Abstract
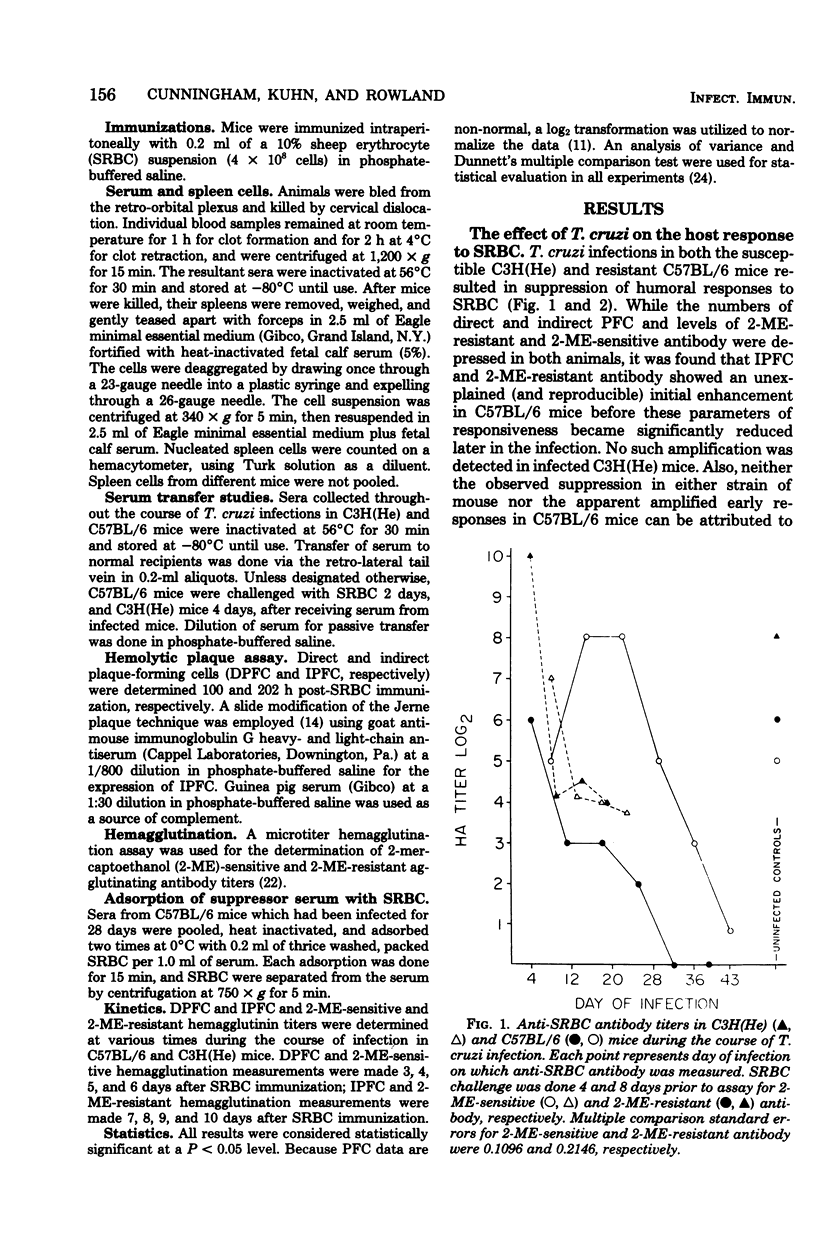
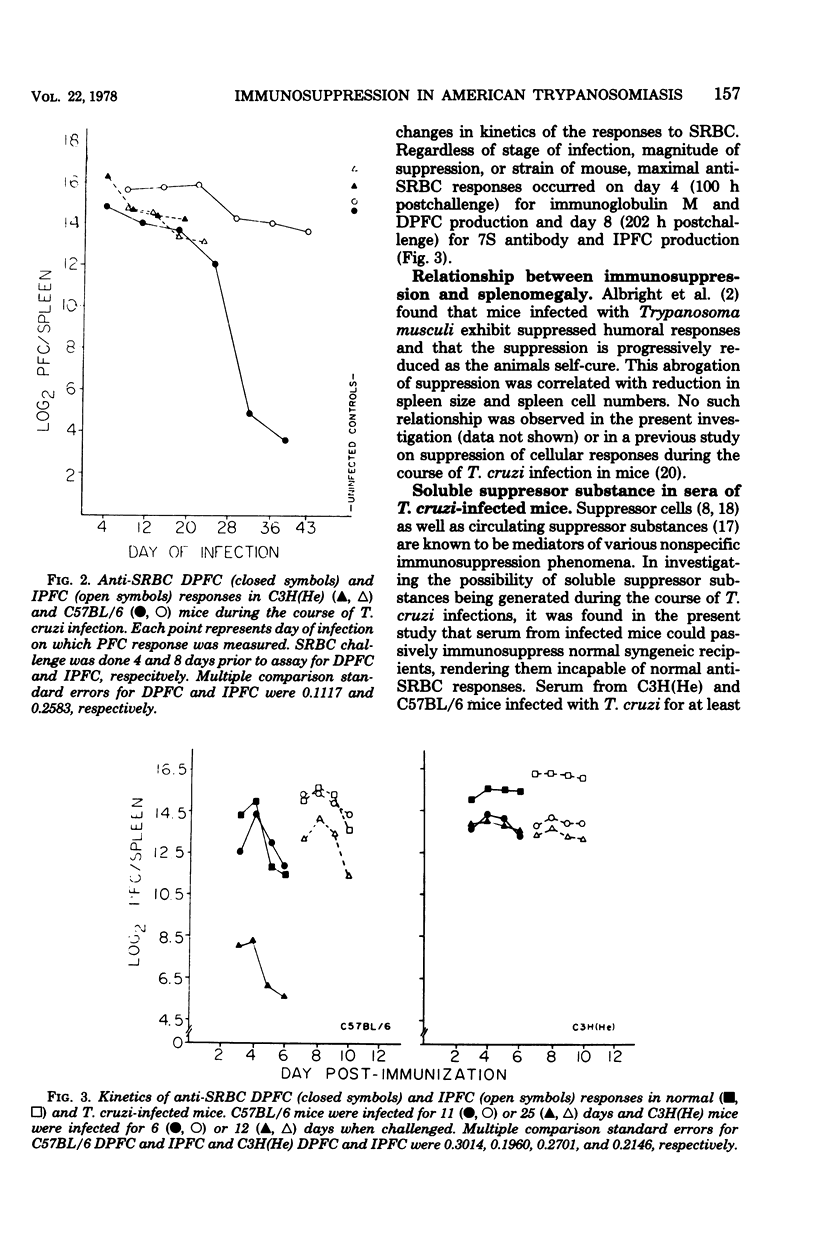
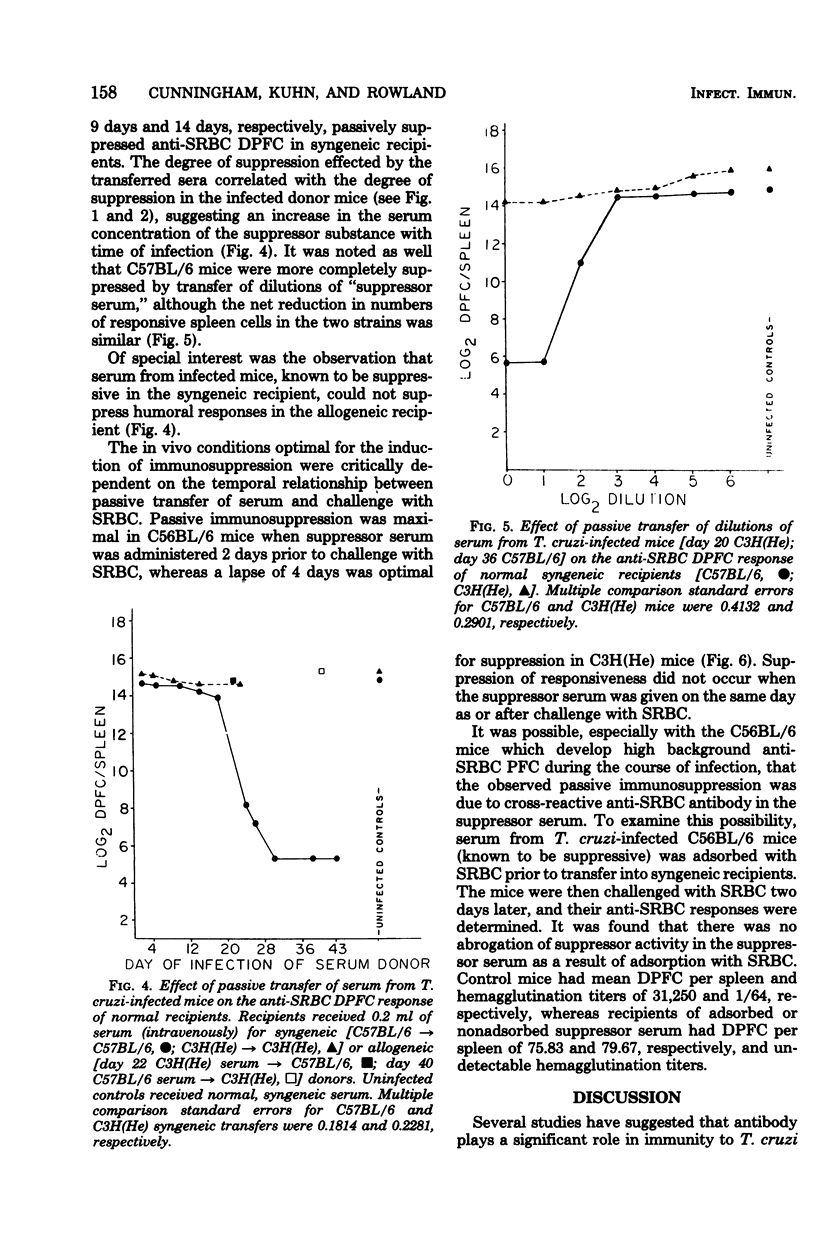
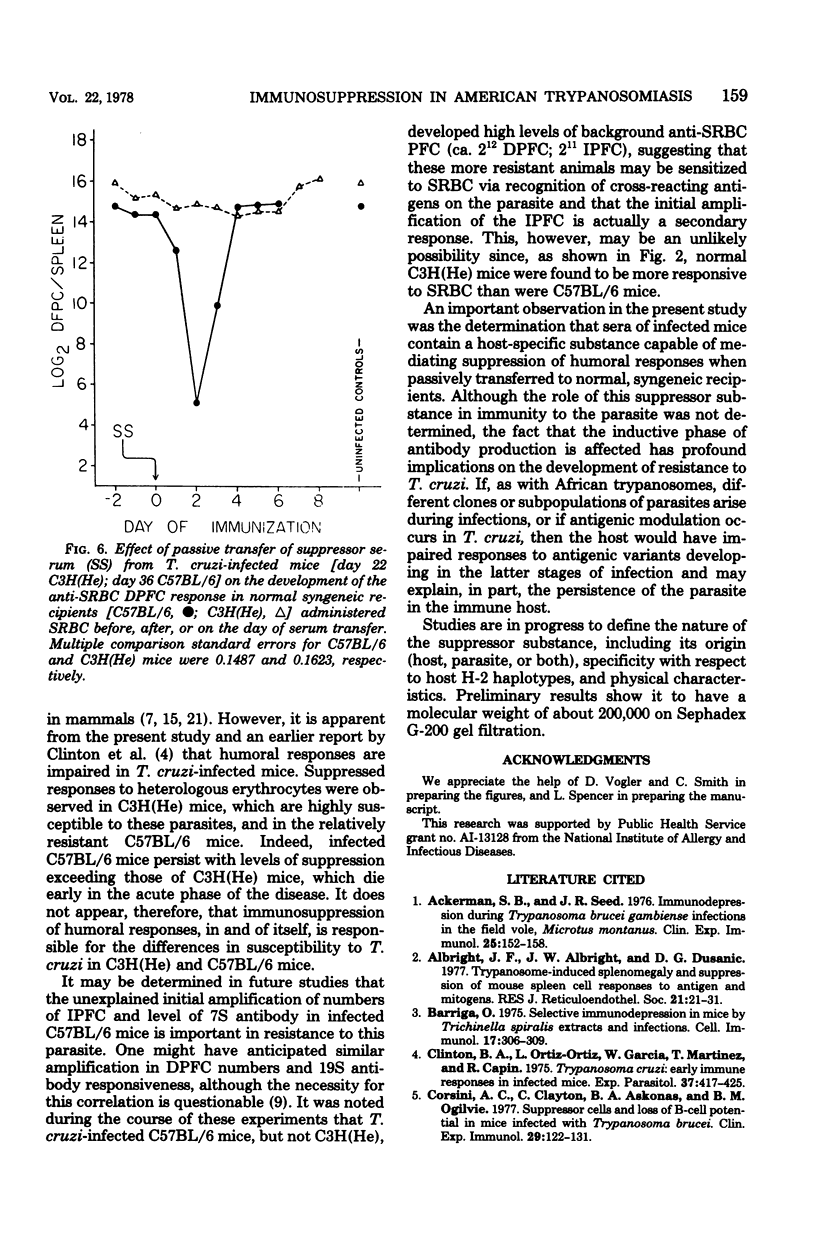
C57BL/6 mice exhibit low parasitemias and often survive Trypanosoma cruzi infections, whereas C3H(He) mice die during the acute phase with relatively high parasitemias. The present study showed that both strains of mice develop nonspecific immunosuppression to challenge with sheep erythrocytes during the course of infection. Several major differences in immunosuppression-related phenomena between the two strains of mice were determined, yet there is no apparent relationship between immunosuppression and resistance to T. cruzi. Both the number of direct plaque-forming cells and the titer of 2-mercaptoethanol-sensitive agglutinating antibody were significantly lower on day 11 for C57BL/6 mice and day 9 for C3H(He) mice. The number of indirect plaque-forming cells and the titer of mercaptoethanol-resistant agglutinating antibody were reduced by day 36 of infection in C57BL/6 mice and 13 days postinfection in C3H(He) mice. In both strains the degree of humoral response suppression of mice increased concomitant with the period of infection, but was not correlated with the changes in spleen cell numbers. Preliminary experiments designed to explore the mechanism underlying the induction and maintenance of immunosuppression in this hostparasite model disclosed the presence of suppressor substance in the serum of T. cruzi-infected mice. The passive transfer of serum from infected mice to syngeneic recipients elicited a state of immunosuppression to sheep erythrocytes, but did not diminish anti-erythrocyte activity in allogeneic recipients. The induction of immunosuppression in normal mice was further found to