Abstract
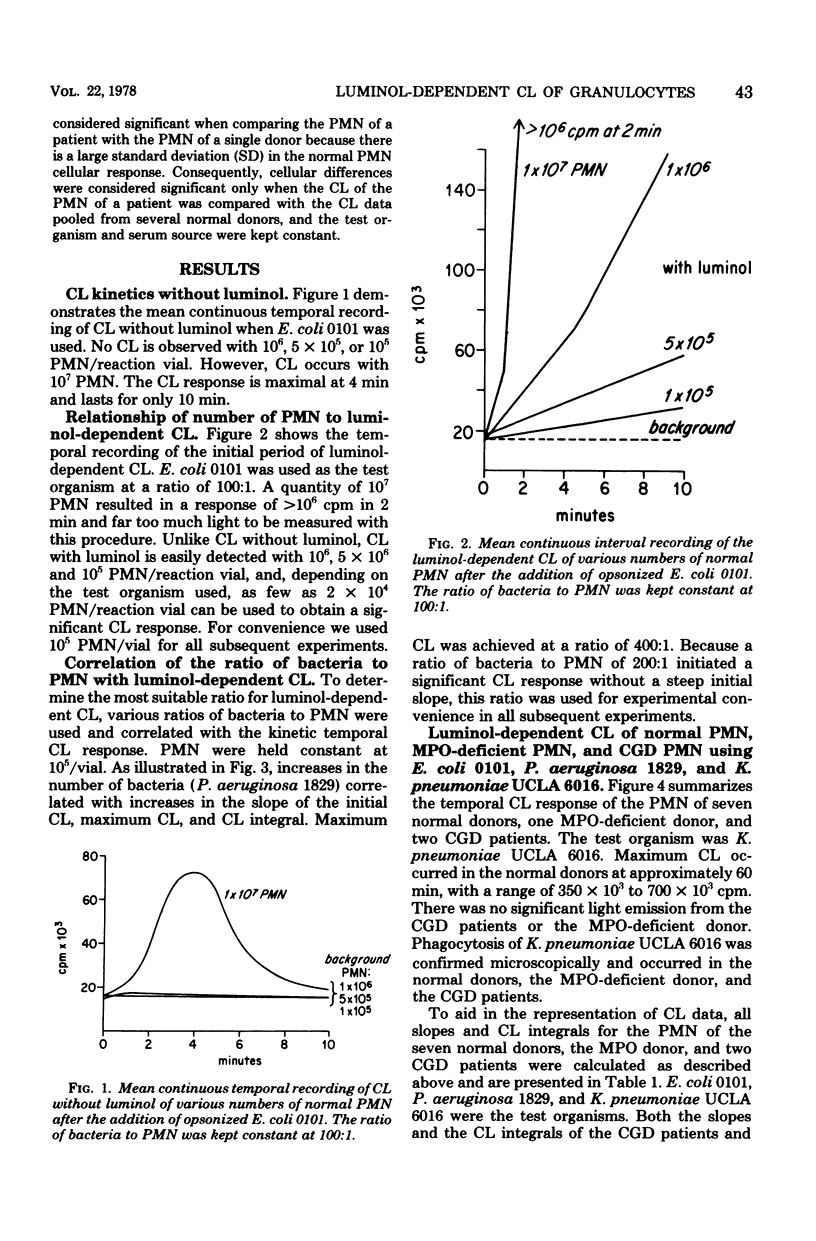
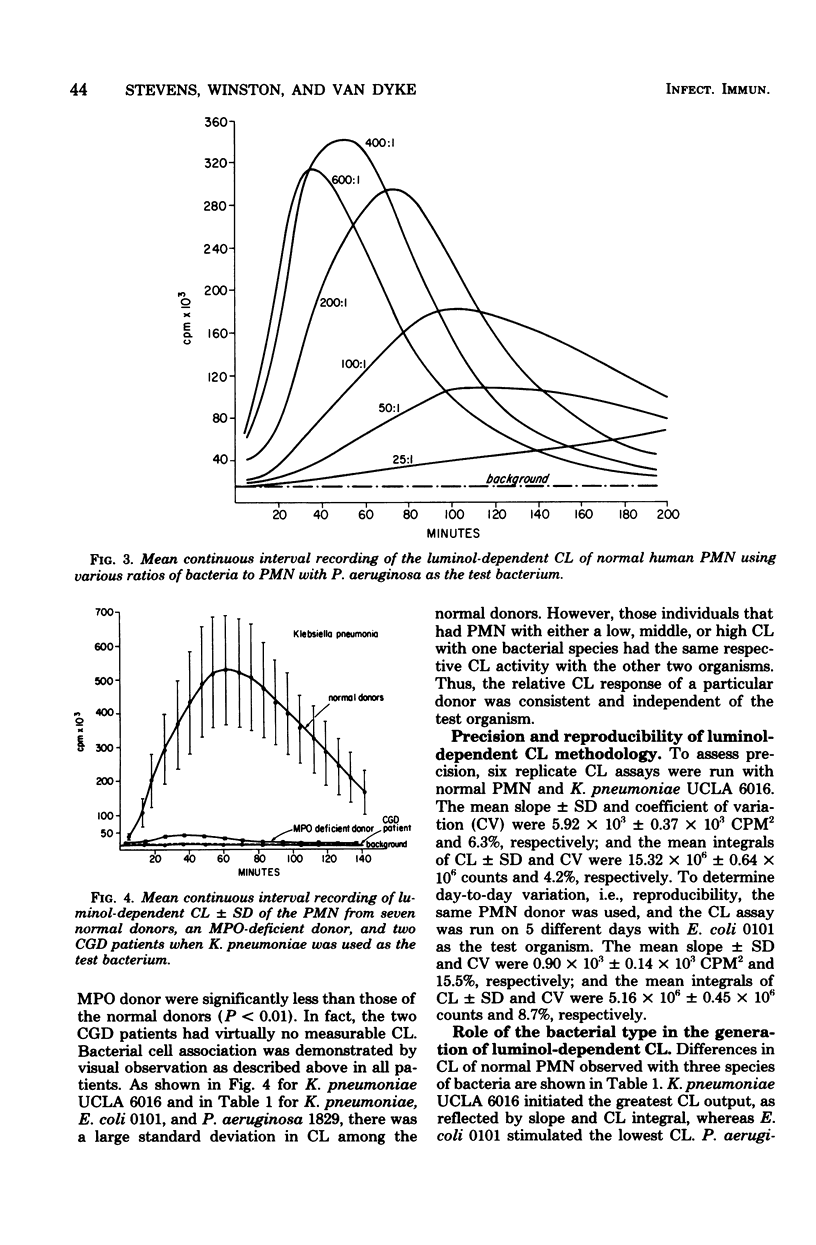
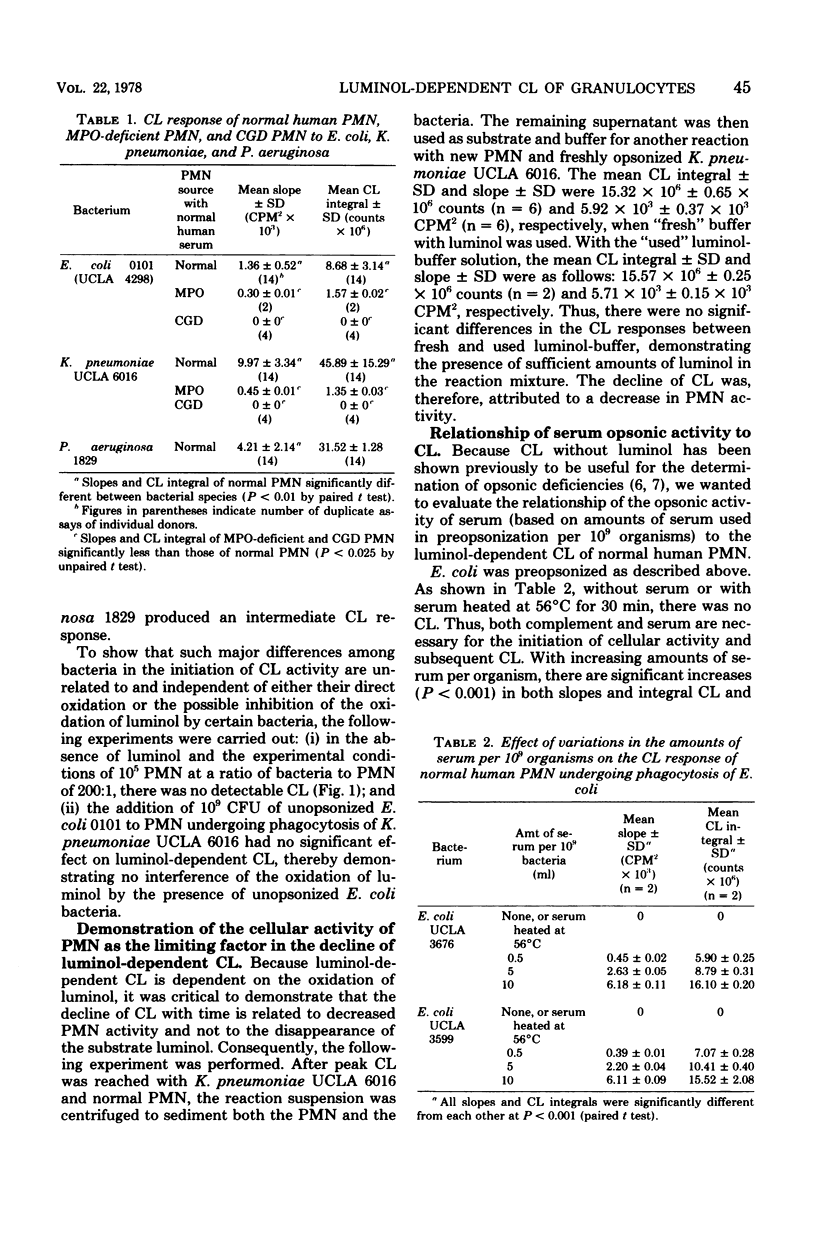
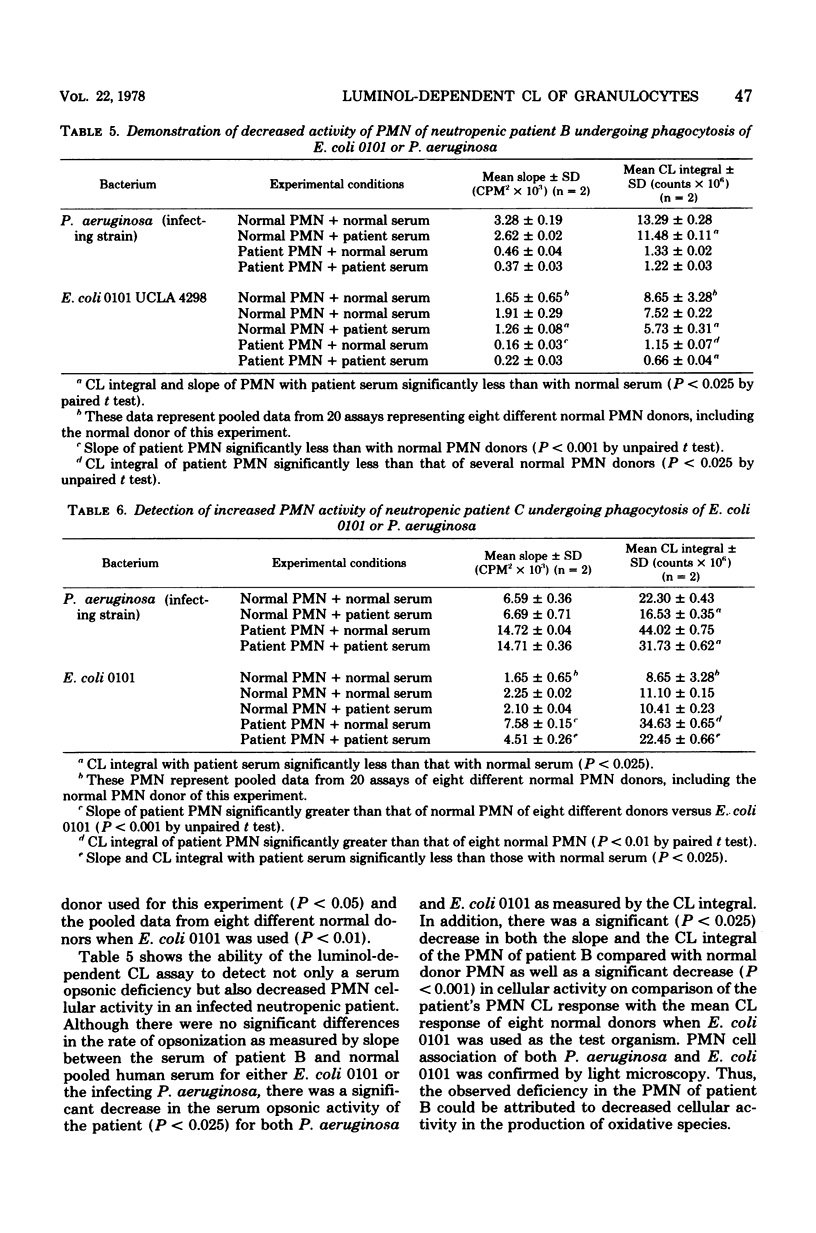
Actively phagocytizing polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) emit light or chemiluminescence (CL) which has been shown to be linked to the oxidative activity of the PMN. The measurement of CL has been demonstrated to be a useful tool for the in vitro assessment of intracellular and opsonophagocytic function of PMN. We have increased the sensitivity of the CL measurement by the addition of luminol to the in vitro reaction of PMN, bacteria, and serum. The presence of luminol, which can be oxidized to emit light, amplifies the detection of CL and PMN cellular activity. This amplification effectively reduces the number of PMN that are necessary for assessment of PMN function from 1 x 10(7) to as low as 2 x 10(4) PMN/assay and permits the evaluation of PMN function in severely neutropenic patients (100 PMN/mm3) in whom cellular PMN function has been heretofore extremely difficult to assess by other methodology. When this luminol-dependent CL method was used, three of eight neutropenic leukemic patients with gram-negative septicemia were found to have deficient opsonic activity and/or increased or depressed cellular oxidative activity. Because the initial slope of CL is dependent on the amount of serum and heat-labile factors, this method can also be used effectively as a simple technique for the analysis of specific rates of opsonophagocytosis of various microorganisms. Additionally, this method can detect the cellular PMN abnormalities of chronic granulomatous disease and myeloperoxidase deficiency. The luminol-dependent CL method is a simple, sensitive, reproducible technique that provides useful information about PMN metabolic activity, particularly in studies in which the number of PMN is limited.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. C. Evaluation of serum opsonic capacity by quantitating the initial chemiluminescent response from phagocytizing polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):828–833. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.828-833.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. C., Loose L. D. Phagocytic activation of a luminol-dependent chemiluminescence in rabbit alveolar and peritoneal macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 8;69(1):245–252. