Abstract
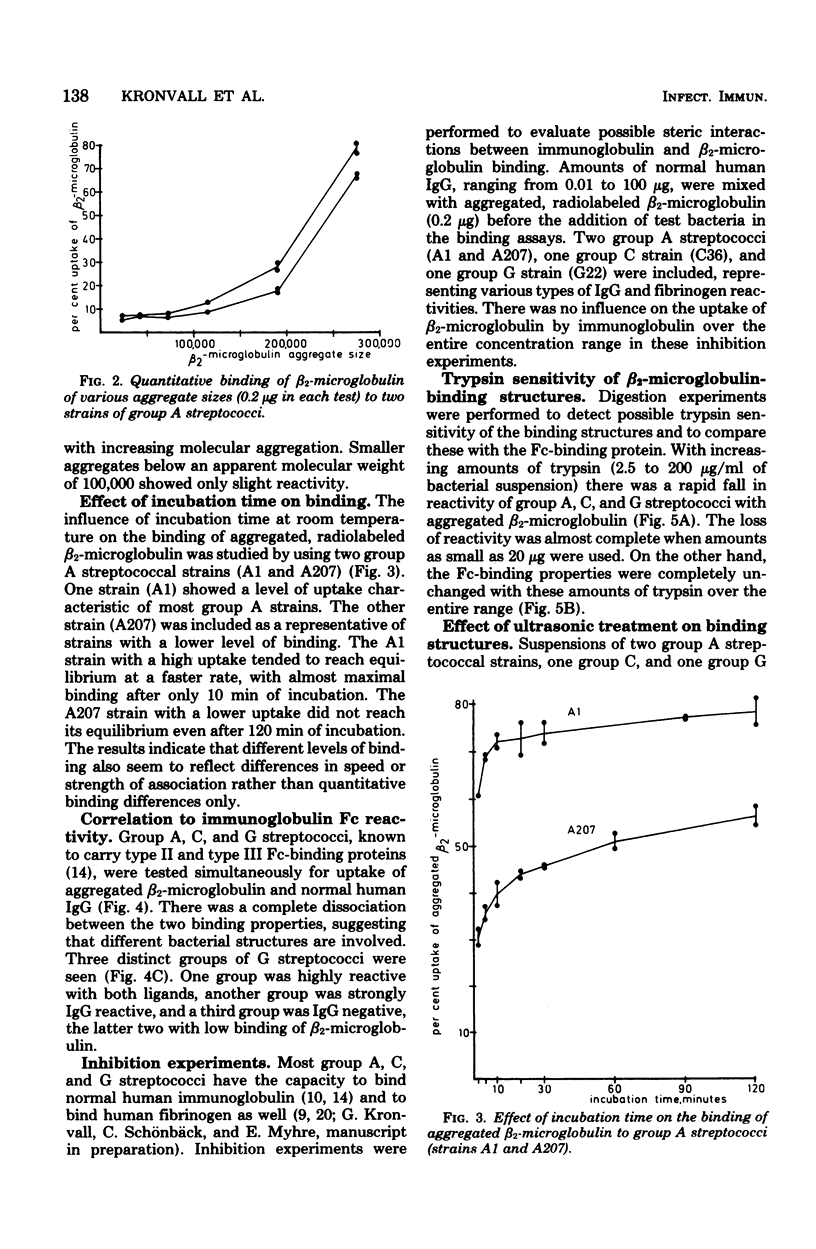
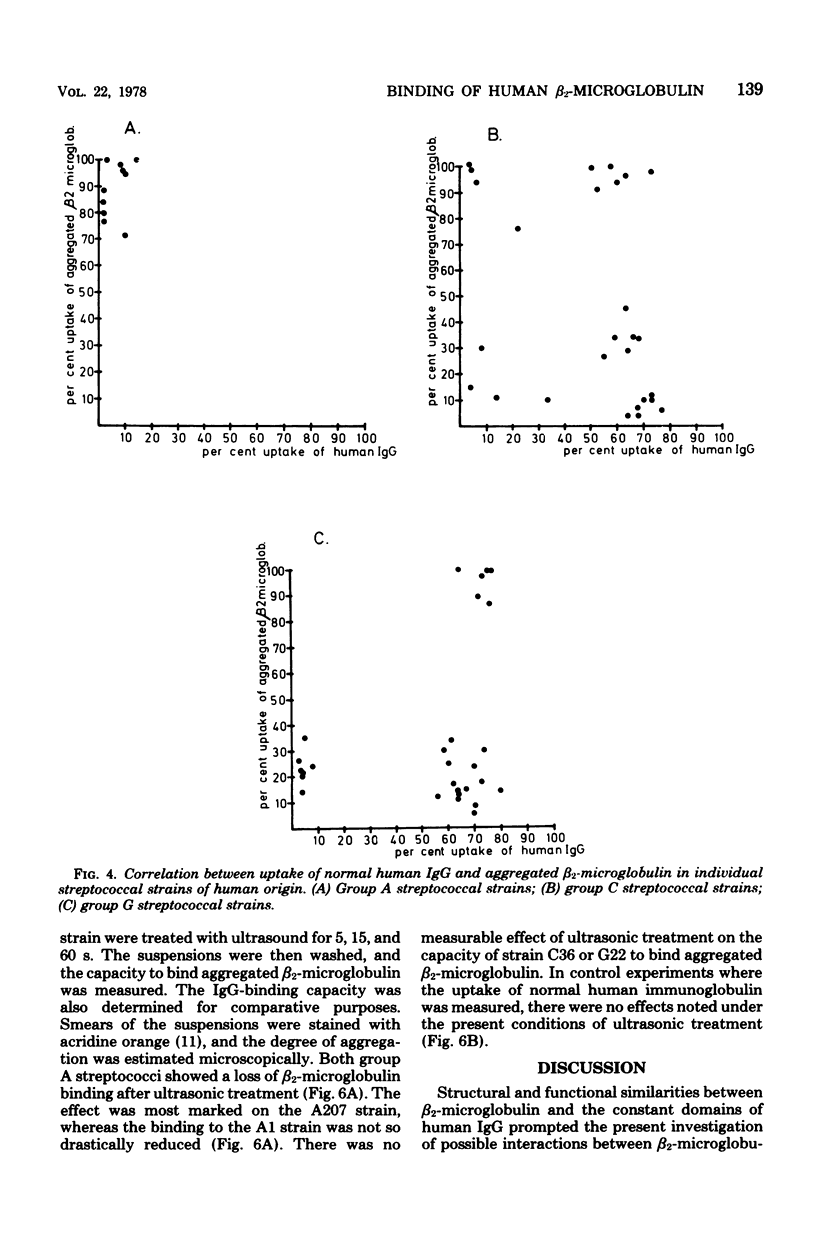
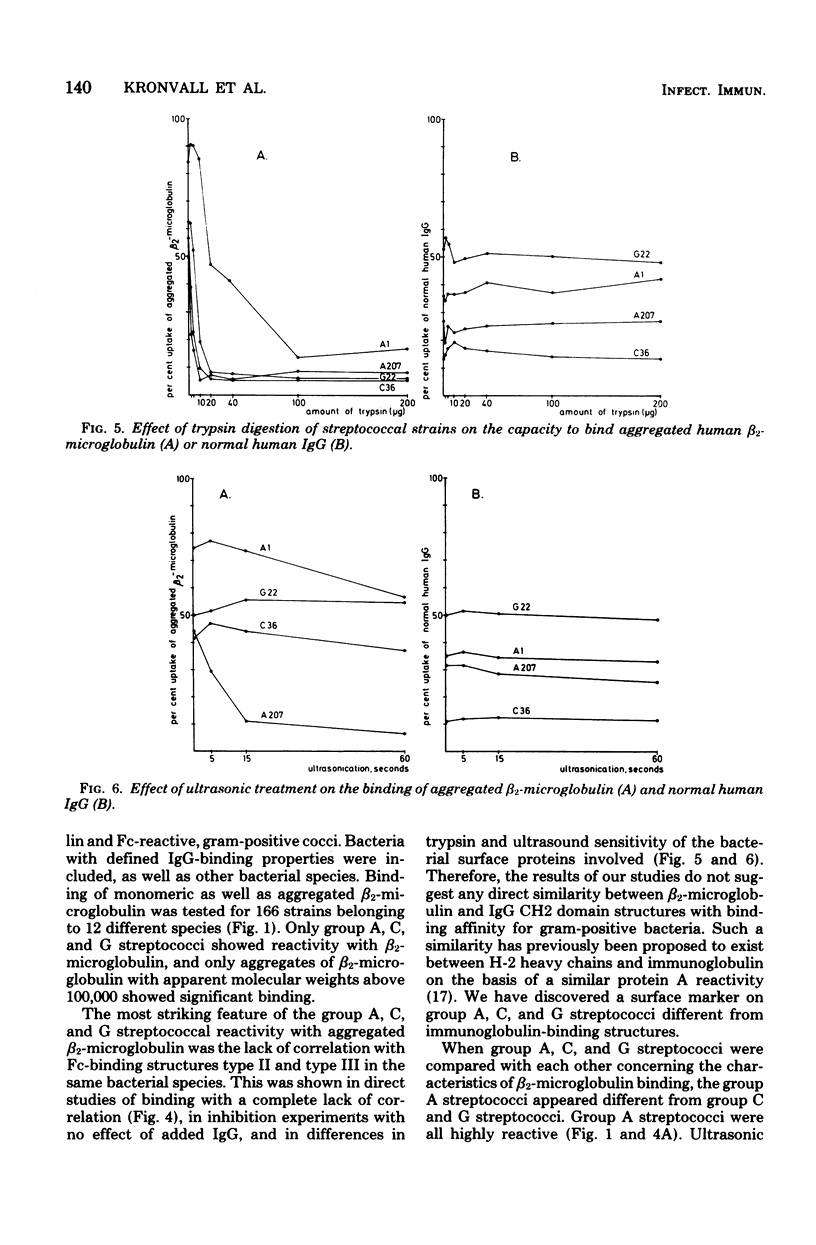
A novel mammalian-microbial "short circuit" has been demonstrated between aggregated human beta2-microglobulin and group A, C, and G streptococci. Bacteria belonging to nine gram-positive and three gram-negative species were tested for binding of radiolabeled beta2-microglobulin. All 10 individual strains of group A streptococci showed a high degree of reactivity with aggregated human beta2-microglobulin. Among 27 group C and 28 group G streptococci, 9 and 6 strains, respectively, were highly reactive, whereas the remaining strains showed a lower, but definite level of beta2-microglobulin binding. Of 11 group B streptococci, 4 were slightly positive. All strains among the other eight species were completely negative. Simultaneous testing of A, C, and G streptococci for immunoglobulin binding showed a lack of correlation between type II and III Fc reactivity and beta2-microglobulin binding. There was no inhibition of uptake of aggregated beta2-microglobulin to reactive strains when excess amounts of human immunoglobulin were added. The beta2-microglobulin-binding surface structure was found to be markedly sensitive to trypsin digestion. The relative trypsin resistance of the immunoglobulin-binding protein in the digestion experiments further demonstrated the dissociation between these two reactivities.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. L., Kubo R. T., Grey H. M. Studies on the cytophilic properties of human beta2 microglobulin. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):997–1000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S. Coupling of enzymes to proteins with glutaraldehyde. Use of the conjugates for the detection of antigens and antibodies. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berggård I., Bearn A. G. Isolation and properties of a low molecular weight beta-2-globulin occurring in human biological fluids. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 10;243(15):4095–4103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berggård I. Isolation and characteristics of a rabbit beta2-microglobulin: comparison with human beta2-microglobulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Apr 23;57(4):1159–1165. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90818-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björck L., Cigén R., Berggård B., Löw B., Berggård I. Relationships between beta2-microglobulin and alloantigens coded for by the major histocompatibility complexes of the rabbit and the guinea pig. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(10):1063–1069. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Gibbons R. J. M protein-associated adherence of Streptococcus pyogenes to epithelial surfaces: prerequisite for virulence. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):826–830. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.826-830.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANTOR F. S., COLE R. M. A fibrinogen precipitating factor (FPF) of group A streptococci. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Oct;102:146–150. doi: 10.3181/00379727-102-25172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A surface component in group A, C, and G streptococci with non-immune reactivity for immunoglobulin G. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1401–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Myhre E. Differential staining of bacteria in clinical specimens using acridine orange buffered at low pH. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Aug;85(4):249–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Williams R. C., Jr Immunologic "short circuits". Ann Intern Med. 1969 May;70(5):1043–1045. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-5-1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B., Kronvall G. Heterogeneity of nonimmune immunoglobulin Fc reactivity among gram-positive cocci: description of three major types of receptors for human immunoglobulin G. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):475–482. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.475-482.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter R. H., Yasmeen D., Assimeh S. N., Poulik M. D. Complement fixing and macrophage opsonizing activities associated with beta2 microglobulin. Immunol Commun. 1974;3(1):19–34. doi: 10.3109/08820137409055743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A., Cunningham B. A., Berggård I., Edelman G. M. 2 -Microglobulin--a free immunoglobulin domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1697–1701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A., Rask L., Sege K., Klareskog L., Anundi H., Ostberg L. Evolutionary relationship between immunoglobulins and transplantation antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1612–1616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Poulik M. D. Initiation of protein synthesis at an unusual position in an immunoglobulin gene? Science. 1972 Jan 14;175(4018):187–189. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4018.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terhorst C., Robb R., Jones C., Strominger J. L. Further structural studies of the heavy chain of HLA antigens and its similarity to immunoglobulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4002–4006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