be dependent on the interval between serum transfer and challenge with antigen. No quantitative differences existed between the magnitude of suppressed humoral responses in mice infected for varying lengths of time and recipients of serum collected from similarly infected mice.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman S. B., Seed J. R. Immunodepression during Trypanosoma brucei gambiense infections in the field vole, Microtus montanus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jul;25(1):152–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albright J. F., Albright J. W., Dusanic D. G. Trypanosome-induced splenomegaly and suppression of mouse spleen cell responses to antigen and mitogens. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1977 Jan;21(1):21–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barriga O. O. Selective immunodepression in mice by Trichinella spiralis extracts and infections. Cell Immunol. 1975 May;17(1):306–309. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(75)80031-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton B. A., Ortiz-Ortiz L., Garcia W., Martinez T., Capin R. Trypanosoma cruzi: early immune responses in infected mice. Exp Parasitol. 1975 Jun;37(3):417–425. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(75)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corsini A. C., Clayton C., Askonas B. A., Ogilvie B. M. Suppressor cells and loss of B-cell potential in mice infected with Trypanosoma brucei. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Jul;29(1):122–131. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandall C. A., Crandall R. B. Ascaris suum: immunosuppression in mice during acute infection. Exp Parasitol. 1976 Dec;40(3):363–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(76)90102-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eardley D. D., Jayawardena A. N. Suppressor cells in mice infected with Trypanosoma brucei. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1029–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearhart P. J. Non-sequential expression of multiple immunoglobulin classes by isolated B-cell clones. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):812–813. doi: 10.1038/269812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good A. H., Miller K. L. Depression of the immune response to sheep erythrocytes in mice infected with Taenia crassiceps larvae. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):449–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.449-456.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb C. F. Application of transformations to normalize the distribution of plaque-forming cells. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):51–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson K. M., Byner C., Freeman J., Terry R. J. Immunodepression, high IgM levels and evasion of the immune response in murine trypanosomiasis. Nature. 1976 Nov 18;264(5583):256–258. doi: 10.1038/264256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayawardena A. N., Waksman B. H. Suppressor cells in experimentally trypanosomiasis. Nature. 1977 Feb 10;265(5594):539–541. doi: 10.1038/265539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K., Henry C., Nordin A. A., Fuji H., Koros A. M., Lefkovits I. Plaque forming cells: methodology and theory. Transplant Rev. 1974;18:130–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1974.tb01588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierszenbaum F., Howard J. G. Mechanisms of resistance against experimental Trypanosoma cruzi infection: the importance of antibodies and antibody-forming capacity in the Biozzi high and low responder mice. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1208–1211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn R. E., Murnane J. E. Trypanosoma cruzi: immune destruction of parasitized mouse fibroblasts in vitro. Exp Parasitol. 1977 Feb;41(1):66–73. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(77)90130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield J. M., Bagasra O. Lymphocyte function in experimental African trypanosomiasis. I. B cell responses to helper T cell-independent and -dependent antigens. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):759–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poels L. G., van Niekerk C. C. Plasmodium berghei: immunosuppression and hyperimmunoglobulinemia. Exp Parasitol. 1977 Jun;42(1):235–247. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(77)90081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland E. C., Kuhn R. E. Suppression of cellular responses in mice during Trypanosoma cruzi infections. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):393–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.393-397.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. W., Gershon R. K. Determination of total and merecaptothanol-resistant antibody in the same serum sample. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Feb;6(2):313–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland G. T., Sayles P. C. Depressed antibody responses to a thymus-dependent antigen in toxoplasmosis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):184–190. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.184-190.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