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80299-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. C., Stjernholm R. L., Reed M. A., Harper T. B., 3rd, Gupta S., Steele R. H., Waring W. W. Correlation of metabolic and chemiluminescent responses of granulocytes from three female siblings with chronic granulomatous disease. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136(4):510–518. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.4.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. C., Stjernholm R. L., Steele R. H. Evidence for the generation of an electronic excitation state(s) in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and its participation in bactericidal activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):679–684. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90545-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehner R. L., Karnovsky M. J., Karnovsky M. L. Degranulation of leukocytes in chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jan;48(1):187–192. doi: 10.1172/JCI105967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catovsky D., Galton D. A., Robinson J. Myeloperoxidase-deficient neutrophils in acute myeloid leukaemia. Scand J Haematol. 1972;9(2):142–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1972.tb00923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheson B. D., Christensen R. L., Sperling R., Kohler B. E., Babior B. M. The origin of the chemiluminescence of phagocytosing granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):789–796. doi: 10.1172/JCI108530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Klebanoff S. J. Neutrophil-mediated tumor cell cytotoxicity: role of the peroxidase system. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1442–1447. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J. A new white cell test which measures individual phagocyte function in a mixed leukocyte population. I. A neutrophil defect in acute myelocytic leukemia. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Feb;81(2):311–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer E., Auclair C., Hakim J., Feliu E., Boucherot J., Troube H., Bernard J. F., Bergogne E., Boivin P. Metabolic activity of phagocytosing granulocytes in chronic granulocytic leukemia: ultrastructural observation of a degranulation defect. Blood. 