reaction and did not alter delayed-type hypersensitivity significantly. This observation may be helpful in understanding the differences in adjuvant properties of S and R brucellae.
Full text
PDF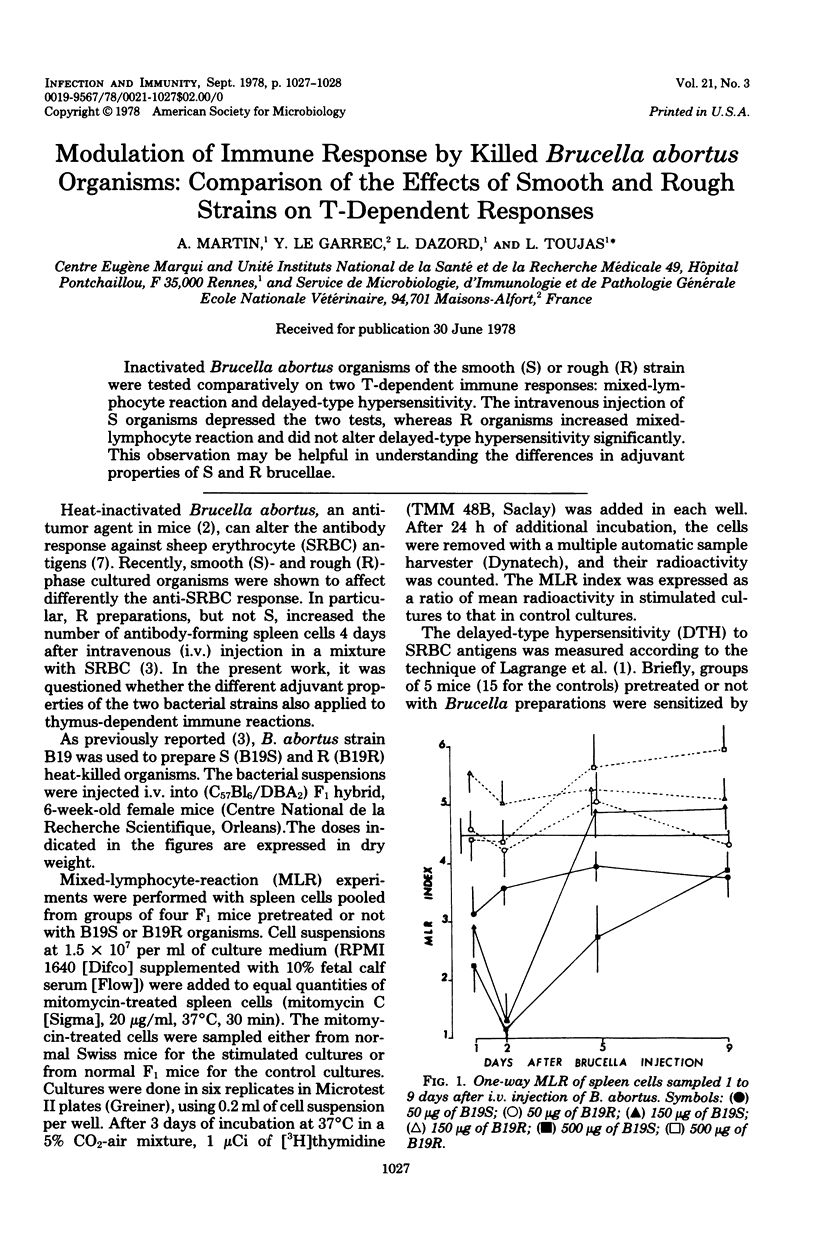
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Lagrange P. H., Mackaness G. B., Miller T. E., Pardon P. Effects of bacterial lipopolysaccharide on the induction and expression of cell-mediated immunity. I. Depression of the afferent arc. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):442–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Garrec Y., Sabolovic D., Toujas L., Dazord L., Guelfi J., Pilet C. Activity of inactivated Burcella on murine tumors: prophylactic effects and combination with specific immunostimulation. Biomedicine. 1974 Jan 20;21(1):40–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Garrec Y., Toujas L., Martin A., Dazord L., Pilet C. Influence of the antigenicity of Brucella preparations on modulation of the immune response to sheep erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):6–11. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.6-11.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. E., Mackaness G. B., Lagrange P. H. Immunopotentiation with BCG. II. Modulation of the response to sheep red blood cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Nov;51(5):1669–1676. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.5.1669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEVEU T., BRANELLEC A., BIOZZI G. PROPRI'ET'ES ADJUVANTES DE CORYNEBACTERIUM PARVUM SUR LA PRODUCTION D'ANTICORPS ET SUR L'INDUCTION DE L'HYPERSENSIBILIT'E RETARD'EE ENVERS LES PROT'EINES CONJUGU'EES. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 May;106:771–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. T. Biological effects of the adjuvant Corynebacterium parvum. I. Inhibition of PHA, mixed lymphocyte and GVH reactivity. Cell Immunol. 1972 Nov;5(3):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toujas L., Sabolovic D., Dazord L., Le Garrec Y., Toujas J. P., Guelfi J., Pilet C. The mechanism of immunostimulation induced by inactivated Brucella abortus. Rev Eur Etud Clin Biol. 1972 Mar;17(3):267–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