1977 Jul;50(1):93–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. T., Brunning R. D., Quie P. G. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte myeloperoxidase deficiency in a patient with myelomonocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1971 Sep 30;285(14):789–790. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197109302851410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. B. A method for assay of catalase with the oxygen cathode. Anal Biochem. 1968 Sep;24(3):431–437. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Cerqueira M., Lind S., Kaplan H. B. Evidence that the superoxide-generating system of human leukocytes is associated with the cell surface. J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;59(2):249–254. doi: 10.1172/JCI108635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Roos D., Kaplan H. B., Weissmann G. Complement and immunoglobulins stimulate superoxide production by human leukocytes independently of phagocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1155–1163. doi: 10.1172/JCI108191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemming V. G., Hall R. T., Rhodes P. G., Shigeoka A. O., Hill H. R. Assessment of group B streptococcal opsonins in human and rabbit serum by neutrophil chemiluminescence. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1379–1387. doi: 10.1172/JCI108593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Johnson H. B., Spiegelberg H. L. The release of granule enzymes from human neutrophils stimulated by aggregated immunoglobulins of different classes and subclasses. J Immunol. 1972 Dec;109(6):1182–1192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. The immunologic release of constituents from neutrophil leukocytes. I. The role of antibody and complement on nonphagocytosable surfaces or phagocytosable particles. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1535–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. R., Gerrard J. M., Hogan N. A., Quie P. G. Hyperactivity of neutrophil leukotactic responses during active bacterial infection. J Clin Invest. 1974 Apr;53(4):996–1002. doi: 10.1172/JCI107666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Keele B. B., Jr, Misra H. P., Lehmeyer J. E., Webb L. S., Baehner R. L., RaJagopalan K. V. The role of superoxide anion generation in phagocytic bactericidal activity. Studies with normal and chronic granulomatous disease leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1357–1372. doi: 10.1172/JCI108055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Clark R. A. Iodination by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: a re-evaluation. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Mar;89(3):675–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Cline M. J. Leukocyte myeloperoxidase deficiency and disseminated candidiasis: the role of myeloperoxidase in resistance to Candida infection. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1478–1488. doi: 10.1172/JCI106114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Hanifin J., Cline M. J. Defective bactericidal activity in myeloperoxidase-deficient human neutrophils. Nature. 1969 Jul 5;223(5201):78–79. doi: 10.1038/223078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine P. H., Weinger R. S., Simon J., Scoon K. L., Krinsky N. I. Leukocyte-platelet interaction. Release of hydrogen peroxide by granulocytes as a modulator of platelet reactions. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):955–963. doi: 10.1172/JCI108372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6049–6055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhail L. C., DeChatelet L. R., Shirley P. S., Wilfert C., Johnston R. B., Jr, McCall C. E. Deficiency of NADPH oxidase activity in chronic granulomatous disease. J Pediatr. 1977 Feb;90(2):213–217. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80632-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Herron M. J., Schmidtke J. R., Simmons R. L. Chemiluminescence response of human leukocytes: influence of medium components on light production. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):513–520. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.513-520.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkerton P. H., Robinson J. B. Granulocyte function in untreated acute and chronic granulocytic leukemia. Acta Haematol. 1976;56(2):65–72. doi: 10.1159/000207920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Metcalf J. A. H2O2 release from human granulocytes during phagocytosis. Relationship to superoxide anion formation and cellular catabolism of H2O2: studies with normal and cytochalasin B-treated cells. J Clin Invest. 1977 Dec;60(6):1266–1279. doi: 10.1172/JCI108886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Metcalf J., Oshino N., Chance B. H2O2 release from human granulocytes during phagocytosis. I. Documentation, quantitation, and some regulating factors. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):945–955. doi: 10.1172/JCI108024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Klebanoff S. J. Chemiluminescence and superoxide production by myeloperoxidase-deficient leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):50–60. doi: 10.1172/JCI108458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagone A. L., Jr, Mendelson D. S., Metz E. N. The effect of sodium azide on the chemiluminescence of granulocytes--evidence for the generation of multiple oxygen radicals. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Jun;89(6):1333–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salin M. L., McCord J. M. Free radicals and inflammation. Protection of phagocytosine leukocytes by superoxide dismutase. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1319–1323. doi: 10.1172/JCI108208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P., Young L. S. Quantitative granulocyte chemiluminescence in the rapid detection of impaired opsonization of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):796–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.796-804.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjernholm R. L., Allen R. C., Steele R. H., Waring W. W., Harris J. A. Impaired chemiluminescence during phagocytosis of opsonized bacteria. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):313–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.313-314.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. Evaluation of opsonic and leukocyte function with a spectrophotometric test in patients with infection and with phagocytic disorders. Blood. 1973 Jul;42(1):121–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Kinetics of staphylococcal opsonization, attachment, ingestion and killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: a quantitative assay using [3H]thymidine labeled bacteria. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein R. J., Young L. S. Neutrophil function in gram-negative rod bacteremia. The interaction between phagocytic cells, infecting organisms, and humoral factors. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):190–199. doi: 10.1172/JCI108449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



